Deck 13: Chemical Thermodynamics
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/56
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Chemical Thermodynamics
1
Many of the following questions assume that a truncated table of standard-state thermodynamic data is attached to the exam. The table usually contains data for 6-10 compounds, which pertain to the particular questions on that exam.
-For which of the following processes would S be negative?
A) the melting of ice
B) the freezing of water
C) the evaporation of a liquid
D) the breakup of a large molecule into smaller molecules
E) these all have positive S values
the freezing of water
2
Many of the following questions assume that a truncated table of standard-state thermodynamic data is attached to the exam. The table usually contains data for 6-10 compounds, which pertain to the particular questions on that exam.
-Which of the following processes would have a negative entropy change?
A) decomposition of hydrogen peroxide
B) conversion of dry ice to gaseous CO2
C) melting of ice
D) formation of Al2O3 from its elements
E) dissolution of salt in water
formation of Al2O3 from its elements
3
In any spontaneous process if the entropy change of the system is negative, the entropy change of the surroundings must be:
A) positive
B) negative
C) may be either positive or negative
D) must be zero
A) positive
B) negative
C) may be either positive or negative
D) must be zero
positive
4
The second law of thermodynamics states that Suniverse is positive for a spontaneous process. However, our bodies are constantly carrying out spontaneous reactions in which simple molecules and compounds are used to make more complex ordered molecules such as proteins as well as more complex structures such as cells and tissues. According to the second law of thermodynamics how can these reactions be taking place spontaneously?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following reactions would have a positive value for S?
A) 3 NO(g) NO2(g) + N2O(g)
B) 2 CO2(g) 2 CO(g) + O2(g)
C) 2 I(g) I2(g)
D) NH3(g) NH3(l)
E) None of these reactions would have a positive S.
A) 3 NO(g) NO2(g) + N2O(g)
B) 2 CO2(g) 2 CO(g) + O2(g)
C) 2 I(g) I2(g)
D) NH3(g) NH3(l)
E) None of these reactions would have a positive S.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following reaction would be more likely to have a positive value for S°?
A) 2 H2O(g) 2 H2(g) + O2(g)
B) N2(g) + 3 H2(g) 2 NH3(g)
C) CO2(g) + H2(g) CO(g) + H2O(g)
D) H2O(l) H2O(s)
E) None of these reactions would have a positive S.
A) 2 H2O(g) 2 H2(g) + O2(g)
B) N2(g) + 3 H2(g) 2 NH3(g)
C) CO2(g) + H2(g) CO(g) + H2O(g)
D) H2O(l) H2O(s)
E) None of these reactions would have a positive S.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following reactions would have a negative S°?
A) H2(g) 2 H(g)
B) H2(l) H2(g)
C) H2(g) + Cl2(g) 2 HCl(g)
D) 2 H2(g) + CO(g) CH3OH(g)
E) none of the above
A) H2(g) 2 H(g)
B) H2(l) H2(g)
C) H2(g) + Cl2(g) 2 HCl(g)
D) 2 H2(g) + CO(g) CH3OH(g)
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Without using thermodynamic tables, predict the signs of H ° and S ° for the following reaction. CCl4(l) CCl4(g)
A) H ° > 0 and S ° > 0
B) H ° < 0 and S ° > 0
C) H ° > 0 and S ° < 0
D) H ° < 0 and S ° < 0
E) none of these
A) H ° > 0 and S ° > 0
B) H ° < 0 and S ° > 0
C) H ° > 0 and S ° < 0
D) H ° < 0 and S ° < 0
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following reactions will most likely have a positive S°?
A) CO(g) + 2H2(g) CH3OH(l)
B) NaCl(s) Na+(aq) + Cl - (aq)
C) CH4(g) + 2 O2(g) CO2(g) + 2 H2O(l)
D) 3H2(g) + N2(g) 2 NH3(g)
E) none of these
A) CO(g) + 2H2(g) CH3OH(l)
B) NaCl(s) Na+(aq) + Cl - (aq)
C) CH4(g) + 2 O2(g) CO2(g) + 2 H2O(l)
D) 3H2(g) + N2(g) 2 NH3(g)
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Carbonated beverages can be made by bubbling carbon dioxide gas through the aqueous beverage and allowing the carbon dioxide to dissolve. Predict the signs of H  and S 11ee9e79_dbe5_b5a7_9fac_f7a63aa32526_TB9692_11 for the following reaction without using tables.
and S 11ee9e79_dbe5_b5a7_9fac_f7a63aa32526_TB9692_11 for the following reaction without using tables.
CO2(g) CO2(aq)
A) H 11ee9e79_dbe5_b5a7_9fac_f7a63aa32526_TB9692_11 = +, S 11ee9e79_dbe5_b5a7_9fac_f7a63aa32526_TB9692_11 = +
B) H 11ee9e79_dbe5_b5a7_9fac_f7a63aa32526_TB9692_11 = - , S 11ee9e79_dbe5_b5a7_9fac_f7a63aa32526_TB9692_11 = +
C) H 11ee9e79_dbe5_b5a7_9fac_f7a63aa32526_TB9692_11 = - , S 11ee9e79_dbe5_b5a7_9fac_f7a63aa32526_TB9692_11 = -
D) H 11ee9e79_dbe5_b5a7_9fac_f7a63aa32526_TB9692_11 = +, S 11ee9e79_dbe5_b5a7_9fac_f7a63aa32526_TB9692_11 = 0
E) H 11ee9e79_dbe5_b5a7_9fac_f7a63aa32526_TB9692_11 = 0, S 11ee9e79_dbe5_b5a7_9fac_f7a63aa32526_TB9692_11 = -
 and S 11ee9e79_dbe5_b5a7_9fac_f7a63aa32526_TB9692_11 for the following reaction without using tables.
and S 11ee9e79_dbe5_b5a7_9fac_f7a63aa32526_TB9692_11 for the following reaction without using tables.CO2(g) CO2(aq)
A) H 11ee9e79_dbe5_b5a7_9fac_f7a63aa32526_TB9692_11 = +, S 11ee9e79_dbe5_b5a7_9fac_f7a63aa32526_TB9692_11 = +
B) H 11ee9e79_dbe5_b5a7_9fac_f7a63aa32526_TB9692_11 = - , S 11ee9e79_dbe5_b5a7_9fac_f7a63aa32526_TB9692_11 = +
C) H 11ee9e79_dbe5_b5a7_9fac_f7a63aa32526_TB9692_11 = - , S 11ee9e79_dbe5_b5a7_9fac_f7a63aa32526_TB9692_11 = -
D) H 11ee9e79_dbe5_b5a7_9fac_f7a63aa32526_TB9692_11 = +, S 11ee9e79_dbe5_b5a7_9fac_f7a63aa32526_TB9692_11 = 0
E) H 11ee9e79_dbe5_b5a7_9fac_f7a63aa32526_TB9692_11 = 0, S 11ee9e79_dbe5_b5a7_9fac_f7a63aa32526_TB9692_11 = -

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The value of S  for this reaction is:
for this reaction is:
2 Fe3+(aq) + Cu(s) 2 Fe2+(aq) + Cu2+(aq)

A) between -400 and -200 J/molrxn-K
B) between -200 and 0 J/molrxn-K
C) between 0 and 200 J/molrxn-K
D) between 200 and 400 J/molrxn-K
E) more than 400 J/molrxn-K
 for this reaction is:
for this reaction is: 2 Fe3+(aq) + Cu(s) 2 Fe2+(aq) + Cu2+(aq)

A) between -400 and -200 J/molrxn-K
B) between -200 and 0 J/molrxn-K
C) between 0 and 200 J/molrxn-K
D) between 200 and 400 J/molrxn-K
E) more than 400 J/molrxn-K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Use the Sac ° values for tin metal ( Sac ° = -124.35 J/molrxn-K), chlorine gas ( Sac ° = -107.33 J/molrxn-K), and tin tetrachloride ( Sac ° = -570.7 J/molrxn-K) to calculate S ° for the following reaction.
Sn(s) + 2 Cl2(g) SnCl4(l)
A) -339.0
B) -231.7
C) 231.7
D) 339.0
E) none of the above
Sn(s) + 2 Cl2(g) SnCl4(l)
A) -339.0
B) -231.7
C) 231.7
D) 339.0
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Use the following data to calculate S for the reaction:
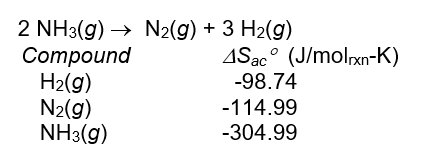
A) -198.8 J/molrxn-K
B) -91.26 J/molrxn-K
C) -106.22 J/molrxn-K
D) 91.26 J/molrxn-K
E) 198.8 J/molrxn-K
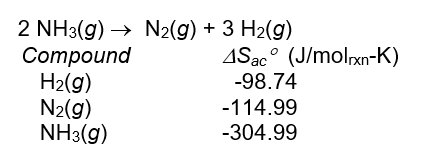
A) -198.8 J/molrxn-K
B) -91.26 J/molrxn-K
C) -106.22 J/molrxn-K
D) 91.26 J/molrxn-K
E) 198.8 J/molrxn-K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If a reaction is spontaneous, what can be said about the reverse reaction under the same conditions?
A) The reverse reaction is nonspontaneous.
B) The reverse reaction is spontaneous also.
C) The reverse reaction is at equilibrium.
D) This cannot be determined.
A) The reverse reaction is nonspontaneous.
B) The reverse reaction is spontaneous also.
C) The reverse reaction is at equilibrium.
D) This cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Given that H ° for the reaction shown below is 92.2 kJ/molrxn, calculate G ° at 25 ° C.
2 NH3(g) N2(g) + 3 H2(g)

A) -106.5 kJ/molrxn
B) -33.0 kJ/molrxn
C) 33.0 kJ/molrxn
D) 106.5 kJ/molrxn
E) none of these
2 NH3(g) N2(g) + 3 H2(g)

A) -106.5 kJ/molrxn
B) -33.0 kJ/molrxn
C) 33.0 kJ/molrxn
D) 106.5 kJ/molrxn
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
For which of the following highly exothermic processes would you expect H ° and G ° to be about the same?
A) 2 Al(s) + 3/2 O2(g) Al2O3(s)
B) 2 H2(g) + O2(g) 2 H2O(g)
C) 2 Na(s) + 2 H2O(l) 2 NaOH(aq) + H2(g)
D) 2 NO(g) N2O4(g)
E) 2 Al(s) + Fe2O3(s) 2 Fe(s) + Al2O3(s)
A) 2 Al(s) + 3/2 O2(g) Al2O3(s)
B) 2 H2(g) + O2(g) 2 H2O(g)
C) 2 Na(s) + 2 H2O(l) 2 NaOH(aq) + H2(g)
D) 2 NO(g) N2O4(g)
E) 2 Al(s) + Fe2O3(s) 2 Fe(s) + Al2O3(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following combinations of H ° and S ° indicates a nonspontaneous reaction under all conditions of temperature?
A) H ° > 0 and S ° > 0
B) H ° < 0 and S ° > 0
C) F H ° > 0 and S ° < 0
D) H ° < 0 and S ° < 0
E) none of these
A) H ° > 0 and S ° > 0
B) H ° < 0 and S ° > 0
C) F H ° > 0 and S ° < 0
D) H ° < 0 and S ° < 0
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Under which one of the following conditions will the following reaction be spontaneous as written? 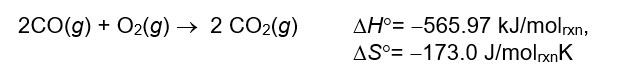
A) spontaneous at all temperatures
B) spontaneous at high temperatures
C) spontaneous at low temperatures
D) not spontaneous at any temperature
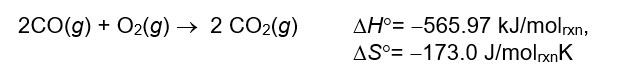
A) spontaneous at all temperatures
B) spontaneous at high temperatures
C) spontaneous at low temperatures
D) not spontaneous at any temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following combinations of Ho and So can result in a reaction changing from nonspontaneous to spontaneous when the temperature increases?
A) Ho < 0 and So > 0
B) Ho < 0 and So < 0
C) Ho = 0 and So < 0
D) Ho = 0 and So > 0
E) Ho > 0 and So > 0
A) Ho < 0 and So > 0
B) Ho < 0 and So < 0
C) Ho = 0 and So < 0
D) Ho = 0 and So > 0
E) Ho > 0 and So > 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which statement correctly describes the following reaction? 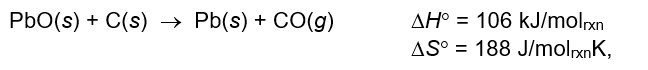
A) The reaction is spontaneous at all temperatures.
B) The reaction is spontaneous only below about 300 K.
C) The reaction becomes spontaneous at about 300 K.
D) The reaction becomes spontaneous at about 560 K.
E) The reaction is spontaneous only above 2000 K.
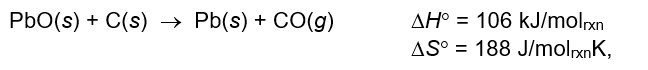
A) The reaction is spontaneous at all temperatures.
B) The reaction is spontaneous only below about 300 K.
C) The reaction becomes spontaneous at about 300 K.
D) The reaction becomes spontaneous at about 560 K.
E) The reaction is spontaneous only above 2000 K.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The entropy change in the process: 2 H(g) H2(g) is -98.74 J/molrxnK. The enthalpy of atom combination of the H2 molecule is 435 kJ/molrxn. Estimate the approximate temperature above which the formation of H2 molecules from H atoms will no longer be a spontaneous process.
A) 500 K
B) 1250 K
C) 2300 K
D) 4400 K
E) 6500 K
A) 500 K
B) 1250 K
C) 2300 K
D) 4400 K
E) 6500 K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following relationships between Kp and Kc is correct for the reaction
N2(g) + 3 H2(g) 2 NH3(g)
When the reaction is carried out at 100 ℃?
A) Kp = Kc
B) Kp < Kc
C) Kp > Kc
D) Kp < 0, Kc < 0
N2(g) + 3 H2(g) 2 NH3(g)
When the reaction is carried out at 100 ℃?
A) Kp = Kc
B) Kp < Kc
C) Kp > Kc
D) Kp < 0, Kc < 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The Kp for the following equation is 3.2 x 10 - 3. Calculate the value of Kc at 25 o C.
COCl2(g) CO(g) + Cl2(g)
A) 7.8 x 10 - 2
B) 6.6 x 10 - 3
C) 1.6 x 10 - 3
D) 1.3 x 10 - 4
E) none of these
COCl2(g) CO(g) + Cl2(g)
A) 7.8 x 10 - 2
B) 6.6 x 10 - 3
C) 1.6 x 10 - 3
D) 1.3 x 10 - 4
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Assume that Kp = 1.75 for the reaction.
CO2(g) + C(s)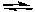 2 CO(g)
2 CO(g)
Calculate Kp for the following reaction.
CO(g) 1/2 CO2(g) + 1/2 C(s)
1/2 CO2(g) + 1/2 C(s)
A) 0.756
B) 1.32
C) 1.75
D) 3.06
E) none of the above
CO2(g) + C(s)
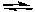 2 CO(g)
2 CO(g)Calculate Kp for the following reaction.
CO(g)
 1/2 CO2(g) + 1/2 C(s)
1/2 CO2(g) + 1/2 C(s)A) 0.756
B) 1.32
C) 1.75
D) 3.06
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The composition of the following system at equilibrium at 1000 K is 0.202 atm CO2, 0.594 atm CO, and 5 kg C
2 CO(g) CO2(g) + C(s)
CO2(g) + C(s)
What is the equilibrium constant for this reaction?
A) 2.94
B) 14.56
C) 0.572
D) 0.337
E) none of the above
2 CO(g)
 CO2(g) + C(s)
CO2(g) + C(s)What is the equilibrium constant for this reaction?
A) 2.94
B) 14.56
C) 0.572
D) 0.337
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Given the equilibrium constant for the following reaction,
H2(g) + Cl2(g)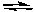 2 HCl(g) Kp = 2.5 x 104
2 HCl(g) Kp = 2.5 x 104
If equimolar amounts of H2 and Cl2 are allowed to reach equilibrium in a system in which no HCl was present initially, the ratio of the partial pressures of H2 to Cl2 at equilibrium will be
A) larger than 1.
B) smaller than 1.
C) equal to 1.
D) a value that can't be generalized by any of the above statements.
H2(g) + Cl2(g)
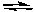 2 HCl(g) Kp = 2.5 x 104
2 HCl(g) Kp = 2.5 x 104If equimolar amounts of H2 and Cl2 are allowed to reach equilibrium in a system in which no HCl was present initially, the ratio of the partial pressures of H2 to Cl2 at equilibrium will be
A) larger than 1.
B) smaller than 1.
C) equal to 1.
D) a value that can't be generalized by any of the above statements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which statement concerning the following reaction isn't true?
2 HI(g)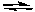 H2(g) + I2(g)
H2(g) + I2(g)
A) At equilibrium, the concentrations of the three gases do not change with time.
B) Kp = Kc
C) The partial pressures of I2 and H2 are equal at equilibrium, regardless of the initial pressures of HI, H2, and I2.
D) HI decomposes as fast as it is formed once equilibrium is established.
E) The percent dissociation of HI does not depend on the total pressure.
2 HI(g)
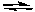 H2(g) + I2(g)
H2(g) + I2(g)A) At equilibrium, the concentrations of the three gases do not change with time.
B) Kp = Kc
C) The partial pressures of I2 and H2 are equal at equilibrium, regardless of the initial pressures of HI, H2, and I2.
D) HI decomposes as fast as it is formed once equilibrium is established.
E) The percent dissociation of HI does not depend on the total pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The standard free energy change for the evaporation of water is found to be +8.56 kJ/molrxn.
H2O(l) H2O(g)
This says that the evaporation of water is nonspontaneous under standard conditions. If a beaker of water is set out on a table in the room why will it spontaneously evaporate?
H2O(l) H2O(g)
This says that the evaporation of water is nonspontaneous under standard conditions. If a beaker of water is set out on a table in the room why will it spontaneously evaporate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following statements is true?
A) G = G o when the reaction is at equilibrium.
B) G is a measure of how far the reaction is from equilibrium.
C) G o is positive for reactions that have too much reactant in the standard state.
D) The value of G does not depend on the temperature of the reaction.
E) None of these statements are true.
A) G = G o when the reaction is at equilibrium.
B) G is a measure of how far the reaction is from equilibrium.
C) G o is positive for reactions that have too much reactant in the standard state.
D) The value of G does not depend on the temperature of the reaction.
E) None of these statements are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following statements is false?
A) G is equal to G o when the system is at the standard state.
B) G is zero when the system is at equilibrium.
C) G measures how far the reaction is from equilibrium.
D) When G is positive, the reaction should proceed forward to form more product.
E) All of the above statements are true.
A) G is equal to G o when the system is at the standard state.
B) G is zero when the system is at equilibrium.
C) G measures how far the reaction is from equilibrium.
D) When G is positive, the reaction should proceed forward to form more product.
E) All of the above statements are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If the following reaction is spontaneous as written, under standard conditions,
Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s)
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Kc > 1 and G° > 0
B) Kc > 1 and G° < 0
C) Kc < 1 and G° < 0
D) Kc > 1 and G° = 0
E) Kc < 1 and G° = 0
Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s)
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Kc > 1 and G° > 0
B) Kc > 1 and G° < 0
C) Kc < 1 and G° < 0
D) Kc > 1 and G° = 0
E) Kc < 1 and G° = 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
For the reaction, 2 SO3(g) 2 SO2(g) + O2(g), the following thermodynamic data are available.

What is the equilibrium constant for this reaction at 25 ° C?
A) between 10-50 and 10-30
B) between 10-30 and 10-20
C) roughly 1
D) between 1020 and 1030
E) between 1030 and 1050

What is the equilibrium constant for this reaction at 25 ° C?
A) between 10-50 and 10-30
B) between 10-30 and 10-20
C) roughly 1
D) between 1020 and 1030
E) between 1030 and 1050

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
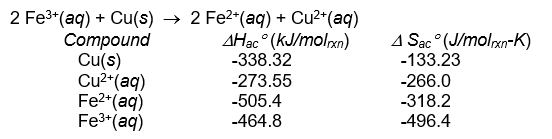
The equilibrium constant for this reaction at 25°C is:
A) between 10-30 and 10-16
B) between 10-16 and 10-10
C) between 10-10 and 106
D) between 106 and 1016
E) larger than 1016

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
G° = -53.6 kJ/molrxn for the following reaction at 25°C.
Zn2+(aq) + 4 NH3(aq) Zn(NH3)42+(aq)
What is the value of the complex formation equilibrium constant for this reaction?
A) 5 x 10-21
B) 4 x 10-10
C) 2.5 x 109
D) 2.0 x 1020
E) 1.2 x 1023
Zn2+(aq) + 4 NH3(aq) Zn(NH3)42+(aq)
What is the value of the complex formation equilibrium constant for this reaction?
A) 5 x 10-21
B) 4 x 10-10
C) 2.5 x 109
D) 2.0 x 1020
E) 1.2 x 1023

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Use the following information to answer this question.
H2(g) + F2(g) 2 HF(g) G ° = -190 kJ/molrxn
H2(g) + Cl2(g) 2 HCl(g) G ° = -546 kJ/molrxn
H2(g) + Br2(g) 2 HBr(g) G ° = -106 kJ/molrxn
H2(g) + I2(g) 2 HI(g) G ° = 4 kJ/molrxn
An excess of H2 is allowed to react with equal amounts of F2, Cl2, Br2, and I2 in a sealed flask. Which of the following products is present in the largest concentration at equilibrium?
A) HF
B) HCl
C) HBr
D) HI
E) All four products are present in equal concentrations.
H2(g) + F2(g) 2 HF(g) G ° = -190 kJ/molrxn
H2(g) + Cl2(g) 2 HCl(g) G ° = -546 kJ/molrxn
H2(g) + Br2(g) 2 HBr(g) G ° = -106 kJ/molrxn
H2(g) + I2(g) 2 HI(g) G ° = 4 kJ/molrxn
An excess of H2 is allowed to react with equal amounts of F2, Cl2, Br2, and I2 in a sealed flask. Which of the following products is present in the largest concentration at equilibrium?
A) HF
B) HCl
C) HBr
D) HI
E) All four products are present in equal concentrations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction if G° at 298 K is -16.5 kJ/molrxn?
N2(g) + 3 H2(g) 2 NH3(g)
A) 2.0 x 10-5
B) 1.3 x 10-3
C) 780
D) 4.6 x 106
E) 220
N2(g) + 3 H2(g) 2 NH3(g)
A) 2.0 x 10-5
B) 1.3 x 10-3
C) 780
D) 4.6 x 106
E) 220

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Ka for benzoic acid (C6H5CO2H) is 3.0 x 10-5. What is the free energy change for the dissociation of this acid at 25°C?
A) -25.8 kJ/molrxn
B) -2.2 kJ/molrxn
C) 2.2 kJ/molrxn
D) 25.8 kJ/molrxn
E) none of the above
A) -25.8 kJ/molrxn
B) -2.2 kJ/molrxn
C) 2.2 kJ/molrxn
D) 25.8 kJ/molrxn
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which statement is true if the following reaction is spontaneous as written?
Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s)
A) Kc is larger than 1, G° is negative, and E° is positive.
B) Kc is larger than 1, G° is positive, and E° is negative.
C) Kc is larger than 1, G° is negative, and E° is negative.
D) Kc is smaller than 1, G° is negative, and E° is positive.
E) Kc is smaller than 1, G° is positive, and E° is negative.
Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s)
A) Kc is larger than 1, G° is negative, and E° is positive.
B) Kc is larger than 1, G° is positive, and E° is negative.
C) Kc is larger than 1, G° is negative, and E° is negative.
D) Kc is smaller than 1, G° is negative, and E° is positive.
E) Kc is smaller than 1, G° is positive, and E° is negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What happens to the magnitude of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction as the temperature of the system increases?
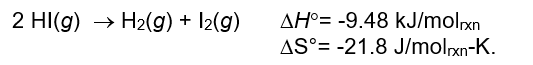
A) Kc first increases and then decreases.
B) Kc first decreases and then increases.
C) Kc increases.
D) Kc decreases.
E) It is impossible to determine what happens to Kc.
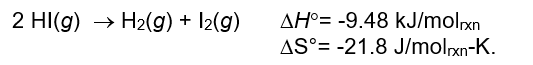
A) Kc first increases and then decreases.
B) Kc first decreases and then increases.
C) Kc increases.
D) Kc decreases.
E) It is impossible to determine what happens to Kc.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following statements is true about G ° , and K for the following reaction when the temperature is increased?
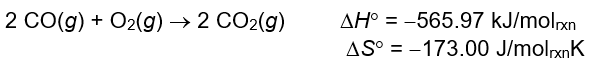
A) As temperature increases, G ° will increase (become more positive), and K will increase .
B) As temperature increases, G ° will decrease (become more negative), and K will decrease.
C) As temperature increases, G ° ncreases (become more positive) and K decreases.
D) As temperature increases, G ° decreases (becomes more negative) and K increases.
E) None of these are true.
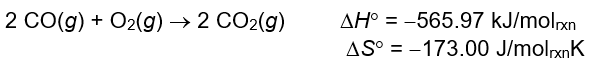
A) As temperature increases, G ° will increase (become more positive), and K will increase .
B) As temperature increases, G ° will decrease (become more negative), and K will decrease.
C) As temperature increases, G ° ncreases (become more positive) and K decreases.
D) As temperature increases, G ° decreases (becomes more negative) and K increases.
E) None of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Although the diatomic molecule N2 has an extremely strong nitrogen/nitrogen triple bond, it will break apart into nitrogen atoms
(N2(g) 2 N(g)) if it is heated to a high enough temperature because
A) the value of G becomes more positive as the temperature increases.
B) the unfavorable enthalpy change for the reaction disappears at higher temperatures.
C) the entropy change for the reaction is favorable and this factor becomes more important as the temperature of the system increases.
D) the equilibrium constant for the reaction decreases with temperature.
E) none of the above statements is a correct explanation.
(N2(g) 2 N(g)) if it is heated to a high enough temperature because
A) the value of G becomes more positive as the temperature increases.
B) the unfavorable enthalpy change for the reaction disappears at higher temperatures.
C) the entropy change for the reaction is favorable and this factor becomes more important as the temperature of the system increases.
D) the equilibrium constant for the reaction decreases with temperature.
E) none of the above statements is a correct explanation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Calculate the standard free energy change, G ° , and standard entropy change, S ° , for the following reaction at 298 K.
Cl2(g) + 3 F2(g) 2ClF3(g)

A) -123 kJ/molrxn, -134 J/molrxn-K
B) -246 kJ/molrxn, -268 J/molrxn-K
C) -326 kJ/molrxn, -268 J/molrxn-K
D) -51 kJ/molrxn, -586 J/molrxn-K
E) -148 kJ/molrxn, -134 J/molrxn-K
Cl2(g) + 3 F2(g) 2ClF3(g)

A) -123 kJ/molrxn, -134 J/molrxn-K
B) -246 kJ/molrxn, -268 J/molrxn-K
C) -326 kJ/molrxn, -268 J/molrxn-K
D) -51 kJ/molrxn, -586 J/molrxn-K
E) -148 kJ/molrxn, -134 J/molrxn-K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Calculate the standard free energy, G ° , in kJ/molrxn for the reaction below.
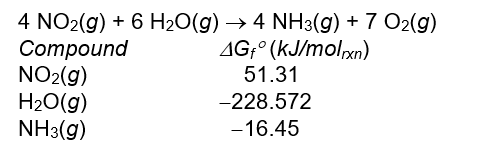
A) -1232.0 kJ/molrxn
B) 1232.0 kJ/molrxn
C)-478.9 kJ/molrxn
D) 478.9 kJ/molrxn
E) none of these
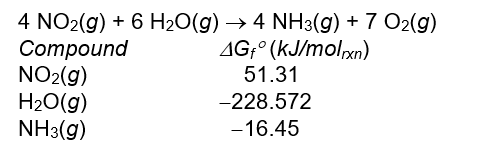
A) -1232.0 kJ/molrxn
B) 1232.0 kJ/molrxn
C)-478.9 kJ/molrxn
D) 478.9 kJ/molrxn
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Calculate the standard enthalpy change, H ° , and standard entropy change, S ° , for the following reaction at 298 K.
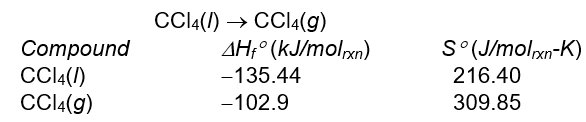
A) 93.45 kJ/molrxn, 32.5 J/molrxn-K
B) 32.5 kJ/molrxn, 93.45 J/molrxn-K
C) -32.5 kJ/molrxn, 93.45 J/molrxn-K
D) -32.5 kJ/molrxn, -93.45 J/molrxn-K
E) -93.45 kJ/molrxn, 32.5 J/molrxn-K
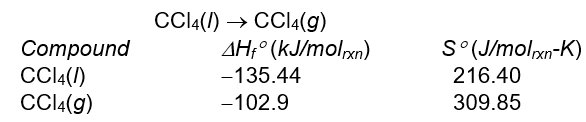
A) 93.45 kJ/molrxn, 32.5 J/molrxn-K
B) 32.5 kJ/molrxn, 93.45 J/molrxn-K
C) -32.5 kJ/molrxn, 93.45 J/molrxn-K
D) -32.5 kJ/molrxn, -93.45 J/molrxn-K
E) -93.45 kJ/molrxn, 32.5 J/molrxn-K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
For each of the following variables what is the appropriate sign that is favorable for a spontaneous reaction?
A) H ° = +, S ° = +, G ° = +, E ° = +
B) H ° = -, S ° = +, G ° = +, E° = +
C) H ° = +, S ° = +, G ° = - , E ° = +
D) H ° = +, S ° = +, G ° = +, E ° = -
E) H ° = -, F S ° = +, G ° = -, E °F +
A) H ° = +, S ° = +, G ° = +, E ° = +
B) H ° = -, S ° = +, G ° = +, E° = +
C) H ° = +, S ° = +, G ° = - , E ° = +
D) H ° = +, S ° = +, G ° = +, E ° = -
E) H ° = -, F S ° = +, G ° = -, E °F +

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In chapter 12 you used Eo to predict when a redox reaction would be spontaneous. In chapter 13 Go was used to predict if a reaction was spontaneous. Which of the following describes the relationship between Go and Eo?
A) when Go is positive, Eo is negative
B) when Go is positive, Eo is positive
C) when Go is negative, Eo is negative
D) when Go is negative, Eo is zero
E) There is no relationship between Go and Eo.
A) when Go is positive, Eo is negative
B) when Go is positive, Eo is positive
C) when Go is negative, Eo is negative
D) when Go is negative, Eo is zero
E) There is no relationship between Go and Eo.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The equilibrium constant for the following reaction is Kp = 4.1 x 10-3
COCl2(g) CO(g) + Cl2(g)
CO(g) + Cl2(g)
Calculate the equilibrium pressure of CO in a closed vessel that initially contained 0.30 atm of COCl2 and no CO or Cl2.
COCl2(g)
 CO(g) + Cl2(g)
CO(g) + Cl2(g)Calculate the equilibrium pressure of CO in a closed vessel that initially contained 0.30 atm of COCl2 and no CO or Cl2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The equilibrium constant for the following reaction is Kp = 1.0 x 104.
2 NO(g) + O2(g) 2 NO2(g)
2 NO2(g)
Calculate the equilibrium pressure of oxygen in a system that initially contains 0.50 atm of NO, 0.10 atm of O2, and 0.20 atm of NO2.
2 NO(g) + O2(g)
 2 NO2(g)
2 NO2(g)Calculate the equilibrium pressure of oxygen in a system that initially contains 0.50 atm of NO, 0.10 atm of O2, and 0.20 atm of NO2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What is the value of S o per mole of CH3OH produced in this reaction?
A) -219.2 J/molrxnK
B) -164.1 J/molrxnK
C) -88.4 J/molrxnK
D) 88.4 J/molrxnK
E) 219.2 J/molrxnK
A) -219.2 J/molrxnK
B) -164.1 J/molrxnK
C) -88.4 J/molrxnK
D) 88.4 J/molrxnK
E) 219.2 J/molrxnK

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What is F G o per mole of CH3OH produced in this reaction at 25 o C?
A) -155.5 kJ/molrxn
B) -24.8 kJ/molrxn
C) +24.8 kJ/molrxn
D) 155.5 kJ/molrxn
E) none of the above
A) -155.5 kJ/molrxn
B) -24.8 kJ/molrxn
C) +24.8 kJ/molrxn
D) 155.5 kJ/molrxn
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following statements about this reaction is true?
A) The reaction can never become favorable.
B) The reaction can never become unfavorable.
C) The reaction will become more favorable as the temperature is increased.
D) The reaction will become less favorable as the temperature is increased.
E) Temperature has no effect on whether this reaction is favorable.
A) The reaction can never become favorable.
B) The reaction can never become unfavorable.
C) The reaction will become more favorable as the temperature is increased.
D) The reaction will become less favorable as the temperature is increased.
E) Temperature has no effect on whether this reaction is favorable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Kp = 2.1 x 106 for the following reaction at a given temperature.
2 NH3(g) N2(g) + 3 H2(g)
N2(g) + 3 H2(g)
Starting with ammonia at 4.00 atm in a fixed-volume container, calculate the equilibrium pressures of all three gases. Justify any approximations used in solving this problem.
2 NH3(g)
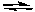 N2(g) + 3 H2(g)
N2(g) + 3 H2(g)Starting with ammonia at 4.00 atm in a fixed-volume container, calculate the equilibrium pressures of all three gases. Justify any approximations used in solving this problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The following equilibrium is established in the gas phase at 600 K by heating phosgene, COCl2.
COCl2(g)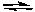 CO(g) + Cl2(g) Kp = 4.10 x 10-3
CO(g) + Cl2(g) Kp = 4.10 x 10-3
If the initial pressure of phosgene is 0.120 atm, what is the equilibrium pressure of Cl2?
A) 4.9 x 10-4 atm
B) 2.0 x 10-2 atm
C) 2.2 x 10-2 atm
D) 0.10 atm
E) none of these
COCl2(g)
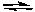 CO(g) + Cl2(g) Kp = 4.10 x 10-3
CO(g) + Cl2(g) Kp = 4.10 x 10-3If the initial pressure of phosgene is 0.120 atm, what is the equilibrium pressure of Cl2?
A) 4.9 x 10-4 atm
B) 2.0 x 10-2 atm
C) 2.2 x 10-2 atm
D) 0.10 atm
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The equilibrium constant for the following gas-phase reaction is 68.0.
2 IBr(g) I2(g) + Br2(g)
I2(g) + Br2(g)
At equilibrium, twice as much Br2 is present as IBr and the partial pressure of I2 is 1 atm. What is the equilibrium partial pressure of IBr?
A) 0.0074 atm
B) 0.0037 atm
C) 0.029 atm
D) 0.059 atm
E) 136 atm
2 IBr(g)
 I2(g) + Br2(g)
I2(g) + Br2(g)At equilibrium, twice as much Br2 is present as IBr and the partial pressure of I2 is 1 atm. What is the equilibrium partial pressure of IBr?
A) 0.0074 atm
B) 0.0037 atm
C) 0.029 atm
D) 0.059 atm
E) 136 atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The equilibrium constant for the reaction of NO(g) with Cl2(g) to produce NOCl(g) is 52. If 0.50 atm of NO and 0.25 atm of Cl2 react to equilibrium in a closed system that initially contained no NOCl, calculate the partial pressures of all three components at equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
At a fixed temperature and 1.00 atm total pressure, NO2 gas and N2O4 gas are in equilibrium.
2 NO2(g)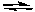 N2O4(g)
N2O4(g)
What is the effect of increasing the total pressure to 10.0 atm at a constant temperature?
A) Kp increases, but the partial pressure of N2O4 decreases.
B) Kp decreases, but the partial pressure of N2O4 increases.
C) Both Kp and the partial pressure of N2O4 decrease.
D) Both Kp and the partial pressure of N2O4 increase.
E) Kp remains the same and the partial pressure of N2O4 increases.
2 NO2(g)
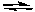 N2O4(g)
N2O4(g)What is the effect of increasing the total pressure to 10.0 atm at a constant temperature?
A) Kp increases, but the partial pressure of N2O4 decreases.
B) Kp decreases, but the partial pressure of N2O4 increases.
C) Both Kp and the partial pressure of N2O4 decrease.
D) Both Kp and the partial pressure of N2O4 increase.
E) Kp remains the same and the partial pressure of N2O4 increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



