Deck 12: Memory Devices
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/116
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Memory Devices
1
How many address bits would be required for a memory that stores 64, 4- bit words?
A) 6
B) 4
C) 2
D) 8
A) 6
B) 4
C) 2
D) 8
6
2
Which of the following are the four basic parts of ROM architecture?
A) Row decoder, column decoder, register array, and output buffer
B) Input buffer, output buffer, register array, and row decoder
C) Digital- to- analog converter, row decoder, column decoder, and output buffer
D) Row decoder, register array, binary up- counter, and output buffer
A) Row decoder, column decoder, register array, and output buffer
B) Input buffer, output buffer, register array, and row decoder
C) Digital- to- analog converter, row decoder, column decoder, and output buffer
D) Row decoder, register array, binary up- counter, and output buffer
Row decoder, column decoder, register array, and output buffer
3
Which of the following is an advantage that an EEPROM has over an EPROM?
A) The EEPROM can be erased with ultraviolet light in much less time than an EPROM.
B) The EEPROM can be erased and reprogrammed without removal from the circuit.
C) The EEPROM has the ability to erase and reprogram individual words.
D) The EEPROM may be reprogrammed much faster than an EPROM but it must be removed from the circuit.
E) Both B and C
A) The EEPROM can be erased with ultraviolet light in much less time than an EPROM.
B) The EEPROM can be erased and reprogrammed without removal from the circuit.
C) The EEPROM has the ability to erase and reprogram individual words.
D) The EEPROM may be reprogrammed much faster than an EPROM but it must be removed from the circuit.
E) Both B and C
Both B and C
4
Capacity, when used to define memory devices, normally refers to the number of:
A) memory words that may be stored in a designated memory device.
B) bits that may be stored in a designated memory device.
C) nibbles that may be stored in a designated memory device.
D) bytes that may be stored in a designated memory device.
A) memory words that may be stored in a designated memory device.
B) bits that may be stored in a designated memory device.
C) nibbles that may be stored in a designated memory device.
D) bytes that may be stored in a designated memory device.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A computer's internal memory consists of:
A) mass memory.
B) semiconductor devices.
C) static memory devices.
D) Both B and C
A) mass memory.
B) semiconductor devices.
C) static memory devices.
D) Both B and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
How many address lines would be required for a 4 K × 4 memory?
A) 10
B) 12
C) 13
D) 14
A) 10
B) 12
C) 13
D) 14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following are normally used to initialize a computer system's hardware?
A) Static memory
B) External mass memory
C) Volatile memory
D) Bootstrap memory
A) Static memory
B) External mass memory
C) Volatile memory
D) Bootstrap memory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following terms best describes Read- Only- Memory (ROM)?
A) Volatile, used to store information that does not change during system operation
B) Volatile, used to store information that changes during system operation
C) Nonvolatile, used to store information that does not change during system operation
D) Nonvolatile, used to store information that changes during system operation
A) Volatile, used to store information that does not change during system operation
B) Volatile, used to store information that changes during system operation
C) Nonvolatile, used to store information that does not change during system operation
D) Nonvolatile, used to store information that changes during system operation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Of the following memory devices, which two would store the same number of bits?
1. 1024 K × 8
2.1M*10
3.2M*4
4.1M*4
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 1 and 4
D) 2 and 3
E) None of the above
1. 1024 K × 8
2.1M*10
3.2M*4
4.1M*4
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 1 and 4
D) 2 and 3
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A major disadvantage of the Mask- Programmed ROM (MROM) is that it:
A) cannot be reprogrammed if the stored data needs to be changed.
B) has an extremely short life expectancy and requires frequent replacement.
C) is very expensive to change the stored data when system requirements change.
D) is time consuming to change the stored data when system requirements change.
A) cannot be reprogrammed if the stored data needs to be changed.
B) has an extremely short life expectancy and requires frequent replacement.
C) is very expensive to change the stored data when system requirements change.
D) is time consuming to change the stored data when system requirements change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
How many bits of information could normally be stored in a memory device with a capacity of 256 K?
A) 262,144
B) 204,800
C) 256,000
D) 2,097,152
A) 262,144
B) 204,800
C) 256,000
D) 2,097,152

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Suppose that a computer system has a read/write line identified as https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9839/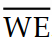 . When writing to memory:
. When writing to memory:
A) write = 0, and the data presently stored in the designated memory location would be written to a new memory location.
B) write = 0, and the data presently stored in the designated memory location would be lost as the new data is written.
C) write = 1, and the data presently stored in the designated memory location would be lost as the new data is written.
D) write = 1, and the data presently stored in the designated memory location would be written to a new memory location.
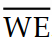 . When writing to memory:
. When writing to memory:A) write = 0, and the data presently stored in the designated memory location would be written to a new memory location.
B) write = 0, and the data presently stored in the designated memory location would be lost as the new data is written.
C) write = 1, and the data presently stored in the designated memory location would be lost as the new data is written.
D) write = 1, and the data presently stored in the designated memory location would be written to a new memory location.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Most ROM ICs have tri- state outputs that:
A) allow for three separate data input lines.
B) isolate the registers from the data bus during read operations.
C) allow the bidirectional flow of data between the bus lines and the ROM registers.
D) permit the connection of many ROM chips to a common data bus.
A) allow for three separate data input lines.
B) isolate the registers from the data bus during read operations.
C) allow the bidirectional flow of data between the bus lines and the ROM registers.
D) permit the connection of many ROM chips to a common data bus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is used to erase an EPROM?
A) Fusible- links
B) Photographic negatives
C) Voltage pulses
D) Ultraviolet light
A) Fusible- links
B) Photographic negatives
C) Voltage pulses
D) Ultraviolet light

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following best describes Random Access Memory (RAM)?
A) A type of memory in which access time is the same for each memory location
B) A type of memory in which access time depends on memory location
C) A type of memory that can be written into only once but can be read from an infinite number of times
D) Mass memory
A) A type of memory in which access time is the same for each memory location
B) A type of memory in which access time depends on memory location
C) A type of memory that can be written into only once but can be read from an infinite number of times
D) Mass memory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
How many bytes can be stored in an 8K × 8 memory chip?
A) 8,000
B) 64,000
C) 65,536
D) 8,192
A) 8,000
B) 64,000
C) 65,536
D) 8,192

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
How many data outputs are required for a 64 × 8 memory chip?
A) 32
B) 8
C) 64
D) 16
A) 32
B) 8
C) 64
D) 16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The delay between the application of an address to a ROM and the appearance of valid data at its outputs is called:
A) tPHL.
B) access time, tacc.
C) output enable time, tOE.
D) tPLH.
A) tPHL.
B) access time, tacc.
C) output enable time, tOE.
D) tPLH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Data that is stored in ROM is often referred to as:
A) shareware.
B) hardware.
C) firmware.
D) software.
A) shareware.
B) hardware.
C) firmware.
D) software.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following best describes volatile memory?
A) Memory that retains stored information when electrical power is removed
B) Magnetic memory
C) Nonmagnetic memory
D) Memory that loses stored information when electrical power is removed
A) Memory that retains stored information when electrical power is removed
B) Magnetic memory
C) Nonmagnetic memory
D) Memory that loses stored information when electrical power is removed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following best describes static memory devices?
A) Semiconductor memory devices in which stored data will not be retained with the power applied unless constantly "refreshed"
B) Semiconductor memory devices in which stored data is retained as long as power is applied
C) Memory devices that are magnetic in nature that require constant "refreshing"
D) Memory devices that are magnetic in nature that do not require constant "refreshing"
A) Semiconductor memory devices in which stored data will not be retained with the power applied unless constantly "refreshed"
B) Semiconductor memory devices in which stored data is retained as long as power is applied
C) Memory devices that are magnetic in nature that require constant "refreshing"
D) Memory devices that are magnetic in nature that do not require constant "refreshing"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is a bidirectional bus?
A) Data bus
B) Address bus
C) Control bus
D) Both A and B
A) Data bus
B) Address bus
C) Control bus
D) Both A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following memory devices comes with a window?
A) EPROM
B) ROM
C) MROM
D) RAM
A) EPROM
B) ROM
C) MROM
D) RAM

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
How many 1 K × 4 chips would be required to produce an 8 K × 16 module?
A) 32
B) 16
C) 64
D) 8
A) 32
B) 16
C) 64
D) 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
How many address lines would be required for an 8K × 16 module?
A) 14
B) 12
C) 15
D) 13
A) 14
B) 12
C) 15
D) 13

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of these RAM timing parameters determine(s) its operating speed?
A) tACC
B) tCO and tOD
C) tACC and tCO
D) tRC and tWC
A) tACC
B) tCO and tOD
C) tACC and tCO
D) tRC and tWC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following signals performs the chip- select function for a DRAM memory with address multiplexing?
A)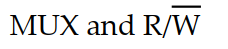
B)
C)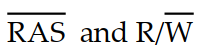
D)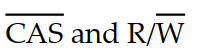
A)
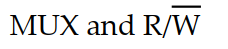
B)
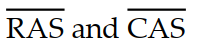
C)
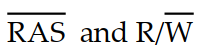
D)
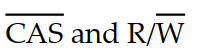

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The main advantage of semiconductor RAM is its ability to:
A) retain stored data when power is interrupted or turned off.
B) be written into and read from rapidly.
C) be randomly accessed.
D) be sequentially accessed.
A) retain stored data when power is interrupted or turned off.
B) be written into and read from rapidly.
C) be randomly accessed.
D) be sequentially accessed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following memories are sequential- access devices?
A) Cache
B) FIFO
C) RAM
D) Power- down storage
A) Cache
B) FIFO
C) RAM
D) Power- down storage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following memories uses a MOS capacitor as its memory cell?
A) SRAM
B) ROM
C) DRAM
D) Both A and B
A) SRAM
B) ROM
C) DRAM
D) Both A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What part of a Flash memory architecture manages all chip functions?
A) I/O pins
B) Program verify command
C) Command register
D) Command code
A) I/O pins
B) Program verify command
C) Command register
D) Command code

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of Flash memory?
A) more expensive than EEPROM
B) in circuit erasure
C) erase faster than EPROM
D) electrically erasable
A) more expensive than EEPROM
B) in circuit erasure
C) erase faster than EPROM
D) electrically erasable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which type of memory cell would normally be associated with a "sense" amplifier?
A) ROM
B) SRAM
C) DRAM
D) Both A and C
A) ROM
B) SRAM
C) DRAM
D) Both A and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is the principal advantage of using address multiplexing with DRAM memory?
A) Reduced memory access time
B) Reduced pin count and a decrease in package size
C) Eliminates the requirement for a chip- select input line thereby reducing the pin count
D) Reduced requirement for constant refreshing of the memory contents
A) Reduced memory access time
B) Reduced pin count and a decrease in package size
C) Eliminates the requirement for a chip- select input line thereby reducing the pin count
D) Reduced requirement for constant refreshing of the memory contents

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In high speed computer systems, which type of memory communicates directly with the microprocessor?
A) Flash
B) Cache
C) FIFO
D) Power- down storage
A) Flash
B) Cache
C) FIFO
D) Power- down storage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The refresh method used with DRAM that allows for interspersed normal operation is called:
A) burst refresh.
B) shared refresh.
C) incremental refresh.
D) distributed refresh.
A) burst refresh.
B) shared refresh.
C) incremental refresh.
D) distributed refresh.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What two functions does a DRAM controller perform?
A) Data selection and CPU accessing
B) Data selection and the refresh operation
C) Address multiplexing and data selection
D) Address multiplexing and the refresh operation
A) Data selection and CPU accessing
B) Data selection and the refresh operation
C) Address multiplexing and data selection
D) Address multiplexing and the refresh operation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Computer main memory is made up of RAM and ROM ICs that are interfaced to the CPU over three groups of signal line or buses comprising:
A) data, control, and address bus.
B) memory, power, and control bus.
C) logic, control, and disable bus.
D) data, ALC, and memory bus.
A) data, control, and address bus.
B) memory, power, and control bus.
C) logic, control, and disable bus.
D) data, ALC, and memory bus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following lists memory devices from the most complex and expensive, to the least complex and expensive?
A) EEPROM, PROM, Flash, and EPROM
B) Flash, EPROM, EEPROM,and PROM
C) EEPROM, Flash, EPROM, and PROM
D) PROM, Flash, EEPROM,and EPROM
A) EEPROM, PROM, Flash, and EPROM
B) Flash, EPROM, EEPROM,and PROM
C) EEPROM, Flash, EPROM, and PROM
D) PROM, Flash, EEPROM,and EPROM

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
EEPROMs are nonvolatile, offer fast read access, and allow rapid in- circuit erasure and reprogramming of individual bytes. Compared to EPROMs, however:
A) EEPROMs suffer from lower density and much higher cost.
B) EEPROMs require much more power and thus must dissipate much more heat.
C) EEPROMs require UV light to reprogram.
D) EEPROMs are not adaptable to most CPUs.
A) EEPROMs suffer from lower density and much higher cost.
B) EEPROMs require much more power and thus must dissipate much more heat.
C) EEPROMs require UV light to reprogram.
D) EEPROMs are not adaptable to most CPUs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
To set up a flash memory chip for read operations:
A) it is necessary first to write all 1st into the command register.
B) it is necessary first to write all zeros into the command register.
C) data must be applied to data bus.
D) output enable must be disabled.
A) it is necessary first to write all 1st into the command register.
B) it is necessary first to write all zeros into the command register.
C) data must be applied to data bus.
D) output enable must be disabled.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The coating on CDR discs is permanently altered when the write laser hits it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Data storage on an optical disc is from the outside of the disc to the inside.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The data bus is a unidirectional bus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
An erasable Programmable ROM (EPROM) is programmed by the user and may be erased and reprogrammed as often as required.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Testing ROM for proper operation is normally more complex than testing RAM.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A write operation may also be referred to as a "fetch" operation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A ROM IC chip normally has a read/write control input.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The "checkerboard" test is normally used to test RAM to determine its ability to store and read 1s and 0s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Flash memory can be used in place of a disk drive in a laptop computer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
When writing data into a SRAM it is necessary to have valid data on the inputs after deactivating the chip and the write command.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
An advantage of DRAM over SRAM is its high speed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A data bit in a DRAM cell is refreshed each time it is read.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A burst refresh and normal memory operation of a DRAM can be interspersed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A 16 K × 8 memory module can be made from four 8 K × 1 chips.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
DRAM chips can be combined for larger capacity and word sizes using the same methods as for other memory types.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Flash memory devices use command codes to control internal operations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Erasing or programming a flash memory device is a one step operation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
FIFO memory is true random access.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Cache memory is used in high speed systems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
If a RAM passes the checkerboard test it is probably good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
FF registers are high- speed memory elements that are used extensively in the internal operations of a digital computer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Auxiliary memory, like CDs, stores massive amounts of data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Every data word, in every computer regardless of size, has an address code.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Memory enable, chip enable, and chip select are terms used to describe a memory function that will completely disable all or part of the memory so that it will not respond to other inputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
15 address lines can identify 64,000 memory locations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
EPROM is easily programmed without special programming hardware.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A powerful laser is required to write data onto a compact disc.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
To access a memory location for a read or write operation, the address code for that particular location is applied to the _______inputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The______nput controls which memory operation is to take place - read or write.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The memory______input is a means for completely disabling all or part of a memory so that it will not respond to other inputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
When the OE pin of a memory device is deactivated, the buffers are in a______ state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Modern hard drives store data by______of the medium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The process of entering data in a ROM is called programming or ______the ROM.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
In order to read a data word from ROM, we need to do two things: apply the appropriate______ inputs, and then activate the ______ inputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
On an optical disc, data is stored by changing______ of the disc surface.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The primary use for NAND flash is______ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The applied______code determines which register in the array will be enabled to place its data word onto the bus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
There will be a ______delay between the application of the ROM's inputs and the appearance of the data outputs during a read operation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Blu- Ray discs are capable of storing______ of data per side.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



