Deck 10: Accounting for Property, Plant, and Equipment
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/64
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Accounting for Property, Plant, and Equipment
1
A building owned by a corporation is always classified as property, plant and equipment.
False
2
The cash or cash equivalent price of items classified as property, plant and equipment best measures the value of the asset on the date of acquisition.
True
3
When land has been purchased for the purpose of constructing a new building, all costs incurred in connection with preparing the land for excavation are considered building costs.
False
4
The interest costs on funds used to acquire an asset should not be capitalized even if a significant period of time is required to bring the asset to a condition or location necessary for its intended use.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
An asset should be recorded at the fair market value of the consideration given up to acquire it or at its fair market value, whichever is higher.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If a capital expenditure related to a machine increases the useful life but does not improve its quality, the expenditure may be debited to accumulated depreciation rather than to the asset account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
An asset's cost less its salvage value is referred to as the depreciable base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Physical factors such as wear and tear set the outside limit for the service life of an asset.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Whenever the economic nature of the asset is the primary determinant of service life, maintenance plays an extremely vital role in prolonging service life.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Companies that desire low depreciation during periods of low productivity and high depreciation during high productivity either adopt or switch to a declining-balance method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The straight-line depreciation method is used most often in actual practice because the assumptions upon which it is based apply to most plant assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Under the declining-balance depreciation method, salvage value is considered only in computing the amount of depreciation for the final year(s) of an asset's service life.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If one of the estimates used in computing depreciation is subsequently found to require adjustments, no change in prior years' financial statements is required.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If an exchange of nonmonetary assets occurs and the exchange has commercial substance, it is presumed that the earnings process related to these assets is completed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
When an exchange of nonmonetary assets with no commercial substance results in a gain and insignificant boot is included as a part of the transaction, the gain to be recognized is limited to the amount of the boot received.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The amount of interest to be capitalized is the higher of actual interest cost incurred during the period or avoidable interest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Plant assets may properly include
A) deposits on machinery not yet received.
B) idle equipment awaiting sale.
C) land held for possible use as a future plant site.
D) none of these.
A) deposits on machinery not yet received.
B) idle equipment awaiting sale.
C) land held for possible use as a future plant site.
D) none of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Cotton Hotel Corporation recently purchased Holiday Hotel and the land on which it is located with a plan to tear down the Holiday Hotel and build a new luxury hotel on the site. The cost of the Holiday Hotel should be
A) depreciated over the period from acquisition to the date the hotel is scheduled to be torn down.
B) written off as an extraordinary loss in the year the hotel is torn down.
C) capitalized as part of the cost of the land.
D) capitalized as part of the cost of the new hotel.
A) depreciated over the period from acquisition to the date the hotel is scheduled to be torn down.
B) written off as an extraordinary loss in the year the hotel is torn down.
C) capitalized as part of the cost of the land.
D) capitalized as part of the cost of the new hotel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If a corporation purchases a lot and building and subsequently tears down the building and uses the property as a parking lot, the proper accounting treatment of the cost of the building would depend on the
A) significance of the cost allocated to the building in relation to the combined cost of the lot and building.
B) length of time for which the building was held prior to its demolition.
C) contemplated future use of the parking lot.
D) intention of management for the property when the building was acquired.
A) significance of the cost allocated to the building in relation to the combined cost of the lot and building.
B) length of time for which the building was held prior to its demolition.
C) contemplated future use of the parking lot.
D) intention of management for the property when the building was acquired.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Historical cost is the basis advocated for recording the acquisition of property, plant, and equipment for all of the following reasons except
A) at the date of acquisition, cost reflects fair market value.
B) property, plant, and equipment items are always acquired at their original historical cost.
C) historical cost involves actual transactions and, as such, is the most reliable basis.
D) gains and losses should not be anticipated but should be recognized when the asset is sold.
A) at the date of acquisition, cost reflects fair market value.
B) property, plant, and equipment items are always acquired at their original historical cost.
C) historical cost involves actual transactions and, as such, is the most reliable basis.
D) gains and losses should not be anticipated but should be recognized when the asset is sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following is not a necessary characteristic for an item to be classified as property, plant, and equipment?
A) Usually subject to depreciation
B) Characterized by physical substance
C) Can be used in operations for at least 5 years
D) Not acquired for resale
A) Usually subject to depreciation
B) Characterized by physical substance
C) Can be used in operations for at least 5 years
D) Not acquired for resale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When funds are borrowed to pay for construction of assets that qualify for capitalization of interest, the excess funds not needed to pay for construction may be temporarily invested in interest-bearing securities. Interest earned on these temporary investments should be
A) offset against interest cost incurred during construction.
B) used to reduce the cost of assets being constructed.
C) multiplied by an appropriate interest rate to determine the amount of interest to be capitalized.
D) recognized as revenue of the period.
A) offset against interest cost incurred during construction.
B) used to reduce the cost of assets being constructed.
C) multiplied by an appropriate interest rate to determine the amount of interest to be capitalized.
D) recognized as revenue of the period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following most accurately reflects the concept of depreciation as used in accounting?
A) The process of charging the decline in value of an economic resource to income in the period in which the benefit occurred.
B) The process of allocating the cost of tangible assets to expense in a systematic and rational manner to those periods expected to benefit from the use of the asset.
C) A method of allocating asset cost to an expense account in a manner which closely matches the physical deterioration of the tangible asset involved.
D) An accounting concept that allocates the portion of an asset used up during the year to the contra asset account for the purpose of properly recording the fair market value of tangible assets.
A) The process of charging the decline in value of an economic resource to income in the period in which the benefit occurred.
B) The process of allocating the cost of tangible assets to expense in a systematic and rational manner to those periods expected to benefit from the use of the asset.
C) A method of allocating asset cost to an expense account in a manner which closely matches the physical deterioration of the tangible asset involved.
D) An accounting concept that allocates the portion of an asset used up during the year to the contra asset account for the purpose of properly recording the fair market value of tangible assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The major difference between the service life of an asset and its physical life is that
A) service life refers to the time an asset will be used by a company and physical life refers to how long the asset will last.
B) physical life is the life of an asset without consideration of salvage value and service life requires the use of salvage value.
C) physical life is always longer than service life.
D) service life refers to the length of time an asset is of use to its original owner, while physical life refers to how long the asset will be used by all owners.
A) service life refers to the time an asset will be used by a company and physical life refers to how long the asset will last.
B) physical life is the life of an asset without consideration of salvage value and service life requires the use of salvage value.
C) physical life is always longer than service life.
D) service life refers to the length of time an asset is of use to its original owner, while physical life refers to how long the asset will be used by all owners.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A graph is set up with "yearly depreciation expense" on the vertical axis and "time" on the horizontal axis. Assuming linear relationships, how would the graphs for straight-line and sum-of-the-years'-digits depreciation, respectively, be drawn?
A) Vertically and sloping down to the right
B) Vertically and sloping up to the right
C) Horizontally and sloping down to the right
D) Horizontally and sloping up to the right
A) Vertically and sloping down to the right
B) Vertically and sloping up to the right
C) Horizontally and sloping down to the right
D) Horizontally and sloping up to the right

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Quayle Company acquired machinery on January 1, 2003 which it depreciated under the straight-line method with an estimated life of fifteen years and no salvage value. On January 1, 2008, Quayle estimated that the remaining life of this machinery was six years with no salvage value. How should this change be accounted for by Quayle?
A) As a prior period adjustment
B) As the cumulative effect of a change in accounting principle in 2008
C) By setting future annual depreciation equal to one-sixth of the book value on January 1, 2008
D) By continuing to depreciate the machinery over the original fifteen year life
A) As a prior period adjustment
B) As the cumulative effect of a change in accounting principle in 2008
C) By setting future annual depreciation equal to one-sixth of the book value on January 1, 2008
D) By continuing to depreciate the machinery over the original fifteen year life

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following nonmonetary exchange transactions represents a culmination of the earning process?
A) Exchange of assets with no difference in future cash flows.
B) Exchange of products by companies in the same line of business with no difference in future cash flows.
C) Exchange of assets with a difference in future cash flows..
D) Exchange of an equivalent interest in similar productive assets that causes the companies involved to remain in essentially the same economic position.
A) Exchange of assets with no difference in future cash flows.
B) Exchange of products by companies in the same line of business with no difference in future cash flows.
C) Exchange of assets with a difference in future cash flows..
D) Exchange of an equivalent interest in similar productive assets that causes the companies involved to remain in essentially the same economic position.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The cost of a nonmonetary asset acquired in exchange for another nonmonetary asset and the exchange has commercial substance is usually recorded at
A) the fair value of the asset given up, and a loss is recognized.
B) the book value of the asset given up, and a loss may be recognized.
C) the fair value of the asset received if it is equally reliable as the fair value of the asset given up.
D) either the fair value of the asset given up or the asset received, whichever one results in the largest gain (smallest loss) to the company.
A) the fair value of the asset given up, and a loss is recognized.
B) the book value of the asset given up, and a loss may be recognized.
C) the fair value of the asset received if it is equally reliable as the fair value of the asset given up.
D) either the fair value of the asset given up or the asset received, whichever one results in the largest gain (smallest loss) to the company.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The King-Kong Corporation exchanges one plant asset for another plant asset and gives cash in the exchange. The exchange is not expected to cause a material change in the future cash flows for either entity. If a gain on the disposal of the old asset is indicated, the gain will
A) be reported in the Other Revenues and Gains section of the income statement.
B) effectively reduce the amount to be recorded as the cost of the new asset.
C) effectively increase the amount to be recorded as the cost of the new asset.
D) be credited directly to the owner's capital account.
A) be reported in the Other Revenues and Gains section of the income statement.
B) effectively reduce the amount to be recorded as the cost of the new asset.
C) effectively increase the amount to be recorded as the cost of the new asset.
D) be credited directly to the owner's capital account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following statements is true regarding capitalization of interest?
A) Interest cost capitalized in connection with the purchase of land to be used as a building site should be debited to the land account and not to the building account.
B) The amount of interest cost capitalized during the period should not exceed the actual interest cost incurred.
C) When excess borrowed funds not immediately needed for construction are temporarily invested, any interest earned should be offset against interest cost incurred when determining the amount of interest cost to be capitalized.
D) The minimum amount of interest to be capitalized is determined by multiplying a weighted average interest rate by the amount of average accumulated expenditures on qualifying assets during the period.
A) Interest cost capitalized in connection with the purchase of land to be used as a building site should be debited to the land account and not to the building account.
B) The amount of interest cost capitalized during the period should not exceed the actual interest cost incurred.
C) When excess borrowed funds not immediately needed for construction are temporarily invested, any interest earned should be offset against interest cost incurred when determining the amount of interest cost to be capitalized.
D) The minimum amount of interest to be capitalized is determined by multiplying a weighted average interest rate by the amount of average accumulated expenditures on qualifying assets during the period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The cost of the land that should be recorded by Seiler Co. is
A) $660,480.
B) $666,880.
C) $669,880.
D) $676,280.
A) $660,480.
B) $666,880.
C) $669,880.
D) $676,280.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The cost of the building that should be recorded by Seiler Co. is
A) $2,403,800.
B) $2,404,840.
C) $2,413,200.
D) $2,414,240.
A) $2,403,800.
B) $2,404,840.
C) $2,413,200.
D) $2,414,240.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
On February 1, 2008, Morgan Corporation purchased a parcel of land as a factory site for $200,000. An old building on the property was demolished, and construction began on a new building which was completed on November 1, 2008. Costs incurred during this period are listed below:
 Morgan should record the cost of the land and new building, respectively, as
Morgan should record the cost of the land and new building, respectively, as
A) $225,000 and $1,115,000.
B) $210,000 and $1,130,000.
C) $210,000 and $1,125,000.
D) $215,000 and $1,125,000.
 Morgan should record the cost of the land and new building, respectively, as
Morgan should record the cost of the land and new building, respectively, asA) $225,000 and $1,115,000.
B) $210,000 and $1,130,000.
C) $210,000 and $1,125,000.
D) $215,000 and $1,125,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
On December 1, Wynne Corporation exchanged 2,000 shares of its $25 par value common stock held in treasury for a parcel of land to be held for a future plant site. The treasury shares were acquired by Wynne at a cost of $40 per share, and on the exchange date the common shares of Wynne had a fair market value of $50 per share. Wynne received $6,000 for selling scrap when an existing building on the property was removed from the site. Based on these facts, the land should be capitalized at
A) $74,000.
B) $80,000.
C) $94,000.
D) $100,000.
A) $74,000.
B) $80,000.
C) $94,000.
D) $100,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
On April 1, Renner Corporation purchased for $855,000 a tract of land on which was located a warehouse and office building. The following data were collected concerning the
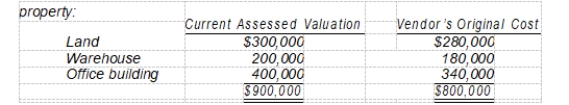 What are the appropriate amounts that Renner should record for the land, warehouse, and office building, respectively?
What are the appropriate amounts that Renner should record for the land, warehouse, and office building, respectively?
A) Land, $280,000; warehouse, $180,000; office building, $340,000.
B) Land, $300,000; warehouse, $200,000; office building, $400,000.
C) Land, $299,250; warehouse, $192,375; office building, $363,375.
D) Land, $285,000; warehouse, $190,000; office building, $380,000.
 What are the appropriate amounts that Renner should record for the land, warehouse, and office building, respectively?
What are the appropriate amounts that Renner should record for the land, warehouse, and office building, respectively?A) Land, $280,000; warehouse, $180,000; office building, $340,000.
B) Land, $300,000; warehouse, $200,000; office building, $400,000.
C) Land, $299,250; warehouse, $192,375; office building, $363,375.
D) Land, $285,000; warehouse, $190,000; office building, $380,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Herman Company exchanged 400 shares of Daily Company common stock, which Herman was holding as an investment, for equipment from West Company. The Daily Company common stock, which had been purchased by Herman for $50 per share, had a quoted market value of $58 per share at the date of exchange. The equipment had a recorded amount on West's books of $21,000. What journal entry should Herman make to record this exchange?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
On January 1, 2007, Carson Company purchased a new machine for $2,100,000. The new machine has an estimated useful life of nine years and the salvage value was estimated to be $75,000. Depreciation was computed on the sum-of-the-years'-digits method. What amount should be shown in Carson's balance sheet at December 31, 2008, net of accumulated depreciation, for this machine?
A) $1,695,000
B) $1,335,000
C) $1,306,666
D) $1,244,250
A) $1,695,000
B) $1,335,000
C) $1,306,666
D) $1,244,250

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Sears Corporation, which has a calendar year accounting period, purchased a new machine for $40,000 on April 1, 2003. At that time Sears expected to use the machine for nine years and then sell it for $4,000. The machine was sold for $22,000 on Sept. 30, 2008. Assuming straight-line depreciation, no depreciation in the year of acquisition, and a full year of depreciation in the year of retirement, the gain to be recognized at the time of sale would be
A) $4,000.
B) $3,000.
C) $2,000.
D) $0.
A) $4,000.
B) $3,000.
C) $2,000.
D) $0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
On January 1, 2008, the Accumulated Depreciation-Machinery account of a particular company showed a balance of $370,000. At the end of 2008, after the adjusting entries were posted, it showed a balance of $395,000. During 2008, one of the machines which cost $125,000 was sold for $60,500 cash. This resulted in a loss of $4,000. Assuming that no other assets were disposed of during the year, how much was depreciation expense for 2008?
A) $85,500
B) $93,500
C) $25,000
D) $60,500
A) $85,500
B) $93,500
C) $25,000
D) $60,500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
During 2008, Geiger Co. sold equipment that had cost $98,000 for $58,800. This resulted in a gain of $4,300. The balance in Accumulated Depreciation-Equipment was $325,000 on January 1, 2008, and $310,000 on December 31. No other equipment was disposed of during 2008. Depreciation expense for 2008 was
A) $15,000.
B) $19,300.
C) $28,500.
D) $58,500.
A) $15,000.
B) $19,300.
C) $28,500.
D) $58,500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Jantz Corporation purchased a machine on July 1, 2005, for $750,000. The machine was estimated to have a useful life of 10 years with an estimated salvage value of $42,000. During 2008, it became apparent that the machine would become uneconomical after December 31, 2012, and that the machine would have no scrap value. Accumulated depreciation on this machine as of December 31, 2007, was $177,000. What should be the charge for depreciation in 2008 under generally accepted accounting principles?
A) $106,200
B) $114,600
C) $123,000
D) $143,250
A) $106,200
B) $114,600
C) $123,000
D) $143,250

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Weston Company purchased a tooling machine on January 3, 2001 for $500,000. The machine was being depreciated on the straight-line method over an estimated useful life of 10 years, with no salvage value. At the beginning of 2008, the company paid $125,000 to overhaul the machine. As a result of this improvement, the company estimated that the useful life of the machine would be extended an additional 5 years (15 years total). What should be the depreciation expense recorded for the machine in 2008?
A) $34,375
B) $41,667
C) $50,000
D) $55,000
A) $34,375
B) $41,667
C) $50,000
D) $55,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Klein Co. purchased machinery on January 2, 2002, for $440,000. The straight-line method is used and useful life is estimated to be 10 years, with a $40,000 salvage value. At the beginning of 2008 Klein spent $96,000 to overhaul the machinery. After the overhaul, Klein estimated that the useful life would be extended 4 years (14 years total), and the salvage value would be $20,000. The depreciation expense for 2008 should be
A) $28,250.
B) $34,500.
C) $40,000.
D) $37,000.
A) $28,250.
B) $34,500.
C) $40,000.
D) $37,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Thucydides Company purchased a new machine on May 1, 1999, for $25,000. At the time of acquisition, the machine was estimated to have a useful life of 10 years and an estimated salvage value of $1,000. The company has recorded monthly depreciation using the straight-line method. On March 1, 2008, the machine was sold for $800. What should be the loss recognized from the sale of the machine?
A) $0
B) $2,000
C) $3,000
D) $3,400
A) $0
B) $2,000
C) $3,000
D) $3,400

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Plato Corporation purchased a machine with a cost of $165,000 and a salvage value of $9,000 on April 1, 2008. The machine will be depreciated over a 12-year useful life using the sum-of-the-years'-digits method. The amount of depreciation Plato Corporation would record for the year ended 12/31/09 would be
A) $22,000.
B) $24,000.
C) $16,500.
D) $22,500.
A) $22,000.
B) $24,000.
C) $16,500.
D) $22,500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
On December 1, 2008, Fiene Company acquired a new delivery truck in exchange for an old delivery truck that it had acquired in 2005. The old truck was purchased for $35,000 and had a book value of $13,300. On the date of the exchange, the old truck had a market value of $14,000. In addition, Fiene paid $45,500 cash for the new truck, which had a list price of $63,000. The exchange lacked commercial substance. At what amount should Fiene record the new truck for financial accounting purposes?
A) $45,500
B) $58,800
C) $59,500
D) $63,000
A) $45,500
B) $58,800
C) $59,500
D) $63,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A machine cost $120,000, has annual depreciation of $20,000, and has accumulated depreciation of $90,000 on December 31, 2007. On April 1, 2008, when the machine has a market value of $27,500, it is exchanged for a machine with a fair value of $135,000 and the proper amount of cash is paid. The exchange lacked commercial substance.
-The gain to be recorded on the exchange is
A) $0.
B) $2,500 gain.
C) $5,000 gain.
D) $15,000 gain.
-The gain to be recorded on the exchange is
A) $0.
B) $2,500 gain.
C) $5,000 gain.
D) $15,000 gain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A machine cost $120,000, has annual depreciation of $20,000, and has accumulated depreciation of $90,000 on December 31, 2007. On April 1, 2008, when the machine has a market value of $27,500, it is exchanged for a machine with a fair value of $135,000 and the proper amount of cash is paid. The exchange lacked commercial substance.
-The new machine should be recorded at
A) $107,500.
B) $122,500.
C) $132,500.
D) $135,000.
-The new machine should be recorded at
A) $107,500.
B) $122,500.
C) $132,500.
D) $135,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Equipment that cost $66,000 and has accumulated depreciation of $30,000 is exchanged for equipment with a fair value of $48,000 and $12,000 cash is received. The exchange lacked commercial substance.
-The gain to be recognized from the exchange is
A) $4,800 gain.
B) $6,000 gain.
C) $18,000 gain.
D) $24,000 gain.
-The gain to be recognized from the exchange is
A) $4,800 gain.
B) $6,000 gain.
C) $18,000 gain.
D) $24,000 gain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Equipment that cost $66,000 and has accumulated depreciation of $30,000 is exchanged for equipment with a fair value of $48,000 and $12,000 cash is received. The exchange lacked commercial substance.
-The new equipment should be recorded at
A) $48,000.
B) $36,000.
C) $30,000.
D) $28,800.
-The new equipment should be recorded at
A) $48,000.
B) $36,000.
C) $30,000.
D) $28,800.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Glen Inc. and Armstrong Co. have an exchange with no commercial substance. The asset given up by Glen Inc. has a book value of $12,000 and a fair market value of $15,000. The asset given up by Armstrong Co. has a book value of $20,000 and a fair market value of $19,000. Boot of $4,000 is received by Armstrong Co.
-What amount should Glen Inc. record for the asset received?
A) $15,000
B) $16,000
C) $19,000
D) $20,000
-What amount should Glen Inc. record for the asset received?
A) $15,000
B) $16,000
C) $19,000
D) $20,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Glen Inc. and Armstrong Co. have an exchange with no commercial substance. The asset given up by Glen Inc. has a book value of $12,000 and a fair market value of $15,000. The asset given up by Armstrong Co. has a book value of $20,000 and a fair market value of $19,000. Boot of $4,000 is received by Armstrong Co.
-What amount should Armstrong Co. record for the asset received?
A) $15,000
B) $16,000
C) $19,000
D) $20,000
-What amount should Armstrong Co. record for the asset received?
A) $15,000
B) $16,000
C) $19,000
D) $20,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Hardin Company received $40,000 in cash and a used computer with a fair value of $120,000 from Page Corporation for Hardin Company's existing computer having a fair value of $160,000 and an undepreciated cost of $150,000 recorded on its books. The transaction has no commercial substance. How much gain should Hardin recognize on this exchange, and at what amount should the acquired computer be recorded, respectively?
A) $0 and $110,000
B) $769 and $110,769
C) $10,000 and $120,000
D) $40,000 and $150,000
A) $0 and $110,000
B) $769 and $110,769
C) $10,000 and $120,000
D) $40,000 and $150,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Jeter Company purchased a new machine on May 1, 2000 for $176,000. At the time of acquisition, the machine was estimated to have a useful life of ten years and an estimated salvage value of $8,000. The company has recorded monthly depreciation using the straight-line method. On March 1, 2009, the machine was sold for $24,000. What should be the loss recognized from the sale of the machine?
A) $0
B) $3,600
C) $8,000
D) $11,600
A) $0
B) $3,600
C) $8,000
D) $11,600

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Rubber Soul Company reported the following data:
 What is Rubber Soul's asset turnover for 2009?
What is Rubber Soul's asset turnover for 2009?
A) 1.04
B) 1.07
C) 1.21
D) 1.44
 What is Rubber Soul's asset turnover for 2009?
What is Rubber Soul's asset turnover for 2009?A) 1.04
B) 1.07
C) 1.21
D) 1.44

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Wheeler Corporation constructed a building at a cost of $20,000,000. Average accumulated expenditures were $8,000,000, actual interest was $ 1,200,000, and avoidable interest was $600,000. If the salvage value is $1,600,000, and the useful life is 40 years, depreciation expense for the first full year using the straight-line method is
A) $475,000.
B) $490,000.
C) $515,000.
D) $675,000.
A) $475,000.
B) $490,000.
C) $515,000.
D) $675,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
On March 1, 2008, Dennis Company purchased land for an office site by paying $540,000 cash. Dennis began construction on the office building on March 1. The following expenditures were incurred for construction:
 The office was completed and ready for occupancy on July 1. To help pay for construction, $720,000 was borrowed on March 1, 2008 on a 9%, 3 -year note payable. Other than the construction note, the only debt outstanding during 2008 was a $300,000, 12%, 6-year note payable dated January 1, 2008.
The office was completed and ready for occupancy on July 1. To help pay for construction, $720,000 was borrowed on March 1, 2008 on a 9%, 3 -year note payable. Other than the construction note, the only debt outstanding during 2008 was a $300,000, 12%, 6-year note payable dated January 1, 2008.
-The actual interest cost incurred during 2008 was
A) $90,000.
B) $100,800.
C) $50,400.
D) $84,000.
 The office was completed and ready for occupancy on July 1. To help pay for construction, $720,000 was borrowed on March 1, 2008 on a 9%, 3 -year note payable. Other than the construction note, the only debt outstanding during 2008 was a $300,000, 12%, 6-year note payable dated January 1, 2008.
The office was completed and ready for occupancy on July 1. To help pay for construction, $720,000 was borrowed on March 1, 2008 on a 9%, 3 -year note payable. Other than the construction note, the only debt outstanding during 2008 was a $300,000, 12%, 6-year note payable dated January 1, 2008.-The actual interest cost incurred during 2008 was
A) $90,000.
B) $100,800.
C) $50,400.
D) $84,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
On March 1, 2008, Dennis Company purchased land for an office site by paying $540,000 cash. Dennis began construction on the office building on March 1. The following expenditures were incurred for construction:
 The office was completed and ready for occupancy on July 1. To help pay for construction, $720,000 was borrowed on March 1, 2008 on a 9%, 3 -year note payable. Other than the construction note, the only debt outstanding during 2008 was a $300,000, 12%, 6-year note payable dated January 1, 2008.
The office was completed and ready for occupancy on July 1. To help pay for construction, $720,000 was borrowed on March 1, 2008 on a 9%, 3 -year note payable. Other than the construction note, the only debt outstanding during 2008 was a $300,000, 12%, 6-year note payable dated January 1, 2008.
-Assume the weighted-average accumulated expenditures for the construction project are $870,000. The amount of interest cost to be capitalized during 2008 is
A) $78,300.
B) $82,800.
C) $90,000.
D) $100,800.
 The office was completed and ready for occupancy on July 1. To help pay for construction, $720,000 was borrowed on March 1, 2008 on a 9%, 3 -year note payable. Other than the construction note, the only debt outstanding during 2008 was a $300,000, 12%, 6-year note payable dated January 1, 2008.
The office was completed and ready for occupancy on July 1. To help pay for construction, $720,000 was borrowed on March 1, 2008 on a 9%, 3 -year note payable. Other than the construction note, the only debt outstanding during 2008 was a $300,000, 12%, 6-year note payable dated January 1, 2008.-Assume the weighted-average accumulated expenditures for the construction project are $870,000. The amount of interest cost to be capitalized during 2008 is
A) $78,300.
B) $82,800.
C) $90,000.
D) $100,800.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
During 2008, Aber Corporation constructed assets costing $1,000,000. The weighted-average accumulated expenditures on these assets during 2008 was $600,000. To help pay for construction, $440,000 was borrowed at 10% on January 1, 2008, and funds not needed for construction were temporarily invested in short-term securities, yielding $9,000 in interest revenue. Other than the construction funds borrowed, the only other debt outstanding during the year was a $ 500,000, 10-year, 9% note payable dated January 1, 2002. What is the amount of interest that should be capitalized by Aber during 2008?
A) $60,000
B) $30,000
C) $58,400
D) $94,400
A) $60,000
B) $30,000
C) $58,400
D) $94,400

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Petty County owned an idle parcel of real estate consisting of land and a factory building. Petty gave title to this realty to Larson Co. as an incentive for Larson to establish manufacturing operations in Petty County. Larson paid nothing for this realty, which had a fair market value of $250,000 at the date of the grant. Larson should record this nonmonetary transaction as a
A) memo entry only.
B) credit to Contribution Revenue for $250,000.
C) credit to extraordinary income for $250,000.
D) credit to Donated Capital for $250,000.
A) memo entry only.
B) credit to Contribution Revenue for $250,000.
C) credit to extraordinary income for $250,000.
D) credit to Donated Capital for $250,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Mack Co. takes a full year's depreciation expense in the year of an asset's acquisition and no depreciation expense in the year of disposition. Data relating to one of Mack's depreciable assets at December 31, 2008 are as follows:
 Using the same depreciation method as used in 2006, 2007, and 2008, how much depreciation expense should Mack record in 2009 for this asset?
Using the same depreciation method as used in 2006, 2007, and 2008, how much depreciation expense should Mack record in 2009 for this asset?
A) $16,000
B) $24,000
C) $28,000
D) $32,000
 Using the same depreciation method as used in 2006, 2007, and 2008, how much depreciation expense should Mack record in 2009 for this asset?
Using the same depreciation method as used in 2006, 2007, and 2008, how much depreciation expense should Mack record in 2009 for this asset?A) $16,000
B) $24,000
C) $28,000
D) $32,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Gray Football Co. had a player contract with Vance that is recorded in its books at $3,600,000 on July 1, 2008. Day Football Co. had a player contract with Simms that is recorded in its books at $4,500,000 on July 1, 2008. On this date, Gray traded Vance to Day for Simms and paid a cash difference of $450,000. The fair value of the Simms contract was $5,400,000 on the exchange date. The exchange had no commercial substance. After the exchange, the Simms contract should be recorded in Gray's books at
A) $4,050,000.
B) $4,500,000.
C) $4,950,000.
D) $5,400,000.
A) $4,050,000.
B) $4,500,000.
C) $4,950,000.
D) $5,400,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Reed Co. exchanged nonmonetary assets with Wilton Co. No cash was exchanged and the exchange had no commercial substance. The carrying amount of the asset surrendered by Reed exceeded both the fair value of the asset received and Wilton's carrying amount of that asset. Reed should recognize the difference between the carrying amount of the asset it surrendered and
A) the fair value of the asset it received as a loss.
B) the fair value of the asset it received as a gain.
C) Wilton's carrying amount of the asset it received as a loss.
D) Wilton's carrying amount of the asset it received as a gain.
A) the fair value of the asset it received as a loss.
B) the fair value of the asset it received as a gain.
C) Wilton's carrying amount of the asset it received as a loss.
D) Wilton's carrying amount of the asset it received as a gain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A company is constructing an asset for its own use. Construction began in 2007. The asset is being financed entirely with a specific new borrowing. Construction expenditures were made in 2007 and 2008 at the end of each quarter. The total amount of interest cost capitalized in 2008 should be determined by applying the interest rate on the specific new borrowing to the
A) total accumulated expenditures for the asset in 2007 and 2008.
B) average accumulated expenditures for the asset in 2007 and 2008.
C) average expenditures for the asset in 2008.
D) total expenditures for the asset in 2008.
A) total accumulated expenditures for the asset in 2007 and 2008.
B) average accumulated expenditures for the asset in 2007 and 2008.
C) average expenditures for the asset in 2008.
D) total expenditures for the asset in 2008.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



