Deck 22: All About Atoms
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/23
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 22: All About Atoms
1
The magnitude of the orbital angular momentum of an electron is what multiple of 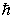 ? (
? ( 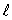 is a positive integer.)
is a positive integer.)
A) 1
B) 1/2
C)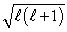
D)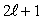
E)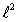
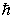 ? (
? ( 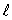 is a positive integer.)
is a positive integer.)A) 1
B) 1/2
C)
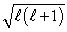
D)
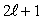
E)
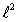
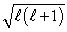
2
The number of possible values of the magnetic quantum number 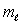 associated with a given value of the orbital quantum number
associated with a given value of the orbital quantum number 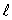 is:
is:
A) 1
B) 2
C)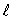
D)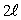
E)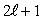
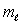 associated with a given value of the orbital quantum number
associated with a given value of the orbital quantum number 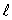 is:
is:A) 1
B) 2
C)
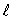
D)
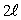
E)
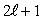
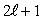
3
An electron is in a quantum state for which there are seven allowed values of the z component of the angular momentum.The magnitude of the angular momentum is:
A)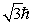
B)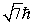
C)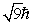
D)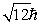
E)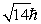
A)
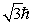
B)
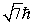
C)
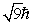
D)
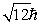
E)
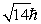
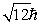
4
An electron in an atom is in a state with 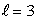 and
and 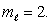 The angle between
The angle between 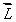 and the z axis is:
and the z axis is:
A) 48.2
B) 60
C) 30
D) 35.3
E) 54.7
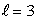 and
and 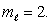 The angle between
The angle between 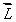 and the z axis is:
and the z axis is:A) 48.2
B) 60
C) 30
D) 35.3
E) 54.7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
An electron in an atom is in a state with 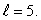 The minimum angle between
The minimum angle between 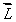 and the z axis is:
and the z axis is:
A) 0
B) 18.0
C) 24.1
D) 36.7
E) 33.6
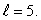 The minimum angle between
The minimum angle between 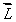 and the z axis is:
and the z axis is:A) 0
B) 18.0
C) 24.1
D) 36.7
E) 33.6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The Stern-Gerlach experiment makes use of:
A) a strong uniform magnetic field
B) a strong non-uniform magnetic field
C) a strong uniform electric field
D) a strong non-uniform electric field
E) strong perpendicular electric and magnetic fields
A) a strong uniform magnetic field
B) a strong non-uniform magnetic field
C) a strong uniform electric field
D) a strong non-uniform electric field
E) strong perpendicular electric and magnetic fields

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The magnetic field 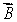 is along the z axis in a Stern-Gerlach experiment. The force it exerts on a magnetic dipole with dipole moment
is along the z axis in a Stern-Gerlach experiment. The force it exerts on a magnetic dipole with dipole moment 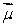 is proportional to:
is proportional to:
A)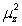
B) B2
C) dB/dz
D) d2B/dz2
E)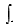 B dz
B dz
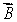 is along the z axis in a Stern-Gerlach experiment. The force it exerts on a magnetic dipole with dipole moment
is along the z axis in a Stern-Gerlach experiment. The force it exerts on a magnetic dipole with dipole moment 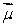 is proportional to:
is proportional to:A)
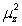
B) B2
C) dB/dz
D) d2B/dz2
E)
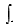 B dz
B dz
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A magnetic dipole 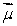 is placed in a strong uniform magnetic field
is placed in a strong uniform magnetic field 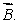 The associated force exerted on the dipole is:
The associated force exerted on the dipole is:
A) along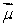
B) along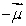
C) along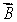
D) along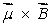
E) zero
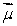 is placed in a strong uniform magnetic field
is placed in a strong uniform magnetic field 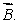 The associated force exerted on the dipole is:
The associated force exerted on the dipole is:A) along
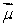
B) along
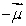
C) along
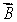
D) along
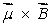
E) zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
To observe the Zeeman effect one uses:
A) a strong uniform magnetic field
B) a strong non-uniform magnetic field
C) a strong uniform electric field
D) a strong non-uniform electric field
E) mutually perpendicular electric and magnetic fields
A) a strong uniform magnetic field
B) a strong non-uniform magnetic field
C) a strong uniform electric field
D) a strong non-uniform electric field
E) mutually perpendicular electric and magnetic fields

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The Pauli exclusion principle is obeyed by:
A) all particles
B) all charged particles
C) all particles with spin quantum numbers of 1/2
D) all particles with spin quantum numbers of 1
E) all particles with mass
A) all particles
B) all charged particles
C) all particles with spin quantum numbers of 1/2
D) all particles with spin quantum numbers of 1
E) all particles with mass

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
No state in an atom can be occupied by more than one electron. This is most closely related to the:
A) wave nature of matter
B) finite value for the speed of light
C) Bohr magneton
D) Pauli exclusion principle
E) the Einstein-de Haas effect
A) wave nature of matter
B) finite value for the speed of light
C) Bohr magneton
D) Pauli exclusion principle
E) the Einstein-de Haas effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
For any atom other that hydrogen and helium all electrons in the same shell have:
A) the same energy
B) the same magnitude of angular momentum
C) the same magnetic quantum number
D) the same spin quantum number
E) none of the above
A) the same energy
B) the same magnitude of angular momentum
C) the same magnetic quantum number
D) the same spin quantum number
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The states being filled from the beginning to end of the lanthanide series of atoms are:
A) n = 3,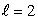 states
states
B) n = 4,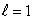 states
states
C) n = 4,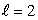 states
states
D) n = 4,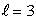 states
states
E) n = 5,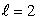 states
states
A) n = 3,
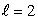 states
statesB) n = 4,
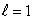 states
statesC) n = 4,
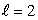 states
statesD) n = 4,
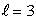 states
statesE) n = 5,
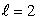 states
states
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The most energetic electron in any atom at the beginning of a period of the periodic table is in:
A) an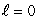 state
state
B) an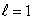 state
state
C) an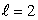 state
state
D) an n = 0 state with unspecified angular momentum
E) an n = 1 state with unspecified angular momentum
A) an
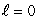 state
stateB) an
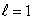 state
stateC) an
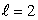 state
stateD) an n = 0 state with unspecified angular momentum
E) an n = 1 state with unspecified angular momentum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The most energetic electron in any atom at the end of a period of the periodic table is in:
A) an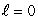 state
state
B) an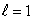 state
state
C) an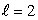 state
state
D) an n = 0 state with unspecified angular momentum
E) an n = 1 state with unspecified angular momentum
A) an
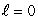 state
stateB) an
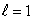 state
stateC) an
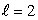 state
stateD) an n = 0 state with unspecified angular momentum
E) an n = 1 state with unspecified angular momentum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The group of atoms at the ends of periods of the periodic table are called:
A) alkali metals
B) rare earths
C) transition metal atoms
D) alkaline atoms
E) inert gas atoms
A) alkali metals
B) rare earths
C) transition metal atoms
D) alkaline atoms
E) inert gas atoms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The group of atoms at the beginning of periods of the periodic table are called:
A) alkali metal atoms
B) rare earth atoms
C) transition metal atoms
D) alkaline atoms
E) inert gas atoms
A) alkali metal atoms
B) rare earth atoms
C) transition metal atoms
D) alkaline atoms
E) inert gas atoms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Suppose the energy required to ionize an argon atom is i, the energy to excite it is e, and its thermal energy at room temperature is t. In increasing order, these three energies are:
A) i, e, t
B) t, i, e
C) e, t, i
D) i, t, e
E) t, e, i
A) i, e, t
B) t, i, e
C) e, t, i
D) i, t, e
E) t, e, i

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The effective charge acting on a single valence electron outside a closed shell is about Ne, where N is:
A) the atomic number of the nucleus
B) the atomic mass of the atom
C) usually between 1 and 3
D) half the atomic number
E) less than 1
A) the atomic number of the nucleus
B) the atomic mass of the atom
C) usually between 1 and 3
D) half the atomic number
E) less than 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A laser must be pumped to achieve:
A) a metastable state
B) fast response
C) stimulated emission
D) population inversion
E) the same wavelength for all photons
A) a metastable state
B) fast response
C) stimulated emission
D) population inversion
E) the same wavelength for all photons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Photons in a laser beam are produced by:
A) transitions from a metastable state
B) transitions from a state that decays rapidly
C) splitting of other photons
D) pumping
E) reflection from mirrors
A) transitions from a metastable state
B) transitions from a state that decays rapidly
C) splitting of other photons
D) pumping
E) reflection from mirrors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In a helium-neon laser, the laser light arises from a transition from a _________ state to a _________ state:
A) He, He
B) Ne, Ne
C) He, Ne
D) Ne, He
E) N, He
A) He, He
B) Ne, Ne
C) He, Ne
D) Ne, He
E) N, He

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A laser beam can be sharply focused because it is:
A) highly coherent
B) plane polarized
C) intense
D) circularly polarized
E) highly directional
A) highly coherent
B) plane polarized
C) intense
D) circularly polarized
E) highly directional

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



