Deck 5: Renal and Acidbase Physiology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/43
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Renal and Acidbase Physiology
1
Secretion of by the distal tubule will be decreased by
A) metabolic alkalosis
B) a high- diet
C) hyperaldosteronism
D) spironolactone administration
E) thiazide diuretic administration
A) metabolic alkalosis
B) a high- diet
C) hyperaldosteronism
D) spironolactone administration
E) thiazide diuretic administration
spironolactone administration
2
Jared and Adam both weigh . Jared drinks of distilled water, and Adam drinks of isotonic . As a result of these ingestions, Adam will have a
A) greater change in intracellular fluid (ICF) volume
B) higher positive free-water clearance
C) greater change in plasma osmolarity
D) higher urine osmolarity
E) higher urine flow rate
A) greater change in intracellular fluid (ICF) volume
B) higher positive free-water clearance
C) greater change in plasma osmolarity
D) higher urine osmolarity
E) higher urine flow rate
higher urine osmolarity
3
A 45-year-old woman develops severe diarrhea while on vacation. She has the following arterial blood values:
Venous blood samples show decreased blood and a normal anion gap.
-The correct diagnosis for this patient is
A) metabolic acidosis
B) metabolic alkalosis
C) respiratory acidosis
D) respiratory alkalosis
E) normal acid-base status
Venous blood samples show decreased blood and a normal anion gap.
-The correct diagnosis for this patient is
A) metabolic acidosis
B) metabolic alkalosis
C) respiratory acidosis
D) respiratory alkalosis
E) normal acid-base status
metabolic acidosis
4
A 45-year-old woman develops severe diarrhea while on vacation. She has the following arterial blood values:
Venous blood samples show decreased blood and a normal anion gap.
-Which of the following statements about this patient is correct?
A) She is hypoventilating
B) The decreased arterial is a result of buffering of excess by
C) The decreased blood is a result of exchange of intracellular for extracellular
D) The decreased blood is a result of increased circulating levels of aldosterone
E) The decreased blood is a result of decreased circulating levels of antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Venous blood samples show decreased blood and a normal anion gap.
-Which of the following statements about this patient is correct?
A) She is hypoventilating
B) The decreased arterial is a result of buffering of excess by
C) The decreased blood is a result of exchange of intracellular for extracellular
D) The decreased blood is a result of increased circulating levels of aldosterone
E) The decreased blood is a result of decreased circulating levels of antidiuretic hormone (ADH)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Use the values below to answer the following question.
Glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure
Bowman space hydrostatic pressure
Bowman space oncotic pressure At what value of glomerular capillary oncotic pressure would glomerular filtration stop?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
Glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure
Bowman space hydrostatic pressure
Bowman space oncotic pressure At what value of glomerular capillary oncotic pressure would glomerular filtration stop?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The reabsorption of filtered
A) results in reabsorption of less than of the filtered load when the plasma concentration of is
B) acidifies tubular fluid to a of 4.4
C) is directly linked to excretion of as
D) is inhibited by decreases in arterial
E) can proceed normally in the presence of a renal carbonic anhydrase inhibitor
A) results in reabsorption of less than of the filtered load when the plasma concentration of is
B) acidifies tubular fluid to a of 4.4
C) is directly linked to excretion of as
D) is inhibited by decreases in arterial
E) can proceed normally in the presence of a renal carbonic anhydrase inhibitor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The following information was obtained in a 20 -year-old college student who was participating in a research study in the Clinical Research Unit:

Assuming that is freely filtered, which of the following statements is most correct?
A) There is net secretion of
B) There is net reabsorption of
C) There is both reabsorption and secretion of
D) The clearance of could be used to measure the glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
E) The clearance of is greater than the clearance of inulin

Assuming that is freely filtered, which of the following statements is most correct?
A) There is net secretion of
B) There is net reabsorption of
C) There is both reabsorption and secretion of
D) The clearance of could be used to measure the glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
E) The clearance of is greater than the clearance of inulin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
To maintain normal balance, total daily excretion of should equal the daily
A) fixed acid production plus fixed acid ingestion
B) excretion
C) filtered load
D) titratable acid excretion
E) filtered load of
A) fixed acid production plus fixed acid ingestion
B) excretion
C) filtered load
D) titratable acid excretion
E) filtered load of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
One gram of mannitol was injected into a woman. After equilibration, a plasma sample had a mannitol concentration of . During the equilibration period, of the injected mannitol was excreted in the urine. The woman's
A) extracellular fluid (ECF) volume is
B) intracellular fluid (ICF) volume is
C) ECF volume is
D) ICF volume is
E) interstitial volume is
A) extracellular fluid (ECF) volume is
B) intracellular fluid (ICF) volume is
C) ECF volume is
D) ICF volume is
E) interstitial volume is

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A 58-year-old man is given a glucose tolerance test. In the test, the plasma glucose concentration is increased and glucose reabsorption and excretion are measured. When the plasma glucose concentration is higher than occurs at transport maximum , the
A) clearance of glucose is zero
B) excretion rate of glucose equals the filtration rate of glucose
C) reabsorption rate of glucose equals the filtration rate of glucose
D) excretion rate of glucose increases with increasing plasma glucose concentrations
E) renal vein glucose concentration equals the renal artery glucose concentration
A) clearance of glucose is zero
B) excretion rate of glucose equals the filtration rate of glucose
C) reabsorption rate of glucose equals the filtration rate of glucose
D) excretion rate of glucose increases with increasing plasma glucose concentrations
E) renal vein glucose concentration equals the renal artery glucose concentration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A negative free-water clearance will occur in a person who
A) drinks of distilled water in 30 minutes
B) begins excreting large volumes of urine with an osmolarity of after a severe head injury
C) is receiving lithium treatment for depression and has polyuria that is unresponsive to the administration of antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
D) has an oat cell carcinoma of the lung, and excretes urine with an osmolarity of
A) drinks of distilled water in 30 minutes
B) begins excreting large volumes of urine with an osmolarity of after a severe head injury
C) is receiving lithium treatment for depression and has polyuria that is unresponsive to the administration of antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
D) has an oat cell carcinoma of the lung, and excretes urine with an osmolarity of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A buffer pair (HA/A has a of 5.4. At a blood of 7.4, the concentration of HA is
A) that of
B) that of
C) equal to that of
D) 10 times that of
E) 100 times that of
A) that of
B) that of
C) equal to that of
D) 10 times that of
E) 100 times that of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following would produce an increase in the reabsorption of isosmotic fluid in the proximal tubule?
A) Increased filtration fraction
B) Extracellular fluid (ECF) volume expansion
C) Decreased peritubular capillary protein concentration
D) Increased peritubular capillary hydrostatic pressure
E) Oxygen deprivation
A) Increased filtration fraction
B) Extracellular fluid (ECF) volume expansion
C) Decreased peritubular capillary protein concentration
D) Increased peritubular capillary hydrostatic pressure
E) Oxygen deprivation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following substances or combinations of substances could be used to measure interstitial fluid volume?
A) Mannitol
B) alone
C) Evans blue
D) Inulin and
E) Inulin and radioactive albumin
A) Mannitol
B) alone
C) Evans blue
D) Inulin and
E) Inulin and radioactive albumin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
At plasma para-aminohippuric acid (PAH) concentrations below the transport maximum , PAH
A) reabsorption is not saturated
B) clearance equals inulin clearance
C) secretion rate equals excretion rate
D) concentration in the renal vein is close to zero
E) concentration in the renal vein equals concentration in the renal artery
A) reabsorption is not saturated
B) clearance equals inulin clearance
C) secretion rate equals excretion rate
D) concentration in the renal vein is close to zero
E) concentration in the renal vein equals concentration in the renal artery

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Compared with a person who ingests of distilled water, a person with water deprivation will have a
A) higher free-water clearance
B) lower plasma osmolarity
C) lower circulating level of antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
D) higher tubular fluid/plasma (TF/P) osmolarity in the proximal tubule
E) higher rate of reabsorption in the collecting ducts
A) higher free-water clearance
B) lower plasma osmolarity
C) lower circulating level of antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
D) higher tubular fluid/plasma (TF/P) osmolarity in the proximal tubule
E) higher rate of reabsorption in the collecting ducts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following would cause an increase in both glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and renal plasma flow (RPF)?
A) Hyperproteinemia
B) A ureteral stone
C) Dilation of the afferent arteriole
D) Dilation of the efferent arteriole
E) Constriction of the efferent arteriole
A) Hyperproteinemia
B) A ureteral stone
C) Dilation of the afferent arteriole
D) Dilation of the efferent arteriole
E) Constriction of the efferent arteriole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A patient has the following arterial blood values:
Which of the following statements about this patient is most likely to be correct?
A) He is hypoventilating
B) He has decreased ionized in blood
C) He has almost complete respiratory compensation
D) He has an acid-base disorder caused by overproduction of fixed acid
E) Appropriate renal compensation would cause his arterial to increase
Which of the following statements about this patient is most likely to be correct?
A) He is hypoventilating
B) He has decreased ionized in blood
C) He has almost complete respiratory compensation
D) He has an acid-base disorder caused by overproduction of fixed acid
E) Appropriate renal compensation would cause his arterial to increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following would best distinguish an otherwise healthy person with severe water deprivation from a person with the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH)?
A) Free-water clearance
B) Urine osmolarity
C) Plasma osmolarity
D) Circulating levels of antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
E) Corticopapillary osmotic gradient
A) Free-water clearance
B) Urine osmolarity
C) Plasma osmolarity
D) Circulating levels of antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
E) Corticopapillary osmotic gradient

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following causes a decrease in renal clearance?
A) Hypoparathyroidism
B) Treatment with chlorothiazide
C) Treatment with furosemide
D) Extracellular fluid (ECF) volume expansion
E) Hypermagnesemia
A) Hypoparathyroidism
B) Treatment with chlorothiazide
C) Treatment with furosemide
D) Extracellular fluid (ECF) volume expansion
E) Hypermagnesemia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A patient arrives at the emergency room with low arterial pressure, reduced tissue turgor, and the following arterial blood values:
Which of the following responses would also be expected to occur in this patient?
A) Hyperventilation
B) Decreased secretion by the distal tubules
C) Increased ratio of to in urine
D) Exchange of intracellular for extracellular
Which of the following responses would also be expected to occur in this patient?
A) Hyperventilation
B) Decreased secretion by the distal tubules
C) Increased ratio of to in urine
D) Exchange of intracellular for extracellular

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A woman has a plasma osmolarity of and a urine osmolarity of 1200 . The correct diagnosis is
A) syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH)
B) water deprivation
C) central diabetes insipidus
D) nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
E) drinking large volumes of distilled water
A) syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH)
B) water deprivation
C) central diabetes insipidus
D) nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
E) drinking large volumes of distilled water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A patient is infused with paraaminohippuric acid (PAH) to measure renal blood flow (RBF). She has a urine flow rate of , a plasma [PAH] of , a urine of , and a hematocrit of . What is her "effective" RBF?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following substances has the highest renal clearance?
A) Para-aminohippuric acid (PAH)
B) Inulin
C) Glucose
D)
E)
A) Para-aminohippuric acid (PAH)
B) Inulin
C) Glucose
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A woman runs a marathon in weather and replaces all volume lost in sweat by drinking distilled water. After the marathon, she will have
A) decreased total body water (TBW)
B) decreased hematocrit
C) decreased intracellular fluid (ICF) volume
D) decreased plasma osmolarity
E) increased intracellular osmolarity
A) decreased total body water (TBW)
B) decreased hematocrit
C) decreased intracellular fluid (ICF) volume
D) decreased plasma osmolarity
E) increased intracellular osmolarity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following causes hyperkalemia?
A) Exercise
B) Alkalosis
C) Insulin injection
D) Decreased serum osmolarity
E) Treatment with -agonists
A) Exercise
B) Alkalosis
C) Insulin injection
D) Decreased serum osmolarity
E) Treatment with -agonists

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is a cause of metabolic alkalosis?
A) Diarrhea
B) Chronic renal failure
C) Ethylene glycol ingestion
D) Treatment with acetazolamide
E) Hyperaldosteronism
F) Salicylate poisoning
A) Diarrhea
B) Chronic renal failure
C) Ethylene glycol ingestion
D) Treatment with acetazolamide
E) Hyperaldosteronism
F) Salicylate poisoning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is an action of parathyroid hormone (PTH) on the renal tubule?
A) Stimulation of adenylate cyclase
B) Inhibition of distal tubule secretion
C) Inhibition of distal tubule reabsorption
D) Stimulation of proximal tubule phosphate reabsorption
E) Inhibition of production of 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol
A) Stimulation of adenylate cyclase
B) Inhibition of distal tubule secretion
C) Inhibition of distal tubule reabsorption
D) Stimulation of proximal tubule phosphate reabsorption
E) Inhibition of production of 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A man presents with hypertension and hypokalemia. Measurement of his arterial blood gases reveals a of 7.5 and a calculated - of . His serum cortisol and urinary vanillylmandelic acid (VMA) are normal, his serum aldosterone is increased, and his plasma renin activity is decreased. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his hypertension?
A) Cushing syndrome
B) Cushing disease
C) Conn syndrome
D) Renal artery stenosis
E) Pheochromocytoma
A) Cushing syndrome
B) Cushing disease
C) Conn syndrome
D) Renal artery stenosis
E) Pheochromocytoma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which set of arterial blood values describes a heavy smoker with a history of emphysema and chronic bronchitis who is becoming increasingly somnolent?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which set of arterial blood values describes a patient with partially compensated respiratory alkalosis after 1 month on a mechanical ventilator?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which set of arterial blood values describes a patient with chronic renal failure (eating a normal protein diet) and decreased urinary excretion of ?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which set of arterial blood values describes a patient with untreated diabetes mellitus and increased urinary excretion of ?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which set of arterial blood values describes a patient with a 5-day history of vomiting?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
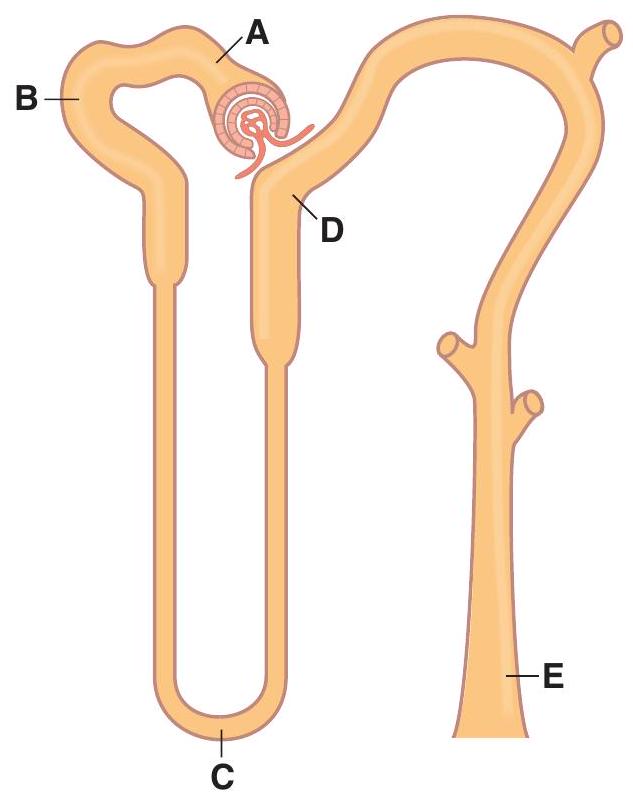
-At which nephron site does the amount of in tubular fluid exceed the amount of filtered in a person on a high- diet?
A) Site A
B) Site B
C) Site C
D) Site D
E) Site E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36

-At which nephron site is the tubular fluid/plasma (TF/P) osmolarity lowest in a person who has been deprived of water?
A) Site A
B) Site B
C) Site C
D) Site D
E) Site E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37

-At which nephron site is the tubular fluid inulin concentration highest during antidiuresis?
A) Site A
B) Site B
C) Site C
D) Site D
E) Site E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38

-At which nephron site is the tubular fluid inulin concentration lowest?
A) Site A
B) Site B
C) Site C
D) Site D
E) Site E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39

-At which nephron site is the tubular fluid glucose concentration highest?
A) Site A
B) Site B
C) Site C
D) Site D
E) Site E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The curves show the percentage of the filtered load remaining in the tubular fluid at various sites along the nephron.
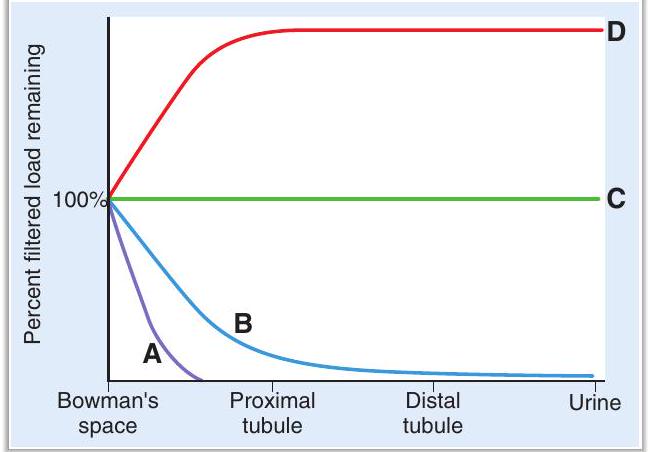
-Which curve describes the inulin profile along the nephron?
A) Curve A
B) Curve B
C) Curve C
D) Curve D

-Which curve describes the inulin profile along the nephron?
A) Curve A
B) Curve B
C) Curve C
D) Curve D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The curves show the percentage of the filtered load remaining in the tubular fluid at various sites along the nephron.

-Which curve describes the alanine profile along the nephron?
A) Curve A
B) Curve B
C) Curve C
D) Curve D

-Which curve describes the alanine profile along the nephron?
A) Curve A
B) Curve B
C) Curve C
D) Curve D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The curves show the percentage of the filtered load remaining in the tubular fluid at various sites along the nephron.

-Which curve describes the paraaminohippuric acid profile along the nephron?
A) Curve A
B) Curve B
C) Curve C
D) Curve D

-Which curve describes the paraaminohippuric acid profile along the nephron?
A) Curve A
B) Curve B
C) Curve C
D) Curve D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A 5-year-old boy swallows a bottle of aspirin (salicylic acid) and is treated in the emergency room. The treatment produces a change in urine that increases the excretion of salicylic acid. What was the change in urine , and what is the mechanism of increased salicylic acid excretion?
A) Acidification, which converts salicylic acid to its HA form
B) Alkalinization, which converts salicylic acid to its form
C) Acidification, which converts salicylic acid to its form
D) Alkalinization, which converts salicylic acid to its HA form
A) Acidification, which converts salicylic acid to its HA form
B) Alkalinization, which converts salicylic acid to its form
C) Acidification, which converts salicylic acid to its form
D) Alkalinization, which converts salicylic acid to its HA form

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



