Deck 3: Demand, Supply, and Market Equilibrium
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/30
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Demand, Supply, and Market Equilibrium
1
In 2007 the price of oil increased, which in turn caused the price of natural gas to rise. This can best be explained by saying that oil and natural gas are:
A) complementary goods and the higher price for oil increased the demand for natural gas.
B) substitute goods and the higher price for oil increased the demand for natural gas.
C) complementary goods and the higher price for oil decreased the supply of natural gas.
D) substitute goods and the higher price for oil decreased the supply of natural gas.
A) complementary goods and the higher price for oil increased the demand for natural gas.
B) substitute goods and the higher price for oil increased the demand for natural gas.
C) complementary goods and the higher price for oil decreased the supply of natural gas.
D) substitute goods and the higher price for oil decreased the supply of natural gas.
substitute goods and the higher price for oil increased the demand for natural gas.
2
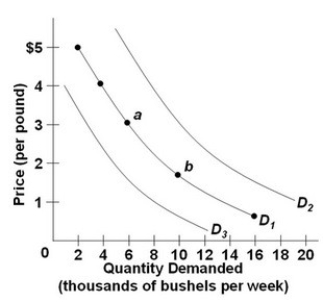 Refer to the above diagram, which shows three demand curves for coffee. Which would cause the change in the quantity of coffee demanded illustrated by the shift from point a to point b?
Refer to the above diagram, which shows three demand curves for coffee. Which would cause the change in the quantity of coffee demanded illustrated by the shift from point a to point b?A) A decrease in the price of coffee
B) An increase in consumer incomes
C) A decrease in the price of sugar
D) An increase in the price of tea
A decrease in the price of coffee
3
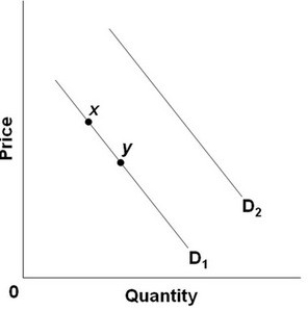 Refer to the above diagram for good X. A shift from D2 to D1 would best be explained by:
Refer to the above diagram for good X. A shift from D2 to D1 would best be explained by:A) an increase in the price of good X.
B) a decrease in the price of good X.
C) an increase in the price of a complementary good Y.
D) an increase in the price of a substitute good Z.
an increase in the price of a complementary good Y.
4
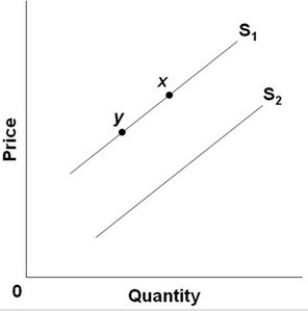 Refer to the above diagram for good R. A shift in the supply curve from S2 to S1 would best be explained by:
Refer to the above diagram for good R. A shift in the supply curve from S2 to S1 would best be explained by:A) government imposing a tax on good R.
B) a decrease in the price of resources used to produce good R.
C) an increase in the price of good R.
D) an improvement in the technology used to produce good R.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Assume a drought in the Great Plains reduces the supply of wheat. Since wheat is a basic ingredient in the production of bread and potatoes are a consumer substitute for bread, we would expect the price of wheat to:
A) rise, the supply of bread to increase, and the demand for potatoes to increase.
B) rise, the supply of bread to decrease, and the demand for potatoes to increase.
C) rise, the supply of bread to decrease, and the demand for potatoes to decrease.
D) fall, the supply of bread to increase, and the demand for potatoes to increase.
A) rise, the supply of bread to increase, and the demand for potatoes to increase.
B) rise, the supply of bread to decrease, and the demand for potatoes to increase.
C) rise, the supply of bread to decrease, and the demand for potatoes to decrease.
D) fall, the supply of bread to increase, and the demand for potatoes to increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
 Refer to the above data. Equilibrium price is:
Refer to the above data. Equilibrium price is:A) $4.
B) $3.
C) $2.
D) $1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7

- Refer to the above diagram. The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be:
A) $1.00 and 200.
B) $1.60 and 130.
C) $.50 and 130.
D) $1.60 and 290.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8

-Refer to the above diagram. A surplus of 160 units would be encountered if price was:
A) $1.10, that is, $1.60 minus $.50.
B) $1.60.
C) $1.00.
D) $.50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9

- Refer to the above diagram. A shortage of 160 units would be encountered if price was:
A) $1.10, that is, $1.60 minus $.50.
B) $1.60.
C) $1.00.
D) $.50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
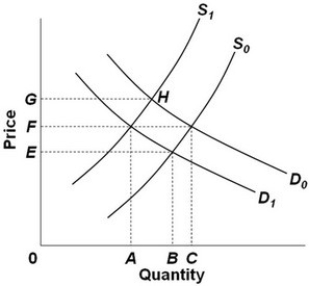 Refer to the above diagram, which shows demand and supply conditions in the competitive market for product X. Given D0, if the supply curve moved from S0 to S1, then:
Refer to the above diagram, which shows demand and supply conditions in the competitive market for product X. Given D0, if the supply curve moved from S0 to S1, then:A) supply has increased and equilibrium quantity has decreased.
B) supply has decreased and equilibrium quantity has decreased.
C) there has been an increase in the quantity supplied.
D) supply has increased and price has risen to 0G.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
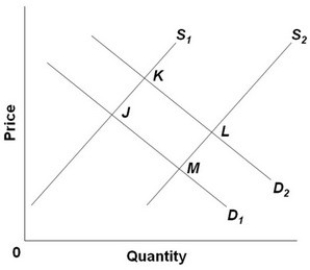
- Refer to the above diagram, in which S1 and D1 represent the original supply and demand curves and S2 and D2 the new curves. In this market:
A) supply has decreased and equilibrium price has increased.
B) demand has increased and equilibrium price has decreased.
C) demand has decreased and equilibrium price has decreased.
D) demand has increased and equilibrium price has increased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
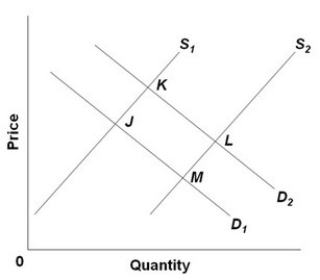
- Refer to the above diagram, in which S1 and D1 represent the original supply and demand curves and S2 and D2 the new curves. In this market:
A) the equilibrium position has shifted from M to K.
B) an increase in demand has been more than offset by an increase in supply.
C) the new equilibrium price and quantity are both greater than they were originally.
D) point M shows the new equilibrium position.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
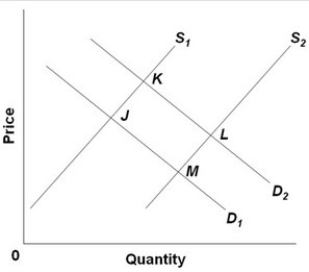
-Refer to the above diagram, in which S1 and D1 represent the original supply and demand curves and S2 and D2 the new curves. In this market the indicated shift in supply may have been caused by:
A) an increase in the wages paid to workers producing this good.
B) the development of more efficient machinery for producing this good.
C) this product becoming less fashionable.
D) an increase in consumer incomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
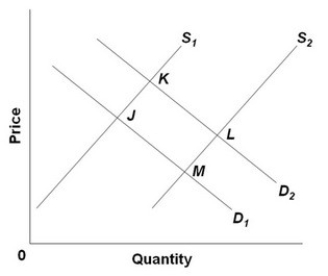
- Refer to the above diagram, in which S1 and D1 represent the original supply and demand curves and S2 and D2 the new curves. In this market the indicated shift in demand may have been caused by:
A) a decline in the number of buyers in the market.
B) a decline in the price of a substitute good.
C) an increase in incomes if the product is a normal good.
D) an increase in incomes if the product is an inferior good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In the following question you are asked to determine, other things equal, the effects of a given change in a determinant of demand or supply for product X upon (1) the demand (D) for, or supply (S) of, X; (2) the equilibrium price (P) of X; and (3) the equilibrium quantity (Q) of X.
- An increase in income, if X is a normal good, will:
A) increase D, increase P, and increase Q.
B) increase D, increase P, and decrease Q.
C) increase S, increase P, and increase Q.
D) decrease D, increase P, and increase Q.
- An increase in income, if X is a normal good, will:
A) increase D, increase P, and increase Q.
B) increase D, increase P, and decrease Q.
C) increase S, increase P, and increase Q.
D) decrease D, increase P, and increase Q.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In the following question you are asked to determine, other things equal, the effects of a given change in a determinant of demand or supply for product X upon (1) the demand (D) for, or supply (S) of, X; (2) the equilibrium price (P) of X; and (3) the equilibrium quantity (Q) of X.
-An increase in the price of a product that is a close substitute for X will:
A) decrease D, increase P, and decrease Q.
B) increase D, increase P, and decrease Q.
C) increase D, increase P, and increase Q.
D) increase D, decrease P, and increase Q.
-An increase in the price of a product that is a close substitute for X will:
A) decrease D, increase P, and decrease Q.
B) increase D, increase P, and decrease Q.
C) increase D, increase P, and increase Q.
D) increase D, decrease P, and increase Q.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In the following question you are asked to determine, other things equal, the effects of a given change in a determinant of demand or supply for product X upon (1) the demand (D) for, or supply (S) of, X; (2) the equilibrium price (P) of X; and (3) the equilibrium quantity (Q) of X.
- A decrease in the number of consumers of product X will:
A) decrease S, decrease P, and decrease Q.
B) increase D, increase P, and increase Q.
C) decrease D, decrease P, and decrease Q.
D) decrease D, decrease P, and increase Q.
- A decrease in the number of consumers of product X will:
A) decrease S, decrease P, and decrease Q.
B) increase D, increase P, and increase Q.
C) decrease D, decrease P, and decrease Q.
D) decrease D, decrease P, and increase Q.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In the following question you are asked to determine, other things equal, the effects of a given change in a determinant of demand or supply for product X upon (1) the demand (D) for, or supply (S) of, X; (2) the equilibrium price (P) of X; and (3) the equilibrium quantity (Q) of X.
-An increase in the tastes and preferences for X will:
A) increase S, decrease P, and increase Q.
B) decrease S, decrease P, and decrease Q.
C) increase D, increase P, and increase Q.
D) decrease D, decrease P, and decrease Q.
-An increase in the tastes and preferences for X will:
A) increase S, decrease P, and increase Q.
B) decrease S, decrease P, and decrease Q.
C) increase D, increase P, and increase Q.
D) decrease D, decrease P, and decrease Q.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In the following question you are asked to determine, other things equal, the effects of a given change in a determinant of demand or supply for product X upon (1) the demand (D) for, or supply (S) of, X; (2) the equilibrium price (P) of X; and (3) the equilibrium quantity (Q) of X.
- An increase in the prices of resources used to produce X will:
A) increase S, increase P, and increase Q.
B) increase D, increase P, and increase Q.
C) decrease S, decrease P, and decrease Q.
D) decrease S, increase P, and decrease Q.
- An increase in the prices of resources used to produce X will:
A) increase S, increase P, and increase Q.
B) increase D, increase P, and increase Q.
C) decrease S, decrease P, and decrease Q.
D) decrease S, increase P, and decrease Q.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In the following question you are asked to determine, other things equal, the effects of a given change in a determinant of demand or supply for product X upon (1) the demand (D) for, or supply (S) of, X; (2) the equilibrium price (P) of X; and (3) the equilibrium quantity (Q) of X.
- An improvement in the technology used to produce X will:
A) decrease S, increase P, and decrease Q.
B) decrease S, increase P, and increase Q.
C) increase S, decrease P, and increase Q.
D) decrease D, decrease P, and decrease Q.
- An improvement in the technology used to produce X will:
A) decrease S, increase P, and decrease Q.
B) decrease S, increase P, and increase Q.
C) increase S, decrease P, and increase Q.
D) decrease D, decrease P, and decrease Q.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In the following question you are asked to determine, other things equal, the effects of a given change in a determinant of demand or supply for product X upon (1) the demand (D) for, or supply (S) of, X; (2) the equilibrium price (P) of X; and (3) the equilibrium quantity (Q) of X.
- A reduction in the number of firms producing X will:
A) increase D, increase P, and increase Q.
B) increase S, decrease P, and increase Q.
C) decrease S, increase P, and decrease Q.
D) decrease S, decrease P, and increase Q.
- A reduction in the number of firms producing X will:
A) increase D, increase P, and increase Q.
B) increase S, decrease P, and increase Q.
C) decrease S, increase P, and decrease Q.
D) decrease S, decrease P, and increase Q.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In the following question you are asked to determine, other things equal, the effects of a given change in a determinant of demand or supply for product X upon (1) the demand (D) for, or supply (S) of, X; (2) the equilibrium price (P) of X; and (3) the equilibrium quantity (Q) of X.
-An increase in the price of a product that is a complement to X will:
A) decrease S, decrease P, and decrease Q.
B) decrease D, decrease P, and decrease Q.
C) increase D, increase P, and increase Q.
D) increase D, increase P, and decrease Q.
-An increase in the price of a product that is a complement to X will:
A) decrease S, decrease P, and decrease Q.
B) decrease D, decrease P, and decrease Q.
C) increase D, increase P, and increase Q.
D) increase D, increase P, and decrease Q.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In the following question you are asked to determine, other things equal, the effects of a given change in a determinant of demand or supply for product X upon (1) the demand (D) for, or supply (S) of, X; (2) the equilibrium price (P) of X; and (3) the equilibrium quantity (Q) of X.
-If X is an inferior good, a decrease in income will:
A) decrease D, decrease P, and decrease Q.
B) decrease D, decrease P, and increase Q.
C) increase S, decrease P, and increase Q.
D) increase D, increase P, and increase Q.
-If X is an inferior good, a decrease in income will:
A) decrease D, decrease P, and decrease Q.
B) decrease D, decrease P, and increase Q.
C) increase S, decrease P, and increase Q.
D) increase D, increase P, and increase Q.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In the following question you are asked to determine, other things equal, the effects of a given change in a determinant of demand or supply for product X upon (1) the demand (D) for, or supply (S) of, X; (2) the equilibrium price (P) of X; and (3) the equilibrium quantity (Q) of X.
-Consumer expectations that the price of X will rise sharply in the future will:
A) increase S, increase P, and increase Q.
B) increase D, increase P, and increase Q.
C) decrease S, increase P, and increase Q.
D) increase D, decrease P, and increase Q.
-Consumer expectations that the price of X will rise sharply in the future will:
A) increase S, increase P, and increase Q.
B) increase D, increase P, and increase Q.
C) decrease S, increase P, and increase Q.
D) increase D, decrease P, and increase Q.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In the following question you are asked to determine, other things equal, the effects of a given change in a determinant of demand or supply for product X upon (1) the demand (D) for, or supply (S) of, X; (2) the equilibrium price (P) of X; and (3) the equilibrium quantity (Q) of X.
-
Consumers expect that the price of X will rise sharply in the future. At the same time, technology used in producing X improves. When both of these occur, what outcome will occur with greatest certainty?
A) increase D, increase S, increase P, and increase Q.
B) increase D, increase S, increase Q, and effect on P uncertain.
C) increase D, increase S, decrease P, and increase Q.
D) increase D, decrease S, increase P, and effect on Q uncertain.
-
Consumers expect that the price of X will rise sharply in the future. At the same time, technology used in producing X improves. When both of these occur, what outcome will occur with greatest certainty?
A) increase D, increase S, increase P, and increase Q.
B) increase D, increase S, increase Q, and effect on P uncertain.
C) increase D, increase S, decrease P, and increase Q.
D) increase D, decrease S, increase P, and effect on Q uncertain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In the following question you are asked to determine, other things equal, the effects of a given change in a determinant of demand or supply for product X upon (1) the demand (D) for, or supply (S) of, X; (2) the equilibrium price (P) of X; and (3) the equilibrium quantity (Q) of X.
-
The price of complementary consumer good Y rises. At the same time, government creates subsidies for firms producing X. When both of these occur, what outcome will occur with greatest certainty?
A) decrease D, increase S, decrease P, and increase Q.
B) decrease D, increase S, decrease P, and effect on Q uncertain.
C) decrease D, increase S, decrease P, and decrease Q.
D) decrease D, decrease S, decrease Q, and effect on P uncertain.
-
The price of complementary consumer good Y rises. At the same time, government creates subsidies for firms producing X. When both of these occur, what outcome will occur with greatest certainty?
A) decrease D, increase S, decrease P, and increase Q.
B) decrease D, increase S, decrease P, and effect on Q uncertain.
C) decrease D, increase S, decrease P, and decrease Q.
D) decrease D, decrease S, decrease Q, and effect on P uncertain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Suppose that in 2008, Ford sold 500,000 Mustangs at an average price of $18,800 per car; in 2009, 600,000 Mustangs were sold at an average price of $22,500 per car. These statements:
A) suggest that the demand for Mustangs decreased between 2008 and 2009.
B) suggest that the supply of Mustangs must have increased between 2008 and 2009.
C) suggest that the demand for Mustangs increased between 2008 and 2009.
D) constitute an exception to the law of demand in that they suggest an upsloping demand curve.
A) suggest that the demand for Mustangs decreased between 2008 and 2009.
B) suggest that the supply of Mustangs must have increased between 2008 and 2009.
C) suggest that the demand for Mustangs increased between 2008 and 2009.
D) constitute an exception to the law of demand in that they suggest an upsloping demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Dynamic pricing used by companies such as Uber:
A) often results in shortages of desired products.
B) has been declared illegal because it harms consumers.
C) creates market prices that are consistently lower than those preset by firms or by law.
D) allows market prices to adjust in real time to changes in supply and demand.
A) often results in shortages of desired products.
B) has been declared illegal because it harms consumers.
C) creates market prices that are consistently lower than those preset by firms or by law.
D) allows market prices to adjust in real time to changes in supply and demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The ride-sharing service Uber uses "surge pricing":
A) to undercut the prices charged by taxi companies.
B) because equilibrium prices do not exist in the ride-sharing market.
C) to discourage customers from wanting rides during off-peak hours.
D) to attract more drivers when demand for rides suddenly increases.
A) to undercut the prices charged by taxi companies.
B) because equilibrium prices do not exist in the ride-sharing market.
C) to discourage customers from wanting rides during off-peak hours.
D) to attract more drivers when demand for rides suddenly increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is a consequence of rent controls established to keep housing affordable for the poor?
A) Less rental housing is available than if the rent controls were not in place.
B) The quality of rental housing improves as landlords seek to attract the best tenants.
C) Landlords are incentivized to produce and offer more rental units to maintain profits.
D) All of these are consequences of rent controls.
A) Less rental housing is available than if the rent controls were not in place.
B) The quality of rental housing improves as landlords seek to attract the best tenants.
C) Landlords are incentivized to produce and offer more rental units to maintain profits.
D) All of these are consequences of rent controls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



