Deck 8: Firms in Perfectly Competitive Markets
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/15
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Firms in Perfectly Competitive Markets
1
In the last 15 years, mobile phone prices have been dropping significantly while the technology and features offered in these phones has increased dramatically. Along with technology advancement and outsourcing the production of mobile phones to countries with low cost of labor such as China, which of these economic phenomena explains the reduction in price?
A) The substitution effect.
B) Competition.
C) The income effect.
D) Elasticity of Demand.
A) The substitution effect.
B) Competition.
C) The income effect.
D) Elasticity of Demand.
Competition.
2
Many entrepreneurs found great economic opportunities in selling mobile phones in the 1990s, but as more entrepreneurs enter the mobile market, the fewer economic the opportunities found. In other words, economic opportunities are exhausted because the additional supply of mobile phones forced down prices. What effect did this have on the profit margin of existing sellers of mobile phones?
A) It had no effect on the profit margin.
B) It increased the profit margin.
C) It decreased the profit margin.
D) None of the above.
A) It had no effect on the profit margin.
B) It increased the profit margin.
C) It decreased the profit margin.
D) None of the above.
It decreased the profit margin.
3
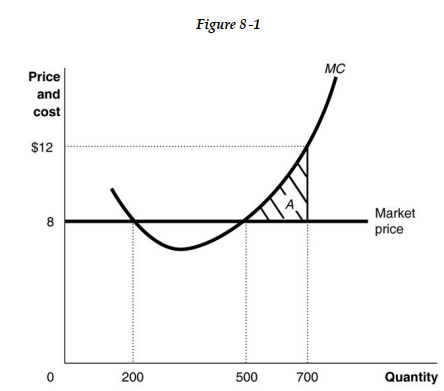
-Refer to Figure 8 -1. If the firm is producing 700 units,
A) it should cut back its output to maximize profit.
B) it is making a profit.
C) it should increase its output to maximize profit.
D) it is making a loss.
it should cut back its output to maximize profit.
4
A perfectly competitive market is in long run equilibrium. At present there are 100 identical firms each producing 5,000 units of output. The prevailing market price is $20. Assume that each firm faces increasing marginal cost. Now suppose there is a sudden increase in demand for the industry's product which causes the price of the good to rise to $24. Which of the following describes the effect of this increase in demand on a typical firm in the industry?
A) In the short run, the typical firm's output remains the same but because of the higher price, its profit increases.
B) In the short run, the typical firm increases its output and makes an above normal profit.
C) In the short run, the typical firm increases its output but its total cost also rises. Hence, the effect on the firm's profit cannot be determined without more information.
D) In the short run, the typical firm increases its output but its total cost also rises, resulting in no change in profit.
A) In the short run, the typical firm's output remains the same but because of the higher price, its profit increases.
B) In the short run, the typical firm increases its output and makes an above normal profit.
C) In the short run, the typical firm increases its output but its total cost also rises. Hence, the effect on the firm's profit cannot be determined without more information.
D) In the short run, the typical firm increases its output but its total cost also rises, resulting in no change in profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In a competitive market, earning an economic profit in the long run is extremely difficult. This difficulty is greatly seen in the Apple iPhone App market. The long run for this market is quite short due to:
A) the ease of entry to the market.
B) Apple's corporate governance structure.
C) the release of Samsung's Galaxy S.
D) the huge demand for apps on the iPhone.
A) the ease of entry to the market.
B) Apple's corporate governance structure.
C) the release of Samsung's Galaxy S.
D) the huge demand for apps on the iPhone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A constant cost perfectly competitive market is in long run equilibrium. At present, there are 1,000 firms each producing 400 units of output. The price of the good is $60. Now suppose there is a sudden increase in demand for the industry's product which causes the price of the good to rise to $64. In the new long run equilibrium, how will the average total cost of producing the good compare to what it was before the price of the good rose?
A) The average total cost will be lower than it was before the price increase because of economies of scale.
B) The average total cost will be higher than it was before the price increase since the increase in demand will drive up input prices.
C) The average total cost will be the same as it was before the price increase.
D) The average total cost will be higher than it was before the price increase because of diseconomies of scale arising from the increased demand.
A) The average total cost will be lower than it was before the price increase because of economies of scale.
B) The average total cost will be higher than it was before the price increase since the increase in demand will drive up input prices.
C) The average total cost will be the same as it was before the price increase.
D) The average total cost will be higher than it was before the price increase because of diseconomies of scale arising from the increased demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The assumption that there are no barriers to new firms entering the market or exiting a market guarantees that any excess profits will be eliminated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If a perfectly competitive industry has a downward sloping long -run supply curve, it suggests that the demand for the industry's product is decreasing over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A perfectly competitive firm in an increasing -cost industry faces an upward sloping long -run demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In response to decreasing profitability of Egyptian apparel producers in the last 2 years due to economic conditions, businessman Alaa Arafa said to producers "The ball has to keep rolling even at a loss of profitability. Lose money but do not lose the market share," It is clear that Arafa was advising others to keep producing and not shut down to maintain their market share. In which of these cases should a producer ignore Arafa's advice and shut down?
A) If the average total cost equals the market price.
B) If the average variable cost is higher than the market price.
C) If the average total cost is higher than the market price, but, the average variable cost is less than the market price.
D) None of the above.
A) If the average total cost equals the market price.
B) If the average variable cost is higher than the market price.
C) If the average total cost is higher than the market price, but, the average variable cost is less than the market price.
D) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Assume that the LCD and plasma television sets industry is perfectly competitive. Suppose a producer develops a successful innovation that enables it to lower its cost of production. What happens in the short run and in the long run?
A) Initially, the firm will be able to increase its profit significantly but in the long run its profits will still be greater than zero but lower than its short run profits because other firms would also innovate.
B) This firm will be able to earn above normal profits indefinitely if it obtains a patent for its innovation.
C) The firm will be able to increase its profits temporarily but in the long run, profits will be eliminated as other firms copy the innovation.
D) The firm will probably incur losses temporarily because of the high cost of the innovation but in the long run it will start earning positive profits.
A) Initially, the firm will be able to increase its profit significantly but in the long run its profits will still be greater than zero but lower than its short run profits because other firms would also innovate.
B) This firm will be able to earn above normal profits indefinitely if it obtains a patent for its innovation.
C) The firm will be able to increase its profits temporarily but in the long run, profits will be eliminated as other firms copy the innovation.
D) The firm will probably incur losses temporarily because of the high cost of the innovation but in the long run it will start earning positive profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In early 2007, Pioneer and JVC, two Japanese electronics firms, each announced that their profits were going to be lower than expected because they had both had to cut prices for LCD and plasma television sets. Which of the following could explain why these firms did not simply raise their prices and increase their profits?
A) Most likely, intense competition between these two major producers probably pushed prices down. Thereafter, each feared that it would lose its customers to the other if it raised its prices.
B) The firms are still making profits, just not as high as expected so there is room to lower prices until one can force the other out of business.
C) In perfect competition, prices are determined by the market and firms will keep lowering prices until there are no profits to be earned.
D) The move to cut prices is probably just a temporary one to gain market share. In the long run the firms will raise prices and be able to increase their profits.
A) Most likely, intense competition between these two major producers probably pushed prices down. Thereafter, each feared that it would lose its customers to the other if it raised its prices.
B) The firms are still making profits, just not as high as expected so there is room to lower prices until one can force the other out of business.
C) In perfect competition, prices are determined by the market and firms will keep lowering prices until there are no profits to be earned.
D) The move to cut prices is probably just a temporary one to gain market share. In the long run the firms will raise prices and be able to increase their profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Writing in the New York Times on the technology boom of the late 1990s, Michael Lewis argues, "The sad truth, for investors, seems to be that most of the benefits of new technologies are passed right through to consumers free of charge." What does Lewis means by the benefits of new technology being "passed right through to consumers free of charge"?
A) In perfect competition, price equals marginal cost of production. In this sense, consumers receive the new technology "free of charge."
B) In the long run, price equals the lowest possible average cost of production. In this sense, consumers receive the new technology "free of charge."
C) Firms in perfect competition are price takers. Since they cannot influence price, they cannot dictate who benefits from new technologies, even if the benefits of new technology being "passed right through to consumers free of charge."
D) In perfect competition, consumers place a value on the food equal to its marginal cost of production and since they are willing to pay the marginal valuation of the good, they are essentially receiving the new technology "free of charge."
A) In perfect competition, price equals marginal cost of production. In this sense, consumers receive the new technology "free of charge."
B) In the long run, price equals the lowest possible average cost of production. In this sense, consumers receive the new technology "free of charge."
C) Firms in perfect competition are price takers. Since they cannot influence price, they cannot dictate who benefits from new technologies, even if the benefits of new technology being "passed right through to consumers free of charge."
D) In perfect competition, consumers place a value on the food equal to its marginal cost of production and since they are willing to pay the marginal valuation of the good, they are essentially receiving the new technology "free of charge."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The market for Egyptian Ramadan lanterns has been penetrated by Chinese producers of the same commodity. These Chinese producers are capturing market share due to the lower price of their products. What is the factor that is helping Chinese producers keep their prices low?
A) The seasonality of demand for Ramadan lanterns.
B) They have a lower average total cost compared to Egyptian producers.
C) The high quality of the Chinese Ramadan lanterns.
D) None of the above.
A) The seasonality of demand for Ramadan lanterns.
B) They have a lower average total cost compared to Egyptian producers.
C) The high quality of the Chinese Ramadan lanterns.
D) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If productive efficiency characterizes an industry, firms in that industry are using the best technology available to produce the goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



