Deck 23: Conduction of Electricity in Solids
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/12
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 23: Conduction of Electricity in Solids
1
The number density n of conductions electrons, the resistivity 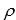 , and the temperature coefficient of resistivity are given below for five materials.Which is a semiconductor?
, and the temperature coefficient of resistivity are given below for five materials.Which is a semiconductor?
A) n = 1029 m-3, 11ef175a_747e_fecd_8934_9df8412bf74a_TB7453_11 = 10-8 . m, = +10-3 K-1
B) n = 1028 m-3, 11ef175a_747e_fecd_8934_9df8412bf74a_TB7453_11 = 10-9 . m, = -10-3 K-1
C) n = 1028 m-3, 11ef175a_747e_fecd_8934_9df8412bf74a_TB7453_11 = 10-9 . m, = +10-3 K-1
D) n = 1015 m-3, 11ef175a_747e_fecd_8934_9df8412bf74a_TB7453_11 = 103 . m, = -10-2 K-1
E) n = 1022 m-3, 11ef175a_747e_fecd_8934_9df8412bf74a_TB7453_11= 10-7 .m, = +10-3 K-1
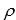 , and the temperature coefficient of resistivity are given below for five materials.Which is a semiconductor?
, and the temperature coefficient of resistivity are given below for five materials.Which is a semiconductor?A) n = 1029 m-3, 11ef175a_747e_fecd_8934_9df8412bf74a_TB7453_11 = 10-8 . m, = +10-3 K-1
B) n = 1028 m-3, 11ef175a_747e_fecd_8934_9df8412bf74a_TB7453_11 = 10-9 . m, = -10-3 K-1
C) n = 1028 m-3, 11ef175a_747e_fecd_8934_9df8412bf74a_TB7453_11 = 10-9 . m, = +10-3 K-1
D) n = 1015 m-3, 11ef175a_747e_fecd_8934_9df8412bf74a_TB7453_11 = 103 . m, = -10-2 K-1
E) n = 1022 m-3, 11ef175a_747e_fecd_8934_9df8412bf74a_TB7453_11= 10-7 .m, = +10-3 K-1
n = 1015 m-3, 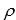 = 103 . m, = -10-2 K-1
= 103 . m, = -10-2 K-1
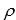 = 103 . m, = -10-2 K-1
= 103 . m, = -10-2 K-1 2
The density of states for a metal depends primarily on:
A) the temperature
B) the energy associated with the state
C) the density of the metal
D) the volume of the sample
E) none of these
A) the temperature
B) the energy associated with the state
C) the density of the metal
D) the volume of the sample
E) none of these
the energy associated with the state
3
The Fermi-Dirac probability function P(E) varies between:
A) 0 and 1
B) 0 and infinity
C) 1 and infinity
D) -1 and 1
E) 0 and EF
A) 0 and 1
B) 0 and infinity
C) 1 and infinity
D) -1 and 1
E) 0 and EF
0 and 1
4
For a metal at absolute temperature T, with Fermi energy EF, the occupancy probability is given by:
A)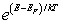
B)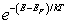
C)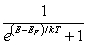
D)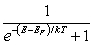
E)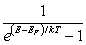
A)
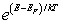
B)
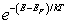
C)
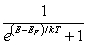
D)
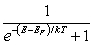
E)
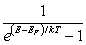

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The occupancy probability for a state with energy equal to the Fermi energy is:
A) 0
B) 0.5
C) 1
D) 1.5
E) 2
A) 0
B) 0.5
C) 1
D) 1.5
E) 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Ther Fermi energy of a metal depends primarily on:
A) the temperature
B) the volume of the sample
C) the mass density of the metal
D) the size of the sample
E) the number density of conduction electrons
A) the temperature
B) the volume of the sample
C) the mass density of the metal
D) the size of the sample
E) the number density of conduction electrons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If the density of states is N(E) and the occupancy probability is P(E), then the density of unoccupied states is:
A) N(E) + P(E)
B) N(E)/P(E)
C) N(E) - P(E)
D) N(E)P(E)
E) P(E)/N(E)
A) N(E) + P(E)
B) N(E)/P(E)
C) N(E) - P(E)
D) N(E)P(E)
E) P(E)/N(E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A hole refers to:
A) a proton
B) a positively charged electron
C) an electron which has somehow lost its charge
D) a microscopic defect in a solid
E) the absence of an electron in an otherwise filled band
A) a proton
B) a positively charged electron
C) an electron which has somehow lost its charge
D) a microscopic defect in a solid
E) the absence of an electron in an otherwise filled band

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
For a pure semiconductor the Fermi level is:
A) in the conduction band
B) well above the conduction band
C) in the valence band
D) well below the valence band
E) near the center of the gap between the valence and conduction bands
A) in the conduction band
B) well above the conduction band
C) in the valence band
D) well below the valence band
E) near the center of the gap between the valence and conduction bands

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
An acceptor replacement atom in silicon might have ______ electrons in its outer shell.
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6
E) 7
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6
E) 7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A donor replacement atom in silicon might have ______ electrons in its outer shell.
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
When a forward bias is applied to a p-n junction the concentration of electrons on the p side:
A) increases slightly
B) increases dramatically
C) decreases slightly
D) decreases dramatically
E) does not change
A) increases slightly
B) increases dramatically
C) decreases slightly
D) decreases dramatically
E) does not change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



