Deck 19: Appendix A: Accounting and the Time Value of Money
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/31
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: Appendix A: Accounting and the Time Value of Money
1
Which of the following transactions would require the use of the present value of an annuity due concept in order to calculate the present value of the asset obtained or liability owed at the date of incurrence?
A) A capital lease is entered into with the initial lease payment due upon the signing of the lease agreement.
B) A capital lease is entered into with the initial lease payment due one month subse-quent to the signing of the lease agreement.
C) A ten-year 8% bond is issued on January 2 with interest payable semiannually on July 1 and January 1 yielding 7%.
D) A ten-year 8% bond is issued on January 2 with interest payable semiannually on July 1 and January 1 yielding 9%.
A) A capital lease is entered into with the initial lease payment due upon the signing of the lease agreement.
B) A capital lease is entered into with the initial lease payment due one month subse-quent to the signing of the lease agreement.
C) A ten-year 8% bond is issued on January 2 with interest payable semiannually on July 1 and January 1 yielding 7%.
D) A ten-year 8% bond is issued on January 2 with interest payable semiannually on July 1 and January 1 yielding 9%.
A capital lease is entered into with the initial lease payment due upon the signing of the lease agreement.
2
On June 1, 2008, Walsh Company sold some equipment to Fischer Company. The two companies entered into an installment sales contract at a rate of 8%. The contract required 8 equal annual payments with the first payment due on June 1, 2008. What type of compound interest table is appropriate for this situation?
A) Present value of an annuity due of 1 table.
B) Present value of an ordinary annuity of 1 table.
C) Future amount of an ordinary annuity of 1 table.
D) Future amount of 1 table.
A) Present value of an annuity due of 1 table.
B) Present value of an ordinary annuity of 1 table.
C) Future amount of an ordinary annuity of 1 table.
D) Future amount of 1 table.
Present value of an annuity due of 1 table.
3
Which of the following transactions would best use the present value of an annuity due of 1 table?
A) Diamond Bar, Inc. rents a truck for 5 years with annual rental payments of $20,000 to be made at the beginning of each year.
B) Michener Co. rents a warehouse for 7 years with annual rental payments of $120,000 to be made at the end of each year.
C) Durant, Inc. borrows $20,000 and has agreed to pay back the principal plus interest in three years.
D) Babbitt, Inc. wants to deposit a lump sum to accumulate $50,000 for the construction of a new parking lot in 4 years.
A) Diamond Bar, Inc. rents a truck for 5 years with annual rental payments of $20,000 to be made at the beginning of each year.
B) Michener Co. rents a warehouse for 7 years with annual rental payments of $120,000 to be made at the end of each year.
C) Durant, Inc. borrows $20,000 and has agreed to pay back the principal plus interest in three years.
D) Babbitt, Inc. wants to deposit a lump sum to accumulate $50,000 for the construction of a new parking lot in 4 years.
Diamond Bar, Inc. rents a truck for 5 years with annual rental payments of $20,000 to be made at the beginning of each year.
4
On December 1, 2008, Michael Hess Company sold some machinery to Shawn Keling Company. The two companies entered into an installment sales contract at a predetermined interest rate. The contract required four equal annual payments with the first payment due on December 1, 2008, the date of the sale. What present value concept is appropriate for this situation?
A) Future amount of an annuity of 1 for four periods
B) Future amount of 1 for four periods
C) Present value of an ordinary annuity of 1 for four periods
D) Present value of an annuity due of 1 for four periods.
A) Future amount of an annuity of 1 for four periods
B) Future amount of 1 for four periods
C) Present value of an ordinary annuity of 1 for four periods
D) Present value of an annuity due of 1 for four periods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If the number of periods is known, the interest rate is determined by
A) dividing the future value by the present value and looking for the quotient in the future value of 1 table.
B) dividing the future value by the present value and looking for the quotient in the present value of 1 table.
C) dividing the present value by the future value and looking for the quotient in the future value of 1 table.
D) multiplying the present value by the future value and looking for the product in the present value of 1 table.
A) dividing the future value by the present value and looking for the quotient in the future value of 1 table.
B) dividing the future value by the present value and looking for the quotient in the present value of 1 table.
C) dividing the present value by the future value and looking for the quotient in the future value of 1 table.
D) multiplying the present value by the future value and looking for the product in the present value of 1 table.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If the interest rate is 10%, the factor for the future value of annuity due of 1 for n = 5, i = 10% is equal to the factor for the future value of an ordinary annuity of 1 for n = 5, i = 10%
A) plus 1.10
B) minus 1.10
C) multiplied by 1.10
D) divided by 1.10
A) plus 1.10
B) minus 1.10
C) multiplied by 1.10
D) divided by 1.10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which statement is false?
A) The factor for the future value of an annuity due is found by multiplying the ordinary annuity table value by one plus the interest rate.
B) The factor for the present value of an annuity due is found by multiplying the ordinary annuity table value by one minus the interest rate.
C) The factor for the future value of an annuity due is found by subtracting 1.00000 from the ordinary annuity table value for one more period.
D) The factor for the present value of an annuity due is found by adding 1.00000 to the ordinary annuity table value for one less period.
A) The factor for the future value of an annuity due is found by multiplying the ordinary annuity table value by one plus the interest rate.
B) The factor for the present value of an annuity due is found by multiplying the ordinary annuity table value by one minus the interest rate.
C) The factor for the future value of an annuity due is found by subtracting 1.00000 from the ordinary annuity table value for one more period.
D) The factor for the present value of an annuity due is found by adding 1.00000 to the ordinary annuity table value for one less period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Ed Sloan wants to withdraw $20,000 (including principal) from an investment fund at the end of each year for five years. How should he compute his required initial investment at the beginning of the first year if the fund earns 10% compounded annually?
A) $20,000 times the future value of a 5-year, 10% ordinary annuity of 1.
B) $20,000 divided by the future value of a 5-year, 10% ordinary annuity of 1.
C) $20,000 times the present value of a 5-year, 10% ordinary annuity of 1.
D) $20,000 divided by the present value of a 5-year, 10% ordinary annuity of 1.
A) $20,000 times the future value of a 5-year, 10% ordinary annuity of 1.
B) $20,000 divided by the future value of a 5-year, 10% ordinary annuity of 1.
C) $20,000 times the present value of a 5-year, 10% ordinary annuity of 1.
D) $20,000 divided by the present value of a 5-year, 10% ordinary annuity of 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Ann Ruth wants to invest a certain sum of money at the end of each year for five years. The investment will earn 6% compounded annually. At the end of five years, she will need
A total of $40,000 accumulated. How should she compute her required annual invest-ment?
A) $40,000 times the future value of a 5-year, 6% ordinary annuity of 1.
B) $40,000 divided by the future value of a 5-year, 6% ordinary annuity of 1.
C) $40,000 times the present value of a 5-year, 6% ordinary annuity of 1.
D) $40,000 divided by the present value of a 5-year, 6% ordinary annuity of 1.
A total of $40,000 accumulated. How should she compute her required annual invest-ment?
A) $40,000 times the future value of a 5-year, 6% ordinary annuity of 1.
B) $40,000 divided by the future value of a 5-year, 6% ordinary annuity of 1.
C) $40,000 times the present value of a 5-year, 6% ordinary annuity of 1.
D) $40,000 divided by the present value of a 5-year, 6% ordinary annuity of 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If an annuity due and an ordinary annuity have the same number of equal payments and the same interest rates, then
A) the present value of the annuity due is less than the present value of the ordinary annuity.
B) the present value of the annuity due is greater than the present value of the ordinary annuity.
C) the future value of the annuity due is equal to the future value of the ordinary annuity.
D) the future value of the annuity due is less than the future value of the ordinary annuity.
A) the present value of the annuity due is less than the present value of the ordinary annuity.
B) the present value of the annuity due is greater than the present value of the ordinary annuity.
C) the future value of the annuity due is equal to the future value of the ordinary annuity.
D) the future value of the annuity due is less than the future value of the ordinary annuity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is false?
A) The future value of a deferred annuity is the same as the future value of an annuity not deferred.
B) A deferred annuity is an annuity in which the rents begin after a specified number of periods.
C) To compute the present value of a deferred annuity, we compute the present value of an ordinary annuity of 1 for the entire period and subtract the present value of the rents which were not received during the deferral period.
D) If the first rent is received at the end of the sixth period, it means the ordinary annuity is deferred for six periods.
A) The future value of a deferred annuity is the same as the future value of an annuity not deferred.
B) A deferred annuity is an annuity in which the rents begin after a specified number of periods.
C) To compute the present value of a deferred annuity, we compute the present value of an ordinary annuity of 1 for the entire period and subtract the present value of the rents which were not received during the deferral period.
D) If the first rent is received at the end of the sixth period, it means the ordinary annuity is deferred for six periods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Items 48 through 51 apply to the appropriate use of interest tables. Given below are the future value factors for 1 at 8% for one to five periods. Each of the items 48 to 51 is based on 8% interest compounded annually.
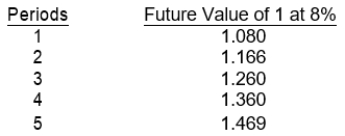
-What amount should be deposited in a bank account today to grow to $10,000 three years from today?
A) $10,000 × 1.260
B) $10,000 × 1.260 × 3
C) $10,000 ÷ 1.260
D) $10,000 ÷ 1.080 × 3

-What amount should be deposited in a bank account today to grow to $10,000 three years from today?
A) $10,000 × 1.260
B) $10,000 × 1.260 × 3
C) $10,000 ÷ 1.260
D) $10,000 ÷ 1.080 × 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Items 48 through 51 apply to the appropriate use of interest tables. Given below are the future value factors for 1 at 8% for one to five periods. Each of the items 48 to 51 is based on 8% interest compounded annually.

-If $3,000 is put in a savings account today, what amount will be available three years from today?
A) $3,000 ÷ 1.260
B) $3,000 × 1.260
C) $3,000 × 1.080 × 3
D) ($3,000 × 1.080) + ($3,000 × 1.166) + ($3,000 × 1.260)

-If $3,000 is put in a savings account today, what amount will be available three years from today?
A) $3,000 ÷ 1.260
B) $3,000 × 1.260
C) $3,000 × 1.080 × 3
D) ($3,000 × 1.080) + ($3,000 × 1.166) + ($3,000 × 1.260)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Items 48 through 51 apply to the appropriate use of interest tables. Given below are the future value factors for 1 at 8% for one to five periods. Each of the items 48 to 51 is based on 8% interest compounded annually.

-What amount will be in a bank account three years from now if $6,000 is invested each year for four years with the first investment to be made today?
A) ($6,000 × 1.260) + ($6,000 × 1.166) + ($6,000 × 1.080) + $6,000
B) $6,000 × 1.360 × 4
C) ($6,000 × 1.080) + ($6,000 × 1.166) + ($6,000 × 1.260) + ($6,000 × 1.360)
D) $6,000 × 1.080 × 4

-What amount will be in a bank account three years from now if $6,000 is invested each year for four years with the first investment to be made today?
A) ($6,000 × 1.260) + ($6,000 × 1.166) + ($6,000 × 1.080) + $6,000
B) $6,000 × 1.360 × 4
C) ($6,000 × 1.080) + ($6,000 × 1.166) + ($6,000 × 1.260) + ($6,000 × 1.360)
D) $6,000 × 1.080 × 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Items 48 through 51 apply to the appropriate use of interest tables. Given below are the future value factors for 1 at 8% for one to five periods. Each of the items 48 to 51 is based on 8% interest compounded annually.

-If $4,000 is put in a savings account today, what amount will be available six years from now?
A) $4,000 × 1.080 × 6
B) $4,000 × 1.080 × 1.469
C) $4,000 × 1.166 × 3
D) $4,000 × 1.260 × 2

-If $4,000 is put in a savings account today, what amount will be available six years from now?
A) $4,000 × 1.080 × 6
B) $4,000 × 1.080 × 1.469
C) $4,000 × 1.166 × 3
D) $4,000 × 1.260 × 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Items 52 through 55 apply to the appropriate use of present value tables. Given below are the present value factors for $1.00 discounted at 10% for one to five periods. Each of the items 52 to 55 is based on 10% interest compounded annually.
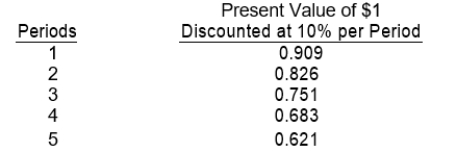
-If an individual put $4,000 in a savings account today, what amount of cash would be available two years from today?
A) $4,000 × 0.826
B) $4,000 × 0.826 × 2
C) $4,000 ÷ 0.826
D) $4,000 ÷ 0.909 × 2

-If an individual put $4,000 in a savings account today, what amount of cash would be available two years from today?
A) $4,000 × 0.826
B) $4,000 × 0.826 × 2
C) $4,000 ÷ 0.826
D) $4,000 ÷ 0.909 × 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Items 52 through 55 apply to the appropriate use of present value tables. Given below are the present value factors for $1.00 discounted at 10% for one to five periods. Each of the items 52 to 55 is based on 10% interest compounded annually.

-What is the present value today of $6,000 to be received six years from today?
A) $6,000 × 0.909 × 6
B) $6,000 × 0.751 × 2
C) $6,000 × 0.621 × 0.909
D) $6,000 × 0.683 × 3

-What is the present value today of $6,000 to be received six years from today?
A) $6,000 × 0.909 × 6
B) $6,000 × 0.751 × 2
C) $6,000 × 0.621 × 0.909
D) $6,000 × 0.683 × 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Items 52 through 55 apply to the appropriate use of present value tables. Given below are the present value factors for $1.00 discounted at 10% for one to five periods. Each of the items 52 to 55 is based on 10% interest compounded annually.

-What amount should be deposited in a bank today to grow to $3,000 three years from today?
A) $3,000 ÷ 0.751
B) $3,000 × 0.909 × 3
C) ($3,000 × 0.909) + ($3,000 × 0.826) + ($3,000 × 0.751)
D) $3,000 × 0.751

-What amount should be deposited in a bank today to grow to $3,000 three years from today?
A) $3,000 ÷ 0.751
B) $3,000 × 0.909 × 3
C) ($3,000 × 0.909) + ($3,000 × 0.826) + ($3,000 × 0.751)
D) $3,000 × 0.751

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Windsor Company will receive $100,000 in 7 years. If the appropriate interest rate is 10%, the present value of the $100,000 receipt is
A) $51,000.
B) $51,316.
C) $151,000.
D) $194,872.
A) $51,000.
B) $51,316.
C) $151,000.
D) $194,872.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Jensen Company will invest $200,000 today. The investment will earn 6% for 5 years, with no funds withdrawn. In 5 years, the amount in the investment fund is
A) $200,000.
B) $260,000.
C) $267,646.
D) $268,058.
A) $200,000.
B) $260,000.
C) $267,646.
D) $268,058.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Finley Company will receive $500,000 in 7 years. If the appropriate interest rate is 10%, the present value of the $500,000 receipt is
A) $255,000.
B) $256,580.
C) $755,000.
D) $974,360.
A) $255,000.
B) $256,580.
C) $755,000.
D) $974,360.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Jasper Company will invest $300,000 today. The investment will earn 6% for 5 years, with no funds withdrawn. In 5 years, the amount in the investment fund is
A) $300,000.
B) $390,000.
C) $401,469.
D) $402,087.
A) $300,000.
B) $390,000.
C) $401,469.
D) $402,087.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Schmitt Corporation will invest $10,000 every December 31st for the next six years (2008- 2013). If Schmitt will earn 12% on the investment, what amount will be in the investment fund on December 31, 2013?
A) $41,114
B) $46,048
C) $81,152
D) $90,890
A) $41,114
B) $46,048
C) $81,152
D) $90,890

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Linton Corporation will invest $10,000 every January 1st for the next six years (2008 - 2013). If Linton will earn 12% on the investment, what amount will be in the investment fund on December 31, 2013?
A) $41,114
B) $46,048
C) $81,152
D) $90,890
A) $41,114
B) $46,048
C) $81,152
D) $90,890

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
On January 1, 2007, Carly Company decided to begin accumulating a fund for asset replacement five years later. The company plans to make five annual deposits of $50,000 at 9% each January 1 beginning in 2007. What will be the balance in the fund, within $10, on January 1, 2012 (one year after the last deposit)? The following 9% interest factors may be used
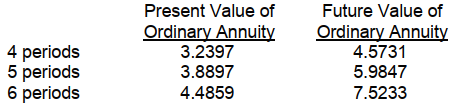
A) $326,166
B) $299,235
C) $272,500
D) $250,000
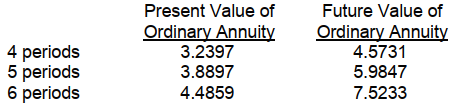
A) $326,166
B) $299,235
C) $272,500
D) $250,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
How much must be invested now to receive $10,000 for 15 years if the first $10,000 is received today and the rate is 9%? 
A) $80,607
B) $87,862
C) $150,000
D) $73,125

A) $80,607
B) $87,862
C) $150,000
D) $73,125

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Find the present value of an investment in plant and equipment if it is expected to provide annual earnings of $21,000 for 15 years and to have a resale value of $40,000 at the end of that period. Assume a 10% rate and earnings at year end. The present value of 1 at 10% for 15 periods is .23939. The present value of an ordinary annuity at 10% for 15 periods is 7.60608. The future value of 1 at 10% for 15 periods is 4.17725.
A) $159,728
B) $169,303
C) $185,276
D) $324,576
A) $159,728
B) $169,303
C) $185,276
D) $324,576

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
For which of the following transactions would the use of the present value of an ordinary annuity concept be appropriate in calculating the present value of the asset obtained or the liability owed at the date of incurrence?
A) A capital lease is entered into with the initial lease payment due one month subsequent to the signing of the lease agreement.
B) A capital lease is entered into with the initial lease payment due upon the signing of the lease agreement.
C) A ten-year 8% bond is issued on January 2 with interest payable semiannually on January 2 and July 1 yielding 7%.
D) A ten-year 8% bond is issued on January 2 with interest payable semiannually on January 2 and July 1 yielding 9%.
A) A capital lease is entered into with the initial lease payment due one month subsequent to the signing of the lease agreement.
B) A capital lease is entered into with the initial lease payment due upon the signing of the lease agreement.
C) A ten-year 8% bond is issued on January 2 with interest payable semiannually on January 2 and July 1 yielding 7%.
D) A ten-year 8% bond is issued on January 2 with interest payable semiannually on January 2 and July 1 yielding 9%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
On January 15, 2008, Flynn Corp. adopted a plan to accumulate funds for environmental improvements beginning July 1, 2012, at an estimated cost of $4,000,000. Flynn plans to make four equal annual deposits in a fund that will earn interest at 10% compounded annually. The first deposit was made on July 1, 2008. Future value factors are as follows:
 Flynn should make four annual deposits of
Flynn should make four annual deposits of
A) $711,618.
B) $782,779.
C) $862,069.
D) $1,000,000.
 Flynn should make four annual deposits of
Flynn should make four annual deposits ofA) $711,618.
B) $782,779.
C) $862,069.
D) $1,000,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
On January 1, 2008, Lex Co. sold goods to Eaton Company. Eaton signed a noninterest-bearing note requiring payment of $80,000 annually for seven years. The first payment was made on January 1, 2008. The prevailing rate of interest for this type of note at date of issuance was 10%. Information on present value factors is as follows:
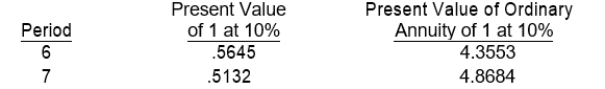 Lex should record sales revenue in January 2008 of
Lex should record sales revenue in January 2008 of
A) $428,419.
B) $389,472.
C) $348,424.
D) $285,600.
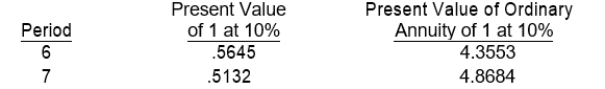 Lex should record sales revenue in January 2008 of
Lex should record sales revenue in January 2008 ofA) $428,419.
B) $389,472.
C) $348,424.
D) $285,600.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
On July 1, 2008, Ed Vance signed an agreement to operate as a franchisee of Kwik Foods, Inc., for an initial franchise fee of $180,000. Of this amount, $60,000 was paid when the agreement was signed and the balance is payable in four equal annual payments of $30,000 beginning July 1, 2009. The agreement provides that the down payment is not refundable and no future services are required of the franchisor. Vance's credit rating indicates that he can borrow money at 14% for a loan of this type. Information on present and future value factors is as follows:
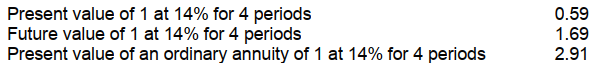 Vance should record the acquisition cost of the franchise on July 1, 2008 at
Vance should record the acquisition cost of the franchise on July 1, 2008 at
A) $130,800.
B) $147,300.
C) $180,000.
D) $202,800.
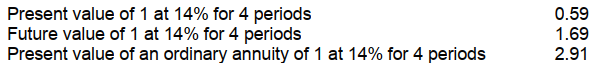 Vance should record the acquisition cost of the franchise on July 1, 2008 at
Vance should record the acquisition cost of the franchise on July 1, 2008 atA) $130,800.
B) $147,300.
C) $180,000.
D) $202,800.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



