Deck 1: Introductory Concepts
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: Introductory Concepts
1
The values of an analog signal flow smoothly from one to the next.
True
2
A sinusoidal waveform is an analog signal.
True
3
Digital data can be processed and transmitted more efficiently and reliably than analog information.
True
4
The field that comprises both mechanical and electronic components is known as electro- mechanics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The decimal number system uses nine different symbols.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The binary number system uses just two symbols.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A waveform that repeats itself at fixed intervals is called a periodic waveform.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Digital systems respond to voltage levels that change abruptly between two levels (high and low).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The amplitude of a digital waveform is the difference in voltage between the LOW and HIGH levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The clock signal synchronizes the other waveforms in a circuit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Clock signals carry pieces of information such as letters and numbers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Serial data is sent along a single conductor, one bit at a time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Parallel data is sent along a single conductor, one bit at a time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When the inputs to a 2- input AND gate are both HIGH, the output is HIGH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
When either input to a 2- input AND gate is LOW, the output is LOW.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
When either input to a 2- input OR gate is HIGH, the output is HIGH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
When both inputs to a 2- input OR gate are both LOW, the output is LOW.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When the input to a logic inverter is HIGH, the output is LOW.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Encoders and decoders perform opposite conversions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A multiplexer converts parallel data to serial data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A demultiplexer is sometimes called a mux.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A flip- flop is a 1- bit storage device.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The DIP package style has two parallel rows of through- hole pins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The PLCC package has J- type leads on all four edges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The flat- pack (FP) IC package style is a surface- mount device.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The FPGA is a fixed- function device.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A circuit that converts an analog waveform to a digital signal is commonly called a(n) ________.
A) ADC
B) CAD
C) DAC
D) PLD
A) ADC
B) CAD
C) DAC
D) PLD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A circuit that converts an digital signal to an analog waveform is commonly called a(n) ________.
A) CAD
B) PLD
C) DAC
D) ADC
A) CAD
B) PLD
C) DAC
D) ADC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Of the circuits listed, the one that is most likely to be found in a CD player is a(n) ________.
A) digital- to- analog converter
B) SPLD
C) programmable logic device
D) analog- to- digital converter
A) digital- to- analog converter
B) SPLD
C) programmable logic device
D) analog- to- digital converter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
On a negative- going pulse, ________.
A) HIGH = 0 and LOW = 1
B) HIGH = 0 and LOW = - 1
C) HIGH = 1 and LOW = 0
D) LOW = - 1 and HIGH = 1
A) HIGH = 0 and LOW = 1
B) HIGH = 0 and LOW = - 1
C) HIGH = 1 and LOW = 0
D) LOW = - 1 and HIGH = 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
On a digital waveform, the transition time from a LOW level to a HIGH level is called ________.
A) fall time
B) period
C) rise time
D) pulse width
A) fall time
B) period
C) rise time
D) pulse width

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
? 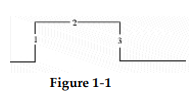
-Which edge in Figure 1- 1 is the leading edge?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) Both 1 and 3

-Which edge in Figure 1- 1 is the leading edge?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) Both 1 and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
? 
-Which edge in Figure 1- 1 is the trailing edge?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) Both 1 and 3

-Which edge in Figure 1- 1 is the trailing edge?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) Both 1 and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
? 
-The time between transition 1 and transition 3 in Figure 1- 1 is the _________.
A) pulse width
B) frequency
C) period
D) amplitude

-The time between transition 1 and transition 3 in Figure 1- 1 is the _________.
A) pulse width
B) frequency
C) period
D) amplitude

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
On a digital waveform, the transition time from a HIGH level to a LOW level is called ________.
A) rise time
B) pulse width
C) period
D) fall time
A) rise time
B) pulse width
C) period
D) fall time

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The time from one leading edge on a digital waveform to the next is the waveform _________.
A) fall time
B) period
C) pulse width
D) rise time
A) fall time
B) period
C) pulse width
D) rise time

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A periodic digital waveform ________ .
A) has both a HIGH and LOW levels
B) repeats itself at a fixed interval
C) has a duty cycle
D) all of the above
A) has both a HIGH and LOW levels
B) repeats itself at a fixed interval
C) has a duty cycle
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The transition times for an ideal digital pulse are __________.
A) zero
B) measured between 0 and 90% of the amplitude
C) infinite
D) measured between 10% to 90% of the amplitude
A) zero
B) measured between 0 and 90% of the amplitude
C) infinite
D) measured between 10% to 90% of the amplitude

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
An oscilloscope display indicates that the period of a digital waveform is 40 µs. What is frequency of this waveform?
A) 2.5 kHz
B) 25 kHz
C) 40 MHz
D) The frequency cannot be determined using the information provided.
A) 2.5 kHz
B) 25 kHz
C) 40 MHz
D) The frequency cannot be determined using the information provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is the duty cycle of a digital waveform with a pulse width of 10 ms a period of 90 ms?
A) 9%
B) 11.1%
C) 90%
D) 10%
A) 9%
B) 11.1%
C) 90%
D) 10%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
On a positive- going pulse, the leading edge is the________.
A) negative- going edge
B) positive- going edge
C) falling edge
D) HIGH- to- LOW transition
A) negative- going edge
B) positive- going edge
C) falling edge
D) HIGH- to- LOW transition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The approximate duty cycle for the digital waveform below is ________ .

A) 50%
B) 30%
C) 80%
D) 20%

A) 50%
B) 30%
C) 80%
D) 20%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
On a negative- going pulse, the leading edge is the ________.
A) LOW- to- HIGH transition
B) negative- going edge
C) rising edge
D) positive- going edge
A) LOW- to- HIGH transition
B) negative- going edge
C) rising edge
D) positive- going edge

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
On a positive- logic pulse, the trailing edge is the ________.
A) rising edge
B) falling edge
C) positive- going edge
D) LOW- to- HIGH transition
A) rising edge
B) falling edge
C) positive- going edge
D) LOW- to- HIGH transition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
On a negative- logic pulse, the trailing edge is the ________.
A) HIGH- to- LOW transition
B) negative- going edge
C) positive- going edge
D) falling edge
A) HIGH- to- LOW transition
B) negative- going edge
C) positive- going edge
D) falling edge

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
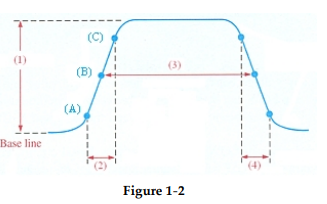
? 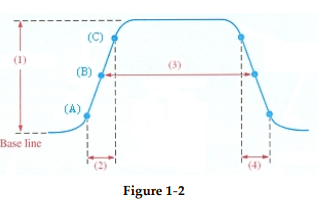
-Item (1) of the nonideal pulse in Figure 1- 2 represents the waveform ________ .
A) transition time
B) pulse width
C) amplitude
D) period

-Item (1) of the nonideal pulse in Figure 1- 2 represents the waveform ________ .
A) transition time
B) pulse width
C) amplitude
D) period

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
? 
-Item (2) of the nonideal pulse in Figure 1- 2 represents the waveform ________ .
A) amplitude
B) rise time
C) fall time
D) pulse width

-Item (2) of the nonideal pulse in Figure 1- 2 represents the waveform ________ .
A) amplitude
B) rise time
C) fall time
D) pulse width

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
? 
-Item (3) of the nonideal pulse in Figure 1- 2 represents the waveform ________ .
A) amplitude
B) rise time
C) fall time
D) pulse width

-Item (3) of the nonideal pulse in Figure 1- 2 represents the waveform ________ .
A) amplitude
B) rise time
C) fall time
D) pulse width

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
? 
-Item (4) of the nonideal pulse in Figure 1- 2 represents the waveform ________ .
A) amplitude
B) rise time
C) fall time
D) pulse width

-Item (4) of the nonideal pulse in Figure 1- 2 represents the waveform ________ .
A) amplitude
B) rise time
C) fall time
D) pulse width

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
When data is set along a single conductor, it is referred to as _.
A) simultaneous data
B) serial data
C) parallel data
D) none of these
A) simultaneous data
B) serial data
C) parallel data
D) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
? 
-The symbol in Figure 1- 3(A) represents the ________function.
A) NOT
B) OR
C) AND
D) AND/OR

-The symbol in Figure 1- 3(A) represents the ________function.
A) NOT
B) OR
C) AND
D) AND/OR

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
? 
-The symbol in Figure 1- 3(B) represents the ________ function.
A) OR
B) XOR
C) NON
D) AND

-The symbol in Figure 1- 3(B) represents the ________ function.
A) OR
B) XOR
C) NON
D) AND

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
? 
-The symbol in Figure 1- 3(C) represents the ________function.
A) XOR
B) AND
C) NOT
D) OR

-The symbol in Figure 1- 3(C) represents the ________function.
A) XOR
B) AND
C) NOT
D) OR

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The output from an AND gate is HIGH when ________.
A) one input is HIGH and the remaining inputs are LOW
B) one input is LOW and the remaining inputs are HIGH
C) all inputs are HIGH
D) all inputs are LOW
A) one input is HIGH and the remaining inputs are LOW
B) one input is LOW and the remaining inputs are HIGH
C) all inputs are HIGH
D) all inputs are LOW

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The output from an AND gate is LOW________.
A) when at least one input is LOW
B) only when all inputs are LOW
C) only when all inputs are HIGH
D) none of the above
A) when at least one input is LOW
B) only when all inputs are LOW
C) only when all inputs are HIGH
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The output from an OR gate is HIGH ________.
A) when at least one input is HIGH
B) only when all inputs are HIGH
C) only when all inputs are LOW
D) none of the above
A) when at least one input is HIGH
B) only when all inputs are HIGH
C) only when all inputs are LOW
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The output from an OR gate is LOW ________.
A) only when all inputs are LOW
B) whenever any input is HIGH
C) only when all inputs are HIGH
D) none of the above
A) only when all inputs are LOW
B) whenever any input is HIGH
C) only when all inputs are HIGH
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which circuit creates an output that indicates whether or not the input values are equal?
A) Comparator
B) Encoder
C) Decoder
D) Multiplexer
A) Comparator
B) Encoder
C) Decoder
D) Multiplexer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which circuit converts information into a specific coded form?
A) Comparator
B) Encoder
C) Decoder
D) Multiplexer
A) Comparator
B) Encoder
C) Decoder
D) Multiplexer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which circuit converts coded information into a noncoded form?
A) Comparator
B) Encoder
C) Decoder
D) Multiplexer
A) Comparator
B) Encoder
C) Decoder
D) Multiplexer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which circuit converts data from serial form to parallel form?
A) Comparator
B) Encoder
C) Multiplexer
D) Demultiplexe
A) Comparator
B) Encoder
C) Multiplexer
D) Demultiplexe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which one of the following is not a binary arithmetic function?
A) Addition
B) Division
C) Subtraction
D) Multiplexing
A) Addition
B) Division
C) Subtraction
D) Multiplexing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Two kinds of data selectors are ________and ________.
A) adders, subtractors
B) multiplexers, demultiplexers
C) comparators, registers
D) encoders, decoders
A) adders, subtractors
B) multiplexers, demultiplexers
C) comparators, registers
D) encoders, decoders

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which one of the circuits listed is made up of flip- flops?
A) A register
B) A multiplexer
C) A comparator
D) A converter
A) A register
B) A multiplexer
C) A comparator
D) A converter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
? 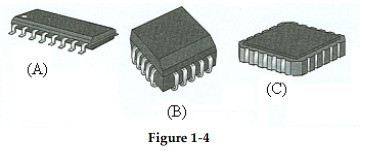
-The package style in Figure 1- 4(A) is a(n) ________.
A) SOIC
B) PLCC
C) LCCC
D) FP

-The package style in Figure 1- 4(A) is a(n) ________.
A) SOIC
B) PLCC
C) LCCC
D) FP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
? 
-The package style in Figure 1- 4(B) is a(n) ________.
A) SOIC
B) PLCC
C) LCCC
D) FP

-The package style in Figure 1- 4(B) is a(n) ________.
A) SOIC
B) PLCC
C) LCCC
D) FP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
? 
-The package style in Figure 1- 4(C) is a(n) ________.
A) SOIC
B) PLCC
C) LCCC
D) FP

-The package style in Figure 1- 4(C) is a(n) ________.
A) SOIC
B) PLCC
C) LCCC
D) FP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The arrow in the figure below points to pin number ________. 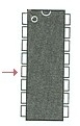
A) 12
B) 5
C) 13
D) 4

A) 12
B) 5
C) 13
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The arrow in the figure below points to pin ________. 
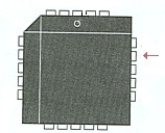
A) 4
B) 17
C) 16
D) 5


A) 4
B) 17
C) 16
D) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which IC package style has no leads?
A) LCCC
B) SOIC
C) PLCC
D) All must have leads.
A) LCCC
B) SOIC
C) PLCC
D) All must have leads.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which one of the following is not a surface- mount IC package?
A) FP
B) SOIC
C) DIP
D) PLCC
A) FP
B) SOIC
C) DIP
D) PLCC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The first step in the PLD programming process is ________.
A) design entry
B) compilation
C) synthesis
D) download
A) design entry
B) compilation
C) synthesis
D) download

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The final step in the PLD programming process is ________.
A) design entry
B) compilation
C) synthesis
D) download
A) design entry
B) compilation
C) synthesis
D) download

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The netlist is generated during the ________phase of the PLD programming process.
A) design entry
B) compilation
C) synthesis
D) download
A) design entry
B) compilation
C) synthesis
D) download

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following is an example of a mechatronics system?
A) A surgical laser
B) An industrial robot
C) A laptop computer
D) None of the above
A) A surgical laser
B) An industrial robot
C) A laptop computer
D) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



