Deck 16: Economic Growth, the Financial System, and Business Cycles
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/18
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Economic Growth, the Financial System, and Business Cycles
1
An unemployment rate of 14 percent for the Arab world was announced in the 36th Arab Labour Conference, held in Amman, Jordan, in November 2010. Which of the following factors have led to this high rate of unemployment in the Arab world?
A) Economic instability.
B) The low quality of education in the Arab world.
C) The high illiteracy rate of the Arab world.
D) All of the above.
A) Economic instability.
B) The low quality of education in the Arab world.
C) The high illiteracy rate of the Arab world.
D) All of the above.
All of the above.
2
Which of the following explains why the labor force participation rate of females is less than half of the labor force participation rate of males in many Arab countries?
A) Women are retiring earlier in life as compared to the past
B) Women are remaining in school longer compared to the past
C) Cultural and religious reasons
D) All the above
A) Women are retiring earlier in life as compared to the past
B) Women are remaining in school longer compared to the past
C) Cultural and religious reasons
D) All the above
Cultural and religious reasons
3
Which of the following demographic groups in the Arab world tend to have an unemployment rate above average?
A) Older population
B) Individuals with lower -level education attainment
C) Youth population
D) Men
A) Older population
B) Individuals with lower -level education attainment
C) Youth population
D) Men
Youth population
4
In developing countries, what factors result in a longer period of unemployment for jobless people?
A) weak economies (low level of GDP)
B) the mismatch between workers' skills and the job market needs
C) low quality of education
D) All of the above
A) weak economies (low level of GDP)
B) the mismatch between workers' skills and the job market needs
C) low quality of education
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Explain why there is a relatively high female labor force participation rate in poor Arab countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Frictional unemployment is the result of
A) the search process of matching workers with jobs.
B) a slowdown in the economy.
C) a persistent mismatch between the skills and characteristics of workers and the requirements of the jobs.
D) the ups and downs in inflation.
A) the search process of matching workers with jobs.
B) a slowdown in the economy.
C) a persistent mismatch between the skills and characteristics of workers and the requirements of the jobs.
D) the ups and downs in inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Lulu supermarkets pays higher wages than Carrefour
A) because Lulu requires higher skilled workers to sell higher -end products.
B) to raise the productivity of Lulu workers.
C) because Lulu is unionized and Carrefour is not.
D) A and B
A) because Lulu requires higher skilled workers to sell higher -end products.
B) to raise the productivity of Lulu workers.
C) because Lulu is unionized and Carrefour is not.
D) A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
To reduce the bias in the consumer price index, the Labor Statistics Department
A) incorporates substitutions by consumers when prices of specific products fall rapidly.
B) updates the market basket every two years, rather than every 10 years.
C) updates the market basket every 10 years, rather than every two years.
D) incorporates substitutions by consumers when prices of specific products rise rapidly.
A) incorporates substitutions by consumers when prices of specific products fall rapidly.
B) updates the market basket every two years, rather than every 10 years.
C) updates the market basket every 10 years, rather than every two years.
D) incorporates substitutions by consumers when prices of specific products rise rapidly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
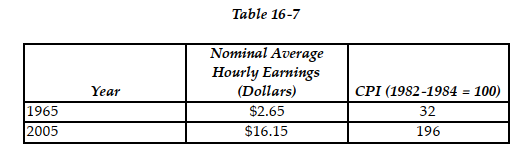 The table above reports the nominal average hourly earnings in private industry and the consumer price index for 1965 and 2005.
The table above reports the nominal average hourly earnings in private industry and the consumer price index for 1965 and 2005.-Refer to Table 16 -7. The real average hourly earnings for 1965 in 1982 -1984 dollars equal
A) $1.35.
B) $84.80.
C) $5.19.
D) $8.28.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
 The table above reports the nominal average hourly earnings in private industry and the consumer price index for 1965 and 2005.
The table above reports the nominal average hourly earnings in private industry and the consumer price index for 1965 and 2005.-Refer to Table 16 -7. The real average hourly earnings for 1965 in 2005 dollars equal
A) $5.19.
B) $8.28.
C) $16.23.
D) $2.65.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Suppose your grandfather earned a salary of $12,000 in 1961. If the CPI is 30 in 1961 and 196 in 2005, then the value of your grandfather's salary in 2005 dollars equals
A) $78,400.
B) $62,500.
C) $23,520.
D) $40,000.
A) $78,400.
B) $62,500.
C) $23,520.
D) $40,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
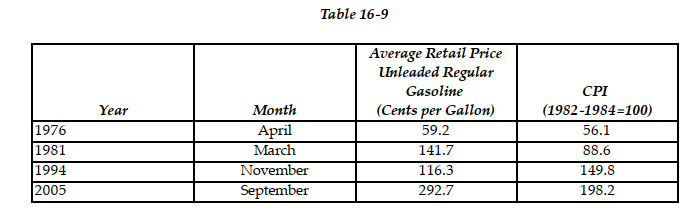
-Refer to Table 16-9. Gasoline prices were at historical highs in the fall of 2005. After adjusting for inflation, how high were these gasoline prices compared to gasoline prices over the last 30 years? The table below reports the consumer price index and the average U.S. retail price for unleaded regular gasoline for four different periods since 1976. Note that the gasoline prices are in cents per gallon.
Calculate the real average retail price of unleaded regular gasoline in 1982-1984 dollars. In which period were gasoline prices the highest in real terms? Also, calculate the real average retail price of unleaded regular gasoline in 2005 dollars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Suppose that in 2011 all prices in the economy double and that all wages and salaries have also doubled. In 2011 you
A) are worse off than you were in 2010 as you can no longer afford to buy as many goods and services.
B) are no better off or worse off than you were in 2010 as the purchasing power of your salary has remained the same.
C) are better off than you were in 2010 as your salary is higher than it was in 2010 and you can now buy more goods and services.
D) cannot determine whether you are better off or worse off than you were in 2010, because the purchasing power of your salary cannot be determined.
A) are worse off than you were in 2010 as you can no longer afford to buy as many goods and services.
B) are no better off or worse off than you were in 2010 as the purchasing power of your salary has remained the same.
C) are better off than you were in 2010 as your salary is higher than it was in 2010 and you can now buy more goods and services.
D) cannot determine whether you are better off or worse off than you were in 2010, because the purchasing power of your salary cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
For bondholders, the government taxes the ________ interest payments received.
A) real minus the inflation
B) inflation
C) nominal
D) real
A) real minus the inflation
B) inflation
C) nominal
D) real

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If inflation increases,
A) real after -tax bond income increases.
B) real after -tax bond income does not change.
C) nominal after -tax bond income decreases.
D) real after -tax bond income decreases.
A) real after -tax bond income increases.
B) real after -tax bond income does not change.
C) nominal after -tax bond income decreases.
D) real after -tax bond income decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
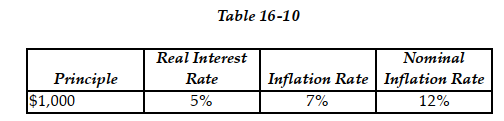
-Refer to Table 16-10. Given the table above, what is the nominal after-tax interest payment if the tax rate is 10%?
A) $38
B) $50
C) $108
D) $120

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17

-Refer to Table 16 -10. Given the table above, what is the real after -tax interest payment if the tax rate is 10%?
A) $38
B) $50
C) $108
D) $120

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is not an example of inflation causing a redistribution of income because the inflation was unanticipated?
A) A bank collects a lower amount of interest from a loan because inflation was under -predicted.
B) Firms have to hire an extra worker to change prices in its store because of inflation.
C) A worker receives a raise in salary that is less than the rate of inflation, because management under -predicted inflation.
D) A bond -holder pays a higher tax and has less after -tax real income because of inflation.
A) A bank collects a lower amount of interest from a loan because inflation was under -predicted.
B) Firms have to hire an extra worker to change prices in its store because of inflation.
C) A worker receives a raise in salary that is less than the rate of inflation, because management under -predicted inflation.
D) A bond -holder pays a higher tax and has less after -tax real income because of inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



