Deck 15: Analysis of the Economy and the Stock Market
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/32
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Analysis of the Economy and the Stock Market
1
The recurring patterns of expansion, boom, contraction, and recession in the economy is known as:
A) monetary policy.
B) fiscal policy.
C) the business cycle.
D) demand fluctuations.
A) monetary policy.
B) fiscal policy.
C) the business cycle.
D) demand fluctuations.
the business cycle.
2
The beginning and ending of a business cycle is considered to occur during a:
A) cycle.
B) trough.
C) peak.
D) contraction.
A) cycle.
B) trough.
C) peak.
D) contraction.
trough.
3
On average, business cycle expansions in Canada last:
A) no more than two years.
B) two to three years.
C) three to five years.
D) five to seven years.
A) no more than two years.
B) two to three years.
C) three to five years.
D) five to seven years.
three to five years.
4
All of the following are lead economic indicators except:
A) real money supply (M1).
B) unemployment rate.
C) new orders for consumer durables.
D) average work week.
A) real money supply (M1).
B) unemployment rate.
C) new orders for consumer durables.
D) average work week.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following statements concerning the stock market and the economy is true?
A) Stock prices consistently turn before the economy.
B) Stock prices consistently turn after the economy.
C) Stock prices and the economy turn roughly at the same time.
D) Stock prices demonstrate little relationship with the economy.
A) Stock prices consistently turn before the economy.
B) Stock prices consistently turn after the economy.
C) Stock prices and the economy turn roughly at the same time.
D) Stock prices demonstrate little relationship with the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
One explanation for stock prices leading the economy involves:
A) a political change, such as a change in administration.
B) investors switching from domestic to international stocks.
C) an investor change in the required return.
D) insider trading based on nonpublic information.
A) a political change, such as a change in administration.
B) investors switching from domestic to international stocks.
C) an investor change in the required return.
D) insider trading based on nonpublic information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following is not a determinant for a change in interest rates?
A) a change in the rate of inflation
B) foreign developments and a change in the exchange rate
C) firms cutting their dividend payments
D) changes in the level of federal government deficits
A) a change in the rate of inflation
B) foreign developments and a change in the exchange rate
C) firms cutting their dividend payments
D) changes in the level of federal government deficits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In order to value the market with the P/E model, it is necessary to analyze:
A) earnings forecasts.
B) P/E ratios.
C) earnings forecasts and P/E ratios.
D) earnings forecasts, P/E ratios, and the required rate of returns.
A) earnings forecasts.
B) P/E ratios.
C) earnings forecasts and P/E ratios.
D) earnings forecasts, P/E ratios, and the required rate of returns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Structural unemployment includes all of the following except:
A) people in transition between jobs.
B) temporary hiring or layoffs due to business cycle influences.
C) regulation within the economy.
D) general economic health in the economy.
A) people in transition between jobs.
B) temporary hiring or layoffs due to business cycle influences.
C) regulation within the economy.
D) general economic health in the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Generally, when interest rates fall, stock prices:
A) rise.
B) fall.
C) remain unchanged.
D) rise or fall depending on the expected inflation premium.
A) rise.
B) fall.
C) remain unchanged.
D) rise or fall depending on the expected inflation premium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following statements regarding the uses of market indicators is false?
A) Historical records of market indicators are used to determine unsystematic risk.
B) Historical records of market averages are used for gauging market trends.
C) The historical returns on market indices are used in computing betas.
D) Market averages and indices are useful to investors in evaluating portfolio performance.
A) Historical records of market indicators are used to determine unsystematic risk.
B) Historical records of market averages are used for gauging market trends.
C) The historical returns on market indices are used in computing betas.
D) Market averages and indices are useful to investors in evaluating portfolio performance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Assume that the dividend payout ratio on the S&P/TSX Composite Index will be 40 per cent when the rate on long-term government bonds falls to 9 per cent. Investors being more risk averse demand an equity risk premium of eight per cent. If the growth rate of dividends is expected to be 10 per cent, what will be the price of the market index if the earnings expectation is $30?
A) $384.00
B) $213.44
C) $266.56
D) $171.43
A) $384.00
B) $213.44
C) $266.56
D) $171.43

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
According to the Keran model, the four active policy variables affecting the economy include all of the following except:
A) fiscal policy.
B) corporate earning.
C) the corporate tax rate.
D) monetary policy.
A) fiscal policy.
B) corporate earning.
C) the corporate tax rate.
D) monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In order to value the market with the constant-growth dividend discount model, it is necessary to analyze:
A) earnings forecasts and P/E ratios.
B) E1, D1, and k.
C) P/E ratios, g, and k.
D) D1, k, and g.
A) earnings forecasts and P/E ratios.
B) E1, D1, and k.
C) P/E ratios, g, and k.
D) D1, k, and g.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Assume that the P/E ratio of the S&P/TSX Composite Index is moving quickly above 22 times, and the associated dividend yield has fallen below 2 per cent. Investors attempting market timing should invest in:
A) defensive stocks to prepare for the pending market slide.
B) aggressive stocks to take advantage of the quickly rising market.
C) interest-sensitive stocks to take advantage of the increase in interest rates that will follow shortly.
D) high-P/E stocks to buy into stocks at the current market valuation.
A) defensive stocks to prepare for the pending market slide.
B) aggressive stocks to take advantage of the quickly rising market.
C) interest-sensitive stocks to take advantage of the increase in interest rates that will follow shortly.
D) high-P/E stocks to buy into stocks at the current market valuation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Under the Keran model, output of goods and services affects three policy variables. Which of the following is one of the variables affected?
A) corporate tax rates
B) total spending
C) fiscal policy
D) monetary policy
A) corporate tax rates
B) total spending
C) fiscal policy
D) monetary policy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The longest expansion on record occurred in the 1970s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The leading indicators were developed in the 1960s and may not be the most accurate in the current economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The market crash of October 1987 saw the Dow lose over 20 per cent of its value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Most analysts today agree that using money as an indicator of future economic activity is extremely inaccurate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Market indexes are designed to measure the performance of both entire stock market and various market segments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Many market participants believe that when the dividend yield on the S&P/TSX Composite Index declines below 5 percent, the market is in for a downward correction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The stock market is a coincident indicator of the economy because investors value current earnings over future earnings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If interest rates rise, the riskless rate of return declines at a faster rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The typical business cycle in the United States seems to lead the stock market's turning point by 6-12 months.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Most investors watch the Bank of Canada because their policies affect the money supply and interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If the economy is in the expansion phase, investors expect corporate earnings to rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
According to the Keran model, the potential output of goods and services in an economy affects three policy variables: fiscal policy, monetary policy and corporate tax rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Is it useful to do a trend analysis of P/E ratios of the S&P/TSX Composite Index over time and extrapolate it to project future expected P/Es?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Explain how dividend yield on the S&P/TSX Composite Index can be used to make market forecasts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
List several government organizations that publish information about the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Data for a fictitious industrial stock index are given below.
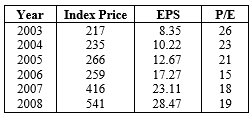
The average annual compound growth rate of EPS is approximately 28 per cent. The average P/E is 20.33. If the earnings growth rate continues at 28 per cent throughout 2009, and the P/E increases to 20, what will the closing index price be for 2009?

The average annual compound growth rate of EPS is approximately 28 per cent. The average P/E is 20.33. If the earnings growth rate continues at 28 per cent throughout 2009, and the P/E increases to 20, what will the closing index price be for 2009?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



