Deck 6: Businesses and Their Costs
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/15
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Businesses and Their Costs
1
The principal-agent problem in corporations arises from:
A) the fact that the principal objective of most corporations is to make profits and not to contribute to charity.
B) a conflict of interest between corporate executives who manage the firm and stockholders who own the firm.
C) the view that workers are agents who are not considered to be the principal asset of the corporations for which they work.
D) a perspective that corporations are agents that represent the principal source of power for government and the national economy.
A) the fact that the principal objective of most corporations is to make profits and not to contribute to charity.
B) a conflict of interest between corporate executives who manage the firm and stockholders who own the firm.
C) the view that workers are agents who are not considered to be the principal asset of the corporations for which they work.
D) a perspective that corporations are agents that represent the principal source of power for government and the national economy.
a conflict of interest between corporate executives who manage the firm and stockholders who own the firm.
2
Suppose you own $50,000 of personal property, $5,000 of stock in General Statics Corporation, a $10,000 savings account, and $20,000 of government bonds. If General Statics goes bankrupt, the most you could lose is:
A) $50,000.
B) $5,000.
C) $35,000.
D) $85,000.
A) $50,000.
B) $5,000.
C) $35,000.
D) $85,000.
$5,000.
3
Alyssa runs a "Dessert of the month" delivery service. To operate her business each year, she spends $30,000 on baking supplies (flour, sugar, etc.), $50,000 on rent for her shop, and $5,000 for utilities. She owns her delivery van, estimating that in alternate uses it could generate $15,000 in income per year. Alyssa has other funds tied up in the business that could earn her $2,000 per year in interest. Alyssa has been offered $50,000 to work full time at a competing bakery. Her bakery generates $160,000 per year in revenue from subscriptions to her monthly service.
Based on the information above, which of the following is true about Alyssa's costs and profits?
A) Alyssa's explicit costs are $67,000 and her implicit costs are $85,000.
B) Alyssa's implicit costs are $67,000 and her economic profits are $93,000.
C) Alyssa's accounting profits are $8,000 and her economic profits are $75,000.
D) Alyssa's explicit costs are $85,000 and her accounting profits are $75,000.
Based on the information above, which of the following is true about Alyssa's costs and profits?
A) Alyssa's explicit costs are $67,000 and her implicit costs are $85,000.
B) Alyssa's implicit costs are $67,000 and her economic profits are $93,000.
C) Alyssa's accounting profits are $8,000 and her economic profits are $75,000.
D) Alyssa's explicit costs are $85,000 and her accounting profits are $75,000.
Alyssa's explicit costs are $85,000 and her accounting profits are $75,000.
4
Alyssa runs a "Dessert of the month" delivery service. To operate her business each year, she spends $30,000 on baking supplies (flour, sugar, etc.), $50,000 on rent for her shop, and $5,000 for utilities. She owns her delivery van, estimating that in alternate uses it could generate $15,000 in income per year. Alyssa has other funds tied up in the business that could earn her $2,000 per year in interest. Alyssa has been offered $50,000 to work full time at a competing bakery. Her bakery generates $160,000 per year in revenue from subscriptions to her monthly service.
Based on the information above, which of the following is true about Alyssa's costs and profits?
A) Alyssa's explicit costs are $67,000 and her implicit costs are $85,000.
B) Alyssa's implicit costs are $67,000 and her economic profits are $93,000.
C) Alyssa's accounting profits are $75,000 and her economic profits are $8,000.
D) Alyssa's explicit costs are $85,000 and her accounting profits are $8,000.
Based on the information above, which of the following is true about Alyssa's costs and profits?
A) Alyssa's explicit costs are $67,000 and her implicit costs are $85,000.
B) Alyssa's implicit costs are $67,000 and her economic profits are $93,000.
C) Alyssa's accounting profits are $75,000 and her economic profits are $8,000.
D) Alyssa's explicit costs are $85,000 and her accounting profits are $8,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Alyssa runs a "Dessert of the month" delivery service. To operate her business each year, she spends $30,000 on baking supplies (flour, sugar, etc.), $50,000 on rent for her shop, and $5,000 for utilities. She owns her delivery van, estimating that in alternate uses it could generate $15,000 in income per year. Alyssa has other funds tied up in the business that could earn her $2,000 per year in interest. Alyssa has been offered $50,000 to work full time at a competing bakery. Her bakery generates $160,000 per year in revenue from subscriptions to her monthly service.
Based on the information above, which of the following can we conclude about Alyssa's business?
A) Alyssa is incurring economic losses, so we would expect her to close her business.
B) Alyssa is earning economic profits, so we would expect her to remain in business.
C) Alyssa's economic profits are greater than her accounting profits.
D) Alyssa would be better off working for the competing bakery.
Based on the information above, which of the following can we conclude about Alyssa's business?
A) Alyssa is incurring economic losses, so we would expect her to close her business.
B) Alyssa is earning economic profits, so we would expect her to remain in business.
C) Alyssa's economic profits are greater than her accounting profits.
D) Alyssa would be better off working for the competing bakery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The law of diminishing returns indicates that:
A) as extra units of a variable resource are added to a fixed resource, marginal product will decline beyond some point.
B) because of economies and diseconomies of scale, a competitive firm's long-run average total cost curve will be U-shaped.
C) the demand for goods produced by purely competitive industries is downsloping.
D) beyond some point, the extra utility derived from additional units of a product will yield the consumer smaller and smaller extra amounts of satisfaction.
A) as extra units of a variable resource are added to a fixed resource, marginal product will decline beyond some point.
B) because of economies and diseconomies of scale, a competitive firm's long-run average total cost curve will be U-shaped.
C) the demand for goods produced by purely competitive industries is downsloping.
D) beyond some point, the extra utility derived from additional units of a product will yield the consumer smaller and smaller extra amounts of satisfaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following best expresses the law of diminishing returns?
A) Because large-scale production allows the realization of economies of scale, the real costs of production vary directly with the level of output.
B) Population growth automatically adjusts to that level at which the average product per worker will be at a maximum.
C) As successive amounts of one resource (labor) are added to fixed amounts of other resources (capital), beyond some point the resulting extra output will decline.
D) Proportionate increases in the inputs of all resources will result in a less-than-proportionate increase in total output.
A) Because large-scale production allows the realization of economies of scale, the real costs of production vary directly with the level of output.
B) Population growth automatically adjusts to that level at which the average product per worker will be at a maximum.
C) As successive amounts of one resource (labor) are added to fixed amounts of other resources (capital), beyond some point the resulting extra output will decline.
D) Proportionate increases in the inputs of all resources will result in a less-than-proportionate increase in total output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
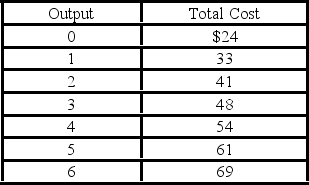 Refer to the above data. The total variable cost of producing 5 units is:
Refer to the above data. The total variable cost of producing 5 units is:A) $61.
B) $48.
C) $37.
D) $24.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9

- Refer to the above information. Average fixed cost is:
A) TVC - MC.
B)
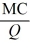
C)
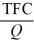
D)
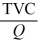

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10

-Refer to the above information. Average total cost is:
A) TVC - MC.
B)
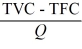
C)
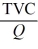
D)
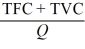

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11

-Refer to the above information. Marginal cost is:
A)
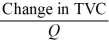
B)
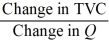
C)
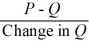
D)
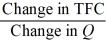

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12

- Refer to the above information. Total cost is:
A) the change in marginal cost.
B) TVC - TFC.
C) TFC + TVC.
D)
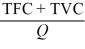

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Use the figure below to answer the following questions:
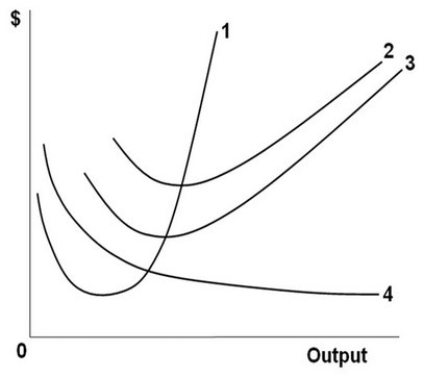 In the above figure, curves 1, 2, 3, and 4 represent the:
In the above figure, curves 1, 2, 3, and 4 represent the:
A) ATC, MC, AFC, and AVC curves respectively.
B) MC, AFC, AVC, and ATC curves respectively.
C) MC, ATC, AVC, and AFC curves respectively.
D) ATC, AVC, AFC, and MC curves respectively.
 In the above figure, curves 1, 2, 3, and 4 represent the:
In the above figure, curves 1, 2, 3, and 4 represent the:A) ATC, MC, AFC, and AVC curves respectively.
B) MC, AFC, AVC, and ATC curves respectively.
C) MC, ATC, AVC, and AFC curves respectively.
D) ATC, AVC, AFC, and MC curves respectively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following statements is most accurate about sunk costs?
A) All fixed costs are sunk costs.
B) Sunk costs are important in business decisions because they need to be recovered.
C) Sunk costs are unrecoverable and therefore shouldn't influence economic decisions.
D) All expenditures, once made, represent sunk costs.
A) All fixed costs are sunk costs.
B) Sunk costs are important in business decisions because they need to be recovered.
C) Sunk costs are unrecoverable and therefore shouldn't influence economic decisions.
D) All expenditures, once made, represent sunk costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following industries would see firms reach their minimum efficient scale at relatively low levels of output?
A) Automobile manufacturers.
B) Software companies.
C) Oil refineries.
D) Hair salons.
A) Automobile manufacturers.
B) Software companies.
C) Oil refineries.
D) Hair salons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



