Deck 11: Decisions, Judgments, and Reasoning
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/29
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Decisions, Judgments, and Reasoning
1
In reasoning, the tendency to search for evidence that confirms a conclusion:
A) Confirmation bias
B) Modus ponens
C) Modus tollens
D) Anchoring and adjustment heuristic
A) Confirmation bias
B) Modus ponens
C) Modus tollens
D) Anchoring and adjustment heuristic
Confirmation bias
2
Consider the following problem. What does it represent?
All A are B.
Some B are C.
Thus, some A are C.
A) Logically valid syllogism
B) Invalid syllogism
C) Confirm the antecedent
D) Illicit conversion
All A are B.
Some B are C.
Thus, some A are C.
A) Logically valid syllogism
B) Invalid syllogism
C) Confirm the antecedent
D) Illicit conversion
Invalid syllogism
3
Which of the following reflects valid conditional reasoning?
A) Deny the antecedent
B) Symbolic comparison
C) Modus ponens
D) Affirming the consequent
A) Deny the antecedent
B) Symbolic comparison
C) Modus ponens
D) Affirming the consequent
Modus ponens
4
Matty and Gloria are out on a date. When Gloria asks Matty where they should go for dinner,he says "I keep hearing about a new Italian restaurant near here, so it must be a great place to eat." Matty is:
A) Showing a confirmation bias
B) Using an availability heuristic
C) Using counterfactual reasoning
D) Using a simulation heuristic
A) Showing a confirmation bias
B) Using an availability heuristic
C) Using counterfactual reasoning
D) Using a simulation heuristic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The Wason card problem is an example of:
A) A mental model
B) Conditional reasoning
C) Availability bias
D) Modus ponens
A) A mental model
B) Conditional reasoning
C) Availability bias
D) Modus ponens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In Piaget's theory of cognitive development, the point at which children begin to go from concrete to formal operations is:
A) Two
B) Four
C) Eight
D) Twelve
A) Two
B) Four
C) Eight
D) Twelve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which is true of judgments of number magnitude?
A) The smaller the difference between the digits, the faster the judgments are made.
B) Just as in psychophysics, the psychological difference is a direct function of physical difference.
C) Judgment time is not affected by semantic congruity.
D) When people make mental comparisons and judgments of purely symbolic quantities, there is a pronounced semantic distance effect.
A) The smaller the difference between the digits, the faster the judgments are made.
B) Just as in psychophysics, the psychological difference is a direct function of physical difference.
C) Judgment time is not affected by semantic congruity.
D) When people make mental comparisons and judgments of purely symbolic quantities, there is a pronounced semantic distance effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Using the following picture and asking "Which {balloon // yo-yo} is higher"(the example from the textbook) will illustrate: 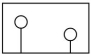
A) The symbolic distance effect
B) The semantic congruity effect
C) Decisions about size differences are sped up when the stimuli differ by a greater amount
D) The magnitude effect

A) The symbolic distance effect
B) The semantic congruity effect
C) Decisions about size differences are sped up when the stimuli differ by a greater amount
D) The magnitude effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When scientists were given evidence that their original theory was wrong:
A) An equal number did/did not alter their theory
B) The majority kept to their original beliefs
C) Nobody took any notice
D) The majority altered their theory
A) An equal number did/did not alter their theory
B) The majority kept to their original beliefs
C) Nobody took any notice
D) The majority altered their theory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Heuristic is:
A) A specific rule or solution procedure that is certain to yield the correct answer if followed correctly
B) An informal "rule of thumb" method for solving problems, not necessarily guaranteed to solve the problem correctly but usually much faster or more tractable than other alternatives
C) The act of someone who reasons; to think logically; to analyze with reason
D) The mental representation of meaning in a reasoning problem
A) A specific rule or solution procedure that is certain to yield the correct answer if followed correctly
B) An informal "rule of thumb" method for solving problems, not necessarily guaranteed to solve the problem correctly but usually much faster or more tractable than other alternatives
C) The act of someone who reasons; to think logically; to analyze with reason
D) The mental representation of meaning in a reasoning problem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Algorithm is:
A) A specific rule or solution procedure that is certain to yield the correct answer if followed correctly
B) An informal "rule of thumb" method for solving problems, not necessarily guaranteed to solve the problem correctly but usually much faster or more tractable than other alternatives
C) The act of someone who reasons; to think logically; to analyze with reason
D) The mental representation of meaning in a reasoning problem
A) A specific rule or solution procedure that is certain to yield the correct answer if followed correctly
B) An informal "rule of thumb" method for solving problems, not necessarily guaranteed to solve the problem correctly but usually much faster or more tractable than other alternatives
C) The act of someone who reasons; to think logically; to analyze with reason
D) The mental representation of meaning in a reasoning problem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
There are two hospitals; one averages 45 births per day, the other 15 births per day. You are asked, "In any given year, which hospital will have a higher percentage of days during which more than 60% of the babies born will be male." The correct answer is ________.
A) The "45" hospital
B) The "15" hospital
C) There is an equal chance of either
D) Neither hospital will have more than 50% males born
A) The "45" hospital
B) The "15" hospital
C) There is an equal chance of either
D) Neither hospital will have more than 50% males born

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Kahneman & Tversky (1973) report having participants read various personality descriptions and then estimate the likelihood or probability that a person was a member of one or another profession. They report:
A) Good use of prior odds in the "bare bones" situation
B) Stereotypic information biased the reported likelihood in the direction of the stereotype
C) Worthless information did not bias the reported likelihood; prior probabilities were retained unless the information was consistent with a stereotype.
D) The descriptive model deviated strongly from the normative model
A) Good use of prior odds in the "bare bones" situation
B) Stereotypic information biased the reported likelihood in the direction of the stereotype
C) Worthless information did not bias the reported likelihood; prior probabilities were retained unless the information was consistent with a stereotype.
D) The descriptive model deviated strongly from the normative model

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Making a decision based on ease of retrieval of relevant examples from memory (e.g., the "words with K in the first/third position" example). This is an informal approach that can be extremely useful in many situations, but which sometimes produces the wrong answer.
A) Representativeness heuristic
B) Bayes' theorem
C) Availability heuristic
D) Confirmation bias
A) Representativeness heuristic
B) Bayes' theorem
C) Availability heuristic
D) Confirmation bias

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The argument that there is a central flaw in "heuristics and bias" research -- that it is a mistake to assume that the correct answer to any decision-making problem must be the normative answer supplied by classic probability theory:
A) Counterfactual thinking
B) Inductive rationalization
C) Adaptive thinking
D) Paradoxically called the "recognition heuristic"
A) Counterfactual thinking
B) Inductive rationalization
C) Adaptive thinking
D) Paradoxically called the "recognition heuristic"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Katy is 26, loves the snow and being outdoors, and is very athletic. If someone immediately thinks that Katy must be a ski instructor who loves to hike, they have fallen victim to:
A) The representative heuristic
B) The conjunction fallacy
C) The availability heuristic
D) The simulation heuristic
A) The representative heuristic
B) The conjunction fallacy
C) The availability heuristic
D) The simulation heuristic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If a coin is tossed eight times, which of the following is most likely to occur?
HHHHTTTT
HTHTHTHT
A) HHHHTTTT
B) HTHTHTH
C) Both are equally likely to occur
D) They will occur on alternate tosses
HHHHTTTT
HTHTHTHT
A) HHHHTTTT
B) HTHTHTH
C) Both are equally likely to occur
D) They will occur on alternate tosses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When a concrete version of the Wason card problem is compared to an abstract version:
A) Performance is better on the concrete version
B) Performance is better on the abstract version
C) Performance is the same on both versions
D) Performing the abstract version helps performance on the concrete version
A) Performance is better on the concrete version
B) Performance is better on the abstract version
C) Performance is the same on both versions
D) Performing the abstract version helps performance on the concrete version

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is implicated in limitations that lead to incorrect reasoning and decision making?
A) Not using a mental model
B) The semantic congruity effect
C) Psychophysics
D) Limitations in working memory processes
A) Not using a mental model
B) The semantic congruity effect
C) Psychophysics
D) Limitations in working memory processes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In general, people's performance on syllogisms becomes worse when they are shown how to use Venn diagrams.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Research suggests that working memory is not necessary for good reasoning and decision making.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In everyday reasoning we rely on mental models of the device or event to make our judgments. These models are usually very accurate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In the statement "If it rains, then the picnic will be cancelled", the ________ is "If it rains".

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A ________ heuristic is when you decide between alternatives based on the first useful information you retrieve about the alternatives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In psychophysics, the amount by which two stimuli must differ so that the difference can be perceived is called ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The notion of ________ refers to the fact that it is often preferable to select a satisfactory answer to a question rather than taking the time and effort to search for the optimal answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
When might you use a Venn diagram? What would be particularly important to keep in mind? [Use an example.]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Describe the research by Fugelsang and colleagues showing that even scientists are prone to the confirmation bias. Be sure to include the neuroimaging findings in your discussion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Define, and use examples to illustrate, the semantic distance effect and the semantic congruity effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



