Deck 3: Accrual Accounting Concepts
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/81
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Accrual Accounting Concepts
1
If an entity purchases a new delivery vehicle it doesn't make sense to expense the full cost of the vehicle at the time it is purchased because:
A) it will be used for many subsequent periods.
B) profit will be too low.
C) vehicles wear out over time and it will be worth less each period.
D) it will eventually be sold.
A) it will be used for many subsequent periods.
B) profit will be too low.
C) vehicles wear out over time and it will be worth less each period.
D) it will eventually be sold.
it will be used for many subsequent periods.
2
Which statement is false?
A) Accrual based accounting records transactions in the period in which the transaction occurs.
B) Applying accrual accounting results in a more accurate measure of profit for the period than cash based accounting.
C) GAAP requires financial reports be prepared using accrual accounting.
D) None, all statements are true.
A) Accrual based accounting records transactions in the period in which the transaction occurs.
B) Applying accrual accounting results in a more accurate measure of profit for the period than cash based accounting.
C) GAAP requires financial reports be prepared using accrual accounting.
D) None, all statements are true.
None, all statements are true.
3
Which statement/s is/are false?
A) The revenue recognition principle is a helpful guide in determining profit for a period.
B) Revenue should be recognised only when it is probable that any future economic benefits associated with the revenue will flow to the entity.
C) Revenue should only be recorded if it can be measured with absolutely certainty.
D) A and B.
A) The revenue recognition principle is a helpful guide in determining profit for a period.
B) Revenue should be recognised only when it is probable that any future economic benefits associated with the revenue will flow to the entity.
C) Revenue should only be recorded if it can be measured with absolutely certainty.
D) A and B.
A and B.
4
When wages are incurred in one period and paid in the next period, this leads to which of the following accounts appearing in the statement of financial position?
A) Service revenue.
B) Accounts receivable.
C) Wages payable.
D) Wages expense.
A) Service revenue.
B) Accounts receivable.
C) Wages payable.
D) Wages expense.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which statement about adjusting entries is false?
A) Adjusting entries are often made because some business events are not recorded as they occur.
B) Adjusting entries are recorded in the general journal but are not posted to the accounts in the general ledger.
C) And adjusting entry would adjust a revenue transaction so it reported when the revenue is earned.
D) Before an adjusting entry for prepaid expense is recorded, assets will be overstated and expenses will be understated.
A) Adjusting entries are often made because some business events are not recorded as they occur.
B) Adjusting entries are recorded in the general journal but are not posted to the accounts in the general ledger.
C) And adjusting entry would adjust a revenue transaction so it reported when the revenue is earned.
D) Before an adjusting entry for prepaid expense is recorded, assets will be overstated and expenses will be understated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which statement about accrual accounting is true?
A) An adjusting entry always involves two statement of financial position accounts.
B) Revenue received before it is earned and expenses paid before being used or consumed are both initially recorded as liabilities.
C) The difference between revenue received in advance and accrued revenue is that accrued revenue has been recorded and needs adjusting whereas revenue received in advance has never been recorded.
D) None; all statements are false.
A) An adjusting entry always involves two statement of financial position accounts.
B) Revenue received before it is earned and expenses paid before being used or consumed are both initially recorded as liabilities.
C) The difference between revenue received in advance and accrued revenue is that accrued revenue has been recorded and needs adjusting whereas revenue received in advance has never been recorded.
D) None; all statements are false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Reese Ltd purchased office supplies costing $4,000 and debited Office supplies for the full amount. At the end of the accounting period, a physical count of office supplies revealed $1,600 still on hand. The appropriate adjusting journal entry to be made at the end of the period would be:
A) Debit Office supplies expense, $1,600; Credit Office supplies, $1,600.
B) Debit Office supplies, $2,400; Credit Office supplies expense, $2,400.
C) Debit Office supplies expense, $2,400; Credit Office supplies, $2,400.
D) Debit Office supplies, $1,600; Credit Office supplies expense, $1,600.
A) Debit Office supplies expense, $1,600; Credit Office supplies, $1,600.
B) Debit Office supplies, $2,400; Credit Office supplies expense, $2,400.
C) Debit Office supplies expense, $2,400; Credit Office supplies, $2,400.
D) Debit Office supplies, $1,600; Credit Office supplies expense, $1,600.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
On 1 July the Winter Shoe Store paid $6,000 to Ace Realty for 6 month's rent beginning 1 July. Prepaid Rent was debited for the full amount. If financial statements are prepared on 31 July, the adjusting entry to be made by the Winter Shoe Store is:
A) Debit Rent expense, $6,000; Credit Prepaid rent, $1,000.
B) Debit Prepaid rent, $1,000; Credit Rent expense, $1,000.
C) Debit Rent expense, $1,000; Credit Prepaid rent, $1,000.
D) Debit Rent expense, $6,000; Credit Prepaid rent, $6,000.
A) Debit Rent expense, $6,000; Credit Prepaid rent, $1,000.
B) Debit Prepaid rent, $1,000; Credit Rent expense, $1,000.
C) Debit Rent expense, $1,000; Credit Prepaid rent, $1,000.
D) Debit Rent expense, $6,000; Credit Prepaid rent, $6,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The balance in the Prepaid rent account before adjustment at the end of the year is $12,000 and represents three months' rent paid on 1 December. The adjusting entry required on 31 December is:
A) Debit Prepaid rent, $4,000; Credit Rent expense $4,000.
B) Debit Prepaid rent, $8,000; Credit Rent expense, $8,000.
C) Debit Rent expense, $12,000; Credit Prepaid rent, $12,000.
D) Debit Rent expense, $4,000; Credit Prepaid rent, $4,000.
A) Debit Prepaid rent, $4,000; Credit Rent expense $4,000.
B) Debit Prepaid rent, $8,000; Credit Rent expense, $8,000.
C) Debit Rent expense, $12,000; Credit Prepaid rent, $12,000.
D) Debit Rent expense, $4,000; Credit Prepaid rent, $4,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Revenues received in advance is classified as an:
A) asset account.
B) revenue account.
C) contra revenue account.
D) liability account.
A) asset account.
B) revenue account.
C) contra revenue account.
D) liability account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The Harris Company Ltd purchased a computer for $3,000 on 1 December. It is estimated that annual depreciation on the computer will be $600. If financial statements are to be prepared on 31 December, the company should make the following adjusting entry:
A) Debit Depreciation expense, $600; Credit Accumulated depreciation, $600.
B) Debit Depreciation expense, $50; Credit Accumulated depreciation, $50.
C) Debit Office equipment $2,400; Credit Accumulated depreciation, $2,400.
D) Debit Office equipment, $3,000; Credit Accumulated depreciation, $3,000.
A) Debit Depreciation expense, $600; Credit Accumulated depreciation, $600.
B) Debit Depreciation expense, $50; Credit Accumulated depreciation, $50.
C) Debit Office equipment $2,400; Credit Accumulated depreciation, $2,400.
D) Debit Office equipment, $3,000; Credit Accumulated depreciation, $3,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which statement about depreciating non-current assets with a limited useful life is true?
A) The cost of a depreciable asset less accumulated depreciation is the carrying amount of the asset.
B) The carrying a mount of a depreciable asset is always equal to its market value because depreciation is a valuation method.
C) The balances of Accumulated depreciation and Depreciation expense should always be equal.
D) None, all statements are false.
A) The cost of a depreciable asset less accumulated depreciation is the carrying amount of the asset.
B) The carrying a mount of a depreciable asset is always equal to its market value because depreciation is a valuation method.
C) The balances of Accumulated depreciation and Depreciation expense should always be equal.
D) None, all statements are false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
McCloud Realty Company Ltd received a cheque for $21,000 on 1 July, which represents six months' rent received in advance. Revenue received in advance account was credited with $21,000. Financial statements will be prepared on 31 July. McCloud Realty Company Ltd should make the following adjusting entry on 31 July:
A) Debit Revenue received in advance, $3,500; Credit Rental revenue, $3,500.
B) Debit Rental revenue, $3,500; Credit Revenue received in advance, $3,500.
C) Debit Revenue received in advance, $21,000; Credit Rental revenue, $21,000.
D) Debit Cash, $21,000; Credit Rental revenue, $21,000.
A) Debit Revenue received in advance, $3,500; Credit Rental revenue, $3,500.
B) Debit Rental revenue, $3,500; Credit Revenue received in advance, $3,500.
C) Debit Revenue received in advance, $21,000; Credit Rental revenue, $21,000.
D) Debit Cash, $21,000; Credit Rental revenue, $21,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
At 31 December 2018, before any year-end adjustments, Hart Company's Insurance Expense account had a balance of $725 and its Prepaid Insurance account had a balance of $1,900. It was determined that $1,500 of the Prepaid Insurance had expired. The adjusted balance for Insurance Expense for the year would be:
A) $1,500.
B) $725.
C) $2,225.
D) $1,175.
A) $1,500.
B) $725.
C) $2,225.
D) $1,175.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A new accountant working for Metcalf Ltd records $800 Depreciation expense on store equipment by debiting Depreciation expense $800 and crediting Cash $800. The effect of this entry is to:
A) adjust the accounts to their proper amounts on 31 December.
B) understate total assets on the statement of financial position as of 31 December.
C) overstate the carrying amount of the depreciable assets at 31 December.
D) understate the carrying amount of the depreciable assets as of 31 December.
A) adjust the accounts to their proper amounts on 31 December.
B) understate total assets on the statement of financial position as of 31 December.
C) overstate the carrying amount of the depreciable assets at 31 December.
D) understate the carrying amount of the depreciable assets as of 31 December.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
On 1 September Carlson Ltd borrowed $10,000 from the bank for three months at the annual interest rate of 9%. Principal and interest are payable to the bank on 1 December. If the company prepares monthly financial statements, the adjusting entry that the company should make for interest on 30 September, would be:
A) Debit Interest expense, $900; Credit Interest payable, $900.
B) Debit Interest expense, $300; Credit Interest payable, $300.
C) Debit Promissory note payable, $900; Credit cash, $900.
D) Debit Interest expense, $75; Credit Interest payable, $75.
A) Debit Interest expense, $900; Credit Interest payable, $900.
B) Debit Interest expense, $300; Credit Interest payable, $300.
C) Debit Promissory note payable, $900; Credit cash, $900.
D) Debit Interest expense, $75; Credit Interest payable, $75.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
On Friday 26 January Snell Tables paid employee wages up to the end of that day. The next payroll will be paid in February. There are three more working days in January (29-31). Employees work 5 days a week and the business pays $800 a day in wages. The adjusting entry to accrue wages expense at the end of January is:
A)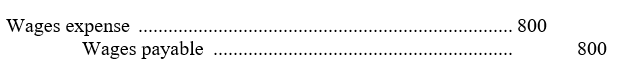
B)
C)
D)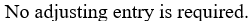
A)
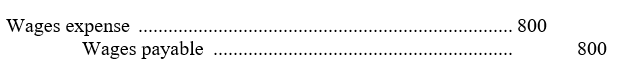
B)

C)

D)
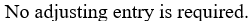

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A business shows a balance in Salaries payable of $40,000 at the end of the month. The next payroll amounting to $50,000 is to be paid in the following month. What will be the journal entry to record the payment of salaries?
A)
B)
C)
D)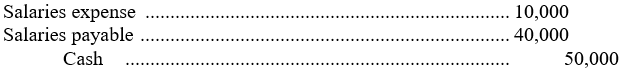
A)

B)

C)

D)
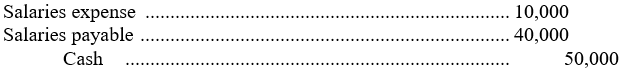

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
After all adjusting entries have been journalised and posted another trial balance is prepared from the ledger accounts. This later trial balance is known as the:
A) unadjusted trial balance.
B) temporary trial balance.
C) permanent trial balance.
D) adjusted trial balance.
A) unadjusted trial balance.
B) temporary trial balance.
C) permanent trial balance.
D) adjusted trial balance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When a business closes its accounts at the end of a financial period, the only accounts remaining open are:
A) permanent accounts.
B) temporary accounts.
C) income statement accounts.
D) revenue accounts.
A) permanent accounts.
B) temporary accounts.
C) income statement accounts.
D) revenue accounts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Temporary accounts of a business include:
A) assets, liabilities and equity accounts.
B) assets only accounts.
C) revenue, expense and dividend accounts.
D) retained earnings only account.
A) assets, liabilities and equity accounts.
B) assets only accounts.
C) revenue, expense and dividend accounts.
D) retained earnings only account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When preparing closing journal entries, the item Salaries expense is closed:
A) directly to the Retained earnings account.
B) directly to the Accumulated expenses account.
C) to the Profit and loss summary account.
D) to the Dividends paid account.
A) directly to the Retained earnings account.
B) directly to the Accumulated expenses account.
C) to the Profit and loss summary account.
D) to the Dividends paid account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The closing entry process results in the balance of the Profit and loss summary account being closed to the:
A) Retained earnings account.
B) Total assets account.
C) Share capital account.
D) Total liabilities account.
A) Retained earnings account.
B) Total assets account.
C) Share capital account.
D) Total liabilities account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The accounting cycle begins with the analysis of transactions and ends with the:
A) preparation of financial statements.
B) posting of transactions to ledger accounts.
C) journalising of adjusting entries.
D) preparation of a post-closing trial balance.
A) preparation of financial statements.
B) posting of transactions to ledger accounts.
C) journalising of adjusting entries.
D) preparation of a post-closing trial balance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
When is a reversing journal entry made?
A) At the end of the financial year in which adjusting entries are made.
B) At the beginning of the next accounting period.
C) At the end of the next accounting period.
D) At the same time as the adjusting entries are made.
A) At the end of the financial year in which adjusting entries are made.
B) At the beginning of the next accounting period.
C) At the end of the next accounting period.
D) At the same time as the adjusting entries are made.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A worksheet is:
A) prescribed in the framework.
B) only used in small businesses with few general ledger accounts.
C) prepared either manually or using a computer spreadsheet.
D) not necessary if the financial statements are being prepared by an accountant.
A) prescribed in the framework.
B) only used in small businesses with few general ledger accounts.
C) prepared either manually or using a computer spreadsheet.
D) not necessary if the financial statements are being prepared by an accountant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The statement of financial position of Redmond Company Ltd includes the following:
 Calculate the following for 2019:
Calculate the following for 2019:
1. Cash received for interest.
2. Cash paid for supplies.
3. Cash paid for wages.
4. Cash received for revenue.
 Calculate the following for 2019:
Calculate the following for 2019:1. Cash received for interest.
2. Cash paid for supplies.
3. Cash paid for wages.
4. Cash received for revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The 2019 income statement for Berring Ltd showed rent expense of $5,500 and salary expense of $5,600. The related statement of financial position account balances at year end 2018 and 2019 were as follows:
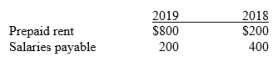 Calculate the following for 2019:
Calculate the following for 2019:
1. Cash paid for rent.
2. Cash paid for wages.
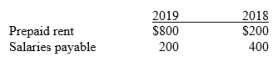 Calculate the following for 2019:
Calculate the following for 2019:1. Cash paid for rent.
2. Cash paid for wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Ronson Ltd prepared the following income statement using the cash basis of accounting:
 Additional data:
Additional data:
1. Depreciation on a company motor vehicle for the year amounted to $8,000. This amount is not included in the expenses above.
2. On 1 January 2019, Ronson paid for a two-year insurance policy on the motor vehicle amounting to $1,800. The total amount is included in the expenses above.
Instructions:
(a) Recast the above income statement on the accrual basis in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles. Show computations and explain each change.
(b) Explain which basis (cash or accrual) provides a better measure of profit.
 Additional data:
Additional data:1. Depreciation on a company motor vehicle for the year amounted to $8,000. This amount is not included in the expenses above.
2. On 1 January 2019, Ronson paid for a two-year insurance policy on the motor vehicle amounting to $1,800. The total amount is included in the expenses above.
Instructions:
(a) Recast the above income statement on the accrual basis in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles. Show computations and explain each change.
(b) Explain which basis (cash or accrual) provides a better measure of profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Before month-end adjustments are made, the 28 February trial balance of Joe's Gardening Services contains revenue of $9,000 and expenses of $4,400. Adjustments are necessary for the following items:
 Calculate the correct profit for Joe's income statement for February.
Calculate the correct profit for Joe's income statement for February.
 Calculate the correct profit for Joe's income statement for February.
Calculate the correct profit for Joe's income statement for February.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
For each of the following oversights, state what total assets will be
-Failure to record revenue earned but not yet received.
A) understated (U)
B) overstated (O)
C) no effect (NE)
-Failure to record revenue earned but not yet received.
A) understated (U)
B) overstated (O)
C) no effect (NE)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
For each of the following oversights, state what total assets will be
-Failure to record expired prepaid rent.
A) understated (U)
B) overstated (O)
C) no effect (NE)
-Failure to record expired prepaid rent.
A) understated (U)
B) overstated (O)
C) no effect (NE)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
For each of the following oversights, state what total assets will be
-Failure to record accrued interest revenue on a loan receivable.
A) understated (U)
B) overstated (O)
C) no effect (NE)
-Failure to record accrued interest revenue on a loan receivable.
A) understated (U)
B) overstated (O)
C) no effect (NE)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
For each of the following oversights, state what total assets will be
-Failure to record depreciation.
A) understated (U)
B) overstated (O)
C) no effect (NE)
-Failure to record depreciation.
A) understated (U)
B) overstated (O)
C) no effect (NE)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
For each of the following oversights, state what total assets will be
-Failure to record accrued wages.
A) understated (U)
B) overstated (O)
C) no effect (NE)
-Failure to record accrued wages.
A) understated (U)
B) overstated (O)
C) no effect (NE)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
For each of the following oversights, state what total assets will be
-Failure to recognise the earned portion of revenue received in advance.
A) understated (U)
B) overstated (O)
C) no effect (NE)
-Failure to recognise the earned portion of revenue received in advance.
A) understated (U)
B) overstated (O)
C) no effect (NE)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
On 31 December 2019, Lance Ltd prepared an income statement and a statement of financial position but failed to take into account three adjusting entries. The incorrect income statement showed a profit of $40,000. The statement of financial position showed total assets, $120,000; total liabilities, $50,000; and equity, $70,000.
The data for the three adjusting entries were:
(1) Depreciation of $7,000 was not recorded on equipment.
(2) Wages amounting to $8,000 for the last two days in December were not paid and not recorded. The next payroll will be in January.
(3) Rent of $12,000 was paid for two months in advance on 31 December. The entire amount was debited to Rent Expense when paid.
Complete the following tabulation to correct the financial statement amounts shown (indicate deductions with parentheses)
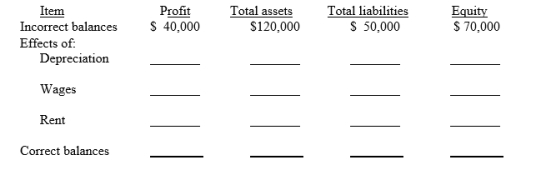
The data for the three adjusting entries were:
(1) Depreciation of $7,000 was not recorded on equipment.
(2) Wages amounting to $8,000 for the last two days in December were not paid and not recorded. The next payroll will be in January.
(3) Rent of $12,000 was paid for two months in advance on 31 December. The entire amount was debited to Rent Expense when paid.
Complete the following tabulation to correct the financial statement amounts shown (indicate deductions with parentheses)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Ellis Ltd accumulates the following adjustment data at 31 December.
1. Revenue of $800 collected in advance has now been earned.
2. Salaries of $600 are unpaid.
3. Prepaid rent totalling $450 has expired.
4. Supplies of $550 have been used.
5. Revenue earned but not yet invoiced totals $750.
6. Electricity expenses of $200 are unpaid.
7. Interest of $250 has accrued on a note payable.
(a) For each of the above items indicate:
1. the type of adjustment (prepaid expense, revenue received in advance, accrued revenue, or accrued expense)
2. the account relationship (asset/liability, liability/revenue, etc.)
3. the status of account balances before adjustment (understatement or overstatement)
4. the adjusting entry.
(b) Assume profit before the adjustments listed above was $16,500. What is the adjusted profit?
Prepare your answer in the tabular form presented below.

1. Revenue of $800 collected in advance has now been earned.
2. Salaries of $600 are unpaid.
3. Prepaid rent totalling $450 has expired.
4. Supplies of $550 have been used.
5. Revenue earned but not yet invoiced totals $750.
6. Electricity expenses of $200 are unpaid.
7. Interest of $250 has accrued on a note payable.
(a) For each of the above items indicate:
1. the type of adjustment (prepaid expense, revenue received in advance, accrued revenue, or accrued expense)
2. the account relationship (asset/liability, liability/revenue, etc.)
3. the status of account balances before adjustment (understatement or overstatement)
4. the adjusting entry.
(b) Assume profit before the adjustments listed above was $16,500. What is the adjusted profit?
Prepare your answer in the tabular form presented below.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Select the best situation
prepaid expense (PE), revenue received in advance (RRA), accrued revenue (AR) or an accrued expense (AE).
-Unrecorded interest earned on investment bonds is $245.
A) prepaid expense (PE)
B) revenue received in advance (RRA)
C)accrued revenue (AR)
D)an accrued expense (AE).
prepaid expense (PE), revenue received in advance (RRA), accrued revenue (AR) or an accrued expense (AE).
-Unrecorded interest earned on investment bonds is $245.
A) prepaid expense (PE)
B) revenue received in advance (RRA)
C)accrued revenue (AR)
D)an accrued expense (AE).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Select the best situation
prepaid expense (PE), revenue received in advance (RRA), accrued revenue (AR) or an accrued expense (AE).
-Rates that have been incurred but have not yet been paid or recorded amount to $300.
A) prepaid expense (PE)
B) revenue received in advance (RRA)
C)accrued revenue (AR)
D)an accrued expense (AE).
prepaid expense (PE), revenue received in advance (RRA), accrued revenue (AR) or an accrued expense (AE).
-Rates that have been incurred but have not yet been paid or recorded amount to $300.
A) prepaid expense (PE)
B) revenue received in advance (RRA)
C)accrued revenue (AR)
D)an accrued expense (AE).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Select the best situation
prepaid expense (PE), revenue received in advance (RRA), accrued revenue (AR) or an accrued expense (AE).
-Legal fees of $1,000 were collected in advance. By year end 60 per cent were still unearned.
A) prepaid expense (PE)
B) revenue received in advance (RRA)
C)accrued revenue (AR)
D)an accrued expense (AE).
prepaid expense (PE), revenue received in advance (RRA), accrued revenue (AR) or an accrued expense (AE).
-Legal fees of $1,000 were collected in advance. By year end 60 per cent were still unearned.
A) prepaid expense (PE)
B) revenue received in advance (RRA)
C)accrued revenue (AR)
D)an accrued expense (AE).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Select the best situation
prepaid expense (PE), revenue received in advance (RRA), accrued revenue (AR) or an accrued expense (AE).
-Prepaid insurance had a $500 balance prior to adjustment. By year end, 40 percent was still unexpired.
A) prepaid expense (PE)
B) revenue received in advance (RRA)
C)accrued revenue (AR)
D)an accrued expense (AE).
prepaid expense (PE), revenue received in advance (RRA), accrued revenue (AR) or an accrued expense (AE).
-Prepaid insurance had a $500 balance prior to adjustment. By year end, 40 percent was still unexpired.
A) prepaid expense (PE)
B) revenue received in advance (RRA)
C)accrued revenue (AR)
D)an accrued expense (AE).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Select the best situation
prepaid expense (PE), revenue received in advance (RRA), accrued revenue (AR) or an accrued expense (AE).
-Unpaid salaries earned by year end but not yet paid or recorded amounted to $1,200.
A) prepaid expense (PE)
B) revenue received in advance (RRA)
C)accrued revenue (AR)
D)an accrued expense (AE).
prepaid expense (PE), revenue received in advance (RRA), accrued revenue (AR) or an accrued expense (AE).
-Unpaid salaries earned by year end but not yet paid or recorded amounted to $1,200.
A) prepaid expense (PE)
B) revenue received in advance (RRA)
C)accrued revenue (AR)
D)an accrued expense (AE).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Match the statements with the appropriate terms :
-Office supplies on hand that will be used in the next period.
A) Prepaid expenses
B) Revenue received in advance
C) Accrued revenues
D) Accrued expenses
-Office supplies on hand that will be used in the next period.
A) Prepaid expenses
B) Revenue received in advance
C) Accrued revenues
D) Accrued expenses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Match the statements with the appropriate terms :
-Rent revenue collected; not yet earned.
A) Prepaid expenses
B) Revenue received in advance
C) Accrued revenues
D) Accrued expenses
-Rent revenue collected; not yet earned.
A) Prepaid expenses
B) Revenue received in advance
C) Accrued revenues
D) Accrued expenses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Match the statements with the appropriate terms :
-Interest earned; not yet collected.
A) Prepaid expenses
B) Revenue received in advance
C) Accrued revenues
D) Accrued expenses
-Interest earned; not yet collected.
A) Prepaid expenses
B) Revenue received in advance
C) Accrued revenues
D) Accrued expenses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Match the statements with the appropriate terms :
-An expense incurred; not yet paid or recorded.
A) Prepaid expenses
B) Revenue received in advance
C) Accrued revenues
D) Accrued expenses
-An expense incurred; not yet paid or recorded.
A) Prepaid expenses
B) Revenue received in advance
C) Accrued revenues
D) Accrued expenses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Match the statements with the appropriate terms :
-A revenue earned; not yet collected or recorded.
A) Prepaid expenses
B) Revenue received in advance
C) Accrued revenues
D) Accrued expenses
-A revenue earned; not yet collected or recorded.
A) Prepaid expenses
B) Revenue received in advance
C) Accrued revenues
D) Accrued expenses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Match the statements with the appropriate terms :
-An expense not yet incurred; paid in advance.
A) Prepaid expenses
B) Revenue received in advance
C) Accrued revenues
D) Accrued expenses
-An expense not yet incurred; paid in advance.
A) Prepaid expenses
B) Revenue received in advance
C) Accrued revenues
D) Accrued expenses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The Strikers, a semi-professional cricket team, prepare financial statements on a monthly basis. Their season begins in November, but in October the team engaged in the following transactions:
(a) Paid $150,000 to Cooma Council as advance rent for use of Cooma Stadium for the six-month period of 1 November to 30 April.
(b) Collected $300,000 cash from sales of season tickets for the team's 20 home games. This amount was credited to Revenue received in advance.
During the month of November, the Strikers played four home games and five away games.
Instructions: Prepare the adjusting entries required at 30 November for the transactions above.
(a) Paid $150,000 to Cooma Council as advance rent for use of Cooma Stadium for the six-month period of 1 November to 30 April.
(b) Collected $300,000 cash from sales of season tickets for the team's 20 home games. This amount was credited to Revenue received in advance.
During the month of November, the Strikers played four home games and five away games.
Instructions: Prepare the adjusting entries required at 30 November for the transactions above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Prepare adjusting entries for the following transactions. Omit explanations.
1. Depreciation on equipment is $840 for the accounting period.
2. Interest of $175 is owing on a loan payable.
3. There was no beginning balance of supplies. During the period $400 of office supplies were purchased. At the end of the period $70 of supplies were on hand.
4. Prepaid rent had a $1,000 normal balance prior to adjustment. By year end $300 had expired.
5. Accrued salaries at the end of the period amounted to $900.
1. Depreciation on equipment is $840 for the accounting period.
2. Interest of $175 is owing on a loan payable.
3. There was no beginning balance of supplies. During the period $400 of office supplies were purchased. At the end of the period $70 of supplies were on hand.
4. Prepaid rent had a $1,000 normal balance prior to adjustment. By year end $300 had expired.
5. Accrued salaries at the end of the period amounted to $900.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Prepare adjusting entries for the following transactions. Omit explanations.
1. Unrecorded interest receivable that has accrued on investment bonds is $270.
2. Rates incurred but not paid or recorded amount to $700.
3. Legal service revenues of $3,000 were collected in advance. By year end $600 was earned.
4. Prepaid insurance had a $400 debit balance prior to adjustment. By year end, 40 percent was still unexpired.
5. Salaries incurred by year end but not yet paid or recorded amounted to $950.
1. Unrecorded interest receivable that has accrued on investment bonds is $270.
2. Rates incurred but not paid or recorded amount to $700.
3. Legal service revenues of $3,000 were collected in advance. By year end $600 was earned.
4. Prepaid insurance had a $400 debit balance prior to adjustment. By year end, 40 percent was still unexpired.
5. Salaries incurred by year end but not yet paid or recorded amounted to $950.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Prepare year-end adjustments for the following transactions. Omit explanations.
1. Accrued interest on notes receivable, $85.
2. Revenues received in advance now earned, $1,000.
3. Three years rent, totalling $36,000, was paid in advance at the beginning of the year.
4. Services totalling $2,100 had been performed but not yet invoiced at the end of the year.
5. Depreciation on equipment totalled $4,500 for the year.
6. Supplies for use totalled $690. By year end, only $100 in supplies remained.
7. Salaries owed to employees at the end of the year total $1,000.
1. Accrued interest on notes receivable, $85.
2. Revenues received in advance now earned, $1,000.
3. Three years rent, totalling $36,000, was paid in advance at the beginning of the year.
4. Services totalling $2,100 had been performed but not yet invoiced at the end of the year.
5. Depreciation on equipment totalled $4,500 for the year.
6. Supplies for use totalled $690. By year end, only $100 in supplies remained.
7. Salaries owed to employees at the end of the year total $1,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Allen Coat Ltd purchased a delivery truck on 1 June for $18,000, paying $8,000 cash and signing a 12%, 2-month note payable for the remaining balance. The truck is expected to depreciate $3,000 each year. Allen Coat Ltd prepares monthly financial statements.
(a) Prepare the general journal entry to record the acquisition of the delivery truck on 1 June.
(b) Prepare any adjusting journal entries that should be made on 30 June
(c) Show how the delivery truck will be reflected on Allen Coat Ltd's statement of financial position on 30 June.
(a) Prepare the general journal entry to record the acquisition of the delivery truck on 1 June.
(b) Prepare any adjusting journal entries that should be made on 30 June
(c) Show how the delivery truck will be reflected on Allen Coat Ltd's statement of financial position on 30 June.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Watson Ltd prepares monthly financial statements. Below are listed some selected accounts and their balances on the 30 September trial balance before any adjustments have been made for the month of September.
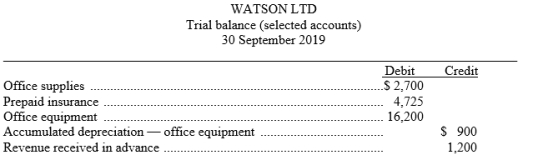 (Note: Debit column does not equal credit column because this is a partial listing of selected account balances.)
(Note: Debit column does not equal credit column because this is a partial listing of selected account balances.)
An analysis of the account balances by the company's accountant provided the following additional information:
1. A physical count of office supplies revealed $1,200 on hand on 30 September.
2. A two-year insurance policy was purchased on 1 June for $5,400.
3. Office equipment depreciates $5,400 per year.
4. The amount of rent received in advance that remains unearned at 30 September is $500.
Using the above additional information, prepare the adjusting entries that should be made by Watson Ltd on 30 September.
 (Note: Debit column does not equal credit column because this is a partial listing of selected account balances.)
(Note: Debit column does not equal credit column because this is a partial listing of selected account balances.)An analysis of the account balances by the company's accountant provided the following additional information:
1. A physical count of office supplies revealed $1,200 on hand on 30 September.
2. A two-year insurance policy was purchased on 1 June for $5,400.
3. Office equipment depreciates $5,400 per year.
4. The amount of rent received in advance that remains unearned at 30 September is $500.
Using the above additional information, prepare the adjusting entries that should be made by Watson Ltd on 30 September.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Prepare the required end-of-period adjusting entries for each independent case listed below.
Case 1:
Thomas Ltd began the year with a $3,000 balance in the Office supplies account. During the year, $8,500 worth of additional office supplies was purchased. A physical count of office supplies on hand at the end of the year revealed that $6,400 worth of office supplies had been used during the year. No adjusting entry has been made.
Case 2:
Carson Ltd has a calendar year-end accounting period. On 1 July, the company purchased office equipment for $28,800. It is estimated that the office equipment will depreciate $400 each month. No adjusting entry has been made.
Case 3:
Yates Realty is in the business of renting several apartment buildings and prepares monthly financial statements. It has been determined that 3 tenants in $600 per month apartments and one tenant in the $1,000 per month apartment had not paid their December rent as of 31 December.
Case 1:
Thomas Ltd began the year with a $3,000 balance in the Office supplies account. During the year, $8,500 worth of additional office supplies was purchased. A physical count of office supplies on hand at the end of the year revealed that $6,400 worth of office supplies had been used during the year. No adjusting entry has been made.
Case 2:
Carson Ltd has a calendar year-end accounting period. On 1 July, the company purchased office equipment for $28,800. It is estimated that the office equipment will depreciate $400 each month. No adjusting entry has been made.
Case 3:
Yates Realty is in the business of renting several apartment buildings and prepares monthly financial statements. It has been determined that 3 tenants in $600 per month apartments and one tenant in the $1,000 per month apartment had not paid their December rent as of 31 December.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The Reality Insurance Agency prepares monthly financial statements. Presented below is an income statement for the month of June that is correct on the basis of information supplied.
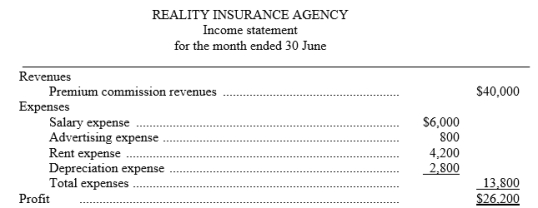 Additional data: When the income statement was prepared, the agency accountant neglected to take into consideration the following information:
Additional data: When the income statement was prepared, the agency accountant neglected to take into consideration the following information:
1. An electricity invoice for $2,000 was received on the last day of the month for electric and gas service for the month of June.
2. A company insurance salesman sold a life insurance policy to a client for a premium of $28,000. The agency invoiced the client for the policy and is entitled to a commission of 20%.
3. Supplies on hand at the beginning of the month were $3,000. The agency purchased additional supplies during the month for $2,500 in cash and $2,200 of supplies were on hand at 30 June.
4. The agency purchased a new car at the beginning of the month for $16,800 cash. The car will depreciate $4,200 per year.
5. Salaries owed to employees at the end of the month total $5,300. The salaries will be paid on July 5.
Prepare a corrected income statement.
 Additional data: When the income statement was prepared, the agency accountant neglected to take into consideration the following information:
Additional data: When the income statement was prepared, the agency accountant neglected to take into consideration the following information:1. An electricity invoice for $2,000 was received on the last day of the month for electric and gas service for the month of June.
2. A company insurance salesman sold a life insurance policy to a client for a premium of $28,000. The agency invoiced the client for the policy and is entitled to a commission of 20%.
3. Supplies on hand at the beginning of the month were $3,000. The agency purchased additional supplies during the month for $2,500 in cash and $2,200 of supplies were on hand at 30 June.
4. The agency purchased a new car at the beginning of the month for $16,800 cash. The car will depreciate $4,200 per year.
5. Salaries owed to employees at the end of the month total $5,300. The salaries will be paid on July 5.
Prepare a corrected income statement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
One part of an adjusting entry is given below.
Indicate the account title for the other part of the entry.
-Revenue received in advance is debited.
Indicate the account title for the other part of the entry.
-Revenue received in advance is debited.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
One part of an adjusting entry is given below.
Indicate the account title for the other part of the entry.
-Prepaid rent is credited.
Indicate the account title for the other part of the entry.
-Prepaid rent is credited.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
One part of an adjusting entry is given below.
Indicate the account title for the other part of the entry.
-Accounts receivable is debited.
Indicate the account title for the other part of the entry.
-Accounts receivable is debited.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
One part of an adjusting entry is given below.
Indicate the account title for the other part of the entry.
-Depreciation expense is debited.
Indicate the account title for the other part of the entry.
-Depreciation expense is debited.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
One part of an adjusting entry is given below.
Indicate the account title for the other part of the entry.
-Electricity expense is debited.
Indicate the account title for the other part of the entry.
-Electricity expense is debited.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
One part of an adjusting entry is given below.
Indicate the account title for the other part of the entry.
-Interest payable is credited.
Indicate the account title for the other part of the entry.
-Interest payable is credited.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
One part of an adjusting entry is given below.
Indicate the account title for the other part of the entry.
-Service revenue is credited (give two possible debit accounts).
Indicate the account title for the other part of the entry.
-Service revenue is credited (give two possible debit accounts).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
One part of an adjusting entry is given below.
Indicate the account title for the other part of the entry.
-Interest receivable is debited.
Indicate the account title for the other part of the entry.
-Interest receivable is debited.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The following ledger accounts are used by the Crawford Greyhound Park:
Accounts receivable
Prepaid printing
Prepaid rent
Admissions revenue received in advance
Printing expense
Rent expense
Admissions revenue
Concessions revenue
Cash
Note payable
Interest expense
Interest payable
Commissions revenue
For each of the following transactions below, prepare the journal entry (if one is required) to record the initial transaction and then prepare the adjusting entry, if any, required on 30 September, the end of the financial year.
(a) On 1 September, paid rent on the track facility for three months, $180,000.
(b) On 1 September, sold season tickets for admission to the racetrack. The racing season is year-round with 25 racing days each month. Season ticket sales totalled $900,000.
(c) On 1 September, borrowed $150,000 from First National Bank by issuing a 12% promissory note payable due in three months.
(d) On 5 September paid $3,000 cash for racing schedules for 20 racing days in September, 25 racing days in October and 15 racing days in November.
(e) The accountant for the concessions company reported that gross receipts for September were $140,000. Ten per cent is due to Crawford and will be remitted by October 10.
Accounts receivable
Prepaid printing
Prepaid rent
Admissions revenue received in advance
Printing expense
Rent expense
Admissions revenue
Concessions revenue
Cash
Note payable
Interest expense
Interest payable
Commissions revenue
For each of the following transactions below, prepare the journal entry (if one is required) to record the initial transaction and then prepare the adjusting entry, if any, required on 30 September, the end of the financial year.
(a) On 1 September, paid rent on the track facility for three months, $180,000.
(b) On 1 September, sold season tickets for admission to the racetrack. The racing season is year-round with 25 racing days each month. Season ticket sales totalled $900,000.
(c) On 1 September, borrowed $150,000 from First National Bank by issuing a 12% promissory note payable due in three months.
(d) On 5 September paid $3,000 cash for racing schedules for 20 racing days in September, 25 racing days in October and 15 racing days in November.
(e) The accountant for the concessions company reported that gross receipts for September were $140,000. Ten per cent is due to Crawford and will be remitted by October 10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Cambridge Ltd has an accounting financial year which ends on 30 June. The company also has a policy of paying the weekly payroll on Friday. Payroll records indicate the following salary costs were incurred.
 (a) Prepare any necessary adjusting journal entries that should be made at year ended on 30 June.
(a) Prepare any necessary adjusting journal entries that should be made at year ended on 30 June.
(b) Prepare the journal entry to record the payment of the weekly payroll on 2 July.
 (a) Prepare any necessary adjusting journal entries that should be made at year ended on 30 June.
(a) Prepare any necessary adjusting journal entries that should be made at year ended on 30 June.(b) Prepare the journal entry to record the payment of the weekly payroll on 2 July.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Presented below is the trial balance and adjusted trial balance for Jim Lankford Ltd on 31 December.
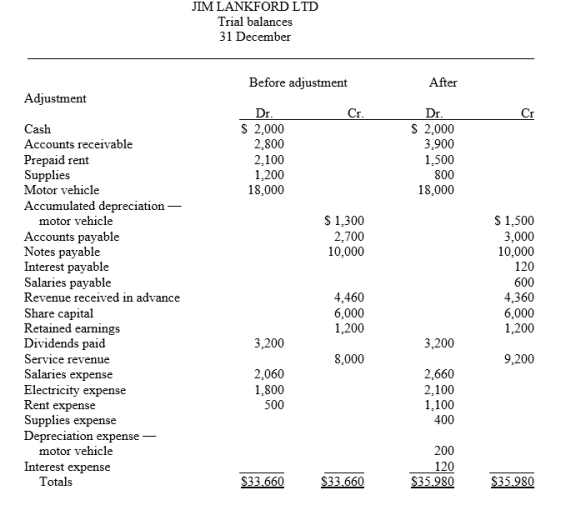 Prepare, in journal form with explanations, the adjusting entries that explain the changes in the balances from the trial balance to the adjusted trial balance.
Prepare, in journal form with explanations, the adjusting entries that explain the changes in the balances from the trial balance to the adjusted trial balance.
 Prepare, in journal form with explanations, the adjusting entries that explain the changes in the balances from the trial balance to the adjusted trial balance.
Prepare, in journal form with explanations, the adjusting entries that explain the changes in the balances from the trial balance to the adjusted trial balance.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The National Koala Park operates a tourist attraction in Pennant Hills. The entity adjusts its accounts at the end of each month. The selected accounts appearing below reflect balances after adjusting entries were prepared on 30 April. The adjusted trial balance shows the following:
 Other data:
Other data:
1. Three months' rent had been prepaid on 1 April.
2. The fencing is being depreciated at $6,000 per year.
3. The revenue received in advance represents tickets sold for future park visits. The tickets were sold at $4.00 each on 1 April. During April, 25 of the tickets were used by customers.
Instructions:
(a) Calculate the following:
1. Monthly rent expense.
2. The age of the fencing in months.
3. The number of tickets sold on 1 April.
(b) Prepare the adjusting entries that were made by the National Koala Park on 30 April.
 Other data:
Other data:1. Three months' rent had been prepaid on 1 April.
2. The fencing is being depreciated at $6,000 per year.
3. The revenue received in advance represents tickets sold for future park visits. The tickets were sold at $4.00 each on 1 April. During April, 25 of the tickets were used by customers.
Instructions:
(a) Calculate the following:
1. Monthly rent expense.
2. The age of the fencing in months.
3. The number of tickets sold on 1 April.
(b) Prepare the adjusting entries that were made by the National Koala Park on 30 April.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The adjusted trial balance of AMBER Ltd appears below. Using the information from the adjusted trial balance, prepare for the month ending 31 December:
1. an income statement
2. a statement of changes in equity
3. a statement of financial position.
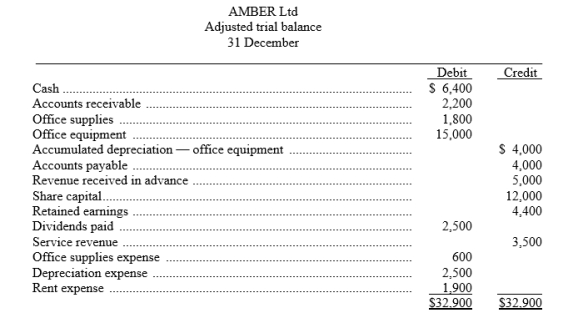
1. an income statement
2. a statement of changes in equity
3. a statement of financial position.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Match the descriptions with their terms :
-Events recorded only in periods the company receives or pays cash
A) Accounting period concept
B) Cash basis
C) Revenue recognition principle
D) Prepaid expenses
E) Matching principle
F) Accrued revenues
G) Depreciation
H) Post-closing trial balance
I) Accrued expenses
J) Carrying amount
-Events recorded only in periods the company receives or pays cash
A) Accounting period concept
B) Cash basis
C) Revenue recognition principle
D) Prepaid expenses
E) Matching principle
F) Accrued revenues
G) Depreciation
H) Post-closing trial balance
I) Accrued expenses
J) Carrying amount

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Match the descriptions with their terms :
-Expenses paid before they are incurred
A) Accounting period concept
B) Cash basis
C) Revenue recognition principle
D) Prepaid expenses
E) Matching principle
F) Accrued revenues
G) Depreciation
H) Post-closing trial balance
I) Accrued expenses
J) Carrying amount
-Expenses paid before they are incurred
A) Accounting period concept
B) Cash basis
C) Revenue recognition principle
D) Prepaid expenses
E) Matching principle
F) Accrued revenues
G) Depreciation
H) Post-closing trial balance
I) Accrued expenses
J) Carrying amount

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Match the descriptions with their terms :
-Cost less accumulated depreciation
A) Accounting period concept
B) Cash basis
C) Revenue recognition principle
D) Prepaid expenses
E) Matching principle
F) Accrued revenues
G) Depreciation
H) Post-closing trial balance
I) Accrued expenses
J) Carrying amount
-Cost less accumulated depreciation
A) Accounting period concept
B) Cash basis
C) Revenue recognition principle
D) Prepaid expenses
E) Matching principle
F) Accrued revenues
G) Depreciation
H) Post-closing trial balance
I) Accrued expenses
J) Carrying amount

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Match the descriptions with their terms :
-The economic life of a business can be divided into artificial time periods
A) Accounting period concept
B) Cash basis
C) Revenue recognition principle
D) Prepaid expenses
E) Matching principle
F) Accrued revenues
G) Depreciation
H) Post-closing trial balance
I) Accrued expenses
J) Carrying amount
-The economic life of a business can be divided into artificial time periods
A) Accounting period concept
B) Cash basis
C) Revenue recognition principle
D) Prepaid expenses
E) Matching principle
F) Accrued revenues
G) Depreciation
H) Post-closing trial balance
I) Accrued expenses
J) Carrying amount

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Match the descriptions with their terms :
-Efforts are related to accomplishments
A) Accounting period concept
B) Cash basis
C) Revenue recognition principle
D) Prepaid expenses
E) Matching principle
F) Accrued revenues
G) Depreciation
H) Post-closing trial balance
I) Accrued expenses
J) Carrying amount
-Efforts are related to accomplishments
A) Accounting period concept
B) Cash basis
C) Revenue recognition principle
D) Prepaid expenses
E) Matching principle
F) Accrued revenues
G) Depreciation
H) Post-closing trial balance
I) Accrued expenses
J) Carrying amount

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Match the descriptions with their terms :
-Includes only permanent - statement of financial position - accounts
A) Accounting period concept
B) Cash basis
C) Revenue recognition principle
D) Prepaid expenses
E) Matching principle
F) Accrued revenues
G) Depreciation
H) Post-closing trial balance
I) Accrued expenses
J) Carrying amount
-Includes only permanent - statement of financial position - accounts
A) Accounting period concept
B) Cash basis
C) Revenue recognition principle
D) Prepaid expenses
E) Matching principle
F) Accrued revenues
G) Depreciation
H) Post-closing trial balance
I) Accrued expenses
J) Carrying amount

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Match the descriptions with their terms :
-Revenue is recognised when earned
A) Accounting period concept
B) Cash basis
C) Revenue recognition principle
D) Prepaid expenses
E) Matching principle
F) Accrued revenues
G) Depreciation
H) Post-closing trial balance
I) Accrued expenses
J) Carrying amount
-Revenue is recognised when earned
A) Accounting period concept
B) Cash basis
C) Revenue recognition principle
D) Prepaid expenses
E) Matching principle
F) Accrued revenues
G) Depreciation
H) Post-closing trial balance
I) Accrued expenses
J) Carrying amount

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Match the descriptions with their terms :
-Revenues earned but not yet received
A) Accounting period concept
B) Cash basis
C) Revenue recognition principle
D) Prepaid expenses
E) Matching principle
F) Accrued revenues
G) Depreciation
H) Post-closing trial balance
I) Accrued expenses
J) Carrying amount
-Revenues earned but not yet received
A) Accounting period concept
B) Cash basis
C) Revenue recognition principle
D) Prepaid expenses
E) Matching principle
F) Accrued revenues
G) Depreciation
H) Post-closing trial balance
I) Accrued expenses
J) Carrying amount

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Match the descriptions with their terms :
-Expenses incurred but not yet paid
A) Accounting period concept
B) Cash basis
C) Revenue recognition principle
D) Prepaid expenses
E) Matching principle
F) Accrued revenues
G) Depreciation
H) Post-closing trial balance
I) Accrued expenses
J) Carrying amount
-Expenses incurred but not yet paid
A) Accounting period concept
B) Cash basis
C) Revenue recognition principle
D) Prepaid expenses
E) Matching principle
F) Accrued revenues
G) Depreciation
H) Post-closing trial balance
I) Accrued expenses
J) Carrying amount

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Match the descriptions with their terms :
-A cost allocation process
A) Accounting period concept
B) Cash basis
C) Revenue recognition principle
D) Prepaid expenses
E) Matching principle
F) Accrued revenues
G) Depreciation
H) Post-closing trial balance
I) Accrued expenses
J) Carrying amount
-A cost allocation process
A) Accounting period concept
B) Cash basis
C) Revenue recognition principle
D) Prepaid expenses
E) Matching principle
F) Accrued revenues
G) Depreciation
H) Post-closing trial balance
I) Accrued expenses
J) Carrying amount

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



