Deck 20: The Federal Government: Taxes, Spending, and Fiscal Policy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/66
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: The Federal Government: Taxes, Spending, and Fiscal Policy
1
The largest source of federal government revenue in the United States is
A) corporate income taxes.
B) individual income taxes.
C) payroll taxes.
D) excise taxes.
A) corporate income taxes.
B) individual income taxes.
C) payroll taxes.
D) excise taxes.
individual income taxes.
2
A mandatory tax that both workers and employers in the United States pay to fund Social Security and Medicare is the
A) corporate income tax.
B) individual income tax.
C) payroll tax.
D) excise tax.
A) corporate income tax.
B) individual income tax.
C) payroll tax.
D) excise tax.
payroll tax.
3
Payroll taxes are paid on
A) earned income.
B) investment income.
C) inheritances.
D) all of the above
A) earned income.
B) investment income.
C) inheritances.
D) all of the above
earned income.
4
If, as your taxable income increases, you pay a smaller percentage of your taxable income in taxes, then the tax is
A) progressive.
B) regressive.
C) proportional.
D) unfair.
A) progressive.
B) regressive.
C) proportional.
D) unfair.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Table 20.1 : 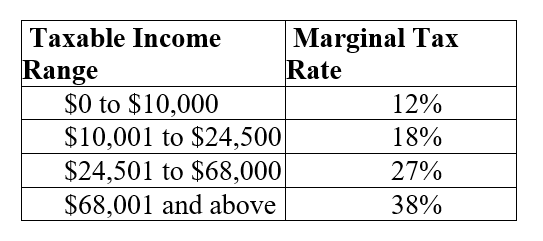 The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Oceania.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Oceania.
The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Oceania.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Oceania.
-Refer to Table 20.1. The income tax paid by George, a single taxpayer with an income of $65,000, is
A) $11,100.
B) $14,745.
C) $15,345.
D) $17,550.
 The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Oceania.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Oceania.
The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Oceania.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Oceania.-Refer to Table 20.1. The income tax paid by George, a single taxpayer with an income of $65,000, is
A) $11,100.
B) $14,745.
C) $15,345.
D) $17,550.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Table 20.1 :  The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Oceania.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Oceania.
The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Oceania.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Oceania.
-Refer to Table 20.1. George is a single taxpayer with an income of $65,000. What is George's marginal tax rate?
A) 19%
B) 27%
C) 38%
D) 57%
 The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Oceania.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Oceania.
The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Oceania.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Oceania.-Refer to Table 20.1. George is a single taxpayer with an income of $65,000. What is George's marginal tax rate?
A) 19%
B) 27%
C) 38%
D) 57%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Table 20.1 :  The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Oceania.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Oceania.
The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Oceania.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Oceania.
-Refer to Table 20.1. George is a single taxpayer with an income of $65,000. What is George's average tax rate?
A) 19.00%
B) 22.68%
C) 23.61%
D) 27%
 The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Oceania.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Oceania.
The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Oceania.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Oceania.-Refer to Table 20.1. George is a single taxpayer with an income of $65,000. What is George's average tax rate?
A) 19.00%
B) 22.68%
C) 23.61%
D) 27%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Table 20.1 :  The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Oceania.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Oceania.
The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Oceania.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Oceania.
-Refer to Table 20.1. The income tax in Oceania is
A) progressive.
B) regressive.
C) proportional.
D) a flat tax.
 The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Oceania.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Oceania.
The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Oceania.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Oceania.-Refer to Table 20.1. The income tax in Oceania is
A) progressive.
B) regressive.
C) proportional.
D) a flat tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Table 20.1 :  The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Oceania.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Oceania.
The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Oceania.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Oceania.
-Refer to Table 20.1. George is a single taxpayer with an income of $65,000. If George earned one extra dollar of income, he would have paid an additional ________ in income tax.
A) $0.19
B) $0.2268
C) $0.27
D) $0.38
 The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Oceania.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Oceania.
The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Oceania.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Oceania.-Refer to Table 20.1. George is a single taxpayer with an income of $65,000. If George earned one extra dollar of income, he would have paid an additional ________ in income tax.
A) $0.19
B) $0.2268
C) $0.27
D) $0.38

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Table 20.1 :  The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Oceania.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Oceania.
The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Oceania.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Oceania.
-Refer to Table 20.1. George is a single taxpayer with an income of $65,000. If George had received a raise of $3,500 at the beginning of the year, he would have paid an additional ________ in income tax.
A) $665
B) $945
C) $1,000
D) $1,330
 The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Oceania.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Oceania.
The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Oceania.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Oceania.-Refer to Table 20.1. George is a single taxpayer with an income of $65,000. If George had received a raise of $3,500 at the beginning of the year, he would have paid an additional ________ in income tax.
A) $665
B) $945
C) $1,000
D) $1,330

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Table 20.1 :  The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Oceania.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Oceania.
The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Oceania.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Oceania.
-Refer to Table 20.1. George is a single taxpayer with an income of $65,000. If George had received a raise of $3,500 at the beginning of the year, his marginal tax rate would be
A) 22.99%.
B) 23.75%.
C) 38%.
D) 95%.
 The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Oceania.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Oceania.
The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Oceania.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Oceania.-Refer to Table 20.1. George is a single taxpayer with an income of $65,000. If George had received a raise of $3,500 at the beginning of the year, his marginal tax rate would be
A) 22.99%.
B) 23.75%.
C) 38%.
D) 95%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Table 20.1 :  The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Oceania.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Oceania.
The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Oceania.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Oceania.
-Refer to Table 20.1. George is a single taxpayer with an income of $65,000. If George had received a raise of $3,500 at the beginning of the year, his average tax rate would be
A) 22.99%.
B) 23.75%.
C) 32.5%.
D) 38%.
 The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Oceania.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Oceania.
The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Oceania.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Oceania.-Refer to Table 20.1. George is a single taxpayer with an income of $65,000. If George had received a raise of $3,500 at the beginning of the year, his average tax rate would be
A) 22.99%.
B) 23.75%.
C) 32.5%.
D) 38%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In the United States, all of the following are deductions generally allowed by the IRS on individual income taxes except
A) mortgage interest.
B) charitable contributions.
C) contributions to retirement plans.
D) rent payments.
A) mortgage interest.
B) charitable contributions.
C) contributions to retirement plans.
D) rent payments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
All of the following are differences between partnerships and corporations except
A) scale of ownership.
B) partnerships pay income taxes on their earnings and corporations do not.
C) in a partnership, partners make key business decisions, but in a corporation a board of directors generally make those decisions.
D) if an owner of a corporation dies, the corporation survives, but this is not necessarily true for partnerships.
A) scale of ownership.
B) partnerships pay income taxes on their earnings and corporations do not.
C) in a partnership, partners make key business decisions, but in a corporation a board of directors generally make those decisions.
D) if an owner of a corporation dies, the corporation survives, but this is not necessarily true for partnerships.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Of the following countries, in which one was the true marginal tax rate faced by the typical worker lowest and the average number of hours worked per week highest from 1993 through 1996?
A) Canada
B) Germany
C) Italy
D) the United States
A) Canada
B) Germany
C) Italy
D) the United States

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following are ways in which corporations can reduce their U.S. tax burdens?
A) taking advantage of deductions and credits
B) shifting foreign profits to overseas subsidiaries
C) deducting past losses from income tax in profitable years
D) all of the above
A) taking advantage of deductions and credits
B) shifting foreign profits to overseas subsidiaries
C) deducting past losses from income tax in profitable years
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Any profit earned by a corporation
A) does not get taxed.
B) gets taxed once.
C) gets taxed twice.
D) gets taxed five times.
A) does not get taxed.
B) gets taxed once.
C) gets taxed twice.
D) gets taxed five times.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Unlike with Social Security taxes, there is no threshold on earnings beyond which the Medicare tax collection stops.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In the United States, income taxes are collected from two different sources: households and corporations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In the United States, although people in different income groups pay different tax rates, every dollar earned by a specific individual is taxed at the same rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In the United States in 2014, the highest marginal tax rate for individual income taxes was 39.6%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Sabrina is a college professor in Houston, Texas who earns a salary of $95,000. She is single, just put down $25,000 on a new townhouse, and has no children. Explain if Sabrina has any way of reducing her payroll taxes or her personal income tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Table 20.2: 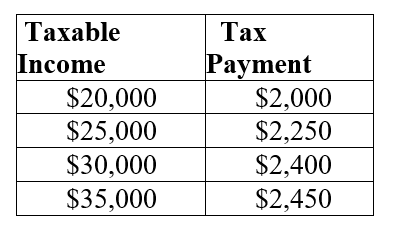 The above table shows the amount of taxes paid on various levels of income.
The above table shows the amount of taxes paid on various levels of income.
-Refer to Table 20.2. Is the tax system represented in the table progressive, regressive, or neither one? How can you tell?
 The above table shows the amount of taxes paid on various levels of income.
The above table shows the amount of taxes paid on various levels of income.-Refer to Table 20.2. Is the tax system represented in the table progressive, regressive, or neither one? How can you tell?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Table 20.3: 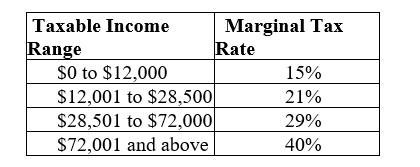 The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Lower Slobbovia.
The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Lower Slobbovia.
There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Lower Slobbovia.
-Refer to Table 20.3. Abner Little is a single taxpayer in the country of Lower Slobbovia who earns an annual income of $80,000. How much income tax will Abner pay, what is his marginal tax rate, and what is his average tax rate? Is this income tax regressive or progressive? How do you know?
 The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Lower Slobbovia.
The table shows the taxable income range and marginal tax rates for a single taxpayer in Lower Slobbovia.There are no exemptions or deductions on personal income taxes in Lower Slobbovia.
-Refer to Table 20.3. Abner Little is a single taxpayer in the country of Lower Slobbovia who earns an annual income of $80,000. How much income tax will Abner pay, what is his marginal tax rate, and what is his average tax rate? Is this income tax regressive or progressive? How do you know?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
For the U.S. federal government, discretionary expenditures refer to
A) spending on entitlement programs.
B) spending on imports and exports.
C) spending on interest on federal debt.
D) spending that must be authorized by Congress each year.
A) spending on entitlement programs.
B) spending on imports and exports.
C) spending on interest on federal debt.
D) spending that must be authorized by Congress each year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following expenditures is classified as a discretionary expenditure of the U.S. federal government?
A) federal employee pensions
B) student loans and grants
C) Social Security
D) food stamps
A) federal employee pensions
B) student loans and grants
C) Social Security
D) food stamps

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The largest portion of discretionary spending is devoted to
A) foreign aid.
B) national defense.
C) paying federal employees.
D) the space program.
A) foreign aid.
B) national defense.
C) paying federal employees.
D) the space program.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
For the U.S. federal government, mandatory spending refers to
A) spending that is not subject to Congress's annual appropriations process.
B) spending that never changes in amount from year to year.
C) spending on federal employee salaries.
D) spending that must be authorized by Congress each year.
A) spending that is not subject to Congress's annual appropriations process.
B) spending that never changes in amount from year to year.
C) spending on federal employee salaries.
D) spending that must be authorized by Congress each year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following expenditures is classified as a mandatory expenditure of the U.S. federal government?
A) federal employee salaries
B) national defense
C) Medicaid
D) foreign aid
A) federal employee salaries
B) national defense
C) Medicaid
D) foreign aid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following categories of federal spending is the largest in the United States?
A) interest on federal debt
B) mandatory spending
C) discretionary spending
D) national defense
A) interest on federal debt
B) mandatory spending
C) discretionary spending
D) national defense

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A vast majority of mandatory federal spending is devoted to
A) entitlement programs.
B) national defense.
C) interest on the national debt.
D) foreign aid.
A) entitlement programs.
B) national defense.
C) interest on the national debt.
D) foreign aid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The Social Security program is ________ in that it redistributes income from ________.
A) progressive; low earners to high earners
B) regressive; low earners to high earners
C) progressive; high earners to low earners
D) regressive; high earners to low earners
A) progressive; low earners to high earners
B) regressive; low earners to high earners
C) progressive; high earners to low earners
D) regressive; high earners to low earners

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The amount by which the federal government's annual expenditures exceed its annual receipts is the
A) federal debt.
B) federal government budget deficit.
C) federal government budget surplus.
D) federal profit.
A) federal debt.
B) federal government budget deficit.
C) federal government budget surplus.
D) federal profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The amount by which the federal government's annual revenues exceed its annual expenditures is the
A) federal debt.
B) federal government budget deficit.
C) federal government budget surplus.
D) federal profit.
A) federal debt.
B) federal government budget deficit.
C) federal government budget surplus.
D) federal profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Since 1970, the U.S. federal government had a budget surplus
A) in almost every year.
B) in a few years in the 1990s.
C) only once, in 2008.
D) The U.S. federal government has not had a budget surplus since 1970.
A) in almost every year.
B) in a few years in the 1990s.
C) only once, in 2008.
D) The U.S. federal government has not had a budget surplus since 1970.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The largest budget deficit the U.S. federal government has ever had was
A) $3.9 trillion in 1975.
B) $3.0 trillion in 2014.
C) $1.4 trillion in 2009.
D) $600 billion in 1997.
A) $3.9 trillion in 1975.
B) $3.0 trillion in 2014.
C) $1.4 trillion in 2009.
D) $600 billion in 1997.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
When the U.S. government runs a budget deficit, its primary way of covering that deficit is
A) printing money.
B) defaulting on its payments.
C) selling stock.
D) issuing bonds.
A) printing money.
B) defaulting on its payments.
C) selling stock.
D) issuing bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The total federal debt is equal to
A) the total value of all U.S. currency in circulation.
B) the sum of all past deficits minus the sum of all past surpluses.
C) the federal budget deficit minus the federal budget surplus.
D) annual federal tax receipts plus annual federal expenditures.
A) the total value of all U.S. currency in circulation.
B) the sum of all past deficits minus the sum of all past surpluses.
C) the federal budget deficit minus the federal budget surplus.
D) annual federal tax receipts plus annual federal expenditures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Entitlement spending is included in discretionary spending for the U.S. government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
When measured as a share of the total federal budget, entitlement spending has doubled over the last 50 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Over half of government spending is discretionary spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
As a percent of GDP, the total U.S. federal debt has been declining since World War II.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
About 6% of annual total federal government expenditures goes toward paying interest on the federal debt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
For the federal government, what is the difference between discretionary spending and mandatory spending? What categories of spending account for the largest amount of the federal government's discretionary spending and mandatory spending?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is a budget deficit? What is a budget surplus? Since 1970, has the U.S. government run more budget deficits or budget surpluses?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The total amount of money the government owes to its creditors is known as ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A retirement system in which the benefits government pays to retirees are paid out of the contributions those retirees make during their working years is called a
A) pay-as-you-go system.
B) fully funded system.
C) pension plan.
D) deferred retirement system.
A) pay-as-you-go system.
B) fully funded system.
C) pension plan.
D) deferred retirement system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Since the Social Security system began in the 1930s, the number of workers per retiree
A) has stayed roughly the same.
B) has declined.
C) has risen.
D) declined through 1960 and has risen ever since.
A) has stayed roughly the same.
B) has declined.
C) has risen.
D) declined through 1960 and has risen ever since.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The Social Security Administration estimates that the Social Security Trust Fund will ________ and that the Medicare Trust Fund will ________.
A) become fully funded by 2036; become fully funded by 2024
B) continue to get smaller as the number of retirees increases; start to grow once funds from Obamacare are funneled to the program
C) grow slowly as more workers retire; decline slowly as medical costs rise
D) run out of funds in about 20 years; run out of funds in about 10 years
A) become fully funded by 2036; become fully funded by 2024
B) continue to get smaller as the number of retirees increases; start to grow once funds from Obamacare are funneled to the program
C) grow slowly as more workers retire; decline slowly as medical costs rise
D) run out of funds in about 20 years; run out of funds in about 10 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Based on the current state of revenue of the Social Security and Medicare programs, the government has two options for funding, which are
A) raising payroll taxes or cutting benefits.
B) raising payroll taxes or raising benefits.
C) cutting payroll taxes or cutting benefits.
D) cutting payroll taxes or raising benefits.
A) raising payroll taxes or cutting benefits.
B) raising payroll taxes or raising benefits.
C) cutting payroll taxes or cutting benefits.
D) cutting payroll taxes or raising benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The Congressional Budget Office estimates that the ratio of publicly held debt to GDP will ________ by 2050 if no entitlement reforms are enacted.
A) remain close to the current high level of 73%
B) fall to only about 55%
C) more than triple to about 250%
D) rise to about 130%
A) remain close to the current high level of 73%
B) fall to only about 55%
C) more than triple to about 250%
D) rise to about 130%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
There are fewer workers per retiree today contributing to Social Security than there were in the 1960s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The government could increase Social Security tax revenues by raising the payroll tax cap beyond its current $110,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following is an example of discretionary fiscal policy?
A) a decrease in income tax receipts with falling income during a recession
B) tax cuts passed by Congress in 2008 to combat the recession
C) a decrease in food stamps issued during an expansion
D) an increase in unemployment insurance payments during a recession
A) a decrease in income tax receipts with falling income during a recession
B) tax cuts passed by Congress in 2008 to combat the recession
C) a decrease in food stamps issued during an expansion
D) an increase in unemployment insurance payments during a recession

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If an increase in government spending of $20 million results in a $100 million increase in GDP, then the spending multiplier is
A) 0.2.
B) 2.5.
C) 5.
D) 20.
A) 0.2.
B) 2.5.
C) 5.
D) 20.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A general formula for the spending multiplier is
A)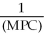
B)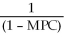
C)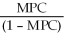
D)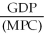
A)
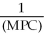
B)
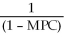
C)
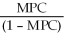
D)
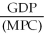

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Among the groundbreaking contributions to economics made by John Maynard Keynes is
A) the insight that recessions can result from a lack of aggregate demand.
B) the development of the spending multiplier.
C) the theory of sticky wages and prices.
D) all of the above
A) the insight that recessions can result from a lack of aggregate demand.
B) the development of the spending multiplier.
C) the theory of sticky wages and prices.
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The recognition lag for fiscal policy is ________ it is for monetary policy.
A) generally longer than
B) generally shorter than
C) roughly the same as
D) There is not a recognition lag for fiscal policy.
A) generally longer than
B) generally shorter than
C) roughly the same as
D) There is not a recognition lag for fiscal policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The crowding out of consumer spending by an increase in taxes will be the greatest when
A) consumers would have spent the entire amount they now must pay in taxes.
B) consumers would have saved the entire amount they now must pay in taxes.
C) consumers would have spent only a fraction of the amount they now must pay in taxes.
D) the government has a history of increasing taxes on a regular basis.
A) consumers would have spent the entire amount they now must pay in taxes.
B) consumers would have saved the entire amount they now must pay in taxes.
C) consumers would have spent only a fraction of the amount they now must pay in taxes.
D) the government has a history of increasing taxes on a regular basis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
When government decides to increase spending, interest rates generally ________ and this change in interest rates ________ investment spending.
A) increase; increases
B) increase; decreases
C) decrease; increases
D) decrease; decreases
A) increase; increases
B) increase; decreases
C) decrease; increases
D) decrease; decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
All of the following were provisions of the 2009 American Reinvestment and Recovery Act except
A) a temporary extension of unemployment benefits.
B) expanded tax credits for parents for their children's college tuition.
C) a reduction in government-funded infrastructure spending.
D) a reduction in employees' payroll tax contributions.
A) a temporary extension of unemployment benefits.
B) expanded tax credits for parents for their children's college tuition.
C) a reduction in government-funded infrastructure spending.
D) a reduction in employees' payroll tax contributions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The Federal Reserve's buying and selling of bonds through their open market operations is an example of fiscal policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The marginal propensity to consume is the proportion of each new dollar's worth of income that is spent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
When increased government spending results in decreased consumer or business spending, the government spending is said to be crowding out the consumer and business spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Deliberately cutting taxes or increasing expenditures to fight an economic downturn is called ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What two fiscal policy actions could the government take if it wants to stimulate the economy during a recession? What two fiscal policy actions could the government take if it wants to slow the economy down during a period of rapid growth and increasing inflation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



