Deck 24: Inflation, Unemployment, and Central Bank Policy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/13
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 24: Inflation, Unemployment, and Central Bank Policy
1
Which of the following best summarises the reaction of the Egyptian Central Banks to the global financial crisis of 2009?
A) They expanded their investments in foreign currency.
B) They lowered the target for the overnight interest rate.
C) They shifted the aggregate demand to the left.
D) They increased the long term interest rate.
A) They expanded their investments in foreign currency.
B) They lowered the target for the overnight interest rate.
C) They shifted the aggregate demand to the left.
D) They increased the long term interest rate.
They lowered the target for the overnight interest rate.
2
You are negotiating a cost of living raise with your boss. Under which of the following circumstances would you ask for the largest raise?
A) The central bank policy raises the unemployment rate above the natural rate.
B) The central bank policy lowers the unemployment rate below the natural rate.
C) The central bank policy targets inflation at its current value.
D) The central bank policy targets inflation at levels below its current value.
A) The central bank policy raises the unemployment rate above the natural rate.
B) The central bank policy lowers the unemployment rate below the natural rate.
C) The central bank policy targets inflation at its current value.
D) The central bank policy targets inflation at levels below its current value.
The central bank policy lowers the unemployment rate below the natural rate.
3
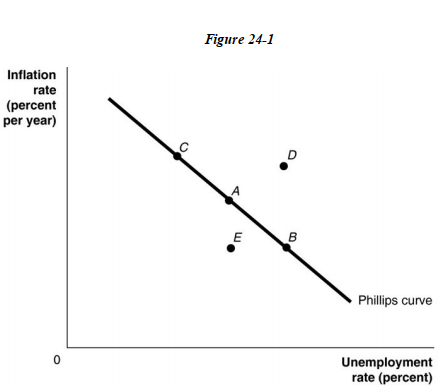
-Refer to Figure 24 -1. Suppose that the economy is currently at point A, and the unemployment rate at A is the natural rate. What policy would the central bank pursue if it wanted the economy to move to point B in the long run?
A) decrease the money supply
B) raise the discount rate
C) buy treasury bills
D) no policy will move the economy to point B in the long run
E) sell treasury bills
no policy will move the economy to point B in the long run
4

-Refer to Figure 24 -1. Suppose that the economy is currently at point A on the short -run Phillips curve in the figure above, and the unemployment rate at A is the natural rate. If the economy was to move to point C, which of the following must be true?
A) Equilibrium GDP must be above potential GDP.
B) The central bank sold treasury bills to cause the move.
C) The central bank conducted contractionary policy to cause the move.
D) Aggregate demand must have decreased.
E) The economy is producing a level of GDP equal to potential GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If the Phillips curve represents a "structural relationship," then
A) unemployment could be permanently decreased along with inflation.
B) contractionary monetary policy could achieve lower inflation while holding unemployment constant.
C) expansionary monetary policy could achieve lower unemployment while holding inflation constant.
D) the Phillips curve represents a policy menu of choices.
A) unemployment could be permanently decreased along with inflation.
B) contractionary monetary policy could achieve lower inflation while holding unemployment constant.
C) expansionary monetary policy could achieve lower unemployment while holding inflation constant.
D) the Phillips curve represents a policy menu of choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Malak's real wage in 2005 is $26.80. If the price level is 104, what is Matt's nominal wage?
A) $25.77
B) $26.80
C) $30.80
D) $27.87
A) $25.77
B) $26.80
C) $30.80
D) $27.87

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Models that focus on "real" rather than "monetary" explanations of fluctuations in real GDP are called
A) nonmonetary business cycle models.
B) short -run macroeconomic models.
C) real business cycle models.
D) rational expectations models.
A) nonmonetary business cycle models.
B) short -run macroeconomic models.
C) real business cycle models.
D) rational expectations models.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A prominent economist was quoted as saying, "The central bank should have the flexibility to respond to potential financial crises without being limited in the actions it might take." Based on this comment, this economist supports a
A) "rules" strategy of the central bank.
B) "crisis" strategy of the central bank.
C) "discretion" strategy of the central bank.
D) "unanticipated" strategy of the central bank.
A) "rules" strategy of the central bank.
B) "crisis" strategy of the central bank.
C) "discretion" strategy of the central bank.
D) "unanticipated" strategy of the central bank.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If the central bank announces that its target for the overnight rate is rising from 4 percent to 4.25 percent, how do you expect workers and firms to react?
A) If the central bank's announcement is not credible, workers and firms will not expect inflation to fall so they will reduce their consumption and investment spending, which will increase aggregate demand and reduce inflation.
B) As long as the central bank's announcement is credible, workers and firms will increase their consumption and investment spending, which will increase aggregate demand and inflation.
C) Workers and firms will incorporate the increase in interest rates into their expectations of inflation, and they will expect inflation to rise as a result of central bank's policy announcement.
D) As long as the central bank's announcement is credible, workers and firms will reduce their consumption and investment spending, which will reduce aggregate demand and reduce inflation.
A) If the central bank's announcement is not credible, workers and firms will not expect inflation to fall so they will reduce their consumption and investment spending, which will increase aggregate demand and reduce inflation.
B) As long as the central bank's announcement is credible, workers and firms will increase their consumption and investment spending, which will increase aggregate demand and inflation.
C) Workers and firms will incorporate the increase in interest rates into their expectations of inflation, and they will expect inflation to rise as a result of central bank's policy announcement.
D) As long as the central bank's announcement is credible, workers and firms will reduce their consumption and investment spending, which will reduce aggregate demand and reduce inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What actions could the central bank take to achieve consistent growth in real GDP at 4 percent per year?
A) The central bank could increase in the growth rate of the money supply by 1% each year until the inflation rate was exactly equal to 4 percent.
B) The central bank could follow contractionary monetary policy that would reduce the overnight rate to zero so investment will rise consistently.
C) The central bank has no direct control over real GDP in the long run, so there are no actions it could take to achieve that goal.
D) The central bank could maintain a growth rate of the money supply of 4 percent, regardless of whether inflation was rising or falling in the economy.
A) The central bank could increase in the growth rate of the money supply by 1% each year until the inflation rate was exactly equal to 4 percent.
B) The central bank could follow contractionary monetary policy that would reduce the overnight rate to zero so investment will rise consistently.
C) The central bank has no direct control over real GDP in the long run, so there are no actions it could take to achieve that goal.
D) The central bank could maintain a growth rate of the money supply of 4 percent, regardless of whether inflation was rising or falling in the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following does Jordan not include in its core inflation rate, a fact that allowed its Central Bank to keep interest rates low in 2010?
A) Food and energy products
B) Insurance
C) Housing costs
D) Clothing
A) Food and energy products
B) Insurance
C) Housing costs
D) Clothing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What are the pros and cons of a "rules strategy" for the central bank in establishing monetary policy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Explain how expansionary monetary policy in Japan was expected to stop deflation and spur economic growth. Was this policy successful? Why or why not?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



