Deck 5: Free Exchange: Individual and International Trade
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/67
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Free Exchange: Individual and International Trade
1
The process of making the best of our limited resources by doing the things we are best at and hiring other people to do the things we are not particularly good at is called
A) absolute advantage.
B) comparative advantage.
C) specialization.
D) protectionism.
A) absolute advantage.
B) comparative advantage.
C) specialization.
D) protectionism.
specialization.
2
Table 5.1: 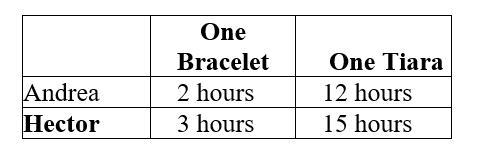 Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.
Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.
-Refer to Table 5.1. Does either Andrea or Hector have an absolute advantage and if so, in what product?
A) Andrea only has an absolute advantage in producing bracelets.
B) Hector only has an absolute advantage in producing bracelets.
C) Andrea has an absolute advantage in producing both products.
D) Hector only has an absolute advantage in producing tiaras.
 Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.
Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.-Refer to Table 5.1. Does either Andrea or Hector have an absolute advantage and if so, in what product?
A) Andrea only has an absolute advantage in producing bracelets.
B) Hector only has an absolute advantage in producing bracelets.
C) Andrea has an absolute advantage in producing both products.
D) Hector only has an absolute advantage in producing tiaras.
Andrea has an absolute advantage in producing both products.
3
Table 5.1:  Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.
Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.
-Refer to Table 5.1. What is Hector's opportunity cost of producing one tiara?
A) 1/5 of a bracelet
B) 1.5 bracelets
C) 4 bracelets
D) 5 bracelets
 Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.
Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.-Refer to Table 5.1. What is Hector's opportunity cost of producing one tiara?
A) 1/5 of a bracelet
B) 1.5 bracelets
C) 4 bracelets
D) 5 bracelets
5 bracelets
4
Table 5.1:  Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.
Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.
-Refer to Table 5.1. What is Andrea's opportunity cost of producing one tiara?
A) 1/6 of a bracelet
B) 2/3 of a bracelet
C) 3 bracelets
D) 6 bracelets
 Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.
Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.-Refer to Table 5.1. What is Andrea's opportunity cost of producing one tiara?
A) 1/6 of a bracelet
B) 2/3 of a bracelet
C) 3 bracelets
D) 6 bracelets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Table 5.1:  Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.
Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.
-Refer to Table 5.1. What is Hector's opportunity cost of producing one bracelet?
A) 1/5 of a tiara
B) 1.5 tiaras
C) 5 tiaras
D) 6 tiaras
 Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.
Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.-Refer to Table 5.1. What is Hector's opportunity cost of producing one bracelet?
A) 1/5 of a tiara
B) 1.5 tiaras
C) 5 tiaras
D) 6 tiaras

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Table 5.1:  Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.
Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.
-Refer to Table 5.1. What is Andrea's opportunity cost of producing one bracelet?
A) 1/6 of a tiara
B) 2/3 of a tiara
C) 6 tiaras
D) 7.5 tiaras
 Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.
Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.-Refer to Table 5.1. What is Andrea's opportunity cost of producing one bracelet?
A) 1/6 of a tiara
B) 2/3 of a tiara
C) 6 tiaras
D) 7.5 tiaras

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Table 5.1:  Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.
Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.
-Refer to Table 5.1. Hector has a comparative advantage in the production of
A) bracelets.
B) tiaras.
C) both products.
D) neither product.
 Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.
Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.-Refer to Table 5.1. Hector has a comparative advantage in the production of
A) bracelets.
B) tiaras.
C) both products.
D) neither product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Table 5.1:  Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.
Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.
-Refer to Table 5.1. Andrea has a comparative advantage in the production of
A) bracelets.
B) tiaras.
C) both products.
D) neither product.
 Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.
Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.-Refer to Table 5.1. Andrea has a comparative advantage in the production of
A) bracelets.
B) tiaras.
C) both products.
D) neither product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Table 5.1:  Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.
Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.
-Refer to Table 5.1. Hector should specialize in the production of
A) bracelets.
B) tiaras.
C) both products.
D) neither product.
 Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.
Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.-Refer to Table 5.1. Hector should specialize in the production of
A) bracelets.
B) tiaras.
C) both products.
D) neither product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Table 5.1:  Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.
Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.
-Refer to Table 5.1. Andrea should specialize in the production of
A) bracelets.
B) tiaras.
C) both products.
D) neither product.
 Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.
Table 5.1 shows the number of labor hours required by Andrea and Hector to each produce one bracelet and one tiara.-Refer to Table 5.1. Andrea should specialize in the production of
A) bracelets.
B) tiaras.
C) both products.
D) neither product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The amount Jacqueline receives for selling cupcakes beyond the minimum she would be willing to sell the cupcakes for is called
A) consumer surplus.
B) producer surplus.
C) cooperative surplus.
D) deadweight loss.
A) consumer surplus.
B) producer surplus.
C) cooperative surplus.
D) deadweight loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The sum of all the net benefits received by the parties to a transaction is called
A) consumer surplus.
B) producer surplus.
C) cooperative surplus.
D) deadweight loss.
A) consumer surplus.
B) producer surplus.
C) cooperative surplus.
D) deadweight loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If Jacqueline is willing to accept $1 for a cupcake and Jameson is willing to pay $3 for a cupcake, and they negotiate a price of $2 for a cupcake, the cooperative surplus is
A) $1.
B) $2.
C) $3.
D) $4.
A) $1.
B) $2.
C) $3.
D) $4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If Jacqueline is willing to accept $1 for a cupcake and Jameson is willing to pay $3 for a cupcake, the consumer surplus will ________ if the negotiated price is $1.50 as opposed to $2.00.
A) increase
B) decrease
C) not change
D) All of the above are possibilities.
A) increase
B) decrease
C) not change
D) All of the above are possibilities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If Jacqueline is willing to accept $1 for a cupcake and Jameson is willing to pay $3 for a cupcake, the producer surplus will ________ if the negotiated price is $1.50 as opposed to $2.00.
A) increase
B) decrease
C) not change
D) All of the above are possibilities.
A) increase
B) decrease
C) not change
D) All of the above are possibilities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Globalization has given U.S. consumers a wider variety of gourmet food products from which to choose and has lowered the prices of these products in general. This, in turn, has encouraged consumers to buy more gourmet food items, which has ________ the amount of cooperative surplus for the buyers and sellers of gourmet food products.
A) increased
B) decreased
C) not changed
D) reduced to zero
A) increased
B) decreased
C) not changed
D) reduced to zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If Jacqueline is willing to accept $1 for a cupcake and Jameson is willing to pay $3 for a cupcake, the cooperative surplus will ________ if the negotiated price is $1.50 as opposed to $2.00.
A) increase
B) decrease
C) not change
D) All of the above are possibilities.
A) increase
B) decrease
C) not change
D) All of the above are possibilities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If Carla can pick more oranges in one hour than Benjamin, then Carla definitely has a comparative advantage in picking oranges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Producer surplus is the amount a seller receives for a good or service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Consumer surplus is the difference between the maximum amount a buyer is willing to pay for a product and the price he actually pays.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
For any transaction, the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus is cooperative surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Table 5.2 : 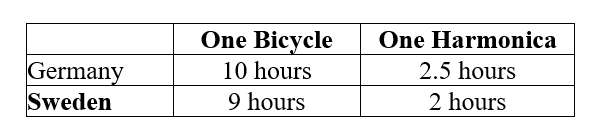
-Refer to Table 5.2. This table shows the number of labor hours required to produce a bicycle and a harmonica in Germany and Sweden.
a. Which country has an absolute advantage in the production of bicycles?
b. Which country has an absolute advantage in the production of harmonicas?
c. What is Germany's opportunity cost of producing one bicycle?
d. What is Sweden's opportunity cost of producing one bicycle?
e. What is Germany's opportunity cost of producing one harmonica?
f. What is Sweden's opportunity cost of producing one harmonica?
g. If each country specializes in the production of the product in which it has a comparative advantage, who should produce bicycles?
h. If each country specializes in the production of the product in which it has a comparative advantage, who should produce harmonicas?

-Refer to Table 5.2. This table shows the number of labor hours required to produce a bicycle and a harmonica in Germany and Sweden.
a. Which country has an absolute advantage in the production of bicycles?
b. Which country has an absolute advantage in the production of harmonicas?
c. What is Germany's opportunity cost of producing one bicycle?
d. What is Sweden's opportunity cost of producing one bicycle?
e. What is Germany's opportunity cost of producing one harmonica?
f. What is Sweden's opportunity cost of producing one harmonica?
g. If each country specializes in the production of the product in which it has a comparative advantage, who should produce bicycles?
h. If each country specializes in the production of the product in which it has a comparative advantage, who should produce harmonicas?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Explain the concepts of consumer surplus, producer surplus, and cooperative surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What three factors that were critical to economic prosperity did Adam Smith observe, and later publish in The Wealth of Nations?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A compulsory payment to government that is generally linked to engaging in some activity is referred to as a
A) tax.
B) subsidy.
C) deadweight loss.
D) quota.
A) tax.
B) subsidy.
C) deadweight loss.
D) quota.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If a tax is imposed in a bargaining game, the players' cooperative surplus
A) increases.
B) declines.
C) remains unchanged.
D) increases for one player and decreases for the other.
A) increases.
B) declines.
C) remains unchanged.
D) increases for one player and decreases for the other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
When a government taxes the sale of beer, cooperative surplus ________ and society gets ________.
A) increases; richer
B) increases; poorer
C) decreases; richer
D) decreases; poorer
A) increases; richer
B) increases; poorer
C) decreases; richer
D) decreases; poorer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Sammy has a drone that he values at $1,500. Dean values the same drone at $2,000. Sammy decides to sell the drone to Dean for $1,800. What is the total cooperative surplus gained as a result of this trade?
A) $0
B) $200
C) $300
D) $500
A) $0
B) $200
C) $300
D) $500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Sammy has a drone that he values at $1,500. Dean values the same drone at $2,000. Sammy decides to sell the drone to Dean for $1,800. If the government imposes a $250 tax on the sale of drones,
A) Sammy and Dean would not be able to complete the transaction.
B) Sammy and Dean would still be able to complete the transaction.
C) the tax would cause a deadweight loss of $500.
D) Both A and C are correct.
A) Sammy and Dean would not be able to complete the transaction.
B) Sammy and Dean would still be able to complete the transaction.
C) the tax would cause a deadweight loss of $500.
D) Both A and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Sammy has a drone that he values at $1,500. Dean values the same drone at $2,000. Sammy decides to sell the drone to Dean for $1,800. If the government imposes a $350 tax on the sale of drones,
A) Sammy and Dean would not be able to complete the transaction.
B) Sammy and Dean would still be able to complete the transaction.
C) the tax would cause a deadweight loss of $500.
D) Both A and C are correct.
A) Sammy and Dean would not be able to complete the transaction.
B) Sammy and Dean would still be able to complete the transaction.
C) the tax would cause a deadweight loss of $500.
D) Both A and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Surplus value that is lost because something is keeping the market from functioning as well as it can is called
A) a tax.
B) a subsidy.
C) rent seeking.
D) deadweight loss.
A) a tax.
B) a subsidy.
C) rent seeking.
D) deadweight loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Attempts to influence the law for your own private economic advantage is called
A) tax imposition.
B) subsidizing.
C) rent seeking.
D) creating a deadweight loss.
A) tax imposition.
B) subsidizing.
C) rent seeking.
D) creating a deadweight loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If rent-seeking behavior reduces competition in a market, cooperative surplus in that market will
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain unchanged.
D) All of the above are equally likely to occur.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain unchanged.
D) All of the above are equally likely to occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A market where goods are sold in violation of governmentally-imposed restrictions is a(n)
A) black market.
B) export market.
C) rent-seeking market.
D) deadweight market.
A) black market.
B) export market.
C) rent-seeking market.
D) deadweight market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If black markets help people meet their needs, they will tend to ________ created by the restrictive government policies.
A) increase the absolute advantage
B) reduce the deadweight losses
C) reduce the cooperative surpluses
D) increase the tax revenues
A) increase the absolute advantage
B) reduce the deadweight losses
C) reduce the cooperative surpluses
D) increase the tax revenues

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A payment that a person receives from the government for engaging in a particular activity is called a
A) bribe.
B) subsidy.
C) consumer surplus.
D) tariff.
A) bribe.
B) subsidy.
C) consumer surplus.
D) tariff.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
When a government subsidizes the sale of milk, cooperative surplus ________ and society gets ________.
A) increases; richer
B) increases; poorer
C) decreases; richer
D) decreases; poorer
A) increases; richer
B) increases; poorer
C) decreases; richer
D) decreases; poorer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Sammy has a drone that he values at $1,500. Dean values the same drone at $2,000. Sammy decides to sell the drone to Dean for $1,800. The government offers a subsidy of $800 to the buyers of drones. Producer surplus is ________ and consumer surplus is ________.
A) $300; $200
B) $300; $1,000
C) $1,100; $800
D) $1,100; $600
A) $300; $200
B) $300; $1,000
C) $1,100; $800
D) $1,100; $600

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Sammy has a drone that he values at $1,500. Dean values the same drone at $2,000. Sammy decides to sell the drone to Dean for $1,800. The government offers a subsidy of $800 to the buyers of drones. When the gains and losses to all parties are netted out, cooperative surplus for Sammy and Dean will be ________ it would have been without the subsidy, and the subsidy ________ produce additional wealth.
A) greater than; would not
B) the same as; would not
C) greater than; would
D) less than; would not
A) greater than; would not
B) the same as; would not
C) greater than; would
D) less than; would not

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Sammy has a drone that he values at $1,500. Frank values the same drone at $1,000. The government offers a subsidy of $800 to the buyers of drones, and Sammy and Frank agree on a price of $1,600. Producer surplus is ________ and consumer surplus is ________.
A) $100; $200
B) $700; $600
C) $200; $1,400
D) $300; $100
A) $100; $200
B) $700; $600
C) $200; $1,400
D) $300; $100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Sammy has a drone that he values at $1,500. Frank values the same drone at $1,000. The government offers a subsidy of $800 to the buyers of drones, and Sammy and Frank agree on a price of $1,600. The cooperative surplus for Sammy and Dean will be
A) $200.
B) $300.
C) $600.
D) $800.
A) $200.
B) $300.
C) $600.
D) $800.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Sammy has a drone that he values at $1,500. Frank values the same drone at $1,000. The government offers a subsidy of $800 to the buyers of drones, and Sammy and Frank agree on a price of $1,600. The subsidy creates a deadweight loss of
A) $0
B) $200
C) $500.
D) $800.
A) $0
B) $200
C) $500.
D) $800.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Taxes can adversely affect free exchange.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A deadweight loss occurs when the market is functioning efficiently.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Rent seeking refers to the asking prices for goods and services being sold on the black market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Black market transactions generally increase the deadweight losses created by restrictive government policies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A subsidy is a negative tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Sanjay has an ATV that he values at $3,000. Marilu is looking for a similar ATV but will only pay up to $2,400. Will trade between these two occur? Is there a policy government could implement that would encourage a trade to occur between Sanjay and Marilu? If so, what is that policy and will the policy make society richer?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Explain which of the following government policies would tend to make more sense in terms of consumer protection: The licensure of interior designers or the licensure of pharmacists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In 2014, tire industry lobbyists pressured the United States government to consider imposing an additional tariff of up to 86% on top of the current 4% tariff on imported Chinese-made tires. This type of behavior where industry lobbyists attempt to influence law for their own economic advantage is called
A) deadweight protection.
B) blackmail.
C) quota manipulation.
D) rent seeking.
A) deadweight protection.
B) blackmail.
C) quota manipulation.
D) rent seeking.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In 2014, tire industry lobbyists pressured the United States government to consider imposing an additional tariff of up to 86% on top of the current 4% tariff on imported Chinese-made tires. The loss that is associated with fewer transactions occurring because of the tariff is called
A) deadweight loss.
B) opportunity loss.
C) lost rent.
D) a subsidized loss.
A) deadweight loss.
B) opportunity loss.
C) lost rent.
D) a subsidized loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
When a government imposes a tariff on imported beer, cooperative surplus ________ and society gets ________.
A) increases; richer
B) increases; poorer
C) decreases; richer
D) decreases; poorer
A) increases; richer
B) increases; poorer
C) decreases; richer
D) decreases; poorer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Surplus value that is lost due to taxes imposed on imported goods which are keeping the market from functioning as well as it can is called
A) the loss of subsidy.
B) the net export deficit.
C) rent seeking loss.
D) the deadweight loss of a tariff.
A) the loss of subsidy.
B) the net export deficit.
C) rent seeking loss.
D) the deadweight loss of a tariff.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
An American farmer sells produce to an individual living in Bermuda. To Americans, the produce is a(n)
A) import.
B) export.
C) quota.
D) tariff.
A) import.
B) export.
C) quota.
D) tariff.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
An American farmer buys an irrigation system from a Norwegian irrigation company based in Oslo. To Americans, the irrigation system is a(n)
A) import.
B) export.
C) quota.
D) tariff.
A) import.
B) export.
C) quota.
D) tariff.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Ultimately, tariffs ________ prices for imported goods and ________ prices for domestic goods.
A) raise; raise
B) raise; lower
C) raise; do not affect
D) do not affect; do not affect
A) raise; raise
B) raise; lower
C) raise; do not affect
D) do not affect; do not affect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Ultimately, tariffs ________ the ability of foreign countries to buy the domestic country's exports and therefore ________ wealth.
A) increase; create
B) increase; destroy
C) reduce; create
D) reduce; destroy
A) increase; create
B) increase; destroy
C) reduce; create
D) reduce; destroy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
To assist pineapple growers in Hawaii, the U.S. government decides to limit the number of pineapples allowed into the country that are grown in Central American countries. Such a restriction is called a(n)
A) import.
B) export.
C) quota.
D) tariff.
A) import.
B) export.
C) quota.
D) tariff.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
To assist pineapple growers in Hawaii, the U.S. government decides to limit the number of pineapples allowed into the country that are grown in Central American countries. Such a restriction prevents many transactions from occurring, and results in opportunity loss which is called a(n)
A) import deficit.
B) deadweight loss of a quota.
C) rent seeking loss.
D) non-cooperative surplus.
A) import deficit.
B) deadweight loss of a quota.
C) rent seeking loss.
D) non-cooperative surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Ultimately, quotas ________ prices for imported goods and ________ prices for domestic goods.
A) raise; raise
B) raise; lower
C) raise; do not affect
D) do not affect; do not affect
A) raise; raise
B) raise; lower
C) raise; do not affect
D) do not affect; do not affect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Ultimately, quotas ________ the ability of foreign countries to buy the domestic country's exports and therefore ________ wealth.
A) increase; create
B) increase; destroy
C) reduce; create
D) reduce; destroy
A) increase; create
B) increase; destroy
C) reduce; create
D) reduce; destroy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Even when transactions are facilitated with money, imports are paid for by exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Tariffs create deadweight losses and destroy wealth, whereas quotas increase cooperative surplus and create wealth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an international organization dedicated to erecting trade barriers between nations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Explain the difference between a tariff and a quota. What impact do tariffs and quotas have on the prices of domestic and imported goods?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Products produced domestically and sold in foreign countries are called ________, and products produced in foreign countries and sold domestically are called ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What is the "chicken tax"and why did it come into existence?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



