Deck 15: Nuclear Chemistry
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/41
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Nuclear Chemistry
1
Which form of radiation will be deflected by an electric field?
A) particles
B) particles
C) rays
D) and particles
E) All three forms of radiation will be deflected by an electric field.
A) particles
B) particles
C) rays
D) and particles
E) All three forms of radiation will be deflected by an electric field.
and particles
2
Which pair represents the same thing?
A) and radiation
B) particles and -10e
C) rays and a proton
D) and particles
E) Each pair represents the same thing.
A) and radiation
B) particles and -10e
C) rays and a proton
D) and particles
E) Each pair represents the same thing.
particles and -10e
3
1H, 2H, and 3H are best described as ____
A) isotopes
B) isobars
C) isotones
D) compounds
E) alpha particle emitters
A) isotopes
B) isobars
C) isotones
D) compounds
E) alpha particle emitters
isotopes
4
9Li, 9Be, and 9C are best described as ____
A) isotopes
B) isobars
C) isotones
D) compounds
E) covalent
A) isotopes
B) isobars
C) isotones
D) compounds
E) covalent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
44P, 50Sc, and 52V are best described as ____
A) isotopes
B) isobars
C) isotones
D) compounds
E) p-block elements
A) isotopes
B) isobars
C) isotones
D) compounds
E) p-block elements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is the identity of X in the following equation?
238U 4He + X
A) 234Pu
B) 242Ra
C) 234U
D) 234Th
E) none of the above
238U 4He + X
A) 234Pu
B) 242Ra
C) 234U
D) 234Th
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is the identity of X in the following equation?
X 3He + -10e
A) 3H
B) 2H
C) 4Li
D) 234Th
E) 3Li
X 3He + -10e
A) 3H
B) 2H
C) 4Li
D) 234Th
E) 3Li

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is the identity of X in the following equation?
65Zn + X 65Cu
A) 3H
B) -10e
C) +10e
D) 01n
E) none of the above
65Zn + X 65Cu
A) 3H
B) -10e
C) +10e
D) 01n
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The decay of 40K to 40Ar can be used to determine the age of very old rocks. What mode of radioactive decay is occurring in the conversion of 40K to 40Ar?
A) emission
B) electron capture
C) positron emission
D) neutron emission
E) none of the above
A) emission
B) electron capture
C) positron emission
D) neutron emission
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is the identity of X in the following equation?
19F + X 16O + 4He
A) 11p
B) 3H
C) +10e
D) 01n
E) none of the above
19F + X 16O + 4He
A) 11p
B) 3H
C) +10e
D) 01n
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Element number 43, technetium, is not naturally occurring but is prepared by nuclear reactions for use in medical imaging. The starting material, 98Mo, captures one neutron to give a new species X. X decays by electron emission to give species Y which is formed in a metastable state. Y then decays to give 99Tc with the emission of a gamma ray. Identify X and Y and write balanced nuclear equations for their formation and decomposition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What is the identity of X in the following equation?
235U + 01 n 99Sr + 135Te + 2X
A) +11p
B) 3H
C) +10e
D) 01n
E) none of the above
235U + 01 n 99Sr + 135Te + 2X
A) +11p
B) 3H
C) +10e
D) 01n
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following decay modes will result in an increase in the atomic number of a nuclide?
A) electron emission
B) positron emission
C) emission
D) ray emission
E) All of the above decay modes will result in an increase in atomic number.
A) electron emission
B) positron emission
C) emission
D) ray emission
E) All of the above decay modes will result in an increase in atomic number.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following nuclides would be the most likely to decay by electron emission?
A) 17Ne
B) 18Ne
C) 19Ne
D) 24Ne
E) They are all equally likely to decay by electron emission.
A) 17Ne
B) 18Ne
C) 19Ne
D) 24Ne
E) They are all equally likely to decay by electron emission.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following nuclides would be the most likely to decay by positron emission?
A) 19Na
B) 20Na
C) 21Na
D) 22Na
E) They are all equally likely to decay by positron emission.
A) 19Na
B) 20Na
C) 21Na
D) 22Na
E) They are all equally likely to decay by positron emission.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A neutron-poor nuclide can decay by:
A) positron emission
B) electron capture
C) decay
D) A neutron-poor nuclide cannot decay by any of these routes.
E) A neutron-poor nuclide can decay by any one of these three routes, depending on the mass of the nuclide.
A) positron emission
B) electron capture
C) decay
D) A neutron-poor nuclide cannot decay by any of these routes.
E) A neutron-poor nuclide can decay by any one of these three routes, depending on the mass of the nuclide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following nuclides would be most likely to be considered neutron-rich?
A) 26Si
B) 55Cr
C) 61Cu
D) 4Li
E) 37Ar
A) 26Si
B) 55Cr
C) 61Cu
D) 4Li
E) 37Ar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following nuclides is most likely to decay by electron capture?
A) 125I
B) 33P
C) 8B
D) 14C
E) 210Pb
A) 125I
B) 33P
C) 8B
D) 14C
E) 210Pb

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The sum of the mass of 11 protons, 12 neutrons, and 11 electrons will be _____ the mass of a 23Na atom.
A) greater than
B) smaller than
C) equal to
D) not related to
A) greater than
B) smaller than
C) equal to
D) not related to

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The exact mass of a 12C atom does not equal the sum of the mass of 6 protons, 6 neutrons, and 6 electrons because
A) a 12C atom has 7 neutrons, not 6.
B) some of the mass of the protons and neutrons is converted to energy when they are combined to form the 12C atom.
C) carbon occurs naturally as a mixture of isotopes with slightly different masses.
D) the enthalpy of atom combination of 12C is negative.
E) none of the above
A) a 12C atom has 7 neutrons, not 6.
B) some of the mass of the protons and neutrons is converted to energy when they are combined to form the 12C atom.
C) carbon occurs naturally as a mixture of isotopes with slightly different masses.
D) the enthalpy of atom combination of 12C is negative.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
223Rn has a binding energy of 1712.325 MeV. What is the binding energy per nucleon?
A) 19.91076 MeV/nucleon
B) 12.49872 MeV/nucleon
C) 34.83745 MeV/nucleon
D) 1.033238 MeV/nucleon
E) 7.678587 MeV/nucleon
A) 19.91076 MeV/nucleon
B) 12.49872 MeV/nucleon
C) 34.83745 MeV/nucleon
D) 1.033238 MeV/nucleon
E) 7.678587 MeV/nucleon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The following data is needed for problems
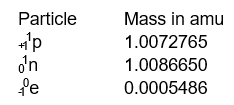
-What is the binding energy in MeV/atpm for a 14C atom which has an exact mass of 14.003242 amu?
A) between 0 and 30 MeV
B) between 30 and 60 MeV
C) between 60 and 90 MeV
D) between 90 and 120 MeV
E) more than 120 MeV

-What is the binding energy in MeV/atpm for a 14C atom which has an exact mass of 14.003242 amu?
A) between 0 and 30 MeV
B) between 30 and 60 MeV
C) between 60 and 90 MeV
D) between 90 and 120 MeV
E) more than 120 MeV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The following data is needed for problems

-What is the exact mass in amu of 31P if its binding energy is 8.481184 MeV/nucleon?
A) 30.97377
B) 30.95322
C) 31.25601
D) 32.22563
E) 30.13725

-What is the exact mass in amu of 31P if its binding energy is 8.481184 MeV/nucleon?
A) 30.97377
B) 30.95322
C) 31.25601
D) 32.22563
E) 30.13725

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The following data is needed for problems

-What is the binding energy per nucleon for 60Co? The exact mass of 60Co is
59)933822 amu.
A) between 6 and 7 MeV/nucleon
B) between 7 and 8 MeV/nucleon
C) between 8 and 9 MeV/nucleon
D) between 9 and 10 MeV/nucleon
E) more than 10 MeV/nucleon

-What is the binding energy per nucleon for 60Co? The exact mass of 60Co is
59)933822 amu.
A) between 6 and 7 MeV/nucleon
B) between 7 and 8 MeV/nucleon
C) between 8 and 9 MeV/nucleon
D) between 9 and 10 MeV/nucleon
E) more than 10 MeV/nucleon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In aging red giant stars, 12C undergoes several different fusion reactions, one of which is shown below. What is the energy released in this reaction in MeV? 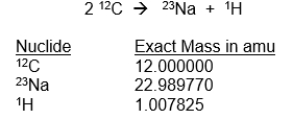
A) between and 0 and 1 MeV
B) between 1 and 2 MeV
C) between 2 and 3 MeV
D) between 3 and 4 MeV
E) more than 4 MeV

A) between and 0 and 1 MeV
B) between 1 and 2 MeV
C) between 2 and 3 MeV
D) between 3 and 4 MeV
E) more than 4 MeV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
All forms of radioactive decay obey a ____ rate law.
A) Zero-order
B) First-order
C) Second-order
D) first or second-order
E) zeroth, first, or second-order
A) Zero-order
B) First-order
C) Second-order
D) first or second-order
E) zeroth, first, or second-order

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A typical rate law for radioactive decay of a nuclide (N) would be:
A) rate = k
B) rate = k(N)1/2
C) rate = k(N)
D) rate = k(N)2
E) The rate law depends on the mode of radioactive decay.
A) rate = k
B) rate = k(N)1/2
C) rate = k(N)
D) rate = k(N)2
E) The rate law depends on the mode of radioactive decay.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
An important component of smoke detectors is the emitter americium-241 which has a half-life of 432 years. What is the rate constant for the decay of 241Am?
A) 432 yr-1
B) 2.31 x 10-3 yr-1
C) 1.60 x 10-3 yr-1
D) 0.693 yr-1
E) none of the above
A) 432 yr-1
B) 2.31 x 10-3 yr-1
C) 1.60 x 10-3 yr-1
D) 0.693 yr-1
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
An important component of smoke detectors is the emitter 241Am. The rate constant for the decay of this isotope is 5.1 x 10-11 dis/s. What is the activity in Curies of the 241Am if each detector contains approximately 1.8 x 10-4 g of the isotope?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
An important component of smoke detectors is the emitter 241Am. The rate constant for the decay of this isotope is 1.6 x 10-3 yr-1. If a smoke detector starts with1.8 x 10-4 g of the isotope, how long will it take until 1.0 x 10-4 g of americium remains?
A) 3.7 x 102 years
B) 3.2 x 102 year
C) 4.5 x 102 years
D) 32 years
E) none of the above
A) 3.7 x 102 years
B) 3.2 x 102 year
C) 4.5 x 102 years
D) 32 years
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
90Sr is a particularly dangerous nuclide formed from the fission of 235U in atomic bombs because it can readily enter the food chain by replacing calcium in plants or animals. If the rate constant for the decay of 90Sr is 0.0274 yr-1, approximately how long will it take for 99.0% of a sample of 90Sr to decay?
A) 168 years
B) 52.0 years
C) 452 years
D) 195 years
E) none of the above
A) 168 years
B) 52.0 years
C) 452 years
D) 195 years
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The cloth wrappings from a mummified bull found in a pyramid in Dashur, Egypt were dated by 14C analysis. The wrappings had 78.0% of the radioactivity of living tissue. Approximately how old are the wrappings? The rate constant for the decay of 14C is 1.21 x 10-4 yr-1.
A) less than 500 years old
B) between 500 and 1500 years old
C) between 1500 and 2500 years old
D) between 2500 and 3500 years old
E) more than 3500 years old
A) less than 500 years old
B) between 500 and 1500 years old
C) between 1500 and 2500 years old
D) between 2500 and 3500 years old
E) more than 3500 years old

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is not an important assumption made in 14C dating?
A) 14C is produced in the atmosphere at a more or less constant rate.
B) A carbon atom typically forms four bonds.
C) Carbon atoms circulate among the atmosphere, the oceans, and living organisms faster than they decay.
D) After death, organisms no longer pick up 14C.
E) All of the above are important assumptions in 14C dating.
A) 14C is produced in the atmosphere at a more or less constant rate.
B) A carbon atom typically forms four bonds.
C) Carbon atoms circulate among the atmosphere, the oceans, and living organisms faster than they decay.
D) After death, organisms no longer pick up 14C.
E) All of the above are important assumptions in 14C dating.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Water at various depths in the ocean is recirculated to the surface at different rates. The length of time elapsed since water has been brought up to the surface of the ocean can be estimated by measuring the radioactivity of the 14C in the CO2 dissolved in the water. If a sample of water brought up from a depth of 1000 meters displays 88.5% of the radioactivity of water at the surface, how "old" is the water? The rate constant for the decay of 14C is 1.21 x 10-4 yr-1.
A) between 900 and 1100 years
B) between 700 and 900 years
C) between 500 and 700 years
D) between 300 and 500 years
E) less than 300 years
A) between 900 and 1100 years
B) between 700 and 900 years
C) between 500 and 700 years
D) between 300 and 500 years
E) less than 300 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The decay of 40K to 40Ar can be used to determine the age of very old rocks. If moon rocks from the Sea of Tranquility have 12.5% of the estimated original amount of 40K, approximately how old are the rocks? 40K decays with a rate constant of 5.06 x 10-10 yr-1.
A) between 106 and 107 years
B) between 108 and 109 years
C) between 1010 and 1011 years
D) between 1012 and 1013 years
E) more than 1013 years
A) between 106 and 107 years
B) between 108 and 109 years
C) between 1010 and 1011 years
D) between 1012 and 1013 years
E) more than 1013 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following is a free radical?
A) H2O
B) H3O+
C) O2-
D) OH-
E) none of the above
A) H2O
B) H3O+
C) O2-
D) OH-
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The energy required to ionize a single water molecule is 2.02 x 10-18 J. What wavelength (in nm) photon would deliver this amount of energy?
A) 98.4 nm
B) 115 nm
C) 3.04 x 1015 nm
D) 536 nm
E) none of the above
A) 98.4 nm
B) 115 nm
C) 3.04 x 1015 nm
D) 536 nm
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The first synthesis of element number 116 (ununhexium) was accomplished in 2000 at the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research in Dubna. The Uuh was prepared in the reaction shown below. What is the mass number of the isotope of Uuh prepared?
248Cm + 48Ca 116Uuh + 4 1n
A) 116
B) 296
C) 200
D) 292
E) none of the above
248Cm + 48Ca 116Uuh + 4 1n
A) 116
B) 296
C) 200
D) 292
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Element 110, darnstatdium, was prepared in the reaction shown below. After it was synthesized it decomposed by decay with a half-life of 270 s. What is the product obtained from the decay?
208Pb + 62Ni 269Ds + 1n
A) 265Hs
B) 265Sg
C) 269Hs
D) 108Bh
E) 267Bh
208Pb + 62Ni 269Ds + 1n
A) 265Hs
B) 265Sg
C) 269Hs
D) 108Bh
E) 267Bh

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The half-lives for four of the heaviest known elements are given below. Does this data support the theoretical predictions that element 114 should be an "island of stability" in a group of very unstable nuclides? Explain.



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Nuclear fission is energetically favorable for ______ elements while nuclear fusion is energetically favorable for ______ elements.
A) the heavier, the lighter
B) the lighter, the heavier
C) metallic, lighter
D) heavier, p-block
E) low electronegativity, f-block
A) the heavier, the lighter
B) the lighter, the heavier
C) metallic, lighter
D) heavier, p-block
E) low electronegativity, f-block

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



