Deck 2: Gravitation, Force, Motion, Equilibrium, Elasticity, Rotation, Center of Mass, Linear Momentum, Potential Eneray, Conservation of Energy, Kinetic Energy, Work, Rolling, Torque, and Angular Momentum
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/16
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Gravitation, Force, Motion, Equilibrium, Elasticity, Rotation, Center of Mass, Linear Momentum, Potential Eneray, Conservation of Energy, Kinetic Energy, Work, Rolling, Torque, and Angular Momentum
1
A particle might be placed
1) inside a uniform spherical shell of mass M, but not at the center
2) inside a uniform spherical shell of mass M, at the center
3) outside a uniform spherical shell of mass M, a distance r from the center
4) outside a uniform solid sphere of mass M, a distance 2r from the center
Rank these situations according to the magnitude of the gravitational force on the particle, least to greatest.
A) All tie
B) 1, 2, 3, 4
C) 1 and 2 tie, then 3 and 4 tie
D) 1 and 2 tie, then 3, then 4
E) 1 and 2 tie, then 4, then 3
1) inside a uniform spherical shell of mass M, but not at the center
2) inside a uniform spherical shell of mass M, at the center
3) outside a uniform spherical shell of mass M, a distance r from the center
4) outside a uniform solid sphere of mass M, a distance 2r from the center
Rank these situations according to the magnitude of the gravitational force on the particle, least to greatest.
A) All tie
B) 1, 2, 3, 4
C) 1 and 2 tie, then 3 and 4 tie
D) 1 and 2 tie, then 3, then 4
E) 1 and 2 tie, then 4, then 3
1 and 2 tie, then 3, then 4
2
The fundamental dimensions of angular momentum are:
A) mass·length·time-1
B) mass·length-2·time-2
C) mass·2·time-1
D) mass·length2·time-2
E) none of these
A) mass·length·time-1
B) mass·length-2·time-2
C) mass·2·time-1
D) mass·length2·time-2
E) none of these
none of these
3
If a wheel is turning at 3.0 rad/s, the time it takes to complete one revolution is about:
A) 0.33 s
B) 0.67 s
C) 1.0 s
D) 1.3 s
E) 2.1 s
A) 0.33 s
B) 0.67 s
C) 1.0 s
D) 1.3 s
E) 2.1 s
2.1 s
4
The fan shown has been turned on and is slowing as it rotates clockwise. The direction of the acceleration of the acceleratrion point X on the fan tip could be:
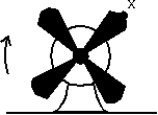
A)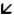
B)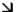
C)
D)
E)

A)
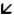
B)
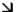
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
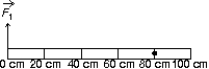
A meter stick on a horizontal frictionless table top is pivoted at the 80-cm mark. A horizontal force 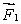 is applied perpendicularly to the end of the stick at 0 cm, as shown. A second horizontal force
is applied perpendicularly to the end of the stick at 0 cm, as shown. A second horizontal force 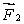 (not shown) is applied at the 100-cm end of the stick.If the stick does not rotate:
(not shown) is applied at the 100-cm end of the stick.If the stick does not rotate:
A)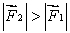 for all orientations of
for all orientations of 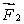
B)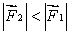 for all orientations of
for all orientations of 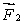
C)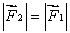 for all orientations of
for all orientations of 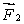
D)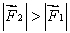 for some orientations of
for some orientations of 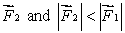 for others
for others
E)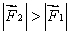 for some orientations of
for some orientations of 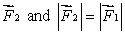 for others
for others
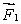 is applied perpendicularly to the end of the stick at 0 cm, as shown. A second horizontal force
is applied perpendicularly to the end of the stick at 0 cm, as shown. A second horizontal force 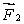 (not shown) is applied at the 100-cm end of the stick.If the stick does not rotate:
(not shown) is applied at the 100-cm end of the stick.If the stick does not rotate:
A)
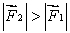 for all orientations of
for all orientations of 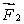
B)
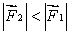 for all orientations of
for all orientations of 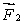
C)
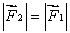 for all orientations of
for all orientations of 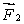
D)
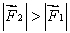 for some orientations of
for some orientations of 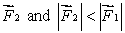 for others
for othersE)
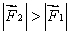 for some orientations of
for some orientations of 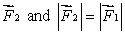 for others
for others
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A small disk of radius R1 is mounted coaxially with a larger disk of radius R2. The disks are securely fastened to each other and the combination is free to rotate on a fixed axle that is perpendicular to a horizontal frictionless table top,as shown in the overhead veiw below. The rotational inertia of the combination is I. A string is wrapped around the larger disk and attached to a block of mass m, on the table. Another string is wrapped around the smaller disk and is pulled with a force 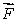 as shown. The acceleration of the block is:
as shown. The acceleration of the block is:
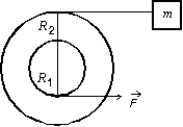
A) R1F/mR2
B) R1R2F/(I - mR2 2)
C) R1R2F/(I + mR2 2)
D) R1R2F/(I - mR1R 2)
E) R1R2F/(I + mR1R 2)
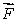 as shown. The acceleration of the block is:
as shown. The acceleration of the block is:
A) R1F/mR2
B) R1R2F/(I - mR2 2)
C) R1R2F/(I + mR2 2)
D) R1R2F/(I - mR1R 2)
E) R1R2F/(I + mR1R 2)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A small disk of radius R1 is fastened coaxially to a larger disk of radius R2. The combination is free to rotate on a fixed axle, which is perpendicular to a horizontal frictionless table top, as shown in the overhead veiw below. The rotational inertia of the combination is I. A string is wrapped around the larger disk and attached to a block of mass m, on the table. Another string is wrapped around the smaller disk and is pulled with a force 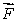 as shown. The tension in the string pulling the block is:
as shown. The tension in the string pulling the block is:
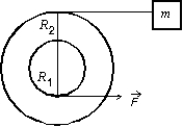
A) R1F/R2
B) mR1R2F/(I - mR22)
C) mR1R2F/(I + mR22)
D) mR1R2F/(I - mR1R 2)
E) mR1R2F/(I + mR1R 2)
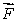 as shown. The tension in the string pulling the block is:
as shown. The tension in the string pulling the block is:
A) R1F/R2
B) mR1R2F/(I - mR22)
C) mR1R2F/(I + mR22)
D) mR1R2F/(I - mR1R 2)
E) mR1R2F/(I + mR1R 2)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The x and y coordinates in meters of the center of mass of the three-particle system shown below are:
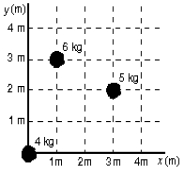
A) 0, 0
B) 1.3 m, 1.7 m
C) 1.4 m, 1.9 m
D) 1.9 m, 2.5 m
E) 1.4 m, 2.5 m

A) 0, 0
B) 1.3 m, 1.7 m
C) 1.4 m, 1.9 m
D) 1.9 m, 2.5 m
E) 1.4 m, 2.5 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The center of mass of a system of particles obeys an equation similar to Newton's second law 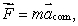 where:
where:
A)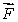 is the total internal force and m is the total mass of the system
is the total internal force and m is the total mass of the system
B)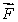 is the total internal force and m is the mass acting on the system
is the total internal force and m is the mass acting on the system
C)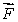 is the total external force and m is the total mass of the system
is the total external force and m is the total mass of the system
D)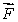 is the force of gravity and m is the mass of Earth
is the force of gravity and m is the mass of Earth
E)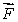 is the force of gravity and m is the total mass of the system
is the force of gravity and m is the total mass of the system
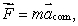 where:
where:A)
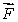 is the total internal force and m is the total mass of the system
is the total internal force and m is the total mass of the systemB)
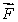 is the total internal force and m is the mass acting on the system
is the total internal force and m is the mass acting on the systemC)
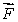 is the total external force and m is the total mass of the system
is the total external force and m is the total mass of the systemD)
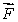 is the force of gravity and m is the mass of Earth
is the force of gravity and m is the mass of EarthE)
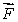 is the force of gravity and m is the total mass of the system
is the force of gravity and m is the total mass of the system
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A simple pendulum consists of a 2.0 kg mass attached to a string. It is released from rest at X as shown. Its speed at the lowest point Y is: 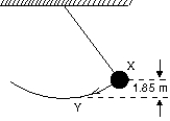
A) 0.90 m/s
B)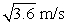
C) 3.6 m/s
D) 6.0 m/s
E) 36 m/s

A) 0.90 m/s
B)
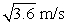
C) 3.6 m/s
D) 6.0 m/s
E) 36 m/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Objects A and B interact with each other via both conservative and nonconservative forces. Let KA and KB be the kinetic energies, U be the potential energy, and Eint be the internal energy. If no external agent does work on the objects then:
A) KA + U is conserved
B) KA + U + Eint is conserved
C) KA + KB + Eint is conserved
D) KA + KB + U is conserved
E) KA + KB + U + Eint is conserved
A) KA + U is conserved
B) KA + U + Eint is conserved
C) KA + KB + Eint is conserved
D) KA + KB + U is conserved
E) KA + KB + U + Eint is conserved

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Three identical springs (X,Y,Z) are arranged as shown. When a 4.0-kg mass is hung on X, the mass descends 3.0 cm. When a 6.0-kg mass is hung on Y, the mass descends:
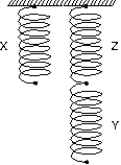
A) 2.0 cm
B) 4.0 cm
C) 4.5 cm
D) 6.0 cm
E) 9.0 cm

A) 2.0 cm
B) 4.0 cm
C) 4.5 cm
D) 6.0 cm
E) 9.0 cm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The speed of a 4.0-N hockey puck, sliding across a level ice surface, decreases at the rate of 0.61 m/s2. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the puck and ice is:
A) 0.062
B) 0.41
C) 0.62
D) 1.2
E) 9.8
A) 0.062
B) 0.41
C) 0.62
D) 1.2
E) 9.8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A heavy wooden block is dragged by a force 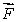 along a rough steel plate, as shown below for two possible situations. The magnitude of
along a rough steel plate, as shown below for two possible situations. The magnitude of  is the same for the two situations. The magnitude of the frictional force in (ii), as compared with that in (i) is:
is the same for the two situations. The magnitude of the frictional force in (ii), as compared with that in (i) is:
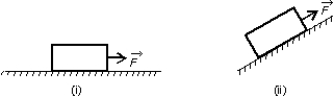
A) the same
B) greater
C) less
D) less for some angles and greater for others
E) can be less or greater, depending on the magnitude of the applied force.
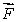 along a rough steel plate, as shown below for two possible situations. The magnitude of
along a rough steel plate, as shown below for two possible situations. The magnitude of 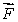 is the same for the two situations. The magnitude of the frictional force in (ii), as compared with that in (i) is:
is the same for the two situations. The magnitude of the frictional force in (ii), as compared with that in (i) is: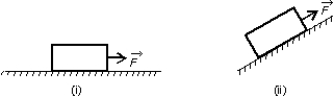
A) the same
B) greater
C) less
D) less for some angles and greater for others
E) can be less or greater, depending on the magnitude of the applied force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Two blocks (A andB) are in contact on a horizontal frictionless surface. A 36-N constant force is applied to A as shown. The magnitude of the force of A on B is:
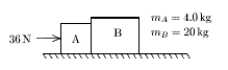
A) 1.5 N
B) 6.0 N
C) 29 N
D) 30 N
E) 36 N

A) 1.5 N
B) 6.0 N
C) 29 N
D) 30 N
E) 36 N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A particle goes from x = -2 m, y = 3 m, z = 1 m to x = 3 m, y = -1 m, z = 4 m. Its displacement is:
A)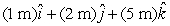
B)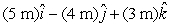
C)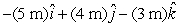
D)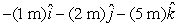
E)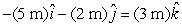
A)
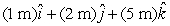
B)
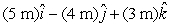
C)
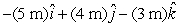
D)
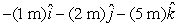
E)
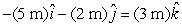

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



