Deck 2: Kinematics: Description of Motion
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/92
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Kinematics: Description of Motion
1
Explain the relationship between velocity and acceleration.
Acceleration is the time rate of change of velocity.
2
Jane swims the length of a 40. meter pool in 10. seconds and immediately swims back to the starting position in another 15. seconds. What was her average velocity?
Zero
3
Discuss the differences between distance and displacement.
Distance is the total path length traversed in moving from one location to another. Displacement is the straight-line distance between two points, along with the direction from the starting point to the final point.
4
Explain how a POSITIVE acceleration could produce a DECELERATION.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Discuss whether a car speedometer measures instantaneous speed or an average speed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In the formula v2 = vo2 + 2 a x, what does x represent?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
An object moving under the influence of only gravity is said to be in ________ ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Contrast Aristotle's predictions concerning free-falling bodies with Galileo's predictions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Consider a heavy object which is thrown straight up, reaches its highest point, and then falls back down to the ground. During what parts of the trajectory was it in "FREE FALL"? (assume here that air friction is negligible)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
"Big Mike" throws a baseball straight up and it eventually falls back to him. When the ball was at its highest point, what was its velocity and what was its acceleration? (remember to include magnitude and direction)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A scalar quantity is described by both a magnitude and a direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A vector quantity is described by both a magnitude and a direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Is it possible for the magnitude of displacement to be greater than the distance traveled.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Speed indicates how fast something is moving and in which direction it is moving.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
It is possible to have constant speed, but still be accelerating.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A negative velocity, approaching zero, represents a negative acceleration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The "acceleration of gravity" is 9.8 m/s2 everywhere on the surface of the Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
An object released from rest experiences free fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The acceleration due to gravity has the same value for all free-falling objects, regardless of their mass or weight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
All of the following are scalars, except
A) time.
B) force.
C) temperature.
D) distance.
E) mass.
A) time.
B) force.
C) temperature.
D) distance.
E) mass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
All of the following are vectors, except
A) force.
B) mass.
C) velocity.
D) displacement.
E) acceleration.
A) force.
B) mass.
C) velocity.
D) displacement.
E) acceleration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Speed is to velocity as distance is to ________.
A) displacement
B) acceleration
C) magnitude
D) temperature
E) direction
A) displacement
B) acceleration
C) magnitude
D) temperature
E) direction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which physical unit is a displacement?
A) 32 ft/s2
B) 40 km, SW
C) 9.8 m/ s2
D) -120 mi/s
E) 186,000 mi
A) 32 ft/s2
B) 40 km, SW
C) 9.8 m/ s2
D) -120 mi/s
E) 186,000 mi

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which physical unit is a velocity?
A) 40 km, SW
B) 186,000 mi
C) 9.8 m/s2
D) -120 mi/s
E) 32 ft/s2
A) 40 km, SW
B) 186,000 mi
C) 9.8 m/s2
D) -120 mi/s
E) 32 ft/s2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The slope of a line connecting two points on a position versus time graph gives
A) instantaneous velocity.
B) average acceleration
C) average velocity.
D) instantaneous acceleration.
E) none of the given answers.
A) instantaneous velocity.
B) average acceleration
C) average velocity.
D) instantaneous acceleration.
E) none of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The slope of a tangent line at a given time value on a position versus time graph gives
A) instantaneous velocity.
B) instantaneous acceleration.
C) average velocity.
D) average acceleration
E) none of the given answers.
A) instantaneous velocity.
B) instantaneous acceleration.
C) average velocity.
D) average acceleration
E) none of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The slope of a line connecting two points on a velocity versus time graph gives
A) instantaneous acceleration.
B) instantaneous velocity.
C) average acceleration
D) average velocity.
E) none of the given answers.
A) instantaneous acceleration.
B) instantaneous velocity.
C) average acceleration
D) average velocity.
E) none of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The slope of a tangent line at a given time value on a velocity versus time graph gives
A) average acceleration
B) average velocity.
C) instantaneous acceleration.
D) instantaneous velocity.
E) none of the given answers.
A) average acceleration
B) average velocity.
C) instantaneous acceleration.
D) instantaneous velocity.
E) none of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A new car manufacturer advertises that their car can go "from zero to sixty in 8 s." This is a description of
A) average acceleration.
B) instantaneous speed.
C) average speed.
D) instantaneous acceleration.
E) none of the given answers.
A) average acceleration.
B) instantaneous speed.
C) average speed.
D) instantaneous acceleration.
E) none of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Suppose that an object travels from one point in space to another. Make a comparison between the displacement and the distance traveled.
A) The displacement can be either greater than, smaller than, or equal to the distance traveled.
B) The displacement is either greater than or equal to the distance traveled.
C) The displacement is either less than or equal to the distance traveled.
D) The displacement is always equal to the distance traveled.
A) The displacement can be either greater than, smaller than, or equal to the distance traveled.
B) The displacement is either greater than or equal to the distance traveled.
C) The displacement is either less than or equal to the distance traveled.
D) The displacement is always equal to the distance traveled.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which graph in Figure 2-1 represents an object at rest?
Figure 2-1

A) graph a
B) graph b
C) graph c
D) graph d
E) both graphs a and d
Figure 2-1

A) graph a
B) graph b
C) graph c
D) graph d
E) both graphs a and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which graph in Figure 2-2 represents a constant non-zero velocity?
Figure 2-2
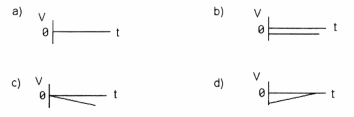
A) graph a
B) graph b
C) graph c
D) graph d
E) both graphs c and d
Figure 2-2
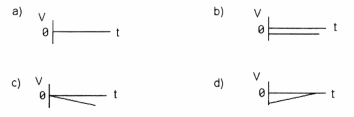
A) graph a
B) graph b
C) graph c
D) graph d
E) both graphs c and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If an object is accelerating, it must therefore undergo
A) a change in speed.
B) a change in direction.
C) a change in velocity.
A) a change in speed.
B) a change in direction.
C) a change in velocity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which graph(s) in Figure 2-3 represent(s) zero acceleration? 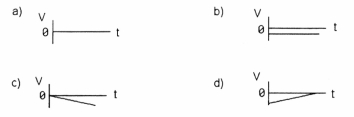
A) only a
B) only b
C) a and b
D) b and c
E) c and d
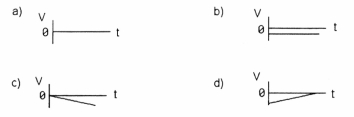
A) only a
B) only b
C) a and b
D) b and c
E) c and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which graph in Figure 2-4 represents constant positive acceleration?
Figure 2-4
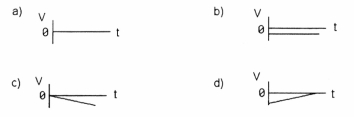
A) graph a
B) graph b
C) graph c
D) graph d
E) both graphs c and d
Figure 2-4
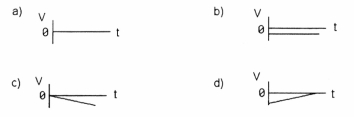
A) graph a
B) graph b
C) graph c
D) graph d
E) both graphs c and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
For constant linear acceleration, the position versus time graph is a
A) sloped line.
B) horizontal line.
C) curve.
D) vertical line.
E) none of the given answers.
A) sloped line.
B) horizontal line.
C) curve.
D) vertical line.
E) none of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
For constant linear acceleration, the velocity versus time graph is a
A) horizontal line.
B) sloped line.
C) curve.
D) vertical line.
E) none of the given answers.
A) horizontal line.
B) sloped line.
C) curve.
D) vertical line.
E) none of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Suppose that an object is moving with constant acceleration. Which of the following is an accurate statement concerning its motion?
A) In equal times its velocity changes by equal amounts.
B) In equal times it moves equal distances.
C) In equal times its speed increases by equal amounts.
A) In equal times its velocity changes by equal amounts.
B) In equal times it moves equal distances.
C) In equal times its speed increases by equal amounts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Can an object's velocity change direction when its acceleration is constant?
A) No, this is not possible because it is always slowing up.
B) No, this is not possible because it is always speeding up.
C) Yes, this is possible, and a car that starts from rest, speeds up, slows to a stop, and then backs up is an example.
D) Yes, this is possible, and a rock thrown straight up is an example.
E) No, this is not possible because it is always speeding up or always slowing down, but it can never turn around.
A) No, this is not possible because it is always slowing up.
B) No, this is not possible because it is always speeding up.
C) Yes, this is possible, and a car that starts from rest, speeds up, slows to a stop, and then backs up is an example.
D) Yes, this is possible, and a rock thrown straight up is an example.
E) No, this is not possible because it is always speeding up or always slowing down, but it can never turn around.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following can never be negative?
A) average velocity
B) displacement
C) instantaneous velocity
D) instantaneous speed
E) acceleration of gravity
A) average velocity
B) displacement
C) instantaneous velocity
D) instantaneous speed
E) acceleration of gravity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
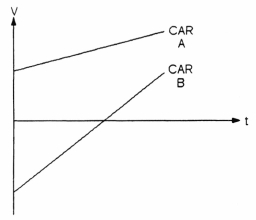
The graph in Figure 2-5 plots the velocity of two cars (A and B) along the same straight road.
Figure 2-5
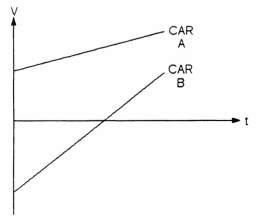
During the time interval shown, which car is AHEAD?
A) Car A
B) Car B
C) insufficient information
Figure 2-5

During the time interval shown, which car is AHEAD?
A) Car A
B) Car B
C) insufficient information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The graph in Figure 2-6 plots the velocity of two cars (A and B) along the same straight road.
Figure 2-6
Which car reverses direction?
A) Car A
B) insufficient information
C) Car B
D) both cars A & B
E) neither car A nor B
Figure 2-6

Which car reverses direction?
A) Car A
B) insufficient information
C) Car B
D) both cars A & B
E) neither car A nor B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Refer to Figure 2-7:
Figure 2-7
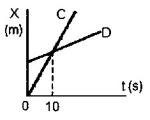
During the first 8 s
A) D is speeding up while C is slowing down
B) their accelerations are equal in magnitude, but opposite in sign.
C) their accelerations are equal in magnitude, and equal in sign.
D) the magnitude of the acceleration of C is greater than the magnitude of the acceleration of D.
E) the magnitude of the acceleration of D is greater than the magnitude of the acceleration of C.
Figure 2-7

During the first 8 s
A) D is speeding up while C is slowing down
B) their accelerations are equal in magnitude, but opposite in sign.
C) their accelerations are equal in magnitude, and equal in sign.
D) the magnitude of the acceleration of C is greater than the magnitude of the acceleration of D.
E) the magnitude of the acceleration of D is greater than the magnitude of the acceleration of C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A car is able to stop in a distance d. Assuming the same braking force, what distance does this car require to stop when it is traveling twice as fast?
A) 4 d
B) d
C)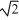 d
d
D) 2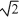 d
d
E) 2 d
A) 4 d
B) d
C)
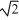 d
dD) 2
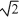 d
dE) 2 d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A can, after having been given a kick, moves up along a smooth hill of ice. It will
A) have a constant acceleration up the hill, but a smaller constant acceleration when it comes back down the hill.
B) have a constant acceleration up the hill, but a larger constant acceleration when it comes back down the hill.
C) have the same acceleration, both up the hill and down the hill.
D) have a varying acceleration along the hill.
E) travel at constant velocity.
A) have a constant acceleration up the hill, but a smaller constant acceleration when it comes back down the hill.
B) have a constant acceleration up the hill, but a larger constant acceleration when it comes back down the hill.
C) have the same acceleration, both up the hill and down the hill.
D) have a varying acceleration along the hill.
E) travel at constant velocity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which physical unit is the SI acceleration of gravity?
A) 32 ft/s2
B) -120 mi/s
C) 186,000 mi
D) 40 km, SW
E) 9.8 m/s2
A) 32 ft/s2
B) -120 mi/s
C) 186,000 mi
D) 40 km, SW
E) 9.8 m/s2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which physical unit represents acceleration in the British system?
A) 32 ft/s2
B) -120 mi/s
C) 40 km, SW
D) 186,000 mi
E) 9.8 m/s2
A) 32 ft/s2
B) -120 mi/s
C) 40 km, SW
D) 186,000 mi
E) 9.8 m/s2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
When an object is released from rest and falls in the absence of friction, which of the following is true concerning its motion?
A) Neither its acceleration nor its velocity is constant.
B) Both its acceleration and its velocity are constant.
C) Its acceleration is constant.
D) Its velocity is constant.
A) Neither its acceleration nor its velocity is constant.
B) Both its acceleration and its velocity are constant.
C) Its acceleration is constant.
D) Its velocity is constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
When a ball is thrown straight up, which of the following is zero at its highest point?
A) displacement
B) acceleration
C) velocity
A) displacement
B) acceleration
C) velocity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
When a ball is thrown straight up, the acceleration at its highest point is
A) horizontal.
B) minimum.
C) downward.
D) zero.
E) upward.
A) horizontal.
B) minimum.
C) downward.
D) zero.
E) upward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A ball is thrown straight up and returns to its starting point under an acceleration due to gravity. Which of the following is true?
A) To compare rise and fall times we need to know the mass of the ball.
B) It took the same time to rise as it took to fall.
C) It took less time to rise than to fall.
D) It took longer to rise than to fall.
A) To compare rise and fall times we need to know the mass of the ball.
B) It took the same time to rise as it took to fall.
C) It took less time to rise than to fall.
D) It took longer to rise than to fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A race car circles 10 times around an 8-km track in 20 min. What is its average speed per lap?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Denis swims the length of a 40. meter pool in 10. seconds and immediately swims back to the starting position in another 15. seconds. What was his average speed?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A race car circles 10 times around an 8-km track in 20 min. What is its average velocity per lap?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Jane walks 31 steps eastward and 16 steps southward. What is her displacement if each step averages 0.82 meters?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Eric watches a jet powered truck during an "air-show." It accelerates from rest to 300. mph in 8.0 seconds. The acceleration was equivalent to how many "g's"?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A car traveling 60 km/h accelerates at the rate of 4.0 m/s2. How much time is required for the car to reach a speed of 90 km/h?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Captain Rickard orders his starship to accelerate from rest at a rate of "1g" (accel = 9.8 m/s2). How long does it take the starship to reach one-tenth the speed of light if light travels 300. megameters/s?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A bat, flying due east at 2 m/s, emits a shriek that is reflected back to it from an oncoming insect flying directly toward the bat at 4 m/s. The insect is 20 m from the bat at the instant the shriek is emitted. Sound travels 340 m/s in air. After what elapsed time does the bat hear the reflected echo?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A bullet moving at 244. m/s strikes a tree and penetrates a distance of 8.34 mm before stopping. What was the average acceleration of the bullet as it slowed?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A bullet moving at 244. m/s strikes a tree and penetrates a distance of 8.34 mm before stopping. Assuming a constant acceleration, how long did it take the bullet to stop?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A car was moving 110. km/hour.
(a) How long did it take to go 25.5 miles?
(b) If it stopped in 35. s, what was its average acceleration (m/s2) as it slowed down?
(a) How long did it take to go 25.5 miles?
(b) If it stopped in 35. s, what was its average acceleration (m/s2) as it slowed down?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Consider a mass initially moving at 7.50 m/s.
(a) How long does it take to move 3.5 km if it accelerates at 0.550 m/s2?
(b) How fast is it moving after this acceleration?
(a) How long does it take to move 3.5 km if it accelerates at 0.550 m/s2?
(b) How fast is it moving after this acceleration?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
An auto accelerates from 7.0 m/s at 0.71 m/s2. It travels a distance of 1.033 km while accelerating.
(a) What is the final speed at the end of that displacement?
(b) How many seconds did it take to accelerate from 7.0 m/s?
(a) What is the final speed at the end of that displacement?
(b) How many seconds did it take to accelerate from 7.0 m/s?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A bullet moving horizontally with a speed of 500 m/s strikes a sandbag and penetrates a distance of 10 cm.
(a) What is the average acceleration of the bullet?
(b) How long does it take to come to rest?
(a) What is the average acceleration of the bullet?
(b) How long does it take to come to rest?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A car with good tires on a dry road can decelerate at about 5 m/s2 when braking. If the car is traveling at 89. km/h:
(a) how long does it take the car to stop under these conditions?
(b) how far does the car travel during this time?
(a) how long does it take the car to stop under these conditions?
(b) how far does the car travel during this time?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Suppose that a Ferrari and a Porsche begin a race with a moving start, and each moves with constant speed. One lap of the track is 2 km. The Ferrari laps the Porsche after the Porsche has completed 9 laps. If the speed of the Ferrari had been 10 km/h less, the Porsche would have traveled 18 laps before being overtaken. What were the speeds of the two cars?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
In a 400-m relay race the anchorman (the person who runs the last 100 m) for the Trojans can run 100 m in 9.8 s. His rival, the anchorman for the Bruins, can cover 100 m in 10.1 s. What is the largest lead the Bruin runner can have when the Trojan runner starts the final leg of the race, in order for the Trojan runner not to lose the race?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
An astronaut on a strange new planet finds that she can jump up to a maximum height of 27. meters when her initial upward speed is 6.0 m/s. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of gravity on the planet?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
An object is thrown vertically and accelerates downward at +9.80 m/s2 (downward is positive and upward is negative)
(a) What is its displacement after 5.00 s if it starts at 2.50 m/s?
(b) How fast is it moving after that 5.00 s?
(a) What is its displacement after 5.00 s if it starts at 2.50 m/s?
(b) How fast is it moving after that 5.00 s?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
-Refer to Figure 2-10. If you start from the Bakery, travel to the Cafe, and then to the Art Gallery, what is the distance you have traveled?
A) 2.5 km
B) 0 km
C) 10.5 km
D) 4.0 km
E) 6.5 km

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72

-Refer to Figure 2-10. If you start from the Bakery, travel to the Art Gallery, and then to the Cafe, in 1.0 hour, what is your average speed?
A) 4.0 km/hr
B) 6.5 km/hr
C) 9.0 km/hr
D) 2.5 km/hr
E) 10.5 km/hr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If you run a complete loop around an outdoor track (400 m) in 100 s, your average speed is
A) 4.0 mph.
B) 0.40 m/s.
C) 40000. m/s.
D) 4.0 km/h.
E) 4.0 m/s.
A) 4.0 mph.
B) 0.40 m/s.
C) 40000. m/s.
D) 4.0 km/h.
E) 4.0 m/s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A motorist travels for 3.0 h at 80 km/h and 4.0 h at 60 km/h. What is her average speed for the trip?
A) 69 km/h
B) 70 km/h
C) 74 km/h
D) 140 km/h
E) 73 km/h
A) 69 km/h
B) 70 km/h
C) 74 km/h
D) 140 km/h
E) 73 km/h

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
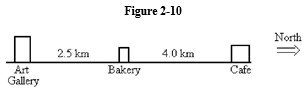
75
-Refer to Figure 2-11. If you start from the Bakery, travel to the Cafe, and then to the Art Gallery, what is your displacement?
A) 6.5 km South
B) 4.0 km South
C) 2.5 km South
D) 9.0 km North
E) 10.5 km North

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Barbara travels 20. km Northward, then travels 40. km Eastward, then continues for 50. km in a Southward direction. What displacement will now take her back to her initial position?
A) 40. km Westward + 30. km Northward
B) 30. km Westward + 40. km Northward
C) 40. km Eastward + 30. km Southward
D) 50. km Northwest
E) 30. km Northward + 30. km Westward
A) 40. km Westward + 30. km Northward
B) 30. km Westward + 40. km Northward
C) 40. km Eastward + 30. km Southward
D) 50. km Northwest
E) 30. km Northward + 30. km Westward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If you run a complete loop around an outdoor track (400 m) in 100 s, your average velocity is
A) 4.0 m/s.
B) 40,000 m/s.
C) 4.00 km/s.
D) 0.25 m/s.
E) zero.
A) 4.0 m/s.
B) 40,000 m/s.
C) 4.00 km/s.
D) 0.25 m/s.
E) zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
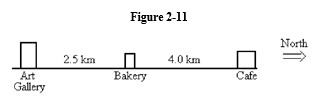
78
Use the Figure 2-12 below to answer the following question(s).
-At t = 0 s
A) rider C is ahead of rider D.
B) riders C and D are at the same position.
C) rider D is moving faster than rider C.
D) rider D is ahead of rider C.
E) rider D is moving slower than rider C.

-At t = 0 s
A) rider C is ahead of rider D.
B) riders C and D are at the same position.
C) rider D is moving faster than rider C.
D) rider D is ahead of rider C.
E) rider D is moving slower than rider C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Use the Figure 2-12 below to answer the following question(s).

-At t = 1 s
A) C and D are both moving.
B) C is ahead of D
C) C and D are both at rest.
D) D is moving, and C is at rest.
E) C is moving, and D is at rest.

-At t = 1 s
A) C and D are both moving.
B) C is ahead of D
C) C and D are both at rest.
D) D is moving, and C is at rest.
E) C is moving, and D is at rest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Use the Figure 2-12 below to answer the following question(s).

-At t = 1 s
A) D has a greater velocity than C.
B) C and D have the same velocity.
C) D is accelerating.
D) C is accelerating.
E) C has a greater velocity than D.

-At t = 1 s
A) D has a greater velocity than C.
B) C and D have the same velocity.
C) D is accelerating.
D) C is accelerating.
E) C has a greater velocity than D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



