Deck 9: Capital Market Theory
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/61
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Capital Market Theory
1
The Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) prices:
A) all the risk of a security.
B) the diversifiable risk of a security.
C) the unsystematic risk of a security.
D) the systematic risk of a security.
A) all the risk of a security.
B) the diversifiable risk of a security.
C) the unsystematic risk of a security.
D) the systematic risk of a security.
the systematic risk of a security.
2
Which of the following is not one of the assumptions of the CAPM?
A) All investors have the same one-period time horizon.
B) There are no personal income taxes.
C) There is no interest rate charged on borrowing.
D) There are no transaction costs.
A) All investors have the same one-period time horizon.
B) There are no personal income taxes.
C) There is no interest rate charged on borrowing.
D) There are no transaction costs.
There is no interest rate charged on borrowing.
3
The market portfolio by definition has a beta of:
A) 0.
B) between 0 and 1.
C) equal to 1.
D) greater than 1.
A) 0.
B) between 0 and 1.
C) equal to 1.
D) greater than 1.
equal to 1.
4
Which of the following regarding investors and the CAPM is true?
A) Investors recognize that all the assumptions of the CAPM are unrealistic.
B) Investors recognize that all of the CAPM assumptions are not unrealistic.
C) Investors are not aware of the assumptions of the CAPM model.
D) Investors recognize the CAPM is useless for individual investors.
A) Investors recognize that all the assumptions of the CAPM are unrealistic.
B) Investors recognize that all of the CAPM assumptions are not unrealistic.
C) Investors are not aware of the assumptions of the CAPM model.
D) Investors recognize the CAPM is useless for individual investors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Market equilibrium exists:
A) when assets are underpriced allowing for speculation.
B) when assets are overpriced allowing for short selling.
C) when assets are priced correctly to allow the markets to clear.
D) when the parties involved in trading have heterogeneous expectations which provide the incentive to trade.
A) when assets are underpriced allowing for speculation.
B) when assets are overpriced allowing for short selling.
C) when assets are priced correctly to allow the markets to clear.
D) when the parties involved in trading have heterogeneous expectations which provide the incentive to trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
When markets are in equilibrium, the CML will be upward sloping:
A) because it shows the optimum combination of risky securities.
B) because the price of risk must always be positive.
C) because it contains all securities weighted by their market values.
D) because the CML indicates the required return for each portfolio risk level.
A) because it shows the optimum combination of risky securities.
B) because the price of risk must always be positive.
C) because it contains all securities weighted by their market values.
D) because the CML indicates the required return for each portfolio risk level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following statements about the difference between the SML and the CML is false?
A) The intercept of both the CML and the SML is RF.
B) The CML prices efficient portfolios, while the SML prices both portfolios and individual securities.
C) The CML and the SML are both assumed to be upward sloping.
D) The CML and the SML measure everything the same except they were derived by different theorists.
A) The intercept of both the CML and the SML is RF.
B) The CML prices efficient portfolios, while the SML prices both portfolios and individual securities.
C) The CML and the SML are both assumed to be upward sloping.
D) The CML and the SML measure everything the same except they were derived by different theorists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Select the true statement regarding the results of CAPM tests.
A) The SML appears not to be linear.
B) The intercept term is a generally found to be higher than the risk-free rate.
C) The slope of the CAPM is steeper than posited by the theory.
D) Investors are rewarded for assuming systematic and unsystematic risk.
A) The SML appears not to be linear.
B) The intercept term is a generally found to be higher than the risk-free rate.
C) The slope of the CAPM is steeper than posited by the theory.
D) Investors are rewarded for assuming systematic and unsystematic risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following statements best summarizes the conclusions reached regarding the stability of betas?
A) Betas for individual securities and large portfolios are unstable.
B) Betas for individual securities are unstable.
C) Betas for individual securities and large portfolios are stable.
D) Betas for large portfolios are unstable.
A) Betas for individual securities and large portfolios are unstable.
B) Betas for individual securities are unstable.
C) Betas for individual securities and large portfolios are stable.
D) Betas for large portfolios are unstable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The slope of the CML is given by:
A) [(RF) - RM]/ RF
B) [(RM) - RF]/ M
C) [(RM) - RF]/ FR
D) [(RF) - RM]/ M
A) [(RF) - RM]/ RF
B) [(RM) - RF]/ M
C) [(RM) - RF]/ FR
D) [(RF) - RM]/ M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Select the correct statement regarding the market portfolio. It:
A) is readily and precisely observable.
B) should include all risky assets.
C) is the lowest point of tangency between the risk-free rate and the efficient frontier.
D) should be composed of stocks or bonds.
A) is readily and precisely observable.
B) should include all risky assets.
C) is the lowest point of tangency between the risk-free rate and the efficient frontier.
D) should be composed of stocks or bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The systematic risk level of a security:
A) does not take into account the variance of the overall market portfolio.
B) is best approximated by the slope of the SML.
C) is measured by the standard deviation of the market and the standard deviation of any individual security.
D) is measured by the security's beta.
A) does not take into account the variance of the overall market portfolio.
B) is best approximated by the slope of the SML.
C) is measured by the standard deviation of the market and the standard deviation of any individual security.
D) is measured by the security's beta.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Questions are based on the following information:
The returns, variances, and covariances of annual returns for XYZ Corp. and AST Inc. have been calculated for the period 1999-2008 (n = 10). The values are:
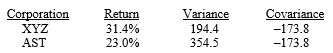
-If the mean return and variance for the market (S&P/TSX Composite Index) for the period were 18.2 percent and 161.1 respectively, and the covariance between XYZ and S&P/TSX Composite Index was 22.0, the beta for XYZ would have been:
A) less than zero, negative.
B) between zero and .50.
C) between .50 and 1.00.
D) greater than 1.00.
The returns, variances, and covariances of annual returns for XYZ Corp. and AST Inc. have been calculated for the period 1999-2008 (n = 10). The values are:
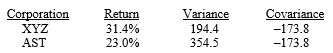
-If the mean return and variance for the market (S&P/TSX Composite Index) for the period were 18.2 percent and 161.1 respectively, and the covariance between XYZ and S&P/TSX Composite Index was 22.0, the beta for XYZ would have been:
A) less than zero, negative.
B) between zero and .50.
C) between .50 and 1.00.
D) greater than 1.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Questions are based on the following information:
The returns, variances, and covariances of annual returns for XYZ Corp. and AST Inc. have been calculated for the period 1999-2008 (n = 10). The values are:
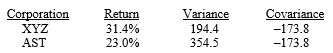
-If the mean return and variance for the market (S&P/TSX Composite Index) for the period were 18.2 percent and 161.1 respectively, and the covariance between AST and S&P/TSX Composite Index was 159.4, the beta for AST would have been:
A) less than zero, negative.
B) between zero and .50.
C) between .50 and 1.00.
D) greater than 1.00.
The returns, variances, and covariances of annual returns for XYZ Corp. and AST Inc. have been calculated for the period 1999-2008 (n = 10). The values are:
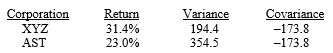
-If the mean return and variance for the market (S&P/TSX Composite Index) for the period were 18.2 percent and 161.1 respectively, and the covariance between AST and S&P/TSX Composite Index was 159.4, the beta for AST would have been:
A) less than zero, negative.
B) between zero and .50.
C) between .50 and 1.00.
D) greater than 1.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Select the statement which correctly describes the calculation of the required rate of return of a portfolio.
A) Given efficient portfolio construction, the return on the portfolio can be greater than the highest yielding asset included in the portfolio.
B) It decreases in direct proportion to the market as the expected return on the market increases.
C) It increases if the risk-free rate increases; everything else remaining constant.
D) It is independent of changes in both the market return and the risk-free rate.
A) Given efficient portfolio construction, the return on the portfolio can be greater than the highest yielding asset included in the portfolio.
B) It decreases in direct proportion to the market as the expected return on the market increases.
C) It increases if the risk-free rate increases; everything else remaining constant.
D) It is independent of changes in both the market return and the risk-free rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In the Capital Asset Pricing Model, the return on any security i is equal to:
A) E(Ri) = RF + [E(RM) - RF] i
B) E(Ri) = RM + [E(RF) - RM] i
C) E(Ri) = RF + [E(RM) - RF] M
D) E(Ri) = RF + [E(RM) - RF] i
A) E(Ri) = RF + [E(RM) - RF] i
B) E(Ri) = RM + [E(RF) - RM] i
C) E(Ri) = RF + [E(RM) - RF] M
D) E(Ri) = RF + [E(RM) - RF] i

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Choose the statement below that is not correct.
A) With the addition of risk-free borrowing and lending, the Markowitz efficient frontier is dominated by a new efficient frontier.
B) With the introduction of risk-free borrowing and lending, the efficient frontier will become a straight line.
C) With the introduction of risk-free borrowing and lending, the efficient frontier will be an arc that is higher than the Markowitz arc which had been the efficient frontier.
D) In equilibrium, all risky assets must still be in the market portfolio.
A) With the addition of risk-free borrowing and lending, the Markowitz efficient frontier is dominated by a new efficient frontier.
B) With the introduction of risk-free borrowing and lending, the efficient frontier will become a straight line.
C) With the introduction of risk-free borrowing and lending, the efficient frontier will be an arc that is higher than the Markowitz arc which had been the efficient frontier.
D) In equilibrium, all risky assets must still be in the market portfolio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In the equation for the Security Market Line (SML), the slope is represented by:
A) RF.
B) i.
C) [E(RM) - RF]
D) i,M i/ M
A) RF.
B) i.
C) [E(RM) - RF]
D) i,M i/ M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which statement is incorrect?
A) The RF is the intercept for the SML.
B) The SML prices the relationship between expected return and risk for individual securities only and cannot price efficient portfolios.
C) In equilibrium the correctly priced assets will lie on the SML.
D) The beta for a stock is the independent variable for the SML and not its slope.
A) The RF is the intercept for the SML.
B) The SML prices the relationship between expected return and risk for individual securities only and cannot price efficient portfolios.
C) In equilibrium the correctly priced assets will lie on the SML.
D) The beta for a stock is the independent variable for the SML and not its slope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The required rate of return is:
A) a minimum realized return.
B) a guaranteed return.
C) a minimum expected return.
D) the maximum return likely to be achieved.
A) a minimum realized return.
B) a guaranteed return.
C) a minimum expected return.
D) the maximum return likely to be achieved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The anticipated return on the market for next period is 15 percent while the prevailing risk-free rate is 4 percent. Alpha Company has a beta equal to one-half of the market beta. The market risk premium is:
A) -11 percent.
B) -5.5 percent.
C) +5.5percent.
D) +11 percent.
A) -11 percent.
B) -5.5 percent.
C) +5.5percent.
D) +11 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The anticipated market return is 15 percent. The risk-free rate is 4 percent, and BC Co. has a beta equal to one-half of the market beta. Its required rate of return is:
A) 15 percent.
B) 11 percent.
C) 9.5 percent.
D) 5.5 percent.
A) 15 percent.
B) 11 percent.
C) 9.5 percent.
D) 5.5 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Most mining companies would have calculated betas that are:
A) equal to zero.
B) between zero and 1.
C) equal to 1.
D) greater than 1.
A) equal to zero.
B) between zero and 1.
C) equal to 1.
D) greater than 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The anticipated market return is 15 percent. The risk-free rate is 4 percent, and AB Co. has a beta equal to one-half of the market beta. Its risk premium is:
A) 15 percent.
B) 11 percent.
C) 9.5 percent.
D) 5.5 percent.
A) 15 percent.
B) 11 percent.
C) 9.5 percent.
D) 5.5 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If markets are efficient and in equilibrium:
A) all assets would lie on the SML.
B) any assets that plot below the SML would be considered undervalued.
C) any assets that lie above the SML would be considered overvalued.
D) no assets would lie on the SML.
A) all assets would lie on the SML.
B) any assets that plot below the SML would be considered undervalued.
C) any assets that lie above the SML would be considered overvalued.
D) no assets would lie on the SML.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Most Canadian bank stocks would have calculated betas that are:
A) equal to zero.
B) between zero and 1.
C) equal to 1.
D) greater than 1.
A) equal to zero.
B) between zero and 1.
C) equal to 1.
D) greater than 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Are betas useful in analyzing required rates of return?
A) Yes, because individual security betas are relatively stable over time.
B) No, because individual security betas are unstable over time.
C) Yes, because portfolio betas are relatively stable over time.
D) No, because portfolio betas are unstable over time.
A) Yes, because individual security betas are relatively stable over time.
B) No, because individual security betas are unstable over time.
C) Yes, because portfolio betas are relatively stable over time.
D) No, because portfolio betas are unstable over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Risk factors in the APT must possess all except which of the following characteristics?
A) Factors must be readily observable in risk/return space.
B) Each factor must have a pervasive influence on stock returns.
C) The factors must influence expected return.
D) Factors must be unpredictable.
A) Factors must be readily observable in risk/return space.
B) Each factor must have a pervasive influence on stock returns.
C) The factors must influence expected return.
D) Factors must be unpredictable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following would not be used as a factor in the APT?
A) The risk-free rate.
B) Unanticipated changes in industrial production.
C) Unanticipated changes in inflation.
D) Unanticipated changes in the default risk premium.
A) The risk-free rate.
B) Unanticipated changes in industrial production.
C) Unanticipated changes in inflation.
D) Unanticipated changes in the default risk premium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The arbitrage pricing theory (APT):
A) is not concerned with a stock's sensitivity to basic economic factors.
B) takes into account more factors than the CAPM and is a more general model.
C) is more concerned about market equilibrium than the CAPM.
D) is easier to use in the investment world because its factors are more readily observable than those of the CAPM.
A) is not concerned with a stock's sensitivity to basic economic factors.
B) takes into account more factors than the CAPM and is a more general model.
C) is more concerned about market equilibrium than the CAPM.
D) is easier to use in the investment world because its factors are more readily observable than those of the CAPM.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The most important role of the capital asset pricing model (CAPM) is to determine:
A) the beta for an individual security or portfolio.
B) the total risk of a security or portfolio.
C) the systematic risk of a security or a portfolio.
D) the required return on a security or portfolio.
A) the beta for an individual security or portfolio.
B) the total risk of a security or portfolio.
C) the systematic risk of a security or a portfolio.
D) the required return on a security or portfolio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following statements regarding beta is true?
A) Beta is an absolute measure of risk.
B) Beta is a relative measure of risk.
C) Beta is a abstract measure of risk.
D) Beta is a geometric measure of risk.
A) Beta is an absolute measure of risk.
B) Beta is a relative measure of risk.
C) Beta is a abstract measure of risk.
D) Beta is a geometric measure of risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Market risk in the CAPM is best measured by the:
A) alpha.
B) beta.
C) standard deviation.
D) coefficient of variation.
A) alpha.
B) beta.
C) standard deviation.
D) coefficient of variation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Betas for aggressive portfolios are greater than one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The CML is assumed to be upward sloping ex ante.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The slope of the CML indicates the total risk of an efficient portfolio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A security that plots above the SML would be a good security to sell short because it is overvalued.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The arbitrage pricing theory is more general than the CAPM.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In equilibrium, all risky assets must have betas equal to 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
All possible portfolios lie on the CML.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Beta is a measure of systematic risk and relates one security's return to the market's return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Most analysts use the S&P/TSX Composite Index as a proxy for the market portfolio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Based on the evidence, the arbitrage pricing model outperforms the CAPM.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Like the CAPM, the APT assumes borrowing and lending can be done at the risk-free rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Both the CAPM and the APT assume that investors have heterogeneous beliefs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Risk is defined relative to a stock's sensitivity to market factors alone under the arbitrage pricing theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The market portfolio has a beta of one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The Security Market Line is the graphical depiction of the Capital Asset Pricing Model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What is the formula for the risk premium for an individual security in the CAPM? What does it represent?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Some securities are considered to be aggressive as they tend to increase in value in a bull market and lose value more quickly in a bear market. What could one conclude about the betas of aggressive securities? What are some examples of the betas of aggressive companies?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
At a given point the SML requires that a security with a beta of 1.10 should have a return of 18 percent. Analysts calculate that a particular stock with an observed beta of 1.10 actually produces a return of 20 percent. Outline the scenario that will restore the security's return to equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A straight line has two mathematical necessities. What are these two necessities and how does the mathematical expression of the CAPM/SML apply to investments?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Suppose the SML has a risk-free rate of 5 percent and an expected market return of 15 percent. Now suppose that the SML shifts, changing slope, so that RF is still 5 percent but E(RM) is now 16 percent. What does this shift suggest about investors' risk aversion? If the slope were to change downward, what would that suggest?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What does a security's beta measure in the single-index model? How is the portfolio's beta related to the individual securities' betas?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In 1992, Fama and French published a study of U.S. stock returns. What three factors did Fama and French use to account for stock returns? What was the major conclusion of their study?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
List two theoretical difficulties in testing the validity of the CAPM. Briefly explain each of these difficulties.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The expected return for the market is 12 percent, with a standard deviation of 20 percent. The expected risk-free rate is 8 percent. Information is available for three mutual funds, all assumed to be efficient, as follows:

(a) Based on the CMI, calculate the market price of risk.
(b) Calculate the expected return on each of these portfolios.

(a) Based on the CMI, calculate the market price of risk.
(b) Calculate the expected return on each of these portfolios.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Given an expected return for the market of 12 percent, with a standard deviation of 20 percent, and a risk-free rate of 8 percent, consider the following data:
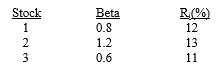
(a) Calculate the required return for each stock using the SML.
(b) Assume that an analyst, using fundamental analysis, develops the estimates labeled Ri for these stocks. Which stock would be recommended for purchase?

(a) Calculate the required return for each stock using the SML.
(b) Assume that an analyst, using fundamental analysis, develops the estimates labeled Ri for these stocks. Which stock would be recommended for purchase?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Given the following information:

(a) Calculate the beta for stock A and stock B.
(b) Calculate the required return for each stock.

(a) Calculate the beta for stock A and stock B.
(b) Calculate the required return for each stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
An analyst estimates that the expected returns on the market (S&P/TSX Composite Index) is 12 percent, with a standard deviation of 15 percent, and the risk-free rate of return (Treasury bill rate) is at 5 percent. Using the following information about the variance of returns of some efficient portfolios, calculate their expected returns using the Capital Market Line approach.
Efficient Portfolio Variance

Efficient Portfolio Variance


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Given the following information:
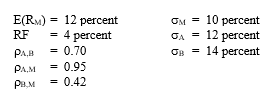
(a) Calculate the betas for A and B.
(b) Determine the equation for the security market line.
(c) Calculate the required rates of return for the two stocks.
(d) Assume that an investor puts 70 percent in the market portfolio and 40 percent in the risk-free asset. What would the expected return and standard deviation of the portfolio be?
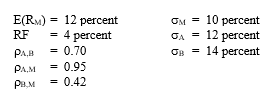
(a) Calculate the betas for A and B.
(b) Determine the equation for the security market line.
(c) Calculate the required rates of return for the two stocks.
(d) Assume that an investor puts 70 percent in the market portfolio and 40 percent in the risk-free asset. What would the expected return and standard deviation of the portfolio be?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



