Deck 9: Inheritance
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/45
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Inheritance
1
Peas are an appropriate choice for studies of genetic inheritance because
A) they can be self-pollinating.
B) they are easy to cross artificially.
C) they breed true.
D) They produce large numbers of progeny.
E) All of the answers are true.
A) they can be self-pollinating.
B) they are easy to cross artificially.
C) they breed true.
D) They produce large numbers of progeny.
E) All of the answers are true.
They produce large numbers of progeny.
2
The position of a gene on a chromosome is known as the
A) locus.
B) centromere.
C) linkage.
D) genotype.
E) allele.
A) locus.
B) centromere.
C) linkage.
D) genotype.
E) allele.
locus.
3
Alternative forms (alleles) of a gene separate into gametes after meiosis with equal probability. This is known as
A) linkage.
B) codominance.
C) the Principle of Segregation.
D) genotype.
E) the Principle of Independent Assortment.
A) linkage.
B) codominance.
C) the Principle of Segregation.
D) genotype.
E) the Principle of Independent Assortment.
the Principle of Segregation.
4
The vinegar fly, Drosophila melanogaster, has a gene that controls the shape of the wings. The wild-type phenotype is flat wings, but a mutation in the gene produces curled wings. You would expect
A) the wild-type phenotype to be dominant.
B) most Drosophila in natural populations to have the wild-type phenotype.
C) all Drosophila with curled wings to be homozygous.
D) all wild-type Drosophila to have the genotype +/-.
E) all wild-type Drosophila to have the genotype +/+.
A) the wild-type phenotype to be dominant.
B) most Drosophila in natural populations to have the wild-type phenotype.
C) all Drosophila with curled wings to be homozygous.
D) all wild-type Drosophila to have the genotype +/-.
E) all wild-type Drosophila to have the genotype +/+.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In mice, a gene controlling coat colour has 2 alleles; B (black) and b (white). A pure breeding black mouse is crossed to a white mouse and all the offspring are black. The offspring are then crossed to white mice. The phenotypes of the offspring of this second cross are expected to be
A) all black
B) 3/4 black, 1/4 white
C) 1/2 black, 1/2 white
D) 1/4 black, 3/4 white
E) all white
A) all black
B) 3/4 black, 1/4 white
C) 1/2 black, 1/2 white
D) 1/4 black, 3/4 white
E) all white

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In dogs, length of hair is controlled by a gene with 2 alleles. Short hair is dominant to long hair. Two heterozygous short-haired dogs are crossed and they produce a short-haired puppy. What is the probability that the puppy is heterozygous?
A) 1/2
B) 2/3
C) 1/3
D) 3/4
E) 1/4
A) 1/2
B) 2/3
C) 1/3
D) 3/4
E) 1/4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The presence or absence of hair on the mid-digital region of a finger is determined by a single autosomal gene. The presence of hair is dominant to the absence of hair. In the pedigree below, shading represents the presence of mid-digital hair.
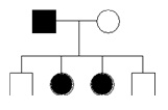 If the parents have a 5th child, what is the probability that it will have mid-digital hair?
If the parents have a 5th child, what is the probability that it will have mid-digital hair?
A) 1/2
B) 2/3
C) 3/4
D) 1/3
E) 1/4
 If the parents have a 5th child, what is the probability that it will have mid-digital hair?
If the parents have a 5th child, what is the probability that it will have mid-digital hair?A) 1/2
B) 2/3
C) 3/4
D) 1/3
E) 1/4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The presence or absence of hair on the mid-digital region of a finger is determined by a single autosomal gene. The presence of hair is dominant to the absence of hair. In the pedigree below, shading represents the presence of mid-digital hair.
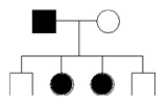 If the parents have a 5th child, what is the probability that it will be female and have mid-digital hair?
If the parents have a 5th child, what is the probability that it will be female and have mid-digital hair?
A) 1/2
B) 3/4
C) 1/8
D) 1/4.
E) 2/3
 If the parents have a 5th child, what is the probability that it will be female and have mid-digital hair?
If the parents have a 5th child, what is the probability that it will be female and have mid-digital hair?A) 1/2
B) 3/4
C) 1/8
D) 1/4.
E) 2/3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A gene controlling flower colour also controls the colour of the stem and seed coat. This phenomenon is known as
A) expressivity.
B) pleiotropy.
C) epistasis.
D) imprinting.
E) codominance.
A) expressivity.
B) pleiotropy.
C) epistasis.
D) imprinting.
E) codominance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The flowers of snapdragons are red, pink or white. Crossing homozygous red snapdragons with homozygous white snapdragons produces offspring that have pink flowers. Which of the following crosses would produce the highest percentage of white flowers?
A) Red x white
B) Pink x pink
C) Red x pink
D) Pink x white
E) A and B are correct as they would produce the same number of white flowers.
A) Red x white
B) Pink x pink
C) Red x pink
D) Pink x white
E) A and B are correct as they would produce the same number of white flowers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Human ABO blood groups are determined by three alleles: IA, IB and i. A man with blood group AB has a number of children by a woman with blood group A. Their first child has blood group B. What is the probability that the second child will also have blood group B?
A) 1/2
B) 1/4
C) 1/8
D) 1/16
E) 3/4
A) 1/2
B) 1/4
C) 1/8
D) 1/16
E) 3/4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In tomatoes, the alleles for a gene controlling fruit shape assort independently of the alleles of a gene controlling fruit colour. Round-shaped fruit are dominant to oval-shaped fruit and red fruit are dominant to yellow fruit. A homozygous, red, round-fruit tomato plant is crossed to a tomato plant with yellow oval fruit to produce an F1 generation. The F1 plants are crossed to pure-breeding red oval plants. The phenotypic ratio for the offspring of this second cross would be expected to be
A) 9 round red: 3 round yellow: 3 oval red: 1 oval yellow.
B) 1 round red: 1 round yellow: 1 oval red: 1 oval yellow.
C) 1 round red: 1 oval red.
D) 3 round red: 1 oval yellow.
E) 1 round red: 3 oval yellow.
A) 9 round red: 3 round yellow: 3 oval red: 1 oval yellow.
B) 1 round red: 1 round yellow: 1 oval red: 1 oval yellow.
C) 1 round red: 1 oval red.
D) 3 round red: 1 oval yellow.
E) 1 round red: 3 oval yellow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In tomatoes, the alleles for a gene controlling fruit shape assort independently of the alleles of a gene controlling fruit colour. Round-shaped fruit are dominant to oval-shaped fruit and red fruit are dominant to yellow fruit. A homozygous, red, round-fruit tomato plant is crossed to a tomato plant with yellow oval fruit to produce an F1 generation. F1 plants were crossed to plants that were homozygous red and heterozygous round. You would expect the offspring to be
A) 9 round red: 3 round yellow: 3 oval red: 1 oval yellow.
B) 1 round red: 1 oval red.
C) 1 round red: 1 round yellow: 1 oval red: 1 oval yellow.
D) 3 round red: 1 oval red.
E) 3 round red: 1 oval yellow.
A) 9 round red: 3 round yellow: 3 oval red: 1 oval yellow.
B) 1 round red: 1 oval red.
C) 1 round red: 1 round yellow: 1 oval red: 1 oval yellow.
D) 3 round red: 1 oval red.
E) 3 round red: 1 oval yellow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In a testcross involving tomatoes, one tomato plant has the genotype O/o ; R/r. The genotype of the other plant is
A) o/o; r/r.
B) O/o; R/r.
C) O/O; R/R.
D) O/O; r/r.
E) o/o; R/R.
A) o/o; r/r.
B) O/o; R/r.
C) O/O; R/R.
D) O/O; r/r.
E) o/o; R/R.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Stem length, seed shape and flower colour in pea plants are determined by three independently assorting genes. Each trait has a dominant and a recessive phenotype. If a plant that is heterozygous for the three traits is allowed to self-fertilise, you would expect 3/8 of the offspring to be
A) homozygous for all three traits.
B) homozygous for the three recessive traits.
C) homozygous for one and heterozygous for two.
D) heterozygous for all three traits.
E) homozygous for two traits and homozygous for one.
A) homozygous for all three traits.
B) homozygous for the three recessive traits.
C) homozygous for one and heterozygous for two.
D) heterozygous for all three traits.
E) homozygous for two traits and homozygous for one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following statements about sex-linked traits in humans is true?
A) Y-linked traits can be observed in 50 per cent of females.
B) Females can be carriers of X-linked traits.
C) Genes on autosomes can be sex-linked.
D) The majority of genes in are sex-linked.
E) Y-linked traits are passed from father to daughter on the Y-linked chromosome.
A) Y-linked traits can be observed in 50 per cent of females.
B) Females can be carriers of X-linked traits.
C) Genes on autosomes can be sex-linked.
D) The majority of genes in are sex-linked.
E) Y-linked traits are passed from father to daughter on the Y-linked chromosome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Haemophilia is a defect in blood clotting. It is a recessive trait that has arisen from a mutation of a gene on the X-chromosome. A boy with haemophilia has parents who have normal blood clotting. If the parents have another child what is the probability it will be normal?
A) 0
B) 1/4
C) 1/2
D) 3/4
E) 3/8
A) 0
B) 1/4
C) 1/2
D) 3/4
E) 3/8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Red-green colour-blindness in humans is a recessive X-linked trait. A man and a woman with normal vision have a colour-blind son. What is the probability that their next child will also be a colour-blind son?
A) 0
B) 1/4
C) 1/2
D) 3/4
E) 3/8
A) 0
B) 1/4
C) 1/2
D) 3/4
E) 3/8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When two genes are linked, most of the phenotypes of the parental traits will be inherited together. For example, eye colour and bristle form in the vinegar fly, Drosophila, are linked. The alleles for white eyes and crooked bristles occur on one chromosome in a fly while the alleles for red eyes and straight bristles occur together on another chromosome. Gametes produced by the fly that contain a chromosome with both the white-eye allele and the straight-bristle allele are referred to as
A) incomplete dominants.
B) recombinants.
C) polymorphic.
D) heterozygotes.
E) mutants.
A) incomplete dominants.
B) recombinants.
C) polymorphic.
D) heterozygotes.
E) mutants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In tomato plants, a gene controlling fruit shape has 2 alleles: O (round) and o (oval). A gene controlling inflorescence (position of the flowers) has two alleles: S (simple) and s (compound). A pure-breeding plant with oval fruit and simple inflorescence is crossed to a pure-breeding plant with round fruit and compound inflorescence. All the offspring have round fruit and simple inflorescence. The offspring are then crossed to plants with oval fruit and compound inflorescence. The phenotypes of this second generation are
Oval simple 200
Round compound 190
Oval compound 50
Round simple 60.
Which statement about the genes is true?
A) The alleles of one gene assort independently of the alleles of the other gene.
B) The recombination frequency between the genes is more than 50 per cent.
C) The gene loci are on separate chromosomes.
D) The genes show incomplete dominance.
E) The genes are linked.
Oval simple 200
Round compound 190
Oval compound 50
Round simple 60.
Which statement about the genes is true?
A) The alleles of one gene assort independently of the alleles of the other gene.
B) The recombination frequency between the genes is more than 50 per cent.
C) The gene loci are on separate chromosomes.
D) The genes show incomplete dominance.
E) The genes are linked.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The distance between genes on a genetic map is calculated using
A) recombination frequency.
B) kilobases of DNA.
C) centimetres.
D) centigrams.
E) map distance.
A) recombination frequency.
B) kilobases of DNA.
C) centimetres.
D) centigrams.
E) map distance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In tomato plants, a gene controlling fruit shape has 2 alleles: O (round) and o (oval). A gene controlling inflorescence (position of the flowers) has two alleles: S (simple) and s (compound). The map distance between the two genes is 22 cM. A pure-breeding plant with oval fruit and compound inflorescence is crossed with a pure-breeding plant with round fruit and simple inflorescence. The F1 have round fruit and simple inflorescence. The F1 are then crossed to plants with oval fruit and compound inflorescence and 100 offspring are produced. How many of the offspring would you expect to have oval fruit and simple inflorescence?
A) 22
B) 11
C) 39
D) 25
E) 50
A) 22
B) 11
C) 39
D) 25
E) 50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A gene that controls coat colour in cattle has 2 alleles; CR (red) and CW (white). The heterozygotes have a roan colour. If roan cattle are crossed to white cattle, which of the following phenotypic ratios would be expected in the offspring?
A) 3 red : 1 white
B) 1 red : 2 roan : 1 white
C) 1 white : 1 roan
D) 1 white : 1 roan : 1 red
E) 2 white: 1 roan
A) 3 red : 1 white
B) 1 red : 2 roan : 1 white
C) 1 white : 1 roan
D) 1 white : 1 roan : 1 red
E) 2 white: 1 roan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Variation in phenotypic expression involves both expressivity and penetrance. Penetrance is
A) the degree to which an allele is expressed individually.
B) the degree to which an allele is dominant.
C) a measure of recombination.
D) the proportion of individuals carrying the allele that show a phenotypic effect.
E) the proportion of the individuals carrying the allele.
A) the degree to which an allele is expressed individually.
B) the degree to which an allele is dominant.
C) a measure of recombination.
D) the proportion of individuals carrying the allele that show a phenotypic effect.
E) the proportion of the individuals carrying the allele.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Polydactyly (extra fingers or toes) in humans is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait. Some heterozygotes, however, do not have any visible abnormality. This situation could result from
A) a reduced level of penetrance.
B) reduced expressivity.
C) incomplete dominance.
D) polygenic inheritance.
E) phenotypic variability
A) a reduced level of penetrance.
B) reduced expressivity.
C) incomplete dominance.
D) polygenic inheritance.
E) phenotypic variability

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In a flowering plant, a mutation in a gene controlling flower structure results in flowers with extra petals. A mutation in another gene results in no flowers (flowerless). Both mutant phenotypes are recessive, and the two genes assort independently. If a plant heterozygous for both mutations self-fertilises, which of the following ratios would you expect in the offspring?
A) 9 wild type: 3 extra petals: 3 flowerless: 1 extra petals, flowerless
B) 9 wild type: 3 extra petals: 4 flowerless
C) 9 wild type: 3 flowerless: 4 extra petals
D) 1 wild type: 1 flowerless: 1 extra petals: 1 extra petals, flowerless
E) 1 wild type: 2 extra petals: 1flowerless
A) 9 wild type: 3 extra petals: 3 flowerless: 1 extra petals, flowerless
B) 9 wild type: 3 extra petals: 4 flowerless
C) 9 wild type: 3 flowerless: 4 extra petals
D) 1 wild type: 1 flowerless: 1 extra petals: 1 extra petals, flowerless
E) 1 wild type: 2 extra petals: 1flowerless

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The colour of wheat seeds is controlled by two genes. The alleles (R1 and r1) of one gene assort independently to the alleles (R2 and r2) of the other gene. R1 and R2 produce a red pigment while r1 and r2 do not produce any pigment. The effect of the alleles is additive so that R1/R1; R2/R2 give dark red colour while r1/r1; r2/r2 produces white. A plant with R1/r1; R2/r2 has intermediate red colour. If the following cross was set up:
R1/r1; R2/r2 x R1/R1; R2/R2
A) none of the offspring would have the deep red colour similar to one of the parents.
B) some of the offspring would be white.
C) some of the offspring would have an intermediate red colour similar to one of the parents.
D) most of the offspring would have the deep red colour similar to one of the parents.
E) all of the offspring would have intermediate colour.
R1/r1; R2/r2 x R1/R1; R2/R2
A) none of the offspring would have the deep red colour similar to one of the parents.
B) some of the offspring would be white.
C) some of the offspring would have an intermediate red colour similar to one of the parents.
D) most of the offspring would have the deep red colour similar to one of the parents.
E) all of the offspring would have intermediate colour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The colour of wheat seeds is controlled by two genes. The alleles (R1 and r1) of one gene assort independently to the alleles (R2 and r2) of the other gene. R1 and R2 produce a red pigment while r1 and r2 do not produce any pigment. The effect of the alleles is additive so that R1/R1; R2/R2 give dark red colour while r1/r1; r2/r2 produces white. A plant with R1/r1; R2/r2 has intermediate red colour. A plant heterozygous at both gene loci was allowed to self-fertilise. What proportion of offspring would be expected to have a colour similar to the parent?
A) 0
B) 1/4
C) 3/4
D) 3/8
E) 1/2
A) 0
B) 1/4
C) 3/4
D) 3/8
E) 1/2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In a organism heterozgyous for a particular allele
A) the individual has two copies of the same allele.
B) the individual has two different copies of the allele.
C) all the gametes produced by the individual are the same.
D) the allele will be expressed to provide the same phenotype in the F1 progeny.
E) the trait of the allele is dominant.
A) the individual has two copies of the same allele.
B) the individual has two different copies of the allele.
C) all the gametes produced by the individual are the same.
D) the allele will be expressed to provide the same phenotype in the F1 progeny.
E) the trait of the allele is dominant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Autosomes are
A) alleles that are sex-linked, and occur only in males or females.
B) an allele for a trait that requires the presence of another gene for expression.
C) chromosomes that are the same in all individual organisms.
D) alleles associated with genetic defects causing disease.
E) chromosomes that are the same in males and females.
A) alleles that are sex-linked, and occur only in males or females.
B) an allele for a trait that requires the presence of another gene for expression.
C) chromosomes that are the same in all individual organisms.
D) alleles associated with genetic defects causing disease.
E) chromosomes that are the same in males and females.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
One of the main reasons that genes assort independently of each other is
A) they are different alleles.
B) they are on different chromosomes.
C) they are on the same chromosome, but distant from each other.
D) they both provide dominant traits to the organism.
E) they provide the same phenotype to the organism.
A) they are different alleles.
B) they are on different chromosomes.
C) they are on the same chromosome, but distant from each other.
D) they both provide dominant traits to the organism.
E) they provide the same phenotype to the organism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The frequency of recombination was used to determine the map order of 4 genes, A-D. The distance from A-B was 4 cM; A-C was 30 cM; A-D was 20 cM; B-C was 26 cM; C-D was 40. What is the correct order of the genes?
A) A-B-C-D.
B) A-C-D-B.
C) B-C-A-D.
D) C-B-A-D.
E) D-B-A-C.
A) A-B-C-D.
B) A-C-D-B.
C) B-C-A-D.
D) C-B-A-D.
E) D-B-A-C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The principle of independent segregation results in
A) all individuals carrying a pair of genes that influence a particular inherited trait.
B) alleles of each gene segregating from each other in the production of gametes.
C) each individual inheriting one allele of each gene from each parent.
D) the phenotype of one allele may be dominant over the phenotype of another
E) All of these statements are associated with the principal of independent seggregation.
A) all individuals carrying a pair of genes that influence a particular inherited trait.
B) alleles of each gene segregating from each other in the production of gametes.
C) each individual inheriting one allele of each gene from each parent.
D) the phenotype of one allele may be dominant over the phenotype of another
E) All of these statements are associated with the principal of independent seggregation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Linkage is
A) two or more genes on the same chromosome.
B) the tendency for genes to be inherited together.
C) the rate of recombination between different alleles.
D) the distance between alleles on the same chromosome.
E) the number of F2 progeny containing the specific allele.
A) two or more genes on the same chromosome.
B) the tendency for genes to be inherited together.
C) the rate of recombination between different alleles.
D) the distance between alleles on the same chromosome.
E) the number of F2 progeny containing the specific allele.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Epistasis is
A) the phenotype when one gene controls the expression of another gene.
B) an individual with two identical alleles for the same trait.
C) modification of the activity of genes that is independent of the genotype.
D) the interaction between non-allelic genes so that one masks the expression of the other.
E) the allelic make up of an individual.
A) the phenotype when one gene controls the expression of another gene.
B) an individual with two identical alleles for the same trait.
C) modification of the activity of genes that is independent of the genotype.
D) the interaction between non-allelic genes so that one masks the expression of the other.
E) the allelic make up of an individual.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Imprinting is
A) the continuous variation of phenotype due to the effect of multiple genes and the environment.
B) a result of a gene that affects different characteristics in the same organism.
C) the different behaviour of identical alleles as a result of being inherited from the mother.
D) the inheritance of a Y-linked allele.
E) a recessive trait that may be expressed under some conditions.
A) the continuous variation of phenotype due to the effect of multiple genes and the environment.
B) a result of a gene that affects different characteristics in the same organism.
C) the different behaviour of identical alleles as a result of being inherited from the mother.
D) the inheritance of a Y-linked allele.
E) a recessive trait that may be expressed under some conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A geneticist is studying various phenotypic traits in the toes of rats that are controlled by a mixture of both recessive and dominant alleles. He decides to cross some of his subjects with a new mutant strain that carries a dominant trait for no toes. The progeny of this cross would be an example of
A) epigenetics.
B) chromosomal inactivation.
C) epistasis.
D) imprinting.
E) autosomal polymorphism.
A) epigenetics.
B) chromosomal inactivation.
C) epistasis.
D) imprinting.
E) autosomal polymorphism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following statements in relation to individuals carrying the AB blood group is CORRECT?
A) AB individuals have A or B antigens on their red blood cells.
B) AB individuals can receive A, B and AB blood but not O.
C) AB individuals can only receive AB blood.
D) AB individuals can only donate to other AB individuals.
E) AB individuals are considered universal donors.
A) AB individuals have A or B antigens on their red blood cells.
B) AB individuals can receive A, B and AB blood but not O.
C) AB individuals can only receive AB blood.
D) AB individuals can only donate to other AB individuals.
E) AB individuals are considered universal donors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A male patient of Mediterranean origin is rushed into the trauma centre of a major hospital and requires an immediate blood transfusion. The patient's medical history is unknown and there is insufficient time to perform a blood typing analysis. Which blood type should the patient be given and why?
A) O, as this blood type has no antigens.
B) AB, as this is the blood type of universal recipients.
C) A, as this is the most common blood type in the general populous and therefore most likely to be compatible.
D) B, as this blood type is more common in those of Southern European heritage and therefore most likely to be compatible.
E) It doesn't matter, just get some damn blood into him and worry about the blood type later on.
A) O, as this blood type has no antigens.
B) AB, as this is the blood type of universal recipients.
C) A, as this is the most common blood type in the general populous and therefore most likely to be compatible.
D) B, as this blood type is more common in those of Southern European heritage and therefore most likely to be compatible.
E) It doesn't matter, just get some damn blood into him and worry about the blood type later on.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following statements about Gregor Mendel is INCORRECT?
A) Mendel was able to successfully quantify his results because he applied a robust scientific method to his observations.
B) Mendel's data, when first published, was met with widespread acclaim for its significant advancement to our understanding of inheritance.
C) Part of Mendel's success was due to his decision to study pure-bred varieties.
D) Mendel's first conclusion is called the Principle of Segregation.
E) Mendel studied the outcome of various monohybrid crosses.
A) Mendel was able to successfully quantify his results because he applied a robust scientific method to his observations.
B) Mendel's data, when first published, was met with widespread acclaim for its significant advancement to our understanding of inheritance.
C) Part of Mendel's success was due to his decision to study pure-bred varieties.
D) Mendel's first conclusion is called the Principle of Segregation.
E) Mendel studied the outcome of various monohybrid crosses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A farmer has a new plant that has not been previously domesticated and wants to start breeding it to produce larger fruit. As fruit size is a polygenic trait, what approach should the farmer take in attempting to quickly and efficiently increase the fruit size?
A) Randomly inbreed the plant over multiple generations to produce purebred strains.
B) Perform monohybrid crosses.
C) Send the fruit to a lab for QTL analysis and produce a linkage map.
D) Identify the wild progenitor species and use it to increase the available pool for genetic diversity.
E) Select individual plants that have the desired characteristic and inbreed from them.
A) Randomly inbreed the plant over multiple generations to produce purebred strains.
B) Perform monohybrid crosses.
C) Send the fruit to a lab for QTL analysis and produce a linkage map.
D) Identify the wild progenitor species and use it to increase the available pool for genetic diversity.
E) Select individual plants that have the desired characteristic and inbreed from them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
An Honours student is working on a project to determine the distance between two loci. She performs fifty crosses and observes 8 recombination events between the two loci. What is the distance between the two loci?
A) 0.16 cM
B) 0.16 Kb
C) 16 Kb
D) 16 cM
E) There is insufficient data to determine the distance between the two loci.
A) 0.16 cM
B) 0.16 Kb
C) 16 Kb
D) 16 cM
E) There is insufficient data to determine the distance between the two loci.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following crosses is a BACKCROSS?
A) Two independent pure-bred lines crossed with each other.
B) F1 progeny crossed with a pure-breeding parent.
C) F1 progeny crossed with F2 progeny.
D) F1 progeny crossed with F1 progeny.
E) All of the options listed here could be considered a backcross.
A) Two independent pure-bred lines crossed with each other.
B) F1 progeny crossed with a pure-breeding parent.
C) F1 progeny crossed with F2 progeny.
D) F1 progeny crossed with F1 progeny.
E) All of the options listed here could be considered a backcross.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Two alleles control a trait for pathogenicity in a species of bacteria. Those homozygous for allele A cause a virulent disease upon infection of a host, whereas those homozygous for allele B cause no symptoms whatsoever. Bacteria carrying both alleles cause a mild disease upon infection of a host. No other differences in phenotype were observed. If allele A produces a dose-responsive toxin and allele B produces no toxin, what kind of trait would this be?
A) Codominance
B) Incomplete dominance
C) Pleiotropy
D) Sex-linked
E) Epistatic
A) Codominance
B) Incomplete dominance
C) Pleiotropy
D) Sex-linked
E) Epistatic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following is a description of codominance?
A) When one allele makes a partially dominant product and another makes none
B) When two alleles are both non-functional
C) When a single gene has multiple alleles
D) When a single gene has more than one dominant allele
E) All of the options listed here are incorrect
A) When one allele makes a partially dominant product and another makes none
B) When two alleles are both non-functional
C) When a single gene has multiple alleles
D) When a single gene has more than one dominant allele
E) All of the options listed here are incorrect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



