Deck 16: International Trade and Exchange Rates
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/28
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: International Trade and Exchange Rates
1
The domestic opportunity cost of producing a television in the United States is 20 bushels of wheat. In Korea, the domestic opportunity cost of producing a television is 10 bushels of wheat. In this case:
A) Korea has a comparative advantage in the production of wheat.
B) the United States has a comparative advantage in the production of televisions.
C) mutual gains from trade can be obtained if the United States imports televisions from Korea and Korea imports wheat from the United States.
D) mutual gains from trade can be obtained if the United States imports wheat from Korea and Korea imports televisions from the United States.
A) Korea has a comparative advantage in the production of wheat.
B) the United States has a comparative advantage in the production of televisions.
C) mutual gains from trade can be obtained if the United States imports televisions from Korea and Korea imports wheat from the United States.
D) mutual gains from trade can be obtained if the United States imports wheat from Korea and Korea imports televisions from the United States.
mutual gains from trade can be obtained if the United States imports televisions from Korea and Korea imports wheat from the United States.
2
Nation A pays lower wages to workers than nation B. Nation A also uses fewer capital goods per worker than nation B. This suggests that gains from trade are likely to result if:
A) nation A produces products that are more capital-intensive and exports them to nation B in return for products from nation B that are more labor-intensive.
B) nation A produces products that are more labor-intensive and exports them to nation B in return for products from nation B that are more capital-intensive.
C) nation B produces products that are more labor-intensive and exports them to nation A in return for products from nation A that are more capital-intensive.
D) nations A and B each produces capital-intensive and labor-intensive goods and trades them with each other.
A) nation A produces products that are more capital-intensive and exports them to nation B in return for products from nation B that are more labor-intensive.
B) nation A produces products that are more labor-intensive and exports them to nation B in return for products from nation B that are more capital-intensive.
C) nation B produces products that are more labor-intensive and exports them to nation A in return for products from nation A that are more capital-intensive.
D) nations A and B each produces capital-intensive and labor-intensive goods and trades them with each other.
nation A produces products that are more labor-intensive and exports them to nation B in return for products from nation B that are more capital-intensive.
3
The production possibilities for Country X are either 6000 bushels of soybeans or 10,000 bushels of wheat. The production possibilities for Country Y are 2000 bushels of soybeans and 4000 bushels of wheat. Which of the following is true?
A) Country Y should specialize in the growing of soybeans according to the principle of comparative advantage.
B) Country X is the least-cost producer of wheat.
C) The domestic opportunity cost of wheat production is lower in Country Y.
D) The high cost producer of soybeans is Country X.
A) Country Y should specialize in the growing of soybeans according to the principle of comparative advantage.
B) Country X is the least-cost producer of wheat.
C) The domestic opportunity cost of wheat production is lower in Country Y.
D) The high cost producer of soybeans is Country X.
The domestic opportunity cost of wheat production is lower in Country Y.
4
Countries A and B produce only rubber bands and paper clips under the production possibilities schedules shown below:

- Which of the following statements is true?
A) Country A has a comparative advantage in both rubber bands and paper clips.
B) Country A has a comparative advantage in paper clips.
C) Country A has a comparative advantage in rubber bands.
D) Since Country A can produce more of both goods, there is no potentially for mutually beneficial specialization and trade.

- Which of the following statements is true?
A) Country A has a comparative advantage in both rubber bands and paper clips.
B) Country A has a comparative advantage in paper clips.
C) Country A has a comparative advantage in rubber bands.
D) Since Country A can produce more of both goods, there is no potentially for mutually beneficial specialization and trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The table below shows points from straight-line production possibilities schedules for two countries and indicates that: 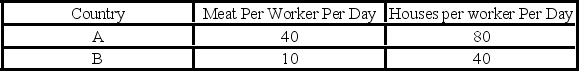
A) Country B can produce more meat than Country A.
B) Country A has a comparative advantage in producing meat.
C) Country B can produce more houses than Country A.
D) Country A has a comparative advantage in producing houses and meat.

A) Country B can produce more meat than Country A.
B) Country A has a comparative advantage in producing meat.
C) Country B can produce more houses than Country A.
D) Country A has a comparative advantage in producing houses and meat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The production possibilities table given below shows how many bushels of either wheat or rice can be produced in India and Canada with 1 unit of input. To achieve gains from specialization: 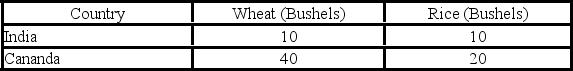
A) India should export rice to Canada and import Canadian wheat.
B) India should export wheat to Canada and import Canadian rice.
C) Canada should produce both wheat and rice and not trade with India.
D) India should produce both wheat and rice and not trade with Canada.

A) India should export rice to Canada and import Canadian wheat.
B) India should export wheat to Canada and import Canadian rice.
C) Canada should produce both wheat and rice and not trade with India.
D) India should produce both wheat and rice and not trade with Canada.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A given unit of resource inputs produces 400 tons of corn or 200 tons of soybeans in nation A, and 300 tons of corn or 100 tons of soybeans in nation B. Which of the following is correct?
A) The domestic opportunity cost of corn is lower in nation A than in nation B.
B) Nation A has a comparative advantage in soybeans.
C) There are no gains from trade between nation A and nation B.
D) The terms of trade favor nation A.
A) The domestic opportunity cost of corn is lower in nation A than in nation B.
B) Nation A has a comparative advantage in soybeans.
C) There are no gains from trade between nation A and nation B.
D) The terms of trade favor nation A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
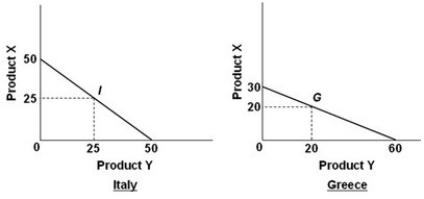
-Refer to the above diagrams. Which of the following is a feasible rate at which X and Y might be exchanged?
A) 1X for 3Y
B) 1X for 1.5Y
C) 1X for 2.5Y
D) 1X for .5Y

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
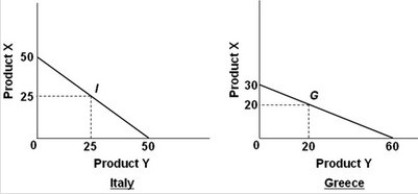
- Refer to the above diagrams. Assume that prior to specialization and trade Italy and Greece preferred points I and G on their production possibilities curves. As a result of complete specialization according to comparative advantage, the resulting gains in output will be:
A) 5X and 15Y.
B) 10Y.
C) 15X and 5Y.
D) 25X.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Autos and chemicals are in units of one million
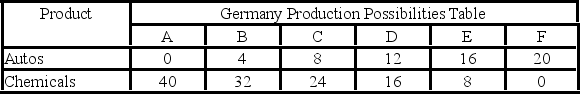

- The data in the above tables show that production in:
A) Germany is subject to increasing domestic opportunity costs and the United States to constant domestic opportunity costs.
B) the United States is subject to increasing domestic opportunity costs and Germany to constant domestic opportunity costs.
C) both Germany and the United States are subject to constant domestic opportunity costs.
D) both Germany and the United States are subject to increasing domestic opportunity costs.


- The data in the above tables show that production in:
A) Germany is subject to increasing domestic opportunity costs and the United States to constant domestic opportunity costs.
B) the United States is subject to increasing domestic opportunity costs and Germany to constant domestic opportunity costs.
C) both Germany and the United States are subject to constant domestic opportunity costs.
D) both Germany and the United States are subject to increasing domestic opportunity costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Autos and chemicals are in units of one million
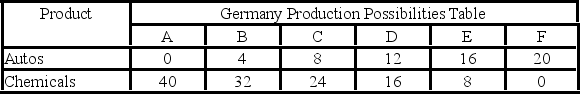

- Refer to the above tables. If Germany and the United States engage in trade, the terms of trade will be between:
A) 3 and 4 units of autos for 1 unit of chemicals.
B) 2 and 4 units of autos for 1 unit of chemicals.
C) 2 and 4 units of chemicals for 1 unit of autos.
D) .33 and .5 unit of autos for 1 unit of chemicals.


- Refer to the above tables. If Germany and the United States engage in trade, the terms of trade will be between:
A) 3 and 4 units of autos for 1 unit of chemicals.
B) 2 and 4 units of autos for 1 unit of chemicals.
C) 2 and 4 units of chemicals for 1 unit of autos.
D) .33 and .5 unit of autos for 1 unit of chemicals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Autos and chemicals are in units of one million
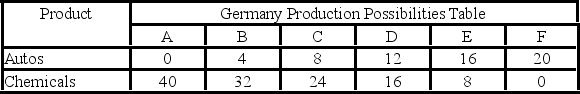

-Refer to the above tables. Assume that prior to specialization and trade Germany and the United States both choose production possibility C. Now if each specializes according to its comparative advantage, the resulting total gains from specialization and trade will be:
A) 8 units of autos.
B) 6 units of autos.
C) 6 units of autos and 8 units of chemicals.
D) 8 units of autos and 6 units of chemicals.


-Refer to the above tables. Assume that prior to specialization and trade Germany and the United States both choose production possibility C. Now if each specializes according to its comparative advantage, the resulting total gains from specialization and trade will be:
A) 8 units of autos.
B) 6 units of autos.
C) 6 units of autos and 8 units of chemicals.
D) 8 units of autos and 6 units of chemicals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Answer the next question on the basis of the following production possibilities data for two countries, Alpha and Beta, which have populations of equal size.
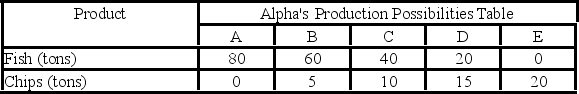
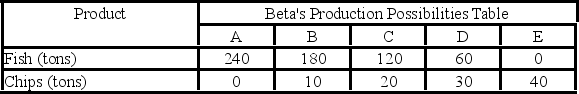
- The domestic opportunity cost of:
A) producing a ton of chips in Alpha is 1/5 of a ton of fish.
B) producing a ton of chips in Beta is 6 tons of fish.
C) catching a ton of fish in Alpha is 5 tons of chips.
D) catching a ton of fish in Beta is 6 tons of chips.


- The domestic opportunity cost of:
A) producing a ton of chips in Alpha is 1/5 of a ton of fish.
B) producing a ton of chips in Beta is 6 tons of fish.
C) catching a ton of fish in Alpha is 5 tons of chips.
D) catching a ton of fish in Beta is 6 tons of chips.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Answer the next question on the basis of the following production possibilities data for two countries, Alpha and Beta, which have populations of equal size.
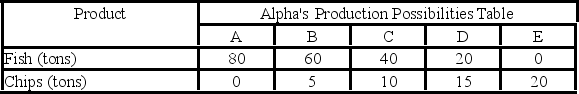
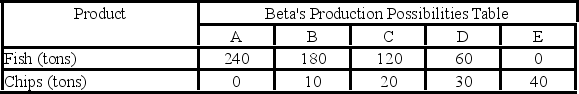
- Beta…
A) should specialize in catching fish and trade with Alpha for chips.
B) should specialize in producing chips and trade with Alpha for fish.
C) will not realize gains from specialization and trade.
D) will export both fish and chips to Alpha.


- Beta…
A) should specialize in catching fish and trade with Alpha for chips.
B) should specialize in producing chips and trade with Alpha for fish.
C) will not realize gains from specialization and trade.
D) will export both fish and chips to Alpha.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Answer the next question on the basis of the following production possibilities data for two countries, Alpha and Beta, which have populations of equal size.
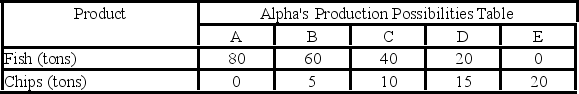
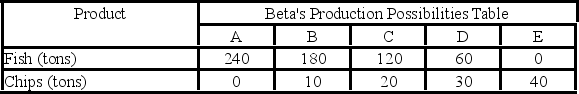
-Suppose that before specialization and trade Alpha chose production alternative C and Beta chose production alternative B. After specialization and trade the gains will be:
A) 20 tons of fish.
B) 20 tons of chips.
C) 20 tons of fish and 20 tons of chips.
D) 240 tons of fish and 20 tons of chips.


-Suppose that before specialization and trade Alpha chose production alternative C and Beta chose production alternative B. After specialization and trade the gains will be:
A) 20 tons of fish.
B) 20 tons of chips.
C) 20 tons of fish and 20 tons of chips.
D) 240 tons of fish and 20 tons of chips.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Answer the next question on the basis of the following production possibilities data for two countries, Alpha and Beta, which have populations of equal size.
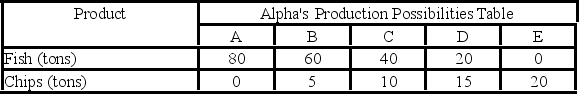
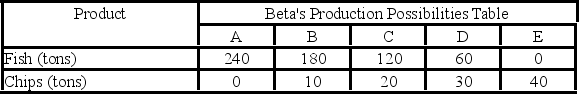
- Assume the production possibilities in Beta double at alternatives A through E while remaining as shown in the table for Alpha. As a result, Beta should:
A) continue to specialize in producing chips.
B) continue to specialize in fishing.
C) no longer specialize and trade.
D) specialize both in fishing and in producing chips and sell the surplus to Alpha.


- Assume the production possibilities in Beta double at alternatives A through E while remaining as shown in the table for Alpha. As a result, Beta should:
A) continue to specialize in producing chips.
B) continue to specialize in fishing.
C) no longer specialize and trade.
D) specialize both in fishing and in producing chips and sell the surplus to Alpha.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If an American can purchase 40,000 British pounds for $90,000, the dollar rate of exchange for the pound is:
A) $1.40.
B) $2.00.
C) $2.25.
D) $6.00.
A) $1.40.
B) $2.00.
C) $2.25.
D) $6.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The Trade Adjustment Assistance Act of 2002:
A) imposes tariffs on any foreign good that causes U.S. workers to lose their jobs.
B) provides financial help to workers displaced by imports or plant relocations abroad.
C) subsidizes domestic companies so they can better compete with foreign imports.
D) imposes tariffs on nations whose firms are engaged predatory dumping.
A) imposes tariffs on any foreign good that causes U.S. workers to lose their jobs.
B) provides financial help to workers displaced by imports or plant relocations abroad.
C) subsidizes domestic companies so they can better compete with foreign imports.
D) imposes tariffs on nations whose firms are engaged predatory dumping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Critics of trade adjustment assistance:
A) claim that it increases the prices of goods, unfairly burdening consumers.
B) ask why jobs lost to trade should be privileged over jobs lost due to other factors.
C) argue that it props up domestic firms that should be allowed to fail so that those resources can be moved to move highly valued uses.
D) ask why companies struggling due to foreign competition deserve assistance over companies struggling for other reasons.
A) claim that it increases the prices of goods, unfairly burdening consumers.
B) ask why jobs lost to trade should be privileged over jobs lost due to other factors.
C) argue that it props up domestic firms that should be allowed to fail so that those resources can be moved to move highly valued uses.
D) ask why companies struggling due to foreign competition deserve assistance over companies struggling for other reasons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is one of the major shortcomings of using tariffs or quotas to "save American jobs"?
A) Trade barriers protect the development of new technology, but the new technology eliminates jobs.
B) Import restrictions alter the composition of domestic employment, but they have minimal effect on the amount of domestic employment.
C) The volume of trade with other nations is limited to a few industries, so trade restrictions would not increase national employment.
D) Major American firms have produced many products in other countries, and would not hire more domestic labor when trade barriers are imposed.
A) Trade barriers protect the development of new technology, but the new technology eliminates jobs.
B) Import restrictions alter the composition of domestic employment, but they have minimal effect on the amount of domestic employment.
C) The volume of trade with other nations is limited to a few industries, so trade restrictions would not increase national employment.
D) Major American firms have produced many products in other countries, and would not hire more domestic labor when trade barriers are imposed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which is a valid counterargument to the call for higher tariffs to save U.S. jobs?
A) They are needed to protect U.S. workers from the dumping of foreign products.
B) Strategic trade policy calls for equal treatment of all trading nations so that they will have the same competitive conditions.
C) U.S. firms and workers must be protected from the ruinous competition of nations where wages for workers are low.
D) Imports may eliminate some U.S. jobs, but they create others, so they may have little or no effect on employment.
A) They are needed to protect U.S. workers from the dumping of foreign products.
B) Strategic trade policy calls for equal treatment of all trading nations so that they will have the same competitive conditions.
C) U.S. firms and workers must be protected from the ruinous competition of nations where wages for workers are low.
D) Imports may eliminate some U.S. jobs, but they create others, so they may have little or no effect on employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which is a valid counterargument to the call for higher tariffs to save U.S. jobs?
A) Nations adversely affected by such tariffs are likely to retaliate, causing a costly trade barrier war.
B) U.S. firms and workers must be shielded from the competitive practices of foreign businesses.
C) Strategic trade policy calls for trading nations to erect trade barriers so that they will have the same competitive conditions.
D) They are needed to protect U.S. workers from poor enforcement of labor standards in other nations.
A) Nations adversely affected by such tariffs are likely to retaliate, causing a costly trade barrier war.
B) U.S. firms and workers must be shielded from the competitive practices of foreign businesses.
C) Strategic trade policy calls for trading nations to erect trade barriers so that they will have the same competitive conditions.
D) They are needed to protect U.S. workers from poor enforcement of labor standards in other nations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act:
A) restricts the importation of goods critical to a strong national defense, when those goods can be produced domestically.
B) imposes anti-dumping duties as needed.
C) helped maintain domestic employment in the 1930s, causing the Great Depression to be less severe.
D) prompted retaliation from other nations and helped cause the Great Depression.
A) restricts the importation of goods critical to a strong national defense, when those goods can be produced domestically.
B) imposes anti-dumping duties as needed.
C) helped maintain domestic employment in the 1930s, causing the Great Depression to be less severe.
D) prompted retaliation from other nations and helped cause the Great Depression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following was not implemented in an effort to liberalize trade?
A) The European Union (EU)
B) The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA)
C) The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT)
D) The Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act
A) The European Union (EU)
B) The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA)
C) The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT)
D) The Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following statements is most accurate about the euro?
A) It is the common currency used by all the nations of the European Union (EU).
B) The United Kingdom gave up the euro with the "Brexit" vote of 2016.
C) It has equalized prices across the EU nations that use the currency.
D) It has facilitated trade between the EU countries that have adopted the currency.
A) It is the common currency used by all the nations of the European Union (EU).
B) The United Kingdom gave up the euro with the "Brexit" vote of 2016.
C) It has equalized prices across the EU nations that use the currency.
D) It has facilitated trade between the EU countries that have adopted the currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is an implication of large U.S. trade deficits?
A) Consumers enjoy greater consumption in the present.
B) U.S. indebtedness increases.
C) Downward pressure is placed on the U.S. dollar.
D) All of these.
A) Consumers enjoy greater consumption in the present.
B) U.S. indebtedness increases.
C) Downward pressure is placed on the U.S. dollar.
D) All of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is not an implication of large U.S. trade deficits?
A) The nation must consume within its production possibilities curve.
B) U.S. productivity is falling.
C) Deficits cause the U.S. dollar to depreciate.
D) All of these are implications of large trade deficits.
A) The nation must consume within its production possibilities curve.
B) U.S. productivity is falling.
C) Deficits cause the U.S. dollar to depreciate.
D) All of these are implications of large trade deficits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Trade Adjustment Assistance provides payments to domestic firms struggling to compete with foreign producers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



