Deck 1: Limits, Alternatives, and Choices
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/21
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: Limits, Alternatives, and Choices
1
According to the Zuckerberg, Seacrest, and Swift illustration:
A) Zuckerberg, Seacrest, and Swift made a mistake by not attending college.
B) Zuckerberg, Seacrest, and Swift did not weigh marginal benefits against marginal costs when making decisions.
C) Opportunity costs vary greatly between individuals and matter in decision making.
D) Attending college has little effect on lifetime earnings.
A) Zuckerberg, Seacrest, and Swift made a mistake by not attending college.
B) Zuckerberg, Seacrest, and Swift did not weigh marginal benefits against marginal costs when making decisions.
C) Opportunity costs vary greatly between individuals and matter in decision making.
D) Attending college has little effect on lifetime earnings.
Opportunity costs vary greatly between individuals and matter in decision making.
2
If a consumer has an income of $120, the price of X is $5, and the price of Y is $8. Which combination of the two goods is unattainable?
A) 20X and 2Y.
B) 8X and 10Y.
C) 12X and 8Y.
D) 2X and 13Y.
A) 20X and 2Y.
B) 8X and 10Y.
C) 12X and 8Y.
D) 2X and 13Y.
2X and 13Y.
3
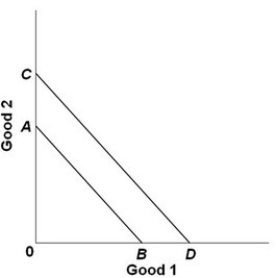
- Refer to the above graph. The shift of the budget line from AB to CD is consistent with:
A) a decrease in money income.
B) an increase in money income.
C) an increase in the price of Good 1 and no change in the price of Good 2.
D) a decrease in the price of Good 2 and no change in the price of Good 1.
an increase in money income.
4
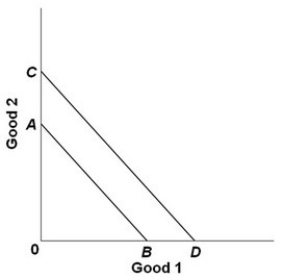
- In the diagram above, Cheri's budget line shifts outward from AB to CD. Which statement below is consistent with this shift?
A) Both prices double; her income doubles.
B) Her income is reduced; no change in either price.
C) Both prices are reduced by 50 percent; her income is reduced by less than 50 percent.
D) Both the price of good 1 and Cheri's income increase; there is no change in the price of good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
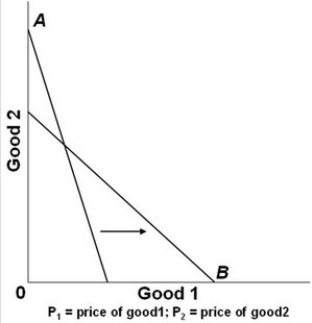 In the graph above, A is the initial budget line and B is the new budget line. Which of the following changes might have occurred?
In the graph above, A is the initial budget line and B is the new budget line. Which of the following changes might have occurred?A) P1 was unchanged, P2 increased, income decreased.
B) P1 decreased, P2 increased, income was unchanged.
C) P1 increased, P2 decreased, income was unchanged.
D) P1 decreased, P2 was unchanged, income increased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Society wants to use its scarce resources efficiently. To achieve this economic goal it must:
A) have full employment and full production.
B) have a fixed resource base and fixed technology.
C) expand the use of capital goods and reduce the use of labor.
D) increase the rental, interest, wage, and profit payments to the factors of production.
A) have full employment and full production.
B) have a fixed resource base and fixed technology.
C) expand the use of capital goods and reduce the use of labor.
D) increase the rental, interest, wage, and profit payments to the factors of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
When an economy is at full employment and full production, more of any one product:
A) cannot be produced because there is full production.
B) can be produced only if there is a general decrease in prices.
C) can be produced only if there is less production of some other products.
D) cannot be produced unless private enterprise does so rather than government.
A) cannot be produced because there is full production.
B) can be produced only if there is a general decrease in prices.
C) can be produced only if there is less production of some other products.
D) cannot be produced unless private enterprise does so rather than government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The following economy produces two products.
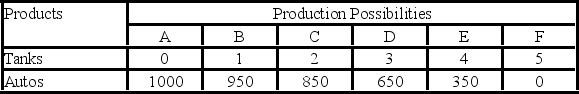
-Refer to the above table. According to the production possibilities schedule, a combination of four tanks and 650 autos is:
A) attainable and involves an efficient use of society's resources.
B) attainable, but would not be in the best interests of a strong national defense.
C) not attainable because it is not listed in the schedule.
D) not attainable because society does not have sufficient resources to produce this combination.

-Refer to the above table. According to the production possibilities schedule, a combination of four tanks and 650 autos is:
A) attainable and involves an efficient use of society's resources.
B) attainable, but would not be in the best interests of a strong national defense.
C) not attainable because it is not listed in the schedule.
D) not attainable because society does not have sufficient resources to produce this combination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The following economy produces two products.
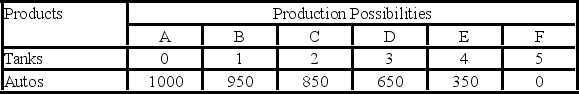
- Given the production possibilities schedule above, a combination of three tanks and 350 autos:
A) illustrates the trade-off between tanks and autos.
B) is attainable but involves the unemployment or inefficient use of some of society's resources.
C) cannot be produced by society, given its current level of resources and production technology.
D) is not attainable because this combination is not listed in the schedule.

- Given the production possibilities schedule above, a combination of three tanks and 350 autos:
A) illustrates the trade-off between tanks and autos.
B) is attainable but involves the unemployment or inefficient use of some of society's resources.
C) cannot be produced by society, given its current level of resources and production technology.
D) is not attainable because this combination is not listed in the schedule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
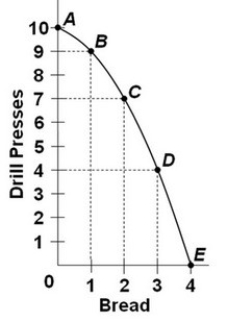 Refer to the graph. The combination of 4 units of drill presses and 2 units of bread is:
Refer to the graph. The combination of 4 units of drill presses and 2 units of bread is:A) unattainable given available resources and technology.
B) attainable if the economy becomes more efficient in allocating resources.
C) attainable and efficient.
D) attainable, but represents an economy not achieving full employment or full production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A point on the frontier of the production possibilities curve is:
A) attainable and the economy is efficient.
B) attainable, but the economy is inefficient.
C) unattainable and the economy is inefficient.
D) unattainable, but the economy is efficient.
A) attainable and the economy is efficient.
B) attainable, but the economy is inefficient.
C) unattainable and the economy is inefficient.
D) unattainable, but the economy is efficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A movement along the production possibilities curve would imply that:
A) the labor force has grown.
B) productivity has increased.
C) productivity has declined.
D) society has chosen a different set of outputs.
A) the labor force has grown.
B) productivity has increased.
C) productivity has declined.
D) society has chosen a different set of outputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If an economy is producing at a point inside a production possibilities curve:
A) the economy is efficient.
B) there is economic growth.
C) resources are unemployed.
D) resources are fully employed.
A) the economy is efficient.
B) there is economic growth.
C) resources are unemployed.
D) resources are fully employed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If an economy that produces capital and consumer goods is operating at a point on its production possibilities curve:
A) it is achieving full employment but not full production.
B) it is achieving full production but not full employment.
C) more capital goods can be produced only at the cost of some consumer goods.
D) the economy is incapable of achieving significant economic growth.
A) it is achieving full employment but not full production.
B) it is achieving full production but not full employment.
C) more capital goods can be produced only at the cost of some consumer goods.
D) the economy is incapable of achieving significant economic growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Assume that for Indy, one hour of study time in economics is perfectly substitutable for an hour of study time in calculus. Indy has exams in both subjects tomorrow and he determines that if he spends all of his time studying economics, he will receive scores of 96 on his economics exam and 45 on his calculus exam. If he studies only calculus, his economics score will be 81 and his calculus score will be 90. Based on this information and assuming that Indy has no better alternative use of his time, what is the opportunity cost of improving his economics score by one (1) point?
A) 1 point on his calculus exam
B) 1/3 point on his calculus exam
C) 3 points on his calculus exam
D) The opportunity cost cannot be determined with the information given.
A) 1 point on his calculus exam
B) 1/3 point on his calculus exam
C) 3 points on his calculus exam
D) The opportunity cost cannot be determined with the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which statement is an economic rationale for the law of increasing opportunity cost?
A) The economy is employing all of its available resources.
B) Many economic resources are better at producing one product than another.
C) In any economy, the state of technology is changing and resources are variable.
D) The economy is achieving productive efficiency by producing goods and services at the least cost.
A) The economy is employing all of its available resources.
B) Many economic resources are better at producing one product than another.
C) In any economy, the state of technology is changing and resources are variable.
D) The economy is achieving productive efficiency by producing goods and services at the least cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
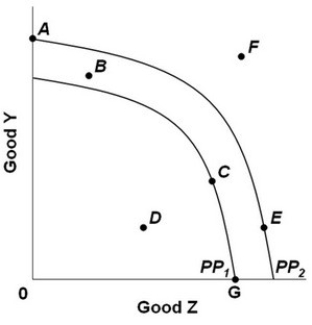 The graph above shows two production possibilities curves for a nation that produces two goods, Y and Z. PP1 and PP2 show the production possibilities for years 1 and 2. The nation's total production then decreased after year 2. This change could be represented by a move from:
The graph above shows two production possibilities curves for a nation that produces two goods, Y and Z. PP1 and PP2 show the production possibilities for years 1 and 2. The nation's total production then decreased after year 2. This change could be represented by a move from:A) F to A.
B) A to E.
C) F to B.
D) E to D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
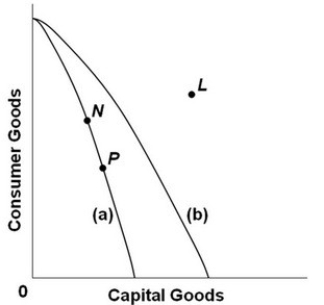
-Refer to the above production possibilities curves. Curve (a) is the current curve for the economy. The movement from curve (a) to curve (b) suggests:
A) a movement from unemployment to full employment.
B) an improvement in capital goods technology but not in consumer goods technology.
C) an improvement in consumer goods technology but not in capital goods technology.
D) a decline in the total output of this society.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
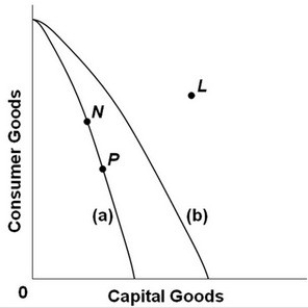
-Refer to the above production possibilities curves. Curve (a) is the current curve for the economy. Other things being equal, society's current choice of point P on curve (a) will:
A) allow it to achieve more rapid economic growth than would the choice of point N.
B) entail a slower rate of economic growth than would the choice of point N.
C) entail the same rate of growth as would the choice of point N.
D) be unobtainable because it exceeds the productive capacity of the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Suppose there are two economies, Alpha and Beta, which have the same production possibilities curves and are on the same point on each curve. If Beta then devotes more resources to investment goods than consumer goods when compared to Alpha, then in the future:
A) Alpha will experience greater economic growth than Beta.
B) Beta will experience greater economic growth than Alpha.
C) Alpha will not be able to achieve full employment or productive efficiency.
D) Beta will not be able to achieve full employment or productive efficiency
A) Alpha will experience greater economic growth than Beta.
B) Beta will experience greater economic growth than Alpha.
C) Alpha will not be able to achieve full employment or productive efficiency.
D) Beta will not be able to achieve full employment or productive efficiency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Economics is the study of the efficient use of scarce resources to achieve maximum satisfaction of economic wants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



