Deck 2: The Global Financial Environment: Markets, Institutions, Interest Rates, and Exchange Rates
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/48
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: The Global Financial Environment: Markets, Institutions, Interest Rates, and Exchange Rates
1
Any asset whose value is derived from the value of some other underlying real or financial asset best describes a(n)
A) Financial instrument.
B) Property, plant, and equipment.
C) Derivative security.
D) Current assets.
E) Accounts receivable.
A) Financial instrument.
B) Property, plant, and equipment.
C) Derivative security.
D) Current assets.
E) Accounts receivable.
Derivative security.
2
Which of the following statements is not correct?
A) A market in which a corporation issues securities for the first time and, in return, receives money is the IPO market.
B) A market in which a corporation issues securities and, in return, receives money is the primary market.
C) A market in which an individual issues securities and, in return, receives money is the mortgage market.
D) A market in which an individual issues securities and, in return, receives money is the secondary market.
E) A market in which individuals trade already-issued securities is the secondary market.
A) A market in which a corporation issues securities for the first time and, in return, receives money is the IPO market.
B) A market in which a corporation issues securities and, in return, receives money is the primary market.
C) A market in which an individual issues securities and, in return, receives money is the mortgage market.
D) A market in which an individual issues securities and, in return, receives money is the secondary market.
E) A market in which individuals trade already-issued securities is the secondary market.
A market in which an individual issues securities and, in return, receives money is the secondary market.
3
The markets in which participants agree today to buy or sell an asset at some future date are known as
A) Physical asset markets.
B) Spot markets.
C) Money markets.
D) Futures markets.
E) Capital markets.
A) Physical asset markets.
B) Spot markets.
C) Money markets.
D) Futures markets.
E) Capital markets.
Futures markets.
4
The financial markets for equity and for intermediate- or long-term debt (one year or longer) are
A) Consumer credit markets.
B) Spot markets.
C) Money markets.
D) Currency markets.
E) Capital markets.
A) Consumer credit markets.
B) Spot markets.
C) Money markets.
D) Currency markets.
E) Capital markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The markets in which transactions for foreign exchange occur are known as
A) Consumer credit markets.
B) Currency markets.
C) Spot markets.
D) Capital markets.
E) Money markets.
A) Consumer credit markets.
B) Currency markets.
C) Spot markets.
D) Capital markets.
E) Money markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Cross-listing occurs when
A) A firm offers shares to the public for the first time.
B) Global financial institutions maintain offices in different time zones around the world and offer anytime trading.
C) The exchange rate is determined by supply and demand for currency.
D) A company lists shares of stock on multiple exchanges to increase its global recognition.
E) A country abandons its own currency and adopts the U.S. dollar as its legal tender.
A) A firm offers shares to the public for the first time.
B) Global financial institutions maintain offices in different time zones around the world and offer anytime trading.
C) The exchange rate is determined by supply and demand for currency.
D) A company lists shares of stock on multiple exchanges to increase its global recognition.
E) A country abandons its own currency and adopts the U.S. dollar as its legal tender.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Around-the-clock trading occurs when
A) Global financial institutions maintain offices in different time zones around the world and offer anytime trading.
B) There is significant government intervention to control the exchange rate via manipulation of the currency's supply and demand.
C) A company lists shares of stock on multiple exchanges to increase its global recognition.
D) A country locks its currency to a specific currency or basket of currencies at a fixed exchange rate.
E) A firm offers shares to the public for the first time.
A) Global financial institutions maintain offices in different time zones around the world and offer anytime trading.
B) There is significant government intervention to control the exchange rate via manipulation of the currency's supply and demand.
C) A company lists shares of stock on multiple exchanges to increase its global recognition.
D) A country locks its currency to a specific currency or basket of currencies at a fixed exchange rate.
E) A firm offers shares to the public for the first time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following statements best defines exchange rate?
A) The price paid to borrow debt capital.
B) The actual rate charged on a loan that compensates investors for postponing consumption, inflation, and risk.
C) The number of units of a given currency that can be purchased for one unit of another currency.
D) The nominal, risk-adjusted rate of return that is actually published in financial publications.
E) The rate of interest that offsets inflation and provides the required real return on a riskless investment.
A) The price paid to borrow debt capital.
B) The actual rate charged on a loan that compensates investors for postponing consumption, inflation, and risk.
C) The number of units of a given currency that can be purchased for one unit of another currency.
D) The nominal, risk-adjusted rate of return that is actually published in financial publications.
E) The rate of interest that offsets inflation and provides the required real return on a riskless investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The framework within which exchange rates are determined today is called
A) The eurocurrency market.
B) The international monetary system.
C) The Bank for International Settlements (BIS) network.
D) The Bretton Woods system.
E) None of the above.
A) The eurocurrency market.
B) The international monetary system.
C) The Bank for International Settlements (BIS) network.
D) The Bretton Woods system.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following statements most closely describes the role of the marginal investor?
A) Facilitates the transfer of funds from savers to demanders of capital.
B) Underwrites and distributes new investment securities and helps businesses obtain financing.
C) Maintains offices in different time zones around the world to offer anytime trading.
D) Decisions and resulting actions determine the market interest rate.
E) Specializes in maintaining inventory of certain stocks in the electronic markets.
A) Facilitates the transfer of funds from savers to demanders of capital.
B) Underwrites and distributes new investment securities and helps businesses obtain financing.
C) Maintains offices in different time zones around the world to offer anytime trading.
D) Decisions and resulting actions determine the market interest rate.
E) Specializes in maintaining inventory of certain stocks in the electronic markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) The interest rate is the minimum rate of return on a common stock that will induce a stockholder to purchase the stock.
B) In a financial market context, risk is the chance that an investment will provide a high return.
C) The exchange rate is the price paid to borrow debt capital.
D) Production opportunities are the returns available within an economy from investment in productive real assets.
E) The exchange rate is the amount by which prices are expected to increase over time.
A) The interest rate is the minimum rate of return on a common stock that will induce a stockholder to purchase the stock.
B) In a financial market context, risk is the chance that an investment will provide a high return.
C) The exchange rate is the price paid to borrow debt capital.
D) Production opportunities are the returns available within an economy from investment in productive real assets.
E) The exchange rate is the amount by which prices are expected to increase over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Four fundamental factors interact to determine supply and demand and, hence, the price (or cost) of capital. Factor(s) on the demand side include
A) The expected rate of inflation.
B) Production opportunities.
C) Risk.
D) Time preferences for consumption.
E) Only statements a and b are correct.
A) The expected rate of inflation.
B) Production opportunities.
C) Risk.
D) Time preferences for consumption.
E) Only statements a and b are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) The nominal risk-free rate compensates investors for postponing consumption, inflation, and risk.
B) The nominal risk-free rate offsets inflation and provides the required real return on a riskless investment.
C) The nominal risk-free rate is correctly calculated as the required real rate plus the expected inflation rate.
D) The inflation premium is calculated as the required real rate multiplied by the expected inflation rate.
E) Another name for the quoted (or stated) rate is the required real rate.
A) The nominal risk-free rate compensates investors for postponing consumption, inflation, and risk.
B) The nominal risk-free rate offsets inflation and provides the required real return on a riskless investment.
C) The nominal risk-free rate is correctly calculated as the required real rate plus the expected inflation rate.
D) The inflation premium is calculated as the required real rate multiplied by the expected inflation rate.
E) Another name for the quoted (or stated) rate is the required real rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following statements best defines the exchange rate risk premium?
A) A premium that occurs when the bond is denominated in the investor's home currency and reflects the risk that arises from investing or doing business in a particular country.
B) A premium that reflects interest rate risk.
C) A premium added to the equilibrium interest rate on a security if that security cannot be converted to cash on short notice and at close to "fair market value."
D) A premium that results when a bond is denominated in the investor's home currency and results from the possibility that an exchange rate change will lead to a loss in a bond's value.
E) A premium that results when a bond is denominated in a currency other than the investor's home currency and results from the possibility that an exchange rate change will lead to a loss in a bond's value.
A) A premium that occurs when the bond is denominated in the investor's home currency and reflects the risk that arises from investing or doing business in a particular country.
B) A premium that reflects interest rate risk.
C) A premium added to the equilibrium interest rate on a security if that security cannot be converted to cash on short notice and at close to "fair market value."
D) A premium that results when a bond is denominated in the investor's home currency and results from the possibility that an exchange rate change will lead to a loss in a bond's value.
E) A premium that results when a bond is denominated in a currency other than the investor's home currency and results from the possibility that an exchange rate change will lead to a loss in a bond's value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following statements best defines the country risk premium?
A) A premium that reflects the risk that arises from investing or doing business in a particular country and it depends on the country's business climate.
B) A premium that reflects interest rate risk.
C) A premium added to the equilibrium interest rate on a security if that security cannot be converted to cash on short notice and at close to "fair market value."
D) A premium that reflects the difference between the interest rate on a U.S. Treasury bond and a corporate bond of equal maturity and marketability.
E) A premium that results when a bond is denominated in a currency other than the investor's home currency and results from the possibility that an exchange rate change will lead to a loss in a bond's value.
A) A premium that reflects the risk that arises from investing or doing business in a particular country and it depends on the country's business climate.
B) A premium that reflects interest rate risk.
C) A premium added to the equilibrium interest rate on a security if that security cannot be converted to cash on short notice and at close to "fair market value."
D) A premium that reflects the difference between the interest rate on a U.S. Treasury bond and a corporate bond of equal maturity and marketability.
E) A premium that results when a bond is denominated in a currency other than the investor's home currency and results from the possibility that an exchange rate change will lead to a loss in a bond's value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Indirect transfers of money and securities can be accomplished in several ways. Which of the following transactions might represent an indirect transaction?
A) Miriam Collins places money in a certificate of deposit (CD) at her commercial bank.
B) Bill Williams buys a share of IBM stock on the NYSE.
C) Marvin Matthews buys 100 shares of a company's stock from Goldman Sachs in an IPO.
D) All of the statements above are indirect transfers.
E) Only statements a and c are indirect transfers.
A) Miriam Collins places money in a certificate of deposit (CD) at her commercial bank.
B) Bill Williams buys a share of IBM stock on the NYSE.
C) Marvin Matthews buys 100 shares of a company's stock from Goldman Sachs in an IPO.
D) All of the statements above are indirect transfers.
E) Only statements a and c are indirect transfers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The nominal, risk-free rate of return
A) Is the rate of return that both offsets inflation and provides the required real return on a riskless investment.
B) Is calculated by adding the real, risk-free rate and the inflation rate.
C) Cannot be observed directly but is often approximated by the quoted rate on U.S. or foreign government securities.
D) All of the statements above are correct.
E) Only statements a and c are correct.
A) Is the rate of return that both offsets inflation and provides the required real return on a riskless investment.
B) Is calculated by adding the real, risk-free rate and the inflation rate.
C) Cannot be observed directly but is often approximated by the quoted rate on U.S. or foreign government securities.
D) All of the statements above are correct.
E) Only statements a and c are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following statements is most correct?
A) Interest rates on U.S. Treasury bonds do not contain any type of risk premia at all. This is why they are used as the nominal, risk-free rate.
B) Interest rates on U.S. Treasury securities are not truly risk free (although nearly so) because they contain a maturity risk premium and a default risk premium.
C) Interest rates on U.S. Treasury securities are not truly risk free (although nearly so) because they contain a country risk premium and an exchange rate risk premium.
D) The difference in required interest rates on U.S. Treasury securities and equivalent corporate bonds is explained almost entirely by the existence of a liquidity premium and a maturity risk premium.
E) Both statements b and c are correct.
A) Interest rates on U.S. Treasury bonds do not contain any type of risk premia at all. This is why they are used as the nominal, risk-free rate.
B) Interest rates on U.S. Treasury securities are not truly risk free (although nearly so) because they contain a maturity risk premium and a default risk premium.
C) Interest rates on U.S. Treasury securities are not truly risk free (although nearly so) because they contain a country risk premium and an exchange rate risk premium.
D) The difference in required interest rates on U.S. Treasury securities and equivalent corporate bonds is explained almost entirely by the existence of a liquidity premium and a maturity risk premium.
E) Both statements b and c are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If the nominal one-year risk-free interest rate in the U.S. is 5 percent and the nominal one-year risk-free interest rate in another country is 8 percent, which of the following statements must be true if the markets are in equilibrium and there are no restrictions on capital flows?
A) The foreign currency is expected to decrease in value relative to the U.S. dollar.
B) Investors will prefer to invest their money in the foreign country because they like to earn a higher interest rate.
C) Investors will prefer to invest their money in the foreign country because their total rate of return in one year will be higher.
D) The foreign currency is expected to increase in value relative to the U.S. dollar.
E) Knowing only the interest rates in the two countries does not give us enough information to make an informed judgment of the direction of movement in the value of the currency.
A) The foreign currency is expected to decrease in value relative to the U.S. dollar.
B) Investors will prefer to invest their money in the foreign country because they like to earn a higher interest rate.
C) Investors will prefer to invest their money in the foreign country because their total rate of return in one year will be higher.
D) The foreign currency is expected to increase in value relative to the U.S. dollar.
E) Knowing only the interest rates in the two countries does not give us enough information to make an informed judgment of the direction of movement in the value of the currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The text characterized a "perfect," or ideal, currency as one having three characteristics. Included in the list of ideal characteristics is (are) which of the following?
A) The currency should be freely floating against the currencies of the country's major trading partners so that the market determines the exchange rate without government intervention.
B) Each country would set its own monetary and fiscal policy solely on the basis of its own economic situation.
C) Complete and unrestricted monetary flows should be permitted, allowing investors and businesses to move their wealth as they choose.
D) All of the statements above are characteristics of an ideal currency.
E) Only statements b and c are correct.
A) The currency should be freely floating against the currencies of the country's major trading partners so that the market determines the exchange rate without government intervention.
B) Each country would set its own monetary and fiscal policy solely on the basis of its own economic situation.
C) Complete and unrestricted monetary flows should be permitted, allowing investors and businesses to move their wealth as they choose.
D) All of the statements above are characteristics of an ideal currency.
E) Only statements b and c are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following statements regarding monetary arrangements is correct?
A) A managed-float arrangement occurs when a country has its own currency but commits to exchange it for a specified foreign money unit at a fixed exchange rate and legislates domestic currency restrictions, unless it has the foreign currency reserves to cover requested exchanges.
B) A fixed peg arrangement occurs when a country locks its currency to a specific currency or basket of currencies at a fixed exchange rate, and the exchange rate is allowed to vary only within plus or minus one percent of the target rate.
C) In a freely-floating-exchange-rate regime, governments may occasionally intervene in the market to buy or sell their currency in order to stabilize fluctuations, while in a managed-float arrangement there is significant government intervention to manage the exchange rate by manipulating the currency's supply and demand.
D) Statements b and c are correct.
E) All of the statements are correct.
A) A managed-float arrangement occurs when a country has its own currency but commits to exchange it for a specified foreign money unit at a fixed exchange rate and legislates domestic currency restrictions, unless it has the foreign currency reserves to cover requested exchanges.
B) A fixed peg arrangement occurs when a country locks its currency to a specific currency or basket of currencies at a fixed exchange rate, and the exchange rate is allowed to vary only within plus or minus one percent of the target rate.
C) In a freely-floating-exchange-rate regime, governments may occasionally intervene in the market to buy or sell their currency in order to stabilize fluctuations, while in a managed-float arrangement there is significant government intervention to manage the exchange rate by manipulating the currency's supply and demand.
D) Statements b and c are correct.
E) All of the statements are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A currency board arrangement for managing the value of a country's currency occurs when
A) The country's currency can be exchanged at a fixed rate into a foreign money unit (such as the euro or dollar) and is backed with sufficient foreign currency reserves to cover requested changes.
B) The country uses a managed float to set the exchange rate for its currency but does not reveal the target rate set by the currency board of the central bank.
C) The central bank of a country pegs the value of the currency to some other money unit but allows it to deviate a small amount (such as ?1%), but which requires explicit approval from a designated committee, called the currency board, to reset the central rate around which the deviations are measured.
D) Withdraws its own currency from circulation and uses the money unit of another country as its official currency.
E) None of the statements above.
A) The country's currency can be exchanged at a fixed rate into a foreign money unit (such as the euro or dollar) and is backed with sufficient foreign currency reserves to cover requested changes.
B) The country uses a managed float to set the exchange rate for its currency but does not reveal the target rate set by the currency board of the central bank.
C) The central bank of a country pegs the value of the currency to some other money unit but allows it to deviate a small amount (such as ?1%), but which requires explicit approval from a designated committee, called the currency board, to reset the central rate around which the deviations are measured.
D) Withdraws its own currency from circulation and uses the money unit of another country as its official currency.
E) None of the statements above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Many emerging market countries would prefer to use a floating rate currency regime but are forced by circumstances to adopt a fixed rate regime. The reasons they would prefer to use a floating rate regime include which of the following?
A) Helps in the fight against inflation because countries must intervene domestically to take counterinflationary actions.
B) Governments can follow domestic policies to reduce unemployment or to stimulate growth without having to explicitly consider international implications of the exchange rate.
C) International reserves do not have to be used to preserve the exchange rate because it is allowed to find its own equilibrium level.
D) All of the statements above are correct.
E) Only statements b and c are correct.
A) Helps in the fight against inflation because countries must intervene domestically to take counterinflationary actions.
B) Governments can follow domestic policies to reduce unemployment or to stimulate growth without having to explicitly consider international implications of the exchange rate.
C) International reserves do not have to be used to preserve the exchange rate because it is allowed to find its own equilibrium level.
D) All of the statements above are correct.
E) Only statements b and c are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A financial analyst has the following data:
Inflation premium (IP) = 5.25%
Real, risk-free rate, r* = 3.2%
According to this information, what is the inflation rate?
A) 2.0525%
B) 5.0872%
C) 3.9570%
D) 4.7500%
E) 6.2500%
Inflation premium (IP) = 5.25%
Real, risk-free rate, r* = 3.2%
According to this information, what is the inflation rate?
A) 2.0525%
B) 5.0872%
C) 3.9570%
D) 4.7500%
E) 6.2500%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A financial analyst has the following data:
Inflation premium (IP) = 5.25%
Real, risk-free rate, r* = 3.2%
According to this information, what is the nominal risk-free rate?
A) 4.75%
B) 5.09%
C) 6.25%
D) 8.45%
E) 7.50%
Inflation premium (IP) = 5.25%
Real, risk-free rate, r* = 3.2%
According to this information, what is the nominal risk-free rate?
A) 4.75%
B) 5.09%
C) 6.25%
D) 8.45%
E) 7.50%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A German investor recently purchased a U.S. blue-chip, A-rated corporate bond with a 10-year maturity. The yield on the bond is 8.2 percent. The default risk premium is 0.5 percent and the liquidity premium is 0.1 percent. The real risk-free rate of return is 2.8 percent and the inflation premium (calculated over 10 years) is 3.3 percent. The maturity risk premium is 1.0 percent, and the country risk premium is 0.3 percent. The nominal risk-free rate of return is 6.1 percent. Given these data, what was the exchange rate risk premium (ERP) on the bond?
A) 0.2%
B) 0.5%
C) 0.8%
D) 1.2%
E) 1.5%
A) 0.2%
B) 0.5%
C) 0.8%
D) 1.2%
E) 1.5%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
You observe from The Wall Street Journal that the 1-year Treasury bill rate is currently 6.0 percent and consider that it is a reasonable proxy for the nominal, risk-free rate. Your economic advisory service is also forecasting that the expected inflation rate for the next year (1-year rate) is 3.0 percent. With this information, calculate the real risk-free return, r*, and the inflation premium, IP.
A) r* = 2.8302%; IP = 3.1698%
B) r* = 2.9126%; IP = 3.0874%
C) r* = 2.9633%; IP = 3.0367%
D) r* = 3.0000%; IP = 3.0000%
E) r* = 3.0275%; IP = 2.9725%
A) r* = 2.8302%; IP = 3.1698%
B) r* = 2.9126%; IP = 3.0874%
C) r* = 2.9633%; IP = 3.0367%
D) r* = 3.0000%; IP = 3.0000%
E) r* = 3.0275%; IP = 2.9725%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Given the following data (all for 1-year):
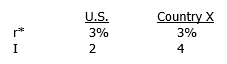 Today's spot exchange rate is 10.5 pesos per dollar. In equilibrium, what is the expected future spot rate (EFS) in one year?
Today's spot exchange rate is 10.5 pesos per dollar. In equilibrium, what is the expected future spot rate (EFS) in one year?
A) P10.7000/$
B) P11.2476/$
C) P10.7059/$
D) P11.2350/$
E) None of the above.
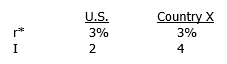 Today's spot exchange rate is 10.5 pesos per dollar. In equilibrium, what is the expected future spot rate (EFS) in one year?
Today's spot exchange rate is 10.5 pesos per dollar. In equilibrium, what is the expected future spot rate (EFS) in one year?A) P10.7000/$
B) P11.2476/$
C) P10.7059/$
D) P11.2350/$
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A financial analyst has the following data:
 Ireland's currency is the euro and today's spot exchange rate is $1.2182 per euro. In equilibrium, what should be the exchange rate one year from now?
Ireland's currency is the euro and today's spot exchange rate is $1.2182 per euro. In equilibrium, what should be the exchange rate one year from now?
A) $0.8503 = 1€
B) $0.9750 = 1€
C) $1.1760 = 1€
D) $1.2500 = 1€
E) $1.3750 = 1€
 Ireland's currency is the euro and today's spot exchange rate is $1.2182 per euro. In equilibrium, what should be the exchange rate one year from now?
Ireland's currency is the euro and today's spot exchange rate is $1.2182 per euro. In equilibrium, what should be the exchange rate one year from now?A) $0.8503 = 1€
B) $0.9750 = 1€
C) $1.1760 = 1€
D) $1.2500 = 1€
E) $1.3750 = 1€

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A U.S. investor recently purchased a U.S. Treasury bond with a 10-year maturity to earn a yield of 4.8 percent. A European investor just purchased a U.S. AAA-rated, "blue-chip" corporate bond with a 10-year maturity for 5.75 percent. This bond can be converted to cash very quickly, so its liquidity premium is small, 0.1 percent. The spread between U.S. Treasury bonds and AAA-rated bonds with similar maturity and liquidity is 0.2 percent. Another European investor purchased a U.S. BBB-rated, corporate bond with a 10-year maturity. The liquidity premium for this BBB-rated bond is 0.5 percent, and the spread between U.S. Treasury bonds and BBB-rated bonds with similar maturity and liquidity is 1.5 percent. What yield will the European investor earn on the U.S. BBB-rated, corporate bond?
A) 6.00%
B) 6.40%
C) 8.75%
D) 6.80%
E) 7.45%
A) 6.00%
B) 6.40%
C) 8.75%
D) 6.80%
E) 7.45%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Briefly explain the three different ways that transfers of capital take place.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Identify and briefly explain the four fundamental factors that interact to determine the price of capital making sure to note whether they affect the demand or supply side.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Differentiate between fixed and floating exchange rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Differentiate between a soft versus a hard currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The general formula used for the nominal, risk-adjusted required rate of return can be written as rRF + RP. Identify and briefly explain the five different components comprising RP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Differentiate between devaluation/revaluation of a currency versus depreciation/appreciation of a currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Summarize the three characteristics of a perfect, or ideal, currency and identify the name economists have given to describe these three characteristics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Is it possible to have a perfect, or ideal, currency? Explain your answer using the United States and China as illustrations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Currency regimes can be divided into two broad groups: floating rates and fixed rates. Identify and briefly explain the two subgroups under floating exchange rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Currency regimes can be divided into two broad groups: floating rates and fixed rates. Identify and briefly explain the three subgroups under fixed exchange rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What factors have been offered for and against fixed exchange rates? Provide at least two factors for each position.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What factors have been offered for and against floating exchange rates? Provide at least two factors for each position.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What is dollarization? Give the arguments for and against dollarization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If the real risk-free rate is 2.75 percent and the expected inflation rate is 3.5 percent, what is the nominal risk-free rate, rRF?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
An analyst has the following information:
Expected inflation rate, I = 3.8%
Real, risk-free rate, r* = 2.5%
What is the inflation premium, IP?
Expected inflation rate, I = 3.8%
Real, risk-free rate, r* = 2.5%
What is the inflation premium, IP?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
An analyst has the following information:
Expected inflation rate, I = 3.8%
Real, risk-free rate, r* = 2.5%
What is the nominal risk-free rate, rRF?
Expected inflation rate, I = 3.8%
Real, risk-free rate, r* = 2.5%
What is the nominal risk-free rate, rRF?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A financial analyst has the following data:
 India's currency is the rupee and today's spot exchange rate is 45.84 rupees per U.S. dollar. In equilibrium, what amount of rupees should be exchanged for one U.S. dollar one year from now?
India's currency is the rupee and today's spot exchange rate is 45.84 rupees per U.S. dollar. In equilibrium, what amount of rupees should be exchanged for one U.S. dollar one year from now?
 India's currency is the rupee and today's spot exchange rate is 45.84 rupees per U.S. dollar. In equilibrium, what amount of rupees should be exchanged for one U.S. dollar one year from now?
India's currency is the rupee and today's spot exchange rate is 45.84 rupees per U.S. dollar. In equilibrium, what amount of rupees should be exchanged for one U.S. dollar one year from now?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A U.S. investor recently purchased a U.S. Treasury bond with a 15-year maturity to earn a yield of 4.45 percent. A British investor just purchased a U.S. AAA-rated, "blue-chip" corporate bond with a 15-year maturity for 5.3 percent. This bond can be converted to cash very quickly, so its liquidity premium is small, 0.15 percent. The spread between U.S. Treasury bonds and AAA-rated bonds with similar maturity and liquidity is 0.25 percent. Another British investor purchased a U.S. A rated, corporate bond with a 15-year maturity. The liquidity premium for this A-rated bond is 0.35 percent, and the spread between U.S. Treasury bonds and A-rated bonds with similar maturity and liquidity is 1 percent. What yield will the British investor earn on the U.S. A-rated, corporate bond?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



