Deck 7: Process Instrumentation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/19
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Process Instrumentation
1
Fill in the blank
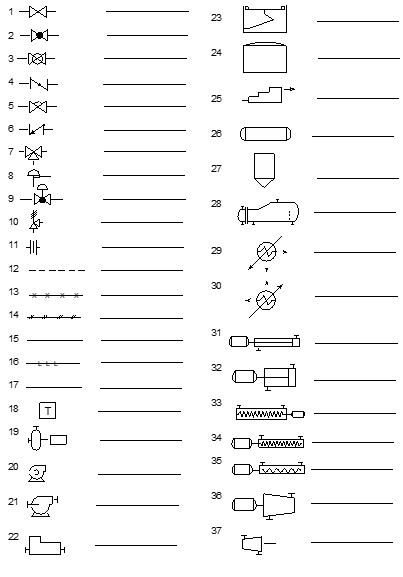
-
-

1. gate valve
2. globe valve
3. ball valve
4. butterfly valve
5. diaphragm valve
6. check valve
7. three way valve
8. relief valve
9. pneumatic operated globe
10. safety valve
11. orifice
12. electric line
13. capillary tubing
14. pneumatic line
15. minor line
16. hydraulic line
17. major line
18. steam trap
19. horizontal centrifugal pump
20. centrifugal pump
21. blower
22. reciprocating compressor
23. external floating roof tank
24. dome roof tank
25. positive displacement pump
26. drum
27. bin
28. kettle reboiler
29. heater
30. condenser
31. reciprocating pump
32. reciprocating compressor
33. rotary screw compressor
34. screw pump
35. progressive cavity
36. centrifugal compressor
37. steam turbine
2. globe valve
3. ball valve
4. butterfly valve
5. diaphragm valve
6. check valve
7. three way valve
8. relief valve
9. pneumatic operated globe
10. safety valve
11. orifice
12. electric line
13. capillary tubing
14. pneumatic line
15. minor line
16. hydraulic line
17. major line
18. steam trap
19. horizontal centrifugal pump
20. centrifugal pump
21. blower
22. reciprocating compressor
23. external floating roof tank
24. dome roof tank
25. positive displacement pump
26. drum
27. bin
28. kettle reboiler
29. heater
30. condenser
31. reciprocating pump
32. reciprocating compressor
33. rotary screw compressor
34. screw pump
35. progressive cavity
36. centrifugal compressor
37. steam turbine
2
Fill in the blank
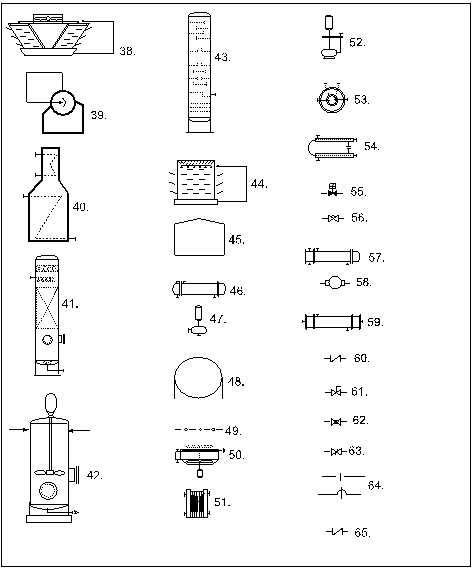
-
-

38. cooling tower- induced draft
39. boiler
40. furnace
41. packed column
42. mixing reactor
43. plate column
44. cooling tower- natural draft
45. cone roof tank
46. shell & tube heat exchanger- multi-pass
47. centrifugal pump- vertical mounted
48. spherical tank
49. data link
50. air cooled heat exchanger
51. plate and frame exchanger
52. sump pump
53. spiral heat exchanger
54. hair pin exchanger
55. solenoid valve
56. diaphragm valve
57' shell and tube heat exchanger
58. vacuum pump
59. heat exchanger- single pass
60. check-valve
61. manual operated valve
62. plug valve
63. butterfly valve
64. non-connecting line
65. stop check valve
39. boiler
40. furnace
41. packed column
42. mixing reactor
43. plate column
44. cooling tower- natural draft
45. cone roof tank
46. shell & tube heat exchanger- multi-pass
47. centrifugal pump- vertical mounted
48. spherical tank
49. data link
50. air cooled heat exchanger
51. plate and frame exchanger
52. sump pump
53. spiral heat exchanger
54. hair pin exchanger
55. solenoid valve
56. diaphragm valve
57' shell and tube heat exchanger
58. vacuum pump
59. heat exchanger- single pass
60. check-valve
61. manual operated valve
62. plug valve
63. butterfly valve
64. non-connecting line
65. stop check valve
3
Draw a level control loop on the top graphic.
Draw a pressure control loop on the top graphic.
Draw a flow control loop on the top graphic.
Draw a temperature control loop on the top graphic.
Draw a pressure control loop on the top graphic.
Draw a flow control loop on the top graphic.
Draw a temperature control loop on the top graphic.
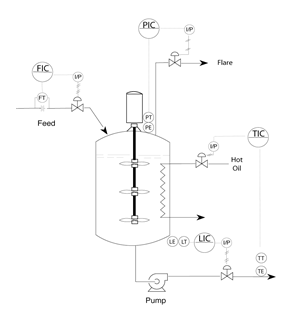
4
List the five elements of a control loop.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
List the three basic designs for valve actuators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Rate or derivative mode is best described as:
A) describes how one control loop overrides the instruction of another.
B) reduces the difference between setpoint and process variable by adjusting the controller output continuously until the offset is eliminated.
C) the difference between the upper and lower range limits.
D) enhances controller output by increasing the output in relationship to the changing process variable.
A) describes how one control loop overrides the instruction of another.
B) reduces the difference between setpoint and process variable by adjusting the controller output continuously until the offset is eliminated.
C) the difference between the upper and lower range limits.
D) enhances controller output by increasing the output in relationship to the changing process variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Reset or Integral mode is best described as:
A) describes how one control loop overrides the instruction of another.
B) reduces the difference between setpoint and process variable by adjusting the controller output continuously until the offset is eliminated.
C) the difference between the upper and lower range limits.
D) enhances controller output by increasing the output in relationship to the changing process variable.
A) describes how one control loop overrides the instruction of another.
B) reduces the difference between setpoint and process variable by adjusting the controller output continuously until the offset is eliminated.
C) the difference between the upper and lower range limits.
D) enhances controller output by increasing the output in relationship to the changing process variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Range is best defined as:
A) The portion of the process controlled by the controller.
B) The difference between the upper and lower range limits.
C) Electrical frequency used by a controller.
D) Pneumatic pulse used to detect differences in process variables.
A) The portion of the process controlled by the controller.
B) The difference between the upper and lower range limits.
C) Electrical frequency used by a controller.
D) Pneumatic pulse used to detect differences in process variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Span is best defined as:
A) The portion of the process controlled by the controller.
B) The difference between the upper and lower range limits.
C) Electrical frequency used by a controller.
D) Pneumatic pulse used to detect differences in process variables.
A) The portion of the process controlled by the controller.
B) The difference between the upper and lower range limits.
C) Electrical frequency used by a controller.
D) Pneumatic pulse used to detect differences in process variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Proportional band is best described as:
A) The portion of the process controlled by the controller.
B) The difference between the upper and lower range limits.
C) The scaling factor used to take a controller from 0% to 100%.
D) Pneumatic pulse used to detect differences in process variables.
A) The portion of the process controlled by the controller.
B) The difference between the upper and lower range limits.
C) The scaling factor used to take a controller from 0% to 100%.
D) Pneumatic pulse used to detect differences in process variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Describe what happens when a controller is placed in manual mode.
A) The control valve locks at a specific output.
B) The controller adjusts the control valve.
C) The control loop shuts down and the valve closes.
D) The controller automatically adjusts to match setpoint..
A) The control valve locks at a specific output.
B) The controller adjusts the control valve.
C) The control loop shuts down and the valve closes.
D) The controller automatically adjusts to match setpoint..

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Describe what happens when a controller is placed in automatic mode:
A) The control valve locks at a specific output.
B) The controller adjusts the control valve.
C) The controller automatically adjusts to match setpoint.
D) The signal from another controller takes over.
A) The control valve locks at a specific output.
B) The controller adjusts the control valve.
C) The controller automatically adjusts to match setpoint.
D) The signal from another controller takes over.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A control loop is:
A) Collection of instruments that work together to automatically control a process.
B) Primary elements/sensors, transmitter, controller, transducer, final control element.
C) Control valves, transmitters, controllers, temperature indicators.
D) a & b
A) Collection of instruments that work together to automatically control a process.
B) Primary elements/sensors, transmitter, controller, transducer, final control element.
C) Control valves, transmitters, controllers, temperature indicators.
D) a & b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A transmitter is best described as:
A) A device designed to convert a measurement into a signal.
B) Compares a signal to a setpoint.
C) Measurement device
D) A device designed to convert an air signal to an electric signal or an electric ssignal to a pneumatic signal.
A) A device designed to convert a measurement into a signal.
B) Compares a signal to a setpoint.
C) Measurement device
D) A device designed to convert an air signal to an electric signal or an electric ssignal to a pneumatic signal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Primary elements for pressure come in the following designs: (Circle all that apply!)
A) bourdon
B) spiral
C) helical
D) bellows
E) bullet
F)hand-held
A) bourdon
B) spiral
C) helical
D) bellows
E) bullet
F)hand-held

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A transducer is best described as:
A) A device designed to convert an air signal to an electric signal or an electric signal to a pneumatic signal.
B) A device designed to convert a measurement into a signal.
C) A device designed to compare a signal to a setpoint.
D) A device used for measurement.
A) A device designed to convert an air signal to an electric signal or an electric signal to a pneumatic signal.
B) A device designed to convert a measurement into a signal.
C) A device designed to compare a signal to a setpoint.
D) A device used for measurement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A 9 psi signal produces a 12 mA electric signal that equals a valve position of:
A) Closed
B) 25%
C) 50%
D) 75%
E) 100%
A) Closed
B) 25%
C) 50%
D) 75%
E) 100%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Cascade control is best described as:
A) A term used to describe how one control loop controls or overrides the instructions of another control loop in order to achieve a desired setpoint.
B) A term used to describe when a control valve is locked into position.
C) A term used to describe automatic control of two or more control loops.
D) A term used to link a DCS and PLC together.
A) A term used to describe how one control loop controls or overrides the instructions of another control loop in order to achieve a desired setpoint.
B) A term used to describe when a control valve is locked into position.
C) A term used to describe automatic control of two or more control loops.
D) A term used to link a DCS and PLC together.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A DCS or PLC is best described as:
A) A window to the process that allows a technician to see and control process variables.
B) A super computer linked to all electronic equipment.
C) Software designed to link a variety of computer equipment to process equipment.
D) A CPU linked to specific pods tied to a microprocessor and software.
A) A window to the process that allows a technician to see and control process variables.
B) A super computer linked to all electronic equipment.
C) Software designed to link a variety of computer equipment to process equipment.
D) A CPU linked to specific pods tied to a microprocessor and software.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



