Deck 11: Data Storage
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/49
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Data Storage
1
Each memory cell can store one byte of information.
False
2
RAM stands for Readily Accessible Memory.
False
3
EEPROMS can be electrically erased and reused.
True
4
Due to their ability to be easily erased and reused, magnetic memory devices are widely used for RAM.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The term "storage"
refers to CD- ROMs, floppy disks, and hard disks.
refers to CD- ROMs, floppy disks, and hard disks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
ROMs are used to store data that is not intended to be changed easily.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Fusible link PROMs are programmed removing the desired fuse links using a highly focused beam of light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
RAMs must have a ? 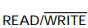 input, in addition to one or more DATA inputs.
input, in addition to one or more DATA inputs.
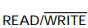 input, in addition to one or more DATA inputs.
input, in addition to one or more DATA inputs.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
One of the advantages of DRAMs is their ability to store data without the need for periodically refreshing the memory contents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Main computer memory is usually DRAM because of high density and low cost while cache memory is usually SRAM because of high speed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A  is a section of memory that is contained within a single chip.
is a section of memory that is contained within a single chip.
 is a section of memory that is contained within a single chip.
is a section of memory that is contained within a single chip.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A rank is a memory section that takes priority over other memory sections.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Flash drives use USB B- type connectors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A flash drive obtains power from the computer to which it is attached.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
DIMMS generally contain DDR SDRAM memory chips.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Referring to a DDR SDRAM, DDR stands for Dual Data Retrieval.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The term "Blu- Ray"
comes from the fact that the disc is read using a blue laser (as opposed to a red laser).
comes from the fact that the disc is read using a blue laser (as opposed to a red laser).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The term "cloud storage" refers to a specific type of memory within your computer or pad.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
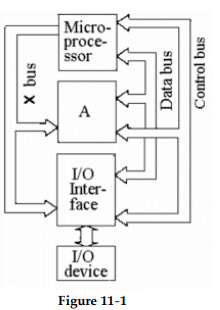
-The block identified as A in Figure 11- 1 is the _________.
A) addresser
B) controller
C) clock
D) memory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20

-The point identified as the "X bus" in Figure 11- 1 is the ________ bus.
A) address
B) I/O
C) memory
D) supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Eight bits of digital data are normally referred to as a ________.
A) cell
B) byte
C) word
D) group
A) cell
B) byte
C) word
D) group

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
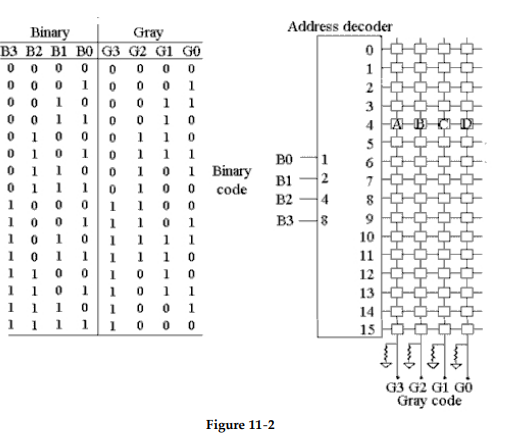
-Refer to Figure 11- 2. What address line or lines are HIGH if it is desired to input a decimal 10 into the code converter (address decoder) and what is the resulting Gray code output value?
A) 10, 1111
B) 10, 1010
C) 2 and 8, 1111
D) 8 and 2, 1010

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23

-What are the values of A, B, C and D in Figure 11- 2?
A) 0 1 1 1
B) 0 1 0 0
C) 0 0 1 0
D) 0 1 1 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24

-Refer to Figure 11- 2. The Binary- to- Gray converter is not working correctly. How could it be checked?
A) Reverse the operation of the converter by applying the Gray code to the G terminals and check for proper output on the B terminals.
B) Measure the inputs and outputs with an ohmmeter to see if any of them are shorted.
C) Step the inputs through their full range and check the outputs with a multi- channel scope or logic analyzer.
D) Any of the above methods could be tried, depending on the particular type of ROM being used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
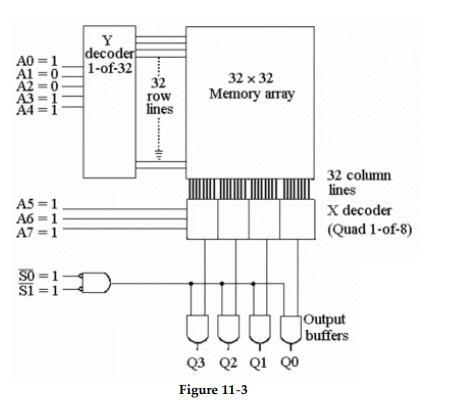
-For the circuit of Figure 11- 3, how many bits are contained in the output data word?
A) 8
B) 32
C) 4
D) 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26

-What memory location is being addressed in Figure 11- 3?
A) 249
B) 5
C) 10111
D) 157

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27

-For the circuit in Figure 11- 3, the value at the Q3 - Q0 outputs will be ________.
A) 1111
B) 1001
C) 0000
D) 1024

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A DRAM has a  because ________ .
because ________ .
A) the address lines are multiplexed to reduce pin count
B) the RAS latches in the address and the CAS latches in data
C) the RAS determines the operation mode and the CAS enables the tri- state outputs
D) none of the above
 because ________ .
because ________ .A) the address lines are multiplexed to reduce pin count
B) the RAS latches in the address and the CAS latches in data
C) the RAS determines the operation mode and the CAS enables the tri- state outputs
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A FIFO _________.
A) allows data to be clocked in and out at different clock rates
B) can be used to smooth out bursts of data into a continuous stream
C) outputs data in the same order that it was input
D) all of the above
A) allows data to be clocked in and out at different clock rates
B) can be used to smooth out bursts of data into a continuous stream
C) outputs data in the same order that it was input
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
ROM access time is defined as ________.
A) being the difference between the READ and WRITE times
B) how long it takes to program the ROM chip
C) the time required to activate the address lines after the ENABLE line is at a valid level
D) the time it takes to get valid output data after a valid address is applied
A) being the difference between the READ and WRITE times
B) how long it takes to program the ROM chip
C) the time required to activate the address lines after the ENABLE line is at a valid level
D) the time it takes to get valid output data after a valid address is applied

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The difference between RAM and ROM is _________.
A) RAM has a read/write signal and ROM doesn't
B) RAM loses data when the power is removed and ROM doesn't
C) RAM has random address access and ROM uses sequential address access
D) all of the above
E) A and B only
A) RAM has a read/write signal and ROM doesn't
B) RAM loses data when the power is removed and ROM doesn't
C) RAM has random address access and ROM uses sequential address access
D) all of the above
E) A and B only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What do the letters PROM stand for?
A) Programmed Registers On Microprocessors
B) Programmed Random Only Memory
C) Programmed Read Only Memory
D) Programmable Read Only Memory
A) Programmed Registers On Microprocessors
B) Programmed Random Only Memory
C) Programmed Read Only Memory
D) Programmable Read Only Memory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following methods is not normally associated with producing PROMs?
A) Shorted junctions
B) Silicon links
C) Metal links
D) spst switches
A) Shorted junctions
B) Silicon links
C) Metal links
D) spst switches

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following best describes EPROMs?
A) EPROMs can be erased by UV light.
B) EPROMs can be erased by shorting all inputs to ground.
C) EPROMs can only be programmed once.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) EPROMs can be erased by UV light.
B) EPROMs can be erased by shorting all inputs to ground.
C) EPROMs can only be programmed once.
D) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which type of ROM can be electrically erased?
A) SRAM
B) EPROM
C) DRAM
D) EEPROM
A) SRAM
B) EPROM
C) DRAM
D) EEPROM

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
How can UV- erasable PROMs be recognized?
A) They will have a small violet dot next to the l pin.
B) By a small window on the chip
C) They can be identified by the fact that their part number always starts with a "U", such as in U12.
D) They are not readily identifiable, since they must always be kept under a small cover.
A) They will have a small violet dot next to the l pin.
B) By a small window on the chip
C) They can be identified by the fact that their part number always starts with a "U", such as in U12.
D) They are not readily identifiable, since they must always be kept under a small cover.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What is RAM?
A) It is memory that is used for short- term temporary data storage within the computer.
B) It is memory that can be used and then automatically reset, or cleared, after being read from or written to.
C) It is the first level of memory used by the computer in all of its operations.
D) It is memory that can be reached by any sub- system within a computer, and at any time.
A) It is memory that is used for short- term temporary data storage within the computer.
B) It is memory that can be used and then automatically reset, or cleared, after being read from or written to.
C) It is the first level of memory used by the computer in all of its operations.
D) It is memory that can be reached by any sub- system within a computer, and at any time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What is the major difference between SRAM and DRAM?
A) DRAMs must be periodically refreshed.
B) The only difference is the terminal from which the data is removed: from the FET Drain or Source.
C) SRAMs can hold data via a static charge, even with power off.
D) Dynamic RAMs are always active; Static RAMs must rest between data read/write cycles.
A) DRAMs must be periodically refreshed.
B) The only difference is the terminal from which the data is removed: from the FET Drain or Source.
C) SRAMs can hold data via a static charge, even with power off.
D) Dynamic RAMs are always active; Static RAMs must rest between data read/write cycles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
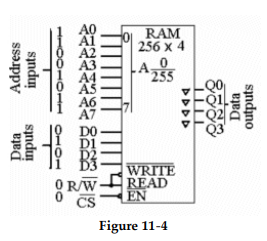
-What is the significance of the inverted triangles on the outputs of the device in Figure 11- 4?
A) They represent buffers and mean that the outputs can drive 40 TTL loads, instead of the normal 10.
B) It means that the outputs will only be active if a change has occurred at that memory location since the last read/write cycle.
C) They represent inverters and mean that the outputs are active- LOW.
D) The IC has tri- state outputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40

-Which of the following is correct for the circuit shown in Figure 11- 4?
A) The chip has not been enabled, since the EN terminal is 0; therefore, nothing will be written to the chip and the output is tri- stated.
B) The read/write line is LOW; therefore decimal 5 is being stored at memory location 211.
C) Decimal 10 is being written into memory location 211.
D) The number 5 is being written to the memory at address location 203.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following is one of the basic characteristics of DRAMs?
A) DRAMs are simpler devices than other type memories.
B) DRAMs have a broader "dynamic" storage range than other types of memories.
C) DRAMs must be periodically refreshed in order to retain data.
D) DRAMs must have a constantly changing input.
A) DRAMs are simpler devices than other type memories.
B) DRAMs have a broader "dynamic" storage range than other types of memories.
C) DRAMs must be periodically refreshed in order to retain data.
D) DRAMs must have a constantly changing input.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A DIMM ________.
A) has contact pins on both sides of the module for larger data paths
B) is available in 30- pin or 72- pin packages
C) has less memory than the newer SIMM modules
D) has contact pins on only one side of the module
A) has contact pins on both sides of the module for larger data paths
B) is available in 30- pin or 72- pin packages
C) has less memory than the newer SIMM modules
D) has contact pins on only one side of the module

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The arrangement of tracks and sectors on a disk is known as the ________.
A) format
B) performance
C) physical address
D) partition
A) format
B) performance
C) physical address
D) partition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The hard drive latency period is defined as ________.
A) the time that it takes a hard drive to switch from read mode to write mode.
B) the time that it takes to spin down a hard drive for power off.
C) the time that it takes for the desired sector to spin under the head once the head is positioned.
D) the time that it takes a hard drive to spin up from 0 rpm to 3600 rpm.
A) the time that it takes a hard drive to switch from read mode to write mode.
B) the time that it takes to spin down a hard drive for power off.
C) the time that it takes for the desired sector to spin under the head once the head is positioned.
D) the time that it takes a hard drive to spin up from 0 rpm to 3600 rpm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The checkerboard pattern test is used to test ________.
A) FPLA
B) RAM
C) ROM
D) EEPROM
A) FPLA
B) RAM
C) ROM
D) EEPROM

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The checksum method is used to test _________.
A) FPLA
B) RAM
C) ROM
D) EEPROM
A) FPLA
B) RAM
C) ROM
D) EEPROM

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following faults will the checkerboard pattern detect in RAM?
A) Ability to store both 0s and 1s
B) Dynamically introduced errors between cells
C) Short between adjacent cells
D) All of the above.
A) Ability to store both 0s and 1s
B) Dynamically introduced errors between cells
C) Short between adjacent cells
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A 64- Mbyte SIMM is installed into a system, but when a memory test is executed, the SIMM is detected as a 32- Mbyte device. What is a possible cause?
A) The voltage on the memory module is incorrect.
B) The address decoder on the SIMM is faulty.
C) The most significant address line is stuck high or low.
D) The memory module was not installed properly.
A) The voltage on the memory module is incorrect.
B) The address decoder on the SIMM is faulty.
C) The most significant address line is stuck high or low.
D) The memory module was not installed properly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The remote servers in a cloud storage system are referred to as ________.
A) clouds
B) nodes
C) users
D) servers.
A) clouds
B) nodes
C) users
D) servers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



