Deck 8: Money, Banking Money Supply
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/113
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Money, Banking Money Supply
1
To say money is a store of value, it mans:
A) the value of money is not affected by inflation.
B) money facilitates purchases and sales.
C) money has purchasing power, but it is not the only asset with store of value
D) all the above.
A) the value of money is not affected by inflation.
B) money facilitates purchases and sales.
C) money has purchasing power, but it is not the only asset with store of value
D) all the above.
money has purchasing power, but it is not the only asset with store of value
2
Under the barter system, one person must want what the other has and vice versa. This is called:
A) the terms of trade.
B) the medium of exchange.
C) double coincidence of wants.
D) double-counting.
A) the terms of trade.
B) the medium of exchange.
C) double coincidence of wants.
D) double-counting.
double coincidence of wants.
3
Without money being used in society:
A) production would cease.
B) the standard of living would rise.
C) specialization would be impossible.
D) coordination of economic activity would be much more difficult.
A) production would cease.
B) the standard of living would rise.
C) specialization would be impossible.
D) coordination of economic activity would be much more difficult.
coordination of economic activity would be much more difficult.
4
Which of the following statements does not describe the barter system?
A) In a barter system, each participant must have something the other participant wants.
B) Barter takes place with someone close.
C) Barter economy does not have a price in terms of exchange value of goods and services.
D) Anonymity is difficult when barter is employed.
A) In a barter system, each participant must have something the other participant wants.
B) Barter takes place with someone close.
C) Barter economy does not have a price in terms of exchange value of goods and services.
D) Anonymity is difficult when barter is employed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following statements best describes a barter system?
A) Money and goods are exchanged for each other.
B) Cigarettes are used as money.
C) Goods are traded directly for other goods.
D) Different commodities are used as money.
A) Money and goods are exchanged for each other.
B) Cigarettes are used as money.
C) Goods are traded directly for other goods.
D) Different commodities are used as money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Money is valuable to society as a whole:
A) in proportion to the amount of gold backing the dollars in circulation.
B) in proportion to the amount in circulation.
C) in a manner independent of the amount in circulation.
D) only if it is in unlimited quantities.
A) in proportion to the amount of gold backing the dollars in circulation.
B) in proportion to the amount in circulation.
C) in a manner independent of the amount in circulation.
D) only if it is in unlimited quantities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Suppose that the value of a nation's money is less in alternative uses than its value in exchange. We can conclude that the nation's money is:
A) a token money.
B) a near money.
C) currency.
D) a commodity money.
A) a token money.
B) a near money.
C) currency.
D) a commodity money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Suppose that for some reason, the price of copper rose to such a level that the copper contained in a penny was worth more than the coin, this would cause:
A) pennies to be hoarded and taken out of circulation.
B) the penny to no longer be offered for a penny's worth of goods and services.
C) the penny to no longer serve as a token money.
D) all of the above to occur.
A) pennies to be hoarded and taken out of circulation.
B) the penny to no longer be offered for a penny's worth of goods and services.
C) the penny to no longer serve as a token money.
D) all of the above to occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Goldsmiths could loan a part of the gold deposited in their vaults because:
A) in those days people were less sophisticated in their financial transactions.
B) not all depositors would claim their gold simultaneously.
C) gold was much in demand.
D) cheques had not yet been invented.
A) in those days people were less sophisticated in their financial transactions.
B) not all depositors would claim their gold simultaneously.
C) gold was much in demand.
D) cheques had not yet been invented.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Suppose that you win $5,000 in a poker game and stuff the currency in your mattress. The money is being used:
A) as a unit of account.
B) as a store of value.
C) as a medium of exchange.
D) as a standard of value.
A) as a unit of account.
B) as a store of value.
C) as a medium of exchange.
D) as a standard of value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
One of the most important functions of early banks was to:
A) issue new currency and coins.
B) create money by making loans.
C) cashing cheques.
D) provide a place for the safe keeping of depositor's assets.
A) issue new currency and coins.
B) create money by making loans.
C) cashing cheques.
D) provide a place for the safe keeping of depositor's assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
When the value of money is less in alternative uses than its value in exchange, it is called:
A) token money.
B) full-valued money.
C) IOU money.
D) currency.
A) token money.
B) full-valued money.
C) IOU money.
D) currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A $20 bill in Canada is an example of:
A) fiat money.
B) token money.
C) a medium of exchange.
D) all of the above.
A) fiat money.
B) token money.
C) a medium of exchange.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If a commodity has qualities of a medium of exchange, unit of account and store of value it can be used as:
A) money.
B) an IOU.
C) a cheque.
D) a credit card.
A) money.
B) an IOU.
C) a cheque.
D) a credit card.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Gold coin was an example of commodity money.
B) "Debasing" of the coinage due to clipping and sweating reduced the acceptability of precious metal coinage as money.
C) Token money is a convertible claim on a commodity money.
D) Coin and paper notes, which are in currently in circulation in Canada, are also known as token money.
A) Gold coin was an example of commodity money.
B) "Debasing" of the coinage due to clipping and sweating reduced the acceptability of precious metal coinage as money.
C) Token money is a convertible claim on a commodity money.
D) Coin and paper notes, which are in currently in circulation in Canada, are also known as token money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If trading requires a double coincidence of wants, we can assume that we are talking about:
A) a mercantile economy.
B) a barter economy.
C) a global economy.
D) an information economy.
A) a mercantile economy.
B) a barter economy.
C) a global economy.
D) an information economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The stock of the medium of exchange in circulation is known as:
A) token money.
B) the gold standard.
C) the money supply.
D) the fiduciary issue.
A) token money.
B) the gold standard.
C) the money supply.
D) the fiduciary issue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A near money provides all of the following functions except serving:
A) as a hedge against inflation.
B) as a unit of account.
C) as a medium of exchange.
D) as a store of value.
A) as a hedge against inflation.
B) as a unit of account.
C) as a medium of exchange.
D) as a store of value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When an asset is a near money, it performs all of the following functions except serving:
A) as a medium of exchange.
B) as a unit of account.
C) as a store of value.
D) as a hedge against inflation.
A) as a medium of exchange.
B) as a unit of account.
C) as a store of value.
D) as a hedge against inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The role of a bank is to:
A) accept deposits and make loans.
B) settle disputes among investors.
C) finance the government's deficit.
D) all the above.
A) accept deposits and make loans.
B) settle disputes among investors.
C) finance the government's deficit.
D) all the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A financial intermediary is:
A) a business that brings borrowers and lenders together.
B) a person who mediates disputes betweens financial institutions.
C) a government agency that regulates financial institutions.
D) an insurance company that covers the risks of banking operations.
A) a business that brings borrowers and lenders together.
B) a person who mediates disputes betweens financial institutions.
C) a government agency that regulates financial institutions.
D) an insurance company that covers the risks of banking operations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When we say that the Canadian banking system is fractional reserve system, it mans:
A) chartered banks loan out only a small fraction of their deposits.
B) chartered banks have to keep a large percentage of their deposit to meet everyday cash withdrawals.
C) chartered banks loan out the entire deposits and do not have to meet their everyday cash withdrawal.
D) chartered banks keep cash equal to just a small percentage of their deposits to meet everyday withdrawals.
A) chartered banks loan out only a small fraction of their deposits.
B) chartered banks have to keep a large percentage of their deposit to meet everyday cash withdrawals.
C) chartered banks loan out the entire deposits and do not have to meet their everyday cash withdrawal.
D) chartered banks keep cash equal to just a small percentage of their deposits to meet everyday withdrawals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Bank reserves are:
A) currency and customer chequing deposits in the banks.
B) currency, customer chequing and savings deposits in the banks.
C) cash balances held by the banks to meet withdrawals by customers or payments to customers.
D) financial assets held by the banks obtained from savers and lent to borrowers.
A) currency and customer chequing deposits in the banks.
B) currency, customer chequing and savings deposits in the banks.
C) cash balances held by the banks to meet withdrawals by customers or payments to customers.
D) financial assets held by the banks obtained from savers and lent to borrowers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Commercial banks in Canada are:
A) government agencies.
B) financial intermediaries.
C) credit unions.
D) savings-and-loan associations.
A) government agencies.
B) financial intermediaries.
C) credit unions.
D) savings-and-loan associations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In a multi-asset world, the most liquid asset is:
A) gold.
B) money.
C) mutual funds.
D) stock market shares.
A) gold.
B) money.
C) mutual funds.
D) stock market shares.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The Bank of Canada provides ____________________ to commercial banks in Canada.
A) deposit balances for inter-bank cheques-clearing settlements
B) printed cheques for bank customers
C) security guards for the vault
D) deposit-insurances
A) deposit balances for inter-bank cheques-clearing settlements
B) printed cheques for bank customers
C) security guards for the vault
D) deposit-insurances

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The most distinctive feature of a commercial bank is that:
A) it makes loans.
B) it provides a passbook to depositors.
C) it acknowledges the funds it receives by issuing a claim against itself.
D) its debt circulates as money.
A) it makes loans.
B) it provides a passbook to depositors.
C) it acknowledges the funds it receives by issuing a claim against itself.
D) its debt circulates as money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
When an asset is described as being liquid, it means that:
A) it is relatively easy to convert the financial asset into precious metals such as gold or silver.
B) it is relatively easy to use it as an hedge against inflation.
C) it serves as a perfect store of value.
D) it is easily converted into money.
A) it is relatively easy to convert the financial asset into precious metals such as gold or silver.
B) it is relatively easy to use it as an hedge against inflation.
C) it serves as a perfect store of value.
D) it is easily converted into money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
When we consider risks of various bank-assets, the most secure bank's asset is:
A) reserves.
B) short-term loans.
C) government bonds.
D) mortgage holdings.
A) reserves.
B) short-term loans.
C) government bonds.
D) mortgage holdings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The Canadian Payments Association coordinates:
A) clearing of interbank cheques.
B) short-term loans of bank-customers.
C) selling of government bonds.
D) mortgage payments.
A) clearing of interbank cheques.
B) short-term loans of bank-customers.
C) selling of government bonds.
D) mortgage payments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which one do you think is an asset of a commercial bank, when we consider the balance sheet of a bank?
A) The demand deposits of its customers.
B) The savings certificates and bank shares sold to the customers.
C) The loans given by the bank to its customers.
D) The deposits by customers in the bank's money market account.
A) The demand deposits of its customers.
B) The savings certificates and bank shares sold to the customers.
C) The loans given by the bank to its customers.
D) The deposits by customers in the bank's money market account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is the most liquid asset?
A) Cheques.
B) Coins and banknotes.
C) Saving bonds
D) Share certificates.
A) Cheques.
B) Coins and banknotes.
C) Saving bonds
D) Share certificates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Bank profits come from:
A) rental income on bank buildings.
B) service charges to customers.
C) interest income on assets minus interest costs of deposits.
D) charges for safe keeping customer deposits.
A) rental income on bank buildings.
B) service charges to customers.
C) interest income on assets minus interest costs of deposits.
D) charges for safe keeping customer deposits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A recent development in the financial services industry is:
A) an increase in the number of banks and credit unions.
B) increased integration of world financial markets.
C) increased use of coins and currency as a medium of exchange.
D) a decrease in the financial services and activities of mutual funds.
A) an increase in the number of banks and credit unions.
B) increased integration of world financial markets.
C) increased use of coins and currency as a medium of exchange.
D) a decrease in the financial services and activities of mutual funds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Banks create money by:
A) granting new loans.
B) printing currency.
C) collecting bad debts.
D) earning profits.
A) granting new loans.
B) printing currency.
C) collecting bad debts.
D) earning profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Fractional reserve banking mans:
A) banks hold cash reserve less than 100 per cent of their deposit liabilities.
B) banks hold reserves in the form of government bonds.
C) banks never run out of currency.
D) all the above.
A) banks hold cash reserve less than 100 per cent of their deposit liabilities.
B) banks hold reserves in the form of government bonds.
C) banks never run out of currency.
D) all the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In a fractional-reserve banking system, the reserves/deposits ratio (rr) is:
A) zero.
B) one.
C) more than one.
D) more than zero, but less than one.
A) zero.
B) one.
C) more than one.
D) more than zero, but less than one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If the reserve/deposit ratio (rr) is 0.2 and the currency ratio (cr) is zero, then the money multiplier is:
A) zero.
B) 0.2.
C) 2.
D) 5.
A) zero.
B) 0.2.
C) 2.
D) 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Banks create money, when banks:
A) extend loans to their customers and add that loan-money to the demand deposits of the customer's account.
B) buy government securities from the Bank of Canada and increase its liquidity.
C) accept cash deposits and keep it bank's vaults.
D) increase their deposits at the Bank of Canada.
A) extend loans to their customers and add that loan-money to the demand deposits of the customer's account.
B) buy government securities from the Bank of Canada and increase its liquidity.
C) accept cash deposits and keep it bank's vaults.
D) increase their deposits at the Bank of Canada.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The currency ratio (cr) is:
A) the ratio of currency held by the public to their loans.
B) the ratio of currency held by the public to their deposits.
C) the ratio of currency in circulation to the government bonds outstanding.
D) the ratio of cash reserves held by the banks to their deposit liabilities.
A) the ratio of currency held by the public to their loans.
B) the ratio of currency held by the public to their deposits.
C) the ratio of currency in circulation to the government bonds outstanding.
D) the ratio of cash reserves held by the banks to their deposit liabilities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The reserve ratio (rr) in the banking system is:
A) cash balances held by the public relative to their outstanding bank loans.
B) cash balances held by banks relative to their outstanding loan assets.
C) cash and central bank deposits held by banks relative to their deposit liabilities.
D) cash balances held by businesses relative to accounts payable.
A) cash balances held by the public relative to their outstanding bank loans.
B) cash balances held by banks relative to their outstanding loan assets.
C) cash and central bank deposits held by banks relative to their deposit liabilities.
D) cash balances held by businesses relative to accounts payable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Higher the reserve ratio, higher is the deposit-creation.
B) Higher the currency-ratio, higher is the deposit-creation.
C) Higher the currency- ratio, higher is the reserve-ratio.
D) Lower the reserve-ratio and lower the currency-ratio, higher is the deposit-creation.
A) Higher the reserve ratio, higher is the deposit-creation.
B) Higher the currency-ratio, higher is the deposit-creation.
C) Higher the currency- ratio, higher is the reserve-ratio.
D) Lower the reserve-ratio and lower the currency-ratio, higher is the deposit-creation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Consider a situation where the reserve ratio is 20% and the cash-ratio is zero. If the cash-reserves in the banking system are $10 billion with zero excess reserves, then:
A) the total loans in the banking system are $50 million.
B) the total deposits in the banking system are $50 million.
C) the total loans in the banking system are $60 million.
D) the total deposits in the banking system are $60 million.
A) the total loans in the banking system are $50 million.
B) the total deposits in the banking system are $50 million.
C) the total loans in the banking system are $60 million.
D) the total deposits in the banking system are $60 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Consider a situation where the reserve ratio is 20% and the cash-ratio is zero. If the cash-reserves in the banking system are $10 billion with zero excess reserves, then:
A) the total loans in the banking system are $50 million.
B) the total loans in the banking system are $40 million.
C) the total loans in the banking system are $60 million.
D) the total deposits in the banking system are $60 million.
A) the total loans in the banking system are $50 million.
B) the total loans in the banking system are $40 million.
C) the total loans in the banking system are $60 million.
D) the total deposits in the banking system are $60 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Assume that reserve ratio is 0.1 and cash-ratio is 0.1. An initial deposit of $1000 will eventually lead to one of the following outcomes:
A) Total loan-creation of $10,000.
B) Total deposit-creation of $10,000.
C) Total loan-creation of $5,000.
D) Total deposit-creation of $5,000.
A) Total loan-creation of $10,000.
B) Total deposit-creation of $10,000.
C) Total loan-creation of $5,000.
D) Total deposit-creation of $5,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Assume that reserve ratio is 0.1 and cash-ratio is 0.1. An initial deposit of $1000 will eventually lead to one of the following outcomes:
A) Total loan-creation of $10,000.
B) Total loan-creation of $9,000.
C) Total loan-creation of $5,000.
D) Total loan-creation of $4,000.
A) Total loan-creation of $10,000.
B) Total loan-creation of $9,000.
C) Total loan-creation of $5,000.
D) Total loan-creation of $4,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The multiple expansion or contraction of the money supply in commercial banks depends upon:
A) all depositors not withdrawing funds simultaneously.
B) a large number of banks not retaining excess reserves.
C) the banks being willing to hold only a fraction of their demand deposits as a cash reserve.
D) all of the above.
A) all depositors not withdrawing funds simultaneously.
B) a large number of banks not retaining excess reserves.
C) the banks being willing to hold only a fraction of their demand deposits as a cash reserve.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Suppose, the current reserve ratio is 20% and the current cash-drain is zero. Currently, the banking system has cash reserves of $10 billion. If the banking system reduces its reserve ratio to 10%, while cash-drain remains zero, eventually it will lead to one of the following outcomes:
A) Excess reserves of $10 billion.
B) Excess reserves of $5 billion.
C) Excess reserves of $1 billion.
D) Excess reserves of $0.1 billion.
A) Excess reserves of $10 billion.
B) Excess reserves of $5 billion.
C) Excess reserves of $1 billion.
D) Excess reserves of $0.1 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Suppose, the current reserve ratio is 20% and the current cash-drain is zero. Currently, the banking system has cash reserves of $10 billion. If the banking system reduces its reserve ratio to 10%, while cash-drain remains zero, eventually it will lead to one of the following outcomes:
A) Excess reserves worth $10 billion.
B) Additional deposit-creation worth of $100 billion.
C) Additional deposit-creation worth of $40 billion.
D) Additional loan-creation worth $50 billion.
A) Excess reserves worth $10 billion.
B) Additional deposit-creation worth of $100 billion.
C) Additional deposit-creation worth of $40 billion.
D) Additional loan-creation worth $50 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Monetary base or high-powered money (H) may best be described as:
A) total demand deposits in the banking system.
B) total loans in the banking system.
C) total reserves of the commercial banks.
D) none of the above.
A) total demand deposits in the banking system.
B) total loans in the banking system.
C) total reserves of the commercial banks.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Collapse of the sub-prime mortgage market led to the financial crisis in 2008 in U.S. economy.
B) Financial crisis was limited to the U.S. financial sector; the Canadian financial market remained unaffected due to the fact that Canada has stronger banking regulations.
C) Several large financial institutions in the United States required bailout.
D) No banks in Canada failed or required bailout, while several U.S banks either failed or required bailout in 2008.
A) Collapse of the sub-prime mortgage market led to the financial crisis in 2008 in U.S. economy.
B) Financial crisis was limited to the U.S. financial sector; the Canadian financial market remained unaffected due to the fact that Canada has stronger banking regulations.
C) Several large financial institutions in the United States required bailout.
D) No banks in Canada failed or required bailout, while several U.S banks either failed or required bailout in 2008.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If a bank's reserve ratio is 10 per cent and it is just meeting that requirement when $10,000 in cash is withdrawn, it must now:
A) decrease its reserves by $1000.
B) increase its reserves by $9000.
C) do nothing since both assets and liabilities are affected equally.
D) make $100,000 in new loans.
A) decrease its reserves by $1000.
B) increase its reserves by $9000.
C) do nothing since both assets and liabilities are affected equally.
D) make $100,000 in new loans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If the cash-drain is zero, the multiple by which the commercial banking system can expand the money supply on the basis of excess reserves is:
A) zero.
B) smaller than the desired reserve ratio.
C) the reciprocal of the bank's cash reserves.
D) larger, the smaller the desired reserve ratio.
A) zero.
B) smaller than the desired reserve ratio.
C) the reciprocal of the bank's cash reserves.
D) larger, the smaller the desired reserve ratio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
If the money supply is $400 billion and the money multiplier is 2, then the monetary base is:
A) $800 billion.
B) $400 billion.
C) $200 billion.
D) $2 billion.
A) $800 billion.
B) $400 billion.
C) $200 billion.
D) $2 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If the monetary base is $300 billion and the money supply is $6000 billion, the value of the money multiplier is:
A) 0.05.
B) 0.2.
C) 20.
D) 6.
A) 0.05.
B) 0.2.
C) 20.
D) 6.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Deposit-creation is higher:
A) the higher their desired cash reserves ratio.
B) higher the cash-deposit ratio.
C) the lower their desired cash reserves ratio.
D) the greater their liquidity.
A) the higher their desired cash reserves ratio.
B) higher the cash-deposit ratio.
C) the lower their desired cash reserves ratio.
D) the greater their liquidity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If excess reserves of $1000 can generate the money supply by $20,000, the desired reserve ratio (rr) requirement is:
A) 0.50.
B) 0.10.
C) 0.05.
D) 0.01.
A) 0.50.
B) 0.10.
C) 0.05.
D) 0.01.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
When an individual deposits cash into a chequing account, it leads to:
A) higher bank reserves, higher bank loans and higher money supply.
B) lower bank reserves, lower bank loans and lower money supply.
C) lower bank reserves, higher banks loans and higher money supply.
D) no changes in bank reserves.
A) higher bank reserves, higher bank loans and higher money supply.
B) lower bank reserves, lower bank loans and lower money supply.
C) lower bank reserves, higher banks loans and higher money supply.
D) no changes in bank reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Suppose Jack deposits $600. Later that day Jane borrows $1200 from the same bank. As a result, the money supply will:
A) increase by $1200.
B) increase by $600.
C) decrease by $600.
D) stay constant.
A) increase by $1200.
B) increase by $600.
C) decrease by $600.
D) stay constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If the banks' desired ratio is 5%, the immediate effect of a $5,000 cheque drawn and cleared against the Zebina bank is to reduce:
A) deposits by $5,000 and have no effect on reserves.
B) deposits and reserves by $5,000.
C) deposits by $5,000 and reserves by $250.
D) deposits and reserves by $200.
A) deposits by $5,000 and have no effect on reserves.
B) deposits and reserves by $5,000.
C) deposits by $5,000 and reserves by $250.
D) deposits and reserves by $200.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The _______________ will rise when there is a fall in either the banks' desired cash reserves ratio or the private sector's desired ratio of cash to bank deposits.
A) money supply multiplier
B) expenditure multiplier
C) level of investment
D) price level
A) money supply multiplier
B) expenditure multiplier
C) level of investment
D) price level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
If the First Citizens Bank has a desired reserve ratio of 10% and suddenly receives $50 million in new deposits, the bank:
A) can expand its lending by all of the $50 million.
B) reduce its lending by $10 million in excess reserves.
C) has $50 million in excess reserves.
D) has $45 million in excess reserves.
A) can expand its lending by all of the $50 million.
B) reduce its lending by $10 million in excess reserves.
C) has $50 million in excess reserves.
D) has $45 million in excess reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The size of the money supply multiplier is determined by:
A) the banks' ratio of cash reserves to total deposits and the public's currency ratio.
B) the ratio of cash reserves to income.
C) the marginal propensity to consume.
D) the banks' ratio of cash reserves to total deposits.
A) the banks' ratio of cash reserves to total deposits and the public's currency ratio.
B) the ratio of cash reserves to income.
C) the marginal propensity to consume.
D) the banks' ratio of cash reserves to total deposits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
If banks and the private sector decide to hold less cash, the ___________ will be larger.
A) expenditure multiplier
B) bank profits
C) money supply multiplier
D) national debt
A) expenditure multiplier
B) bank profits
C) money supply multiplier
D) national debt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
If the public's currency ratio (cr) is 5% and the banks' desired reserve ratio (rr) is 5% the deposit multiplier will be:
A) 20.
B) 10.
C) 10.5.
D) 5.
A) 20.
B) 10.
C) 10.5.
D) 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
If the public's currency ratio (cr) is 5% and the banks' desired reserve ratio (rr) is 5% the money supply multiplier will be:
A) 20.
B) 10.
C) 10.5.
D) 5.
A) 20.
B) 10.
C) 10.5.
D) 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
If the public's currency ratio (cr) is 0% and if the banks' desired reserve ratio (rr) is 5%, an increase in monetary base by $100 will result in an increase in the bank deposits by:
A) $5.
B) $500.
C) $2,000.
D) $2,100.
A) $5.
B) $500.
C) $2,000.
D) $2,100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If the public's currency ratio (cr) is 7.5% and the banks' desired reserve ratio (rr) is 2.5% an increase in high powered money (H) of $100 will result in:
A) an increase in deposits by $1000 and no change in public cash holdings.
B) an increase in deposits by $1000 and an increase in the public's cash holdings by $75.
C) an increase in deposits by $1000 and a decrease in the public's cash holdings by $100.
D) a decrease in deposits by $100 and an increase in the public's cash holdings by $1000.
A) an increase in deposits by $1000 and no change in public cash holdings.
B) an increase in deposits by $1000 and an increase in the public's cash holdings by $75.
C) an increase in deposits by $1000 and a decrease in the public's cash holdings by $100.
D) a decrease in deposits by $100 and an increase in the public's cash holdings by $1000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
When their actual reserve ratio exceeds their desired reserve ratio, banks:
A) do nothing because this is a profitable situation.
B) stop making loans.
C) make more loans in order to earn interest income.
D) request that customers withdraw deposits from the bank.
A) do nothing because this is a profitable situation.
B) stop making loans.
C) make more loans in order to earn interest income.
D) request that customers withdraw deposits from the bank.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If a bank's actual reserve ratio equals 5% and its desired reserve ratio is 2.5%, the bank should:
A) make more loans.
B) stop making loans.
C) send the extra reserves to the central bank.
D) request that customers withdraw deposits from the bank.
A) make more loans.
B) stop making loans.
C) send the extra reserves to the central bank.
D) request that customers withdraw deposits from the bank.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If the currency to deposit ratio equals 0.1 and the desired reserve ratio is 0.1, then the money multiplier is:
A) 5.
B) 2.
C) 5.5.
D) 10.
A) 5.
B) 2.
C) 5.5.
D) 10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72

-Refer to Table 8.1. Suppose individuals in this country hold no cash. Assuming the bank's desired reserve ratio is 10 percent, what will be the banking system's deposits and reserves at the end of the money creation processes (ending with zero excess resources)?
A) Deposits will be $200,000 and reserves will be $20,000.
B) Both deposits and reserves will be $200,000.
C) Deposits will be $2,000,000 and reserves will be $200,000.
D) Both deposits and reserves will be $2,000,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73

-Refer to Table 8.1. Suppose individuals in this country hold no cash. Assuming the reserve ratio is 10 percent, what will be the bank system's loans at the end of the money creation processes?
A) $180,000.
B) $200,000.
C) $1,800,000.
D) $2,000,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Suppose rr is the desired reserve (R/D) and the money supply (M) consists of bank deposits (D) only. Then, the money supply will equal:
A) M = R/rr.
B) M = R/rr + R.
C) M = R/rr-D
D) M=D/rr
A) M = R/rr.
B) M = R/rr + R.
C) M = R/rr-D
D) M=D/rr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
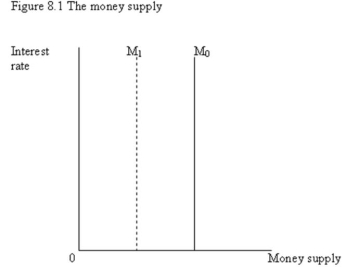
-Refer to Figure 8.1. The vertical money supply curve M0 reflects one of the following:
A) Bond prices and interest rates are inversely related.
B) The stock of money, which is determined by the banks and by the Bank of Canada, does not change when the interest rate changes.
C) Higher interest rates result in higher opportunity costs of supplying money.
D) Lower interest rates result in lower opportunity costs of supplying money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76

-Refer to Figure 8.1. If the banks' desired reserve ratio (rr) and the public's cash ratio (cr) are constant, the shift in the money supply function from M0 to M1 is a result of:
A) an decrease in the number of banks.
B) a increase in the bank lending.
C) a decrease in the monetary base.
D) an increase in the real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Cash in the vault of commercial banks is not counted as part of the money supply, since:
A) it is matched by deposits issued to customers.
B) it is really near-money.
C) it is impossible to count every day.
D) it really belongs to depositors and to count it would involve double-counting.
A) it is matched by deposits issued to customers.
B) it is really near-money.
C) it is impossible to count every day.
D) it really belongs to depositors and to count it would involve double-counting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Use the notations of M as money supply, H as high-powered money, D as the deposits, rr as the desired reserve-deposit ratio and cr as the cash-deposit ratio. Select the false identity from the following identities:
A) M = (1 + cr)D.
B) H = (cr + rr)D.
C) (M/H) = (1 + cr)/(cr + rr).
D) M = (1 + cr)(cr + rr)H.
A) M = (1 + cr)D.
B) H = (cr + rr)D.
C) (M/H) = (1 + cr)/(cr + rr).
D) M = (1 + cr)(cr + rr)H.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Use the notations of M as money supply, H as high-powered money, D as the deposits, rr as the desired reserve-deposit ratio and cr as the cash-deposit ratio. Select the false statements from the following statements:
A) If cr is zero and rr is 0.1, the money multiplier is 10.
B) If cr is 0.1 and rr is 0.1, the money multiplier is 5.5.
C) If cr is 0.1, rr is 0.1 and H is $10 billion, then M will be $50 billion.
D) If M is $55 billion and H is $10 billion, then (1 + cr)/(cr + rr) is 5.5.
A) If cr is zero and rr is 0.1, the money multiplier is 10.
B) If cr is 0.1 and rr is 0.1, the money multiplier is 5.5.
C) If cr is 0.1, rr is 0.1 and H is $10 billion, then M will be $50 billion.
D) If M is $55 billion and H is $10 billion, then (1 + cr)/(cr + rr) is 5.5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Demand deposits are classified as money, because:
A) they sometimes earn interest for the depositor.
B) they are generally acceptable in the payment of debt.
C) banks hold currency equal to their value.
D) they are not classified as liabilities of banks.
A) they sometimes earn interest for the depositor.
B) they are generally acceptable in the payment of debt.
C) banks hold currency equal to their value.
D) they are not classified as liabilities of banks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



