Deck 8: Electric Potential and Gauss Law
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/13
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Electric Potential and Gauss Law
1
If 500 J of work are required to carry a 40-C charge from one point to another, the potential difference between these two points is:
A) 12.5 V
B) 20,000 V
C) 0.08 V
D) depends on the path
E) none of these
A) 12.5 V
B) 20,000 V
C) 0.08 V
D) depends on the path
E) none of these
12.5 V
2
The potential difference between two points is 100 V. If a particle with a charge of 2 C is transported from one of these points to the other, the magnitude of the work done is:
A) 200 J
B) 100 J
C) 50 J
D) 100 V
E) 2 J
A) 200 J
B) 100 J
C) 50 J
D) 100 V
E) 2 J
200 J
3
Positive charge is distributed uniformly throughout a non-conducting sphere. The highest electric potential occurs:
A) at the center
B) at the surface
C) halfway between the center and surface
D) just outside the surface
E) far from the sphere
A) at the center
B) at the surface
C) halfway between the center and surface
D) just outside the surface
E) far from the sphere
at the center
4
Eight identical spherical raindrops are each at a potential V, relative to the potential far away. They coalesce to make one spherical raindrop whose potential is:
A) V/8
B) V/2
C) 2V
D) 4V
E) 8V
A) V/8
B) V/2
C) 2V
D) 4V
E) 8V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Equipotential surfaces associated with an electric dipole are:
A) spheres centered on the dipole
B) cylinders with axes along the dipole moment
C) planes perpendicular to the dipole moment
D) planes parallel to the dipole moment
E) none of the above
A) spheres centered on the dipole
B) cylinders with axes along the dipole moment
C) planes perpendicular to the dipole moment
D) planes parallel to the dipole moment
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The potential difference between its ends of a 2-meter stick that is parallel to a uniform electric field is 400 V.The magnitude of the electric field is:
A) zero
B) 100 V/m
C) 200 V/m
D) 400 V/m
E) 800 V/m
A) zero
B) 100 V/m
C) 200 V/m
D) 400 V/m
E) 800 V/m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A conducting sphere has charge Q and its electric potential is V, relative to the potential far away. If the charge is doubled to 2Q, the potential is:
A) V
B) 2V
C) 4V
D) V/2
E) V/4
A) V
B) 2V
C) 4V
D) V/2
E) V/4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Consider Gauss law: 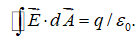 Which of the following is true?
Which of the following is true?
A)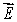 must be the electric field due to the enclosed charge
must be the electric field due to the enclosed charge
B) If q = 0 then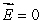 everywhere on the Gaussian surface
everywhere on the Gaussian surface
C) If the three particles inside have charges of +q, +q and-2q, then the integral is zero
D) On the surface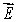 is everywhere parallel to
is everywhere parallel to 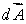
E) If a charge is placed outside the surface, then it cannot affect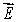 on the at any point on the surface
on the at any point on the surface
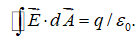 Which of the following is true?
Which of the following is true?A)
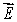 must be the electric field due to the enclosed charge
must be the electric field due to the enclosed chargeB) If q = 0 then
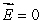 everywhere on the Gaussian surface
everywhere on the Gaussian surfaceC) If the three particles inside have charges of +q, +q and-2q, then the integral is zero
D) On the surface
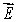 is everywhere parallel to
is everywhere parallel to 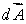
E) If a charge is placed outside the surface, then it cannot affect
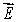 on the at any point on the surface
on the at any point on the surface
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
10 C of charge are placed on a spherical conducting shell. A particle with a charge of -3-C point charge is placed at the center of the cavity. The net charge in coulombs on the inner surface of the shell is:
A) -7
B) -3
C) 0
D) +3
E) +7
A) -7
B) -3
C) 0
D) +3
E) +7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
10 C of charge are placed on a spherical conducting shell. A particle with a charge of -3C is placed at the center of the cavity. The net charge in coulombs on the outer surface of the shell is:
A) -7
B) -3
C) 0
D) +3
E) +7
A) -7
B) -3
C) 0
D) +3
E) +7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Charge is distributed uniformly along a long straight wire. The electric field 2 cm from the wire is 20 N/C. The electric field 4 cm from the wire is:
A) 120 N/C
B) 80 N/C
C) 40 N/C
D) 10 N/C
E) 5 N/C
A) 120 N/C
B) 80 N/C
C) 40 N/C
D) 10 N/C
E) 5 N/C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A long line of charge with 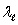 charge per unit length runs along the cylindrical axis of a cylindrical shell which carries a charge per unit length of c.The charge per unit length on the inner and outer surfaces of the shell, respectively are:
charge per unit length runs along the cylindrical axis of a cylindrical shell which carries a charge per unit length of c.The charge per unit length on the inner and outer surfaces of the shell, respectively are:
A)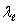 and c
and c
B)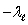 and c +
and c + 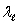
C)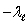 and c - c
and c - c
D)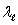 + c and c -
+ c and c - 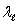
E)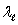 - c and c +
- c and c + 
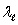 charge per unit length runs along the cylindrical axis of a cylindrical shell which carries a charge per unit length of c.The charge per unit length on the inner and outer surfaces of the shell, respectively are:
charge per unit length runs along the cylindrical axis of a cylindrical shell which carries a charge per unit length of c.The charge per unit length on the inner and outer surfaces of the shell, respectively are:A)
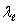 and c
and cB)
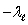 and c +
and c + 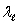
C)
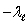 and c - c
and c - cD)
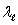 + c and c -
+ c and c - 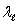
E)
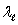 - c and c +
- c and c + 

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Charge is distributed uniformly on the surface of a large flat plate. The electric field 2 cm from the plate is 30 N/C. The electric field 4 cm from the plate is:
A) 120 N/C
B) 80 N/C
C) 30 N/C
D) 15 N/C
E) 7.5 N/C
A) 120 N/C
B) 80 N/C
C) 30 N/C
D) 15 N/C
E) 7.5 N/C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



