Deck 37: Orthopedic
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/56
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 37: Orthopedic
1
A hinge joint is type of
A) fibrous joint.
B) ball-and-socket joint.
C) cartilaginous joint.
D) synovial joint.
A) fibrous joint.
B) ball-and-socket joint.
C) cartilaginous joint.
D) synovial joint.
synovial joint.
2
A youth with an ankle injury was playing basketball and says he "turned real hard." This describes a(n)
A) tearing force injury.
B) direct force injury.
C) twisting force injury.
D) indirect force injury.
A) tearing force injury.
B) direct force injury.
C) twisting force injury.
D) indirect force injury.
twisting force injury.
3
What is a Colles' fracture?
A) An oblique fracture of the ulna
B) A fracture of the distal tibia
C) A comminuted fracture of the femur
D) A fracture in the distal radius
A) An oblique fracture of the ulna
B) A fracture of the distal tibia
C) A comminuted fracture of the femur
D) A fracture in the distal radius
A fracture in the distal radius
4
Which is a likely complication of a closed femur fracture?
A) Formation of blood clots that move to the brain, causing a stroke.
B) A light-headed feeling as blood rushes to the site of the fracture.
C) Severed nerves that paralyze the lower leg.
D) Blood collecting in the thigh tissues and slowing blood flow throughout the leg.
A) Formation of blood clots that move to the brain, causing a stroke.
B) A light-headed feeling as blood rushes to the site of the fracture.
C) Severed nerves that paralyze the lower leg.
D) Blood collecting in the thigh tissues and slowing blood flow throughout the leg.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What is a luxation?
A) A complete fracture of a bone.
B) A partial dislocation of a joint.
C) A partial fracture of a bone.
D) A complete dislocation of a joint.
A) A complete fracture of a bone.
B) A partial dislocation of a joint.
C) A partial fracture of a bone.
D) A complete dislocation of a joint.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What does this picture show? 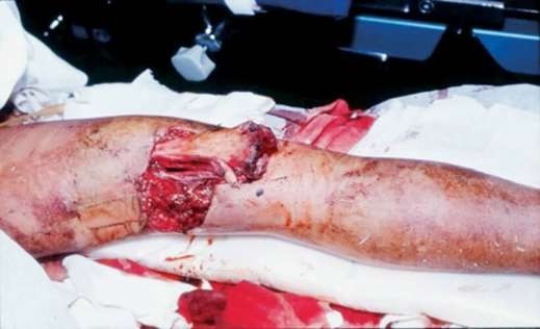
A) An open tibia fracture.
B) A closed femur fracture.
C) An open femur fracture.
D) A closed tibia fracture.

A) An open tibia fracture.
B) A closed femur fracture.
C) An open femur fracture.
D) A closed tibia fracture.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What are the signs and symptoms of a strain?
A) Excruciating pain in the affected area and loosening of all connective tissue
B) Pain with movement, little or no swelling, possible tenderness to the area, possible bruising
C) Generalized pain, bruising of the affected area, and severe swelling
D) Generalized pain, generalized swelling, loosening of connective tissue in area
A) Excruciating pain in the affected area and loosening of all connective tissue
B) Pain with movement, little or no swelling, possible tenderness to the area, possible bruising
C) Generalized pain, bruising of the affected area, and severe swelling
D) Generalized pain, generalized swelling, loosening of connective tissue in area

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What are the 6 Ps of assessing orthopedic trauma?
A) Pulses, peristalsis, paresthesia, pott, pallor, pain
B) Pressure, peristalsis, pulses, paralysis, pallor, pain
C) Pain, pallor, paresthesia, pulses, paralysis, pressure
D) Pott, pulses, pain, paralysis, pressure, paresthesia
A) Pulses, peristalsis, paresthesia, pott, pallor, pain
B) Pressure, peristalsis, pulses, paralysis, pallor, pain
C) Pain, pallor, paresthesia, pulses, paralysis, pressure
D) Pott, pulses, pain, paralysis, pressure, paresthesia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A woman accidentally rolled a car over her husband's foot and ankle while backing the car out of the driveway. You see no obvious signs of injury and the husband denies pain. You should
A) ask the patient to gently flex and relax his ankle.
B) assist the patient in standing and carefully walking.
C) manually stabilize the foot and ankle and apply a splint.
D) palpate the area for crepitus or subcutaneous emphysema.
A) ask the patient to gently flex and relax his ankle.
B) assist the patient in standing and carefully walking.
C) manually stabilize the foot and ankle and apply a splint.
D) palpate the area for crepitus or subcutaneous emphysema.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which is an acceptable reason for splinting?
A) To compress nerves and lessen pain.
B) To limit the motion of a fractured bone.
C) To stop all blood flow through an extremity.
D) To provide complete care for the patient on-scene.
A) To compress nerves and lessen pain.
B) To limit the motion of a fractured bone.
C) To stop all blood flow through an extremity.
D) To provide complete care for the patient on-scene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which is a sign that a splint is too tight?
A) The patient says that it feels like the splint is "squeezing" the extremity.
B) The patient's fingers become flushed and warm.
C) The patient says he cannot move the splinted area.
D) The patient's fingers turn pale and become cold.
A) The patient says that it feels like the splint is "squeezing" the extremity.
B) The patient's fingers become flushed and warm.
C) The patient says he cannot move the splinted area.
D) The patient's fingers turn pale and become cold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A splint should be long enough to immobilize
A) the area above and below the injury.
B) from the injured area to proximal joints.
C) only the affected area and below the injury.
D) from the injured area to distal joints.
A) the area above and below the injury.
B) from the injured area to proximal joints.
C) only the affected area and below the injury.
D) from the injured area to distal joints.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which is an example of a soft splint?
A) Bipolar traction splint
B) SAM splint
C) Sling and swathe
D) Buddy taping
A) Bipolar traction splint
B) SAM splint
C) Sling and swathe
D) Buddy taping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
You should ask your medical director or EMS agency coordinator regarding the use of
A) traction splints on open femur fractures.
B) rigid splints on closed femur fractures.
C) traction splints on closed femur fractures.
D) rigid splints on open femur fractures.
A) traction splints on open femur fractures.
B) rigid splints on closed femur fractures.
C) traction splints on closed femur fractures.
D) rigid splints on open femur fractures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What does this image depict? 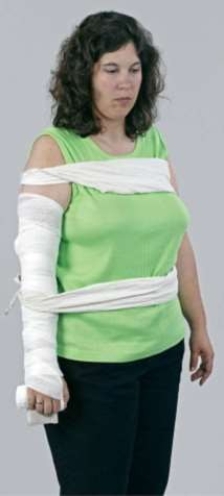
A) A chest injury immobilized in a straight position.
B) An elbow injury immobilized in a straight position.
C) A forearm injury immobilized in a straight position.
D) A humerus injury immobilized in a straight position.

A) A chest injury immobilized in a straight position.
B) An elbow injury immobilized in a straight position.
C) A forearm injury immobilized in a straight position.
D) A humerus injury immobilized in a straight position.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What does this image depict? 
A) Immobilization of a hip injury
B) Immobilization of a femur injury
C) Immobilization of an ankle injury
D) Immobilization of a lower leg injury

A) Immobilization of a hip injury
B) Immobilization of a femur injury
C) Immobilization of an ankle injury
D) Immobilization of a lower leg injury

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
This image depicts the last application step of which splint? 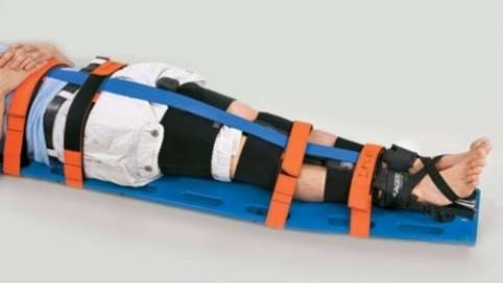
A) The SEFRS Adaptor
B) The Sager SX 405 Unipolar Traction Splint
C) A SAM Splint
D) A Bipolar Traction Splint

A) The SEFRS Adaptor
B) The Sager SX 405 Unipolar Traction Splint
C) A SAM Splint
D) A Bipolar Traction Splint

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A broken finger that has been taped with an anatomical splint is also called
A) finger taping.
B) buddy taping.
C) support taping.
D) open taping.
A) finger taping.
B) buddy taping.
C) support taping.
D) open taping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which type of hip dislocation is most often caused by a motor vehicle crash?
A) An anterior dislocation
B) A distal dislocation
C) A posterior dislocation
D) A lateral dislocation
A) An anterior dislocation
B) A distal dislocation
C) A posterior dislocation
D) A lateral dislocation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When splinting legs together, you should
A) move the good leg toward the bad leg.
B) tie the straps directly next to the patient.
C) move the bad leg toward the good leg.
D) place ties at the feet, ankles, and knees.
A) move the good leg toward the bad leg.
B) tie the straps directly next to the patient.
C) move the bad leg toward the good leg.
D) place ties at the feet, ankles, and knees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In a straight immobilization of the knee, the outside board should extend from the
A) hip to the ankle.
B) knee to the ankle.
C) hip to the knee.
D) armpit to the ankle.
A) hip to the ankle.
B) knee to the ankle.
C) hip to the knee.
D) armpit to the ankle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The ischium bone is located in the
A) pelvis.
B) skull.
C) shoulder.
D) ankle.
A) pelvis.
B) skull.
C) shoulder.
D) ankle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What are the main parts of a muscle?
A) Insertion, origin, and body
B) Body, tendon, and sinew
C) Origin, ligament, and insertion
D) Tendon, sinew, and ligament
A) Insertion, origin, and body
B) Body, tendon, and sinew
C) Origin, ligament, and insertion
D) Tendon, sinew, and ligament

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A linear fracture is a fracture that is__________ the bone's long axis.
A) shattered on
B) diagonal to
C) parallel to the
D) at a right angle to
A) shattered on
B) diagonal to
C) parallel to the
D) at a right angle to

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Most sprains and strains can be treated with
A) ice, rest, and elevation.
B) rest, taping, and splinting.
C) elevation, ice, and bandages.
D) taping, bandages, and splinting.
A) ice, rest, and elevation.
B) rest, taping, and splinting.
C) elevation, ice, and bandages.
D) taping, bandages, and splinting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
At a car crash, a patient is in cardiac arrest. While positioning her for CPR you suspect she has a closed femur fracture. Once you have regained a pulse and she is breathing, you should
A) temporarily stabilize her with a long board and expedite transport to the hospital.
B) temporarily stabilize her leg with a traction splint and expedite transport to the hospital.
C) stabilize her leg with a traction splint and check her breathing every 5 minutes.
D) stabilize her leg with two long boards and check her breathing every 5 minutes.
A) temporarily stabilize her with a long board and expedite transport to the hospital.
B) temporarily stabilize her leg with a traction splint and expedite transport to the hospital.
C) stabilize her leg with a traction splint and check her breathing every 5 minutes.
D) stabilize her leg with two long boards and check her breathing every 5 minutes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The skeletal system is divided into the
A) axial and appendicular skeletons.
B) anterior and posterior skeletons.
C) axial and anterior skeletons.
D) upper and lower skeletons.
A) axial and appendicular skeletons.
B) anterior and posterior skeletons.
C) axial and anterior skeletons.
D) upper and lower skeletons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is a swathe?
A) A dressing used to clean blood from a wound
B) A board used to immobilize an injured wrist
C) A bandage that secures a dressed arm to the chest
D) The wrap that acts as a sling to support an injured arm
A) A dressing used to clean blood from a wound
B) A board used to immobilize an injured wrist
C) A bandage that secures a dressed arm to the chest
D) The wrap that acts as a sling to support an injured arm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The distal radius connects to the
A) elbow.
B) thumb.
C) pinky.
D) ulna.
A) elbow.
B) thumb.
C) pinky.
D) ulna.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What are the three main parts of skeletal muscles?
A) Body, tendons, and ligaments
B) Fibers, nerves, and blood vessels
C) Origin, insertion, and body
D) Body, fibers, and connective tissue
A) Body, tendons, and ligaments
B) Fibers, nerves, and blood vessels
C) Origin, insertion, and body
D) Body, fibers, and connective tissue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which is an example of a direct force injury?
A) Straining your back while lifting.
B) Twisting your ankle while playing tennis.
C) Breaking your hand in a closing door.
D) All of these are correct.
A) Straining your back while lifting.
B) Twisting your ankle while playing tennis.
C) Breaking your hand in a closing door.
D) All of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What type of fracture is pictured here? 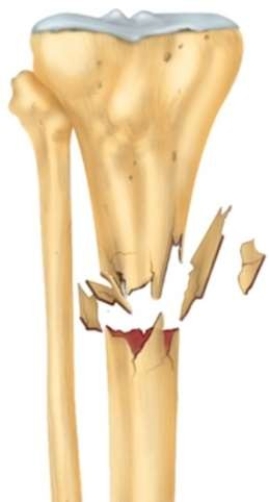
A) Comminuted
B) Open
C) Linear
D) Greenstick

A) Comminuted
B) Open
C) Linear
D) Greenstick

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What is an epiphyseal plate?
A) The mark left after a bone fracture heals
B) The posterior region of the scapula
C) The area of cartilage involved in bone growth
D) The anterior region of the pelvic girdle
A) The mark left after a bone fracture heals
B) The posterior region of the scapula
C) The area of cartilage involved in bone growth
D) The anterior region of the pelvic girdle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The bony upper left region of this femur is called the 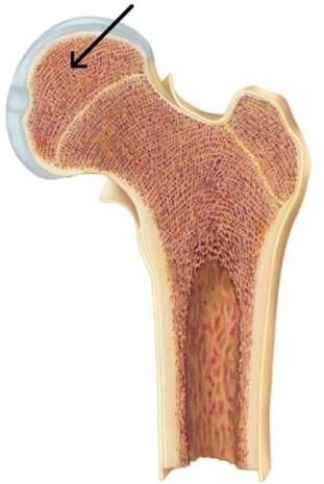
A) epiphysis.
B) epiphyseal plate.
C) diaphysis.
D) compact bone.

A) epiphysis.
B) epiphyseal plate.
C) diaphysis.
D) compact bone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In a closed fracture of a femur, you should
A) check for a dislocation of the hip joint.
B) check for signs of significant internal bleeding.
C) determine what type of fracture is present.
D) All of these are correct.
A) check for a dislocation of the hip joint.
B) check for signs of significant internal bleeding.
C) determine what type of fracture is present.
D) All of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
After a joint dislocation, the increasing pain is often caused by
A) awareness of the extent of the damage.
B) increased vascular flow to the area.
C) increased nerve sensitivity in the area.
D) spasms from the surrounding muscles.
A) awareness of the extent of the damage.
B) increased vascular flow to the area.
C) increased nerve sensitivity in the area.
D) spasms from the surrounding muscles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What is a sprain?
A) A small fracture along the diaphysis
B) The stretching or tearing of a ligament
C) The twisting, pulling, or tearing of a muscle
D) A loss of synovial fluid in a joint
A) A small fracture along the diaphysis
B) The stretching or tearing of a ligament
C) The twisting, pulling, or tearing of a muscle
D) A loss of synovial fluid in a joint

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Why can a knee dislocation be a life threatening injury?
A) Venous return is compromised by the damaged joint.
B) There is infection from the reduction of blood flow.
C) The popliteal artery can be cut or compressed.
D) A blood clot can form in the femoral artery.
A) Venous return is compromised by the damaged joint.
B) There is infection from the reduction of blood flow.
C) The popliteal artery can be cut or compressed.
D) A blood clot can form in the femoral artery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
When assessing a patient with musculoskeletal trauma, what does PMS stand for?
A) Pain, movement, symptoms.
B) Posterior, medial, sagittal.
C) Pulse, movement, sensation.
D) Pulse, movement, symptoms.
A) Pain, movement, symptoms.
B) Posterior, medial, sagittal.
C) Pulse, movement, sensation.
D) Pulse, movement, symptoms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A man complains of minor pain in his knee after running in a marathon, and you see only slight swelling. You should advise the patient to
A) apply a hot pad to his knee.
B) apply an ice pack to his knee.
C) submerge his knee in cool water.
D) None of these are correct.
A) apply a hot pad to his knee.
B) apply an ice pack to his knee.
C) submerge his knee in cool water.
D) None of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
When splinting a tibia, the splint should cover
A) the knee and the ankle.
B) the hip and knee.
C) the hip, knee, and ankle.
D) only the fractured bone.
A) the knee and the ankle.
B) the hip and knee.
C) the hip, knee, and ankle.
D) only the fractured bone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Most sprains and strains can be treated with
A) splints, rest, and stabilization.
B) rest, ice, and elevation.
C) ice, heat, and compression.
D) elevation, stabilization, and ice.
A) splints, rest, and stabilization.
B) rest, ice, and elevation.
C) ice, heat, and compression.
D) elevation, stabilization, and ice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
When you see somebody holding his injured wrist to his chest, this is called
A) self-support.
B) an anatomical splint.
C) a body splint.
D) joint stabilization.
A) self-support.
B) an anatomical splint.
C) a body splint.
D) joint stabilization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which is an acceptable reason for splinting?
A) To compress nerves and lessen a patient's pain
B) To stop all blood flow in an extremity
C) To take care of a injury at the scene
D) To prevent a closed injury from becoming an open injury
A) To compress nerves and lessen a patient's pain
B) To stop all blood flow in an extremity
C) To take care of a injury at the scene
D) To prevent a closed injury from becoming an open injury

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
When applying a splint, which step comes FIRST?
A) Pad the area to reduce discomfort.
B) Assessing PMS proximal to the injury.
C) Assessing PMS distal to the injury.
D) Covering open wounds with a dressing.
A) Pad the area to reduce discomfort.
B) Assessing PMS proximal to the injury.
C) Assessing PMS distal to the injury.
D) Covering open wounds with a dressing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
After 624 applying a splint to a patient's forearm, the radial pulse on the splinted extremity weakens. You should
A) immobilize the area, loosen the splint, and readjust it.
B) take the splint off completely and have the patient self-splint.
C) place pads into the splint to loosen it.
D) leave it alone unless the arm entirely loses its pulse.
A) immobilize the area, loosen the splint, and readjust it.
B) take the splint off completely and have the patient self-splint.
C) place pads into the splint to loosen it.
D) leave it alone unless the arm entirely loses its pulse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
When using a triangular bandage to sling an arm, the knot should be located
A) in the armpit.
B) in the hand.
C) on the back of the neck.
D) to the side of the neck.
A) in the armpit.
B) in the hand.
C) on the back of the neck.
D) to the side of the neck.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What is a traction splint?
A) A device that immobilizes a long bone fracture.
B) A splint with a boot so the patient can walk.
C) A device that immobilizes wrist and ankle joints.
D) A splint made of a hard material.
A) A device that immobilizes a long bone fracture.
B) A splint with a boot so the patient can walk.
C) A device that immobilizes wrist and ankle joints.
D) A splint made of a hard material.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If necessary, when should you apply padding to a splint?
A) Never apply padding to a splint.
B) Before placing the splint against the patient.
C) At the time you place the splint against the patient.
D) After placing the splint against the patient.
A) Never apply padding to a splint.
B) Before placing the splint against the patient.
C) At the time you place the splint against the patient.
D) After placing the splint against the patient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Because of the force involved, an injury to pelvis also requires
A) spinal stabilization.
B) an inspection for chest injury.
C) a full body splint.
D) an inspection for upper limb fractures.
A) spinal stabilization.
B) an inspection for chest injury.
C) a full body splint.
D) an inspection for upper limb fractures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In a motor vehicle crash, the knees strike the dashboard and transmit the force through the femur to the hip. You should suspect a(n) _______ dislocation.
A) anterior
B) Medial
C) posterior
D) distal
A) anterior
B) Medial
C) posterior
D) distal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What does this image depict? 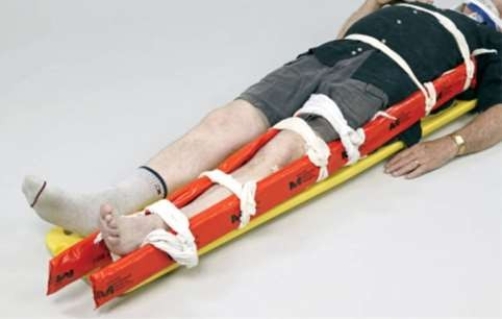
A) Immobilization of a femur fracture
B) Immobilization of a pelvic fracture
C) Immobilization of a hip dislocation
D) Immobilization of an ankle injury

A) Immobilization of a femur fracture
B) Immobilization of a pelvic fracture
C) Immobilization of a hip dislocation
D) Immobilization of an ankle injury

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What does this image depict? 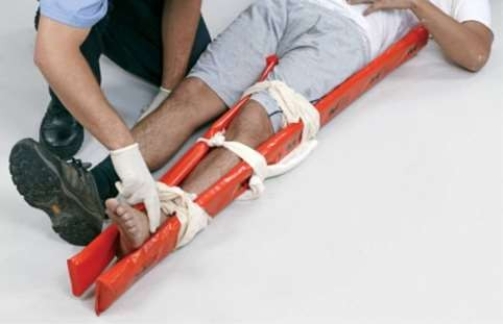
A) Immobilization of the lower leg by an air splint.
B) Immobilization of the lower leg by a SAM splint.
C) Immobilization of the lower leg by padded boards.
D) Immobilization of the lower leg by a traction splint.

A) Immobilization of the lower leg by an air splint.
B) Immobilization of the lower leg by a SAM splint.
C) Immobilization of the lower leg by padded boards.
D) Immobilization of the lower leg by a traction splint.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
According to the text, what are the possible splints for a pelvic injury?
A) Long padded board splint, vacuum splint, and using the leg as a splint.
B) Long backboard with a blanket or pillow between the legs, scoop stretcher, PASG.
C) Preformed leg splint, pillow or blanket, air splint, vacuum splint.
D) Long backboard, scoop stretcher, PASG, pelvic sling, STORM wrap and cravats.
A) Long padded board splint, vacuum splint, and using the leg as a splint.
B) Long backboard with a blanket or pillow between the legs, scoop stretcher, PASG.
C) Preformed leg splint, pillow or blanket, air splint, vacuum splint.
D) Long backboard, scoop stretcher, PASG, pelvic sling, STORM wrap and cravats.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
When splinting a femur fracture, the long board on the outside should extend from the
A) armpit to the top of the knee.
B) pelvis to the top of the knee.
C) armpit to the bottom of the foot.
D) groin to the bottom of the foot.
A) armpit to the top of the knee.
B) pelvis to the top of the knee.
C) armpit to the bottom of the foot.
D) groin to the bottom of the foot.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
What is the purpose of the SEFRS?
A) It immobilizes a limb fracture "as found."
B) It tightens a body-length splint.
C) It realigns fractured bones.
D) It permits a victim to walk on a dislocated joint.
A) It immobilizes a limb fracture "as found."
B) It tightens a body-length splint.
C) It realigns fractured bones.
D) It permits a victim to walk on a dislocated joint.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



