Deck 2: Investment Alternatives
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/53
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Investment Alternatives
1
Which of the following is not a usual characteristic of money market securities?
A) They are issued by large credit worthy corporations in large denominations.
B) They are very liquid instrument that trade without a significant liquidity premium.
C) They are of an intermediate to long term maturity.
D) They include T-bills, commercial paper, and bankers' acceptances.
A) They are issued by large credit worthy corporations in large denominations.
B) They are very liquid instrument that trade without a significant liquidity premium.
C) They are of an intermediate to long term maturity.
D) They include T-bills, commercial paper, and bankers' acceptances.
They are of an intermediate to long term maturity.
2
T-bills are sold:
A) on an auction basis every two weeks by the Bank of Canada.
B) in denominations ranging from $1,000 to $1,000,000.
C) for only 91 days maturity.
D) both a. and b.
A) on an auction basis every two weeks by the Bank of Canada.
B) in denominations ranging from $1,000 to $1,000,000.
C) for only 91 days maturity.
D) both a. and b.
both a. and b.
3
Which of the following is true concerning corporate bonds?
A) Mortgage bonds are secured obligations whereas debentures are unsecured.
B) Bonds have a subordinated debenture which functions as a contract between the bondholder and the issuing company.
C) Bonds have superior voting rights to common shareholders.
D) One can buy a bond at any time and receive an immediate interest cheque.
A) Mortgage bonds are secured obligations whereas debentures are unsecured.
B) Bonds have a subordinated debenture which functions as a contract between the bondholder and the issuing company.
C) Bonds have superior voting rights to common shareholders.
D) One can buy a bond at any time and receive an immediate interest cheque.
Mortgage bonds are secured obligations whereas debentures are unsecured.
4
Bonds with a call provision can be:
A) exchanged for common shares at the option of the bondholder.
B) redeemed prior to maturity at option of the issuing company.
C) exchanged for common shares at the option of the issuing company.
D) redeemed prior to maturity at the option of the bondholder.
A) exchanged for common shares at the option of the bondholder.
B) redeemed prior to maturity at option of the issuing company.
C) exchanged for common shares at the option of the issuing company.
D) redeemed prior to maturity at the option of the bondholder.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following statements regarding dividend dates is true?
A) The ex-dividend date is prior to the date of record.
B) The date of record is prior to the declaration date.
C) The ex-dividend date is prior to the declaration date.
D) The date of record is prior to the ex-dividend date.
A) The ex-dividend date is prior to the date of record.
B) The date of record is prior to the declaration date.
C) The ex-dividend date is prior to the declaration date.
D) The date of record is prior to the ex-dividend date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A major difference between a warrant and a call option is that:
A) warrants have less value.
B) warrants allow investors to buy bonds; calls allow investors to buy stock.
C) warrants generally have a longer term.
D) options have a greater leverage effect.
A) warrants have less value.
B) warrants allow investors to buy bonds; calls allow investors to buy stock.
C) warrants generally have a longer term.
D) options have a greater leverage effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Dividends on common stock are typically declared and paid:
A) monthly.
B) quarterly.
C) semi-annually.
D) yearly.
A) monthly.
B) quarterly.
C) semi-annually.
D) yearly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If an investor states that Commercial Bank is undervalued at 15 times, he is referring to the:
A) EPS.
B) dividend yield.
C) market to book ratio.
D) earning multiple.
A) EPS.
B) dividend yield.
C) market to book ratio.
D) earning multiple.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Retractable bonds:
A) give the bondholder the right to sell the bonds back to the issuer prior to maturity.
B) give the issuer the right to buy the bonds back from the issuer prior to maturity.
C) give the bondholder the right to buy additional bonds from the issuer.
D) give the issuer the right to sell additional bonds to the bondholder..
A) give the bondholder the right to sell the bonds back to the issuer prior to maturity.
B) give the issuer the right to buy the bonds back from the issuer prior to maturity.
C) give the bondholder the right to buy additional bonds from the issuer.
D) give the issuer the right to sell additional bonds to the bondholder..

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following statements regarding money market instruments is not true?
A) They tend to be highly marketable.
B) They tend to require a large dollar investment.
C) They tend to have a high probability of default.
D) Their rates tend to move together.
A) They tend to be highly marketable.
B) They tend to require a large dollar investment.
C) They tend to have a high probability of default.
D) Their rates tend to move together.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is a capital market instrument?
A) Repurchase agreements
B) Negotiable CDs
C) Preferred stock
D) Commercial paper
A) Repurchase agreements
B) Negotiable CDs
C) Preferred stock
D) Commercial paper

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following money market instruments is normally used in international trade?
A) Negotiable CDs
B) Commercial paper
C) Repurchase agreements
D) Bankers' acceptances
A) Negotiable CDs
B) Commercial paper
C) Repurchase agreements
D) Bankers' acceptances

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Coupon interest on corporate bonds is typically paid:
A) monthly.
B) quarterly.
C) semi-annually.
D) annually.
A) monthly.
B) quarterly.
C) semi-annually.
D) annually.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The price a bond buyer must pay that includes accrued interest is known as the:
A) call price.
B) coupon rate.
C) premium price.
D) invoice price.
A) call price.
B) coupon rate.
C) premium price.
D) invoice price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Derivative securities include all of the following except:
A) options.
B) forwards.
C) futures.
D) corporate bonds.
A) options.
B) forwards.
C) futures.
D) corporate bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
An unsecured bond that has a claim that is after all other debt holders is known as a(an):
A) debenture.
B) indenture.
C) mortgage bond.
D) subordinated debenture
A) debenture.
B) indenture.
C) mortgage bond.
D) subordinated debenture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is not a reason investors are attracted to asset-backed securities?
A) Investors are often protected by a bond insurer.
B) These securities often have investment-grade credit ratings.
C) These securities have relatively high yields.
D) These securities are generally long-term, stable investments.
A) Investors are often protected by a bond insurer.
B) These securities often have investment-grade credit ratings.
C) These securities have relatively high yields.
D) These securities are generally long-term, stable investments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A three-for-one stock split results in which of the following, compared to before the split?
A) Three times as many shares; the same total book value of equity; one-third the market price per share.
B) Three times as many shares; three times the total book value of equity; three times the market price per share.
C) One-third as many shares; the same total book value of equity; one-third the market price per share.
D) One-third as many shares; one-third the total book value of equity; one-third the market price per share.
A) Three times as many shares; the same total book value of equity; one-third the market price per share.
B) Three times as many shares; three times the total book value of equity; three times the market price per share.
C) One-third as many shares; the same total book value of equity; one-third the market price per share.
D) One-third as many shares; one-third the total book value of equity; one-third the market price per share.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The CDIC provides deposit insurance for the following institutions:
1) Chartered banks
2) Credit Unions and Caisses Populaires
3) Trust companies
4) Insurance companies
A) 1 only
B) 1 and 2
C) 1 and 3
D) 1 and 4
1) Chartered banks
2) Credit Unions and Caisses Populaires
3) Trust companies
4) Insurance companies
A) 1 only
B) 1 and 2
C) 1 and 3
D) 1 and 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is true for bond rating companies?
A) bond ratings are issued exclusively by Moody's
B) bond ratings are of interest only at the time the bond is issued
C) bond ratings can be changed by the rating agency as the issuer's circumstances change
D) the higher the bond rating the greater the interest paid.
A) bond ratings are issued exclusively by Moody's
B) bond ratings are of interest only at the time the bond is issued
C) bond ratings can be changed by the rating agency as the issuer's circumstances change
D) the higher the bond rating the greater the interest paid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Indirect investing means that the investor buys shares on the stock exchange as opposed to directly from the company.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
An example of direct investing would be buying shares in a mutual fund.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Nonmarketable investments would include savings accounts at banks and Canada Savings Bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The purchase of any marketable security would constitute a capital market transaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The Canadian government does not issue non-marketable securities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Money market instruments are generally highly liquid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The money market security most often used as a benchmark for the risk-free rate is the average rate paid on bankers' acceptance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The rate spreads between the different money market securities of the same term tend to be quite small.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The non-traded debt of the Canadian government are Canada Savings Bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Commercial paper is sold in both the capital and money markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Term bonds have a single maturity while serial bonds have several maturity dates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The return on a stripped bond is derived from the difference between the price paid and the face value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The smaller the discount on a zero-coupon bond, the higher the effective return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If a bond has a coupon rate less than the prevailing market yield, it is selling at a discount.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Companies would be more likely to exercise the call features on bonds when interest rates rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The call provision on callable bonds is usually not exercisable immediately but is deferred for a period of time as specified in the bond indenture.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In the case of a corporate bankruptcy, both bondholders and debenture holders are paid before any distributions are paid to preferred or common stockholders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Bond ratings are primarily used to assess price risk for the bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A major Canadian bond rating service is Dominion Bond Rating Service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The earnings retention rate is calculated as dividends paid/net income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The par value of preferred stock sets the maximum value that these stockholders would receive in case of bankruptcy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Compare the cash flows that an investor expects from any pure discount instruments, coupon bonds, zero-coupon bonds, preferred stock and common stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
How are the earnings retention ratio and the dividend payout ratio determined?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Why is the ex-dividend date before the holder-of-record date?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
How is the total book value of equity affected by stock splits? Stock dividends? Are the book values of common stock, capital in excess of par, or retained earnings affected by either?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Why might one say that a stock trading at 10 times earnings could potentially provide a less expensive investment opportunity than a stock with a P/E ratio of 20?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What are one direct and one indirect method for individuals to invest in foreign stocks?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Rank (lowest to highest) the following securities in terms of the risk-expected return trade-off from the investors' viewpoint: common stock, corporate bonds, Government of Canada bonds, options, preferred stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Based on the following partial balance sheet, calculate the book value per share of common equity.





Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
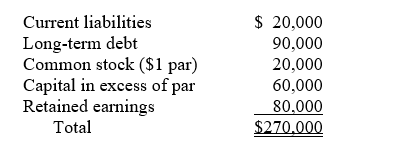
Based on the following partial balance sheet, calculate the price for which the stock originally sold to the public. Assume there has been only one public offering.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The par value of Blaze, Inc., common stock is $1.00; the earnings per share is $2; the market price is $25; and the dividend per share is $1. Calculate the P/E ratio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Referring to the data in question 3 above, what is Blaze's dividend yield?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Referring to the data in question 3 above, what is Blaze's payout ratio?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



