Deck 13: Magnetic Fields Due to Currents
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/12
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Magnetic Fields Due to Currents
1
In an overhead straight wire, the current is north. The magnetic field due to this current, at our point of observation, is:
A) east
B) up
C) north
D) down
E) west
A) east
B) up
C) north
D) down
E) west
west
2
The magnetic field outside a long straight current-carrying wire depends on the distance R from the wire axis according to:
A) R
B) 1/R
C) 1/R2
D) 1/R3
E) 1/R3/2
A) R
B) 1/R
C) 1/R2
D) 1/R3
E) 1/R3/2
1/R
3
Two parallel wires carrying equal currents of 10 A attract each other with a force of 1 mN. If both currents are doubled, the force of attraction will be:
A) 1 mN
B) 4 mN
C) 0.5 mN
D) 0.25 mN
E) 2 mN
A) 1 mN
B) 4 mN
C) 0.5 mN
D) 0.25 mN
E) 2 mN
4 mN
4
Two parallel long wires carry the same current and repel each other with a force F per unit length. If both these currents are doubled and the wire separation tripled, the force per unit length becomes:
A) 2F/9
B) 4F/9
C) 2F/3
D) 4F/3
E) 6F
A) 2F/9
B) 4F/9
C) 2F/3
D) 4F/3
E) 6F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A constant current is sent through a helical coil. The coil:
A) tends to get shorter
B) tends to get longer
C) tends to rotate about its axis
D) produces zero magnetic field at its center
E) none of the above
A) tends to get shorter
B) tends to get longer
C) tends to rotate about its axis
D) produces zero magnetic field at its center
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In Ampere's law,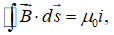 the symbol
the symbol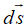 is:
is:
A) an infinitesimal piece of the wire that carries current i
B) in the direction of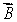
C) perpendicular to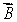
D) a vector whose magnitude is the length of the wire that carries current i
E) none of the above
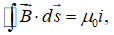 the symbol
the symbol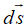 is:
is:A) an infinitesimal piece of the wire that carries current i
B) in the direction of
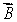
C) perpendicular to
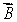
D) a vector whose magnitude is the length of the wire that carries current i
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A long straight wire carrying a 3.0 A current enters a room through a window 1.5 m high and 1.0 m wide. The path integral 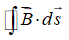 around the window frame has the value (in T.m
around the window frame has the value (in T.m
A) 0.20
B) 2.5x10-7
C) 3.0x 10-7
D) 3.8 x10-6
E) none of these
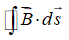 around the window frame has the value (in T.m
around the window frame has the value (in T.mA) 0.20
B) 2.5x10-7
C) 3.0x 10-7
D) 3.8 x10-6
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The magnetic field at any point is given by 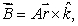 where
where 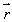 is the position vector of the point and A is a constant. The net current through a circle of radius R, in the xy plane and centered at the origin is given by:
is the position vector of the point and A is a constant. The net current through a circle of radius R, in the xy plane and centered at the origin is given by:
A) AR2/ 0
B) 2 AR/ 0
C) 4 AR3/3 0
D) 2 AR2/ 0
E) AR2/2 0
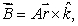 where
where 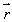 is the position vector of the point and A is a constant. The net current through a circle of radius R, in the xy plane and centered at the origin is given by:
is the position vector of the point and A is a constant. The net current through a circle of radius R, in the xy plane and centered at the origin is given by:A) AR2/ 0
B) 2 AR/ 0
C) 4 AR3/3 0
D) 2 AR2/ 0
E) AR2/2 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The magnetic field B inside a long ideal solenoid is independent of:
A) the current
B) the core material
C) the spacing of the windings
D) the cross-sectional area
E) the direction of the current
A) the current
B) the core material
C) the spacing of the windings
D) the cross-sectional area
E) the direction of the current

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Solenoid 2 has twice the radius and six times the number of turns per unit length as solenoid 1. The ratio of the magnetic field in the interior of 2 to that in the interior of 1 is:
A) 2
B) 4
C) 6
D) 1
E) 1/3
A) 2
B) 4
C) 6
D) 1
E) 1/3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If the radius of a pair of Helmholtz coils is R then the distance between the coils is:
A) R/4
B) R/2
C) R
D) 2R
E) 4R
A) R/4
B) R/2
C) R
D) 2R
E) 4R

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If R is the distance from a magnetic dipole, then the magnetic field it produces is proportional to:
A) R
B) 1/R
C) R2
D) 1/R2
E) 1/R3
A) R
B) 1/R
C) R2
D) 1/R2
E) 1/R3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



