Deck 2: Chemistry, Water and PH
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/35
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Chemistry, Water and PH
1
The subatomic particles with the most mass are:
A) neutrons.
B) electrons.
C) protons.
D) both A and C
A) neutrons.
B) electrons.
C) protons.
D) both A and C
both A and C
2
If the atomic number is 18, then:
A) there are seven electrons in the outermost shell.
B) the atom has 18 electrons in the nucleus.
C) the outermost energy level is full.
D) this atom would be considered reactive.
A) there are seven electrons in the outermost shell.
B) the atom has 18 electrons in the nucleus.
C) the outermost energy level is full.
D) this atom would be considered reactive.
the outermost energy level is full.
3
The mass of matter is proportional to the:
A) density of matter.
B) volume of matter.
C) number of electrons.
D) weight of matter.
E) number of protons.
A) density of matter.
B) volume of matter.
C) number of electrons.
D) weight of matter.
E) number of protons.
weight of matter.
4
Which of the following is not a component of atoms?
A) molecules
B) electrons
C) protons
D) neutrons
A) molecules
B) electrons
C) protons
D) neutrons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Isotopes have been used to:
A) determine the age of fossils.
B) detect bone cancer.
C) create new elements.
D) A and B
E) A, B, and C
A) determine the age of fossils.
B) detect bone cancer.
C) create new elements.
D) A and B
E) A, B, and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
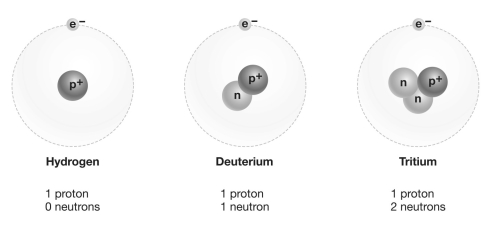 Refer to the figure above and then answer the question that follows.
Refer to the figure above and then answer the question that follows.-Consider carbon-12, carbon-13, and carbon-14 (the numbers indicate atomic mass). Which of these forms of carbon is an isotope?
A) carbon-12
B) carbon-13
C) carbon-14
D) None are isotopes.
E) All are isotopes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
 Refer to the figure above and then answer the question that follows.
Refer to the figure above and then answer the question that follows.-The component of an atom or molecule that is most important in determining its chemical bonding properties is the:
A) neutron.
B) nucleus.
C) proton.
D) electron.
E) isotope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which type of bonding occurs between molecules and not within molecules?
A) ionic
B) polar covalent
C) covalent
D) hydrogen
A) ionic
B) polar covalent
C) covalent
D) hydrogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When an electron passes from one atom to another:
A) attraction occurs between two atoms based on opposite charges.
B) the electron travels in orbitals around both the donor and recipient atom.
C) a proton is also lost from the nucleus.
D) the identity of the atom changes.
A) attraction occurs between two atoms based on opposite charges.
B) the electron travels in orbitals around both the donor and recipient atom.
C) a proton is also lost from the nucleus.
D) the identity of the atom changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The symbol 3CO2 represents:
A) three molecules of carbon dioxide.
B) three carbon atoms and one molecule of oxygen.
C) one atom of carbon and three atoms of oxygen.
D) one atom of oxygen and three of carbon.
A) three molecules of carbon dioxide.
B) three carbon atoms and one molecule of oxygen.
C) one atom of carbon and three atoms of oxygen.
D) one atom of oxygen and three of carbon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is not a compound?
A) a protein
B) glucose
C) methane
D) nitrogen
E) table salt
A) a protein
B) glucose
C) methane
D) nitrogen
E) table salt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
When atoms form bonds, they share or exchange:
A) electrons.
B) protons.
C) neutrons.
D) A and B
E) A, B, and C
A) electrons.
B) protons.
C) neutrons.
D) A and B
E) A, B, and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Two hydrogen atoms (atomic number 1) form a covalent bond. Which of the following is true?
A) Both hydrogen atoms now have two electrons in their outer shell.
B) Both hydrogen atoms now have two protons in their outer shell.
C) One hydrogen atom now has zero protons in its outer shell, and the other has two.
D) One hydrogen atom now has zero electrons in its outer shell, and the other has two.
E) Each hydrogen atom still has one electron in its outer shell.
A) Both hydrogen atoms now have two electrons in their outer shell.
B) Both hydrogen atoms now have two protons in their outer shell.
C) One hydrogen atom now has zero protons in its outer shell, and the other has two.
D) One hydrogen atom now has zero electrons in its outer shell, and the other has two.
E) Each hydrogen atom still has one electron in its outer shell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Oxygen has six electrons in its second outer shell. How many covalent bonds is oxygen likely to make with hydrogen, which has one electron in its first outer shell?
A) eight
B) one
C) two
D) six
E) three
A) eight
B) one
C) two
D) six
E) three

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
H2S is an example of a:
A) structural formula.
B) ball-and-stick formula.
C) molecular formula.
D) space-filling model.
E) none of the above
A) structural formula.
B) ball-and-stick formula.
C) molecular formula.
D) space-filling model.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Covalent bonds form when one atom ________ its ________ with another atom.
A) shares; electrons
B) gives up; neutrons
C) gives up; protons
D) gives up; electrons
E) shares; protons
A) shares; electrons
B) gives up; neutrons
C) gives up; protons
D) gives up; electrons
E) shares; protons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Potassium has one electron in its fourth shell, and chloride has seven electrons in its third shell. Which of the following is most likely to be true?
A) Chloride will give an electron to potassium to form an ionic bond.
B) Potassium will give an electron to chloride to form an ionic bond.
C) The two atoms will share the electron unequally in a polar bond.
D) The two atoms will share an electron equally in a covalent nonpolar bond.
A) Chloride will give an electron to potassium to form an ionic bond.
B) Potassium will give an electron to chloride to form an ionic bond.
C) The two atoms will share the electron unequally in a polar bond.
D) The two atoms will share an electron equally in a covalent nonpolar bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Nitrogen has seven protons, and hydrogen has one proton. Based on your knowledge of the rules of covalent bonding, which of the following molecules will form from the reaction of nitrogen and hydrogen?
A) NH5
B) NH3
C) NH
D) NH2
E) NH4
A) NH5
B) NH3
C) NH
D) NH2
E) NH4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
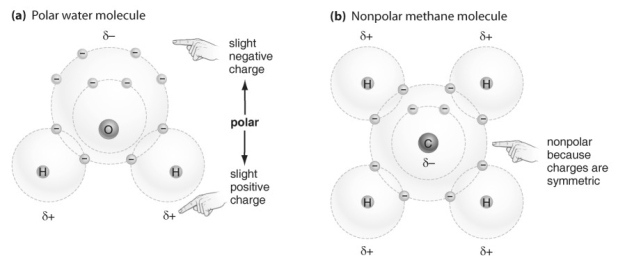 Refer to the figure above and then answer the question that follows.
Refer to the figure above and then answer the question that follows.-In what ways are hydrogen bonds and ionic bonds similar?
A) Both are based on attraction between atoms that carry differences in electrical charge.
B) Both involve an even sharing of electrons between atoms.
C) Both are based on attraction between two atoms that each carry a positive charge.
D) Both are based on repulsion between atoms that carry differences in electrical charge.
E) Both are based on attraction between two atoms that each carry a negative charge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
 Refer to the figure above and then answer the question that follows.
Refer to the figure above and then answer the question that follows.-If an atom has an atomic number of 11, which of the electron shells are filled?
A) the first shell
B) the first and second shell
C) the first, second, and third shell
D) the first, second, third, and fourth shell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze specific reactions within a cell. For catalysis to occur, they require a starting substance to bind directly to the enzyme. What must be true for this binding to happen correctly?
A) Both the enzyme and the starting substance must be hydrophilic.
B) The starting substance must be larger than the enzyme.
C) The enzyme must be acidic, and the starting substance must be basic.
D) Both the enzyme and the starting substance need to have matching shapes.
A) Both the enzyme and the starting substance must be hydrophilic.
B) The starting substance must be larger than the enzyme.
C) The enzyme must be acidic, and the starting substance must be basic.
D) Both the enzyme and the starting substance need to have matching shapes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When you put sugar into your morning coffee or tea, the sugar is the ________, and the tea or coffee is the ________.
A) solvent, solution
B) solvent, solute
C) solute, solution
D) solution, solute
E) solute, solvent
A) solvent, solution
B) solvent, solute
C) solute, solution
D) solution, solute
E) solute, solvent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Chemical reactions that occur within living things change the nucleus of atoms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Protons move at very fast speeds around the outside of the nucleus of an atom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Cigarette smoking and exposure to sunlight ________ the production of free radicals by our bodies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Match column 1 with the items in column 2.
-proton
A) no charge
B) positive charge
C) polar covalent bond
D) electron-proton interaction
E) hydrogen bond
F) negative charge
G) nonpolar covalent bond
H) ionic bond
-proton
A) no charge
B) positive charge
C) polar covalent bond
D) electron-proton interaction
E) hydrogen bond
F) negative charge
G) nonpolar covalent bond
H) ionic bond

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Match column 1 with the items in column 2.
-neutrons
A) no charge
B) positive charge
C) polar covalent bond
D) electron-proton interaction
E) hydrogen bond
F) negative charge
G) nonpolar covalent bond
H) ionic bond
-neutrons
A) no charge
B) positive charge
C) polar covalent bond
D) electron-proton interaction
E) hydrogen bond
F) negative charge
G) nonpolar covalent bond
H) ionic bond

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Match column 1 with the items in column 2.
-electrons
A) no charge
B) positive charge
C) polar covalent bond
D) electron-proton interaction
E) hydrogen bond
F) negative charge
G) nonpolar covalent bond
H) ionic bond
-electrons
A) no charge
B) positive charge
C) polar covalent bond
D) electron-proton interaction
E) hydrogen bond
F) negative charge
G) nonpolar covalent bond
H) ionic bond

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Match column 1 with the items in column 2.
-Results from electrons being transferred between atoms
A) no charge
B) positive charge
C) polar covalent bond
D) electron-proton interaction
E) hydrogen bond
F) negative charge
G) nonpolar covalent bond
H) ionic bond
-Results from electrons being transferred between atoms
A) no charge
B) positive charge
C) polar covalent bond
D) electron-proton interaction
E) hydrogen bond
F) negative charge
G) nonpolar covalent bond
H) ionic bond

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Match column 1 with the items in column 2.
-Results from an unequal sharing of shared electrons
A) no charge
B) positive charge
C) polar covalent bond
D) electron-proton interaction
E) hydrogen bond
F) negative charge
G) nonpolar covalent bond
H) ionic bond
-Results from an unequal sharing of shared electrons
A) no charge
B) positive charge
C) polar covalent bond
D) electron-proton interaction
E) hydrogen bond
F) negative charge
G) nonpolar covalent bond
H) ionic bond

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Match column 1 with the items in column 2.
-Explains the attraction of water molecules for each other
A) no charge
B) positive charge
C) polar covalent bond
D) electron-proton interaction
E) hydrogen bond
F) negative charge
G) nonpolar covalent bond
H) ionic bond
-Explains the attraction of water molecules for each other
A) no charge
B) positive charge
C) polar covalent bond
D) electron-proton interaction
E) hydrogen bond
F) negative charge
G) nonpolar covalent bond
H) ionic bond

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Match column 1 with the items in column 2.
-Would be the least affected by the presence of water
A) no charge
B) positive charge
C) polar covalent bond
D) electron-proton interaction
E) hydrogen bond
F) negative charge
G) nonpolar covalent bond
H) ionic bond
-Would be the least affected by the presence of water
A) no charge
B) positive charge
C) polar covalent bond
D) electron-proton interaction
E) hydrogen bond
F) negative charge
G) nonpolar covalent bond
H) ionic bond

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Match column 1 with the items in column 2.
-Keeps most electrons from escaping the nucleus of an atom
A) no charge
B) positive charge
C) polar covalent bond
D) electron-proton interaction
E) hydrogen bond
F) negative charge
G) nonpolar covalent bond
H) ionic bond
-Keeps most electrons from escaping the nucleus of an atom
A) no charge
B) positive charge
C) polar covalent bond
D) electron-proton interaction
E) hydrogen bond
F) negative charge
G) nonpolar covalent bond
H) ionic bond

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What are the four most important types of elements necessary for life on this planet?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
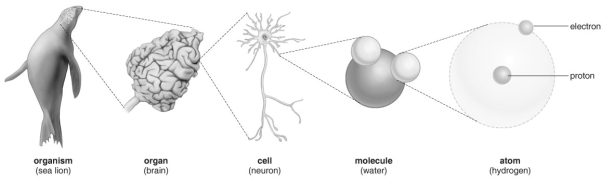 Refer to the figure above and then answer the question that follows.
Refer to the figure above and then answer the question that follows.-Describe at which level life begins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



