Deck 5: Dental Local Anesthetic Drugs
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/81
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Dental Local Anesthetic Drugs
1
Match the following:
-Articaine
A) Ester-type anesthetic
B) First amide available
C) Long-acting anesthetic
D) Available in 4% solution
E) Established safe dose guideline
F) Vasoconstrictor
G) Available 1:20,000
H) Nerve damage
I) Available in 3% solution
J) Sulfur atom in ring structure
-Articaine
A) Ester-type anesthetic
B) First amide available
C) Long-acting anesthetic
D) Available in 4% solution
E) Established safe dose guideline
F) Vasoconstrictor
G) Available 1:20,000
H) Nerve damage
I) Available in 3% solution
J) Sulfur atom in ring structure
Sulfur atom in ring structure
2
Match the following:
-Bupivacaine
A) Ester-type anesthetic
B) First amide available
C) Long-acting anesthetic
D) Available in 4% solution
E) Established safe dose guideline
F) Vasoconstrictor
G) Available 1:20,000
H) Nerve damage
I) Available in 3% solution
J) Sulfur atom in ring structure
-Bupivacaine
A) Ester-type anesthetic
B) First amide available
C) Long-acting anesthetic
D) Available in 4% solution
E) Established safe dose guideline
F) Vasoconstrictor
G) Available 1:20,000
H) Nerve damage
I) Available in 3% solution
J) Sulfur atom in ring structure
Long-acting anesthetic
3
Match the following:
-Epinephrine
A) Ester-type anesthetic
B) First amide available
C) Long-acting anesthetic
D) Available in 4% solution
E) Established safe dose guideline
F) Vasoconstrictor
G) Available 1:20,000
H) Nerve damage
I) Available in 3% solution
J) Sulfur atom in ring structure
-Epinephrine
A) Ester-type anesthetic
B) First amide available
C) Long-acting anesthetic
D) Available in 4% solution
E) Established safe dose guideline
F) Vasoconstrictor
G) Available 1:20,000
H) Nerve damage
I) Available in 3% solution
J) Sulfur atom in ring structure
Vasoconstrictor
4
Match the following:
-Levonordefrin
A) Ester-type anesthetic
B) First amide available
C) Long-acting anesthetic
D) Available in 4% solution
E) Established safe dose guideline
F) Vasoconstrictor
G) Available 1:20,000
H) Nerve damage
I) Available in 3% solution
J) Sulfur atom in ring structure
-Levonordefrin
A) Ester-type anesthetic
B) First amide available
C) Long-acting anesthetic
D) Available in 4% solution
E) Established safe dose guideline
F) Vasoconstrictor
G) Available 1:20,000
H) Nerve damage
I) Available in 3% solution
J) Sulfur atom in ring structure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Match the following:
-Lidocaine
A) Ester-type anesthetic
B) First amide available
C) Long-acting anesthetic
D) Available in 4% solution
E) Established safe dose guideline
F) Vasoconstrictor
G) Available 1:20,000
H) Nerve damage
I) Available in 3% solution
J) Sulfur atom in ring structure
-Lidocaine
A) Ester-type anesthetic
B) First amide available
C) Long-acting anesthetic
D) Available in 4% solution
E) Established safe dose guideline
F) Vasoconstrictor
G) Available 1:20,000
H) Nerve damage
I) Available in 3% solution
J) Sulfur atom in ring structure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Match the following:
-MRD
A) Ester-type anesthetic
B) First amide available
C) Long-acting anesthetic
D) Available in 4% solution
E) Established safe dose guideline
F) Vasoconstrictor
G) Available 1:20,000
H) Nerve damage
I) Available in 3% solution
J) Sulfur atom in ring structure
-MRD
A) Ester-type anesthetic
B) First amide available
C) Long-acting anesthetic
D) Available in 4% solution
E) Established safe dose guideline
F) Vasoconstrictor
G) Available 1:20,000
H) Nerve damage
I) Available in 3% solution
J) Sulfur atom in ring structure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Match the following:
-Mepivacaine
A) Ester-type anesthetic
B) First amide available
C) Long-acting anesthetic
D) Available in 4% solution
E) Established safe dose guideline
F) Vasoconstrictor
G) Available 1:20,000
H) Nerve damage
I) Available in 3% solution
J) Sulfur atom in ring structure
-Mepivacaine
A) Ester-type anesthetic
B) First amide available
C) Long-acting anesthetic
D) Available in 4% solution
E) Established safe dose guideline
F) Vasoconstrictor
G) Available 1:20,000
H) Nerve damage
I) Available in 3% solution
J) Sulfur atom in ring structure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Match the following:
-Paresthesia
A) Ester-type anesthetic
B) First amide available
C) Long-acting anesthetic
D) Available in 4% solution
E) Established safe dose guideline
F) Vasoconstrictor
G) Available 1:20,000
H) Nerve damage
I) Available in 3% solution
J) Sulfur atom in ring structure
-Paresthesia
A) Ester-type anesthetic
B) First amide available
C) Long-acting anesthetic
D) Available in 4% solution
E) Established safe dose guideline
F) Vasoconstrictor
G) Available 1:20,000
H) Nerve damage
I) Available in 3% solution
J) Sulfur atom in ring structure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Match the following:
-Prilocaine
A) Ester-type anesthetic
B) First amide available
C) Long-acting anesthetic
D) Available in 4% solution
E) Established safe dose guideline
F) Vasoconstrictor
G) Available 1:20,000
H) Nerve damage
I) Available in 3% solution
J) Sulfur atom in ring structure
-Prilocaine
A) Ester-type anesthetic
B) First amide available
C) Long-acting anesthetic
D) Available in 4% solution
E) Established safe dose guideline
F) Vasoconstrictor
G) Available 1:20,000
H) Nerve damage
I) Available in 3% solution
J) Sulfur atom in ring structure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Match the following:
-Procaine
A) Ester-type anesthetic
B) First amide available
C) Long-acting anesthetic
D) Available in 4% solution
E) Established safe dose guideline
F) Vasoconstrictor
G) Available 1:20,000
H) Nerve damage
I) Available in 3% solution
J) Sulfur atom in ring structure
-Procaine
A) Ester-type anesthetic
B) First amide available
C) Long-acting anesthetic
D) Available in 4% solution
E) Established safe dose guideline
F) Vasoconstrictor
G) Available 1:20,000
H) Nerve damage
I) Available in 3% solution
J) Sulfur atom in ring structure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Match the following:
-Articaine
A) Intermediate
B) Long
C) Short
-Articaine
A) Intermediate
B) Long
C) Short

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Match the following:
-Bupivacaine
A) Intermediate
B) Long
C) Short
-Bupivacaine
A) Intermediate
B) Long
C) Short

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Match the following:
-Lidocaine plain
A) Intermediate
B) Long
C) Short
-Lidocaine plain
A) Intermediate
B) Long
C) Short

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Match the following:
-Lidocaine
A) Intermediate
B) Long
C) Short
-Lidocaine
A) Intermediate
B) Long
C) Short

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Match the following:
-Mepivacaine plain
A) Intermediate
B) Long
C) Short
-Mepivacaine plain
A) Intermediate
B) Long
C) Short

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Match the following:
-Mepivacaine
A) Intermediate
B) Long
C) Short
-Mepivacaine
A) Intermediate
B) Long
C) Short

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Match the following:
-Prilocaine plain
A) Intermediate
B) Long
C) Short
-Prilocaine plain
A) Intermediate
B) Long
C) Short

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Match the following:
-Prilocaine
A) Intermediate
B) Long
C) Short
-Prilocaine
A) Intermediate
B) Long
C) Short

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Match the following:
-Procaine
A) Intermediate
B) Long
C) Short
-Procaine
A) Intermediate
B) Long
C) Short

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Lidocaine was the first amide local anesthetic drug developed by Lofgren in 1943.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Mepivacaine was prepared as an alternative to lidocaine by Lofgren in Sweden, in 1957.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Prilocaine was first prepared by Lofgren and Tegner in 1953 and approved by the FDA in 1965.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Articaine was synthesized in 1969 by H. Rusching and is the most recently approved dental injectable local anesthetic drug in North America.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Articaine is metabolized primarily in the liver.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The drug of choice for a patient with significant liver disease is articaine because it is metabolized primarily by plasma cholinesterase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The best local anesthesia drug choice for a nursing mother is prilocaine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
3% mepivacaine plain is a better drug choice than 2% lidocaine when a vasoconstrictor is contraindicated because its higher drug content increases the duration of pulpal anesthesia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
2% lidocaine with 1:50,000 epinephrine provides excellent hemostasis for periodontal surgery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Prilocaine can reduce the blood's oxygen carrying capacity which may lead to methemoglobinemia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The higher the pKa of a local anesthetic solution, the slower the onset on anesthesia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Allergic reactions to lidocaine have been documented and the drug shows cross-allergenicity with other currently available amides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Prilocaine has demonstrated a higher than typical incidence of inducing methemoglobinemia due to its metabolite, ortho-toluidine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Bupivacaine's high pKa translates into a slow onset time, which explains why it is a long-acting anesthetic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Lidocaine is not available in which of the following formulations?
A) 2% lidocaine, 1:20,000 levonordefrin
B) 2% lidocaine plain
C) 2% lidocaine, 1:100,000 epinephrine
D) 2% lidocaine, 1:50,000 epinephrine
A) 2% lidocaine, 1:20,000 levonordefrin
B) 2% lidocaine plain
C) 2% lidocaine, 1:100,000 epinephrine
D) 2% lidocaine, 1:50,000 epinephrine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The anesthetic duration of lidocaine plain is:
A) 60 minutes pulpal; 60 to 120 minutes soft tissue
B) 10 to 30 minutes pulpal; 60 to 120 minutes soft tissue
C) 5 to 10 minutes pulpal; 180 to 300 minutes soft tissue
D) 5 to 10 minutes pulpal; 60 to 120 minutes soft tissue
A) 60 minutes pulpal; 60 to 120 minutes soft tissue
B) 10 to 30 minutes pulpal; 60 to 120 minutes soft tissue
C) 5 to 10 minutes pulpal; 180 to 300 minutes soft tissue
D) 5 to 10 minutes pulpal; 60 to 120 minutes soft tissue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The maximum recommended dose for lidocaine is:
A) 5 mg/lb
B) 500 mg per appointment
C) 4.4 mg/lb
D) 2.0 mg/kg
A) 5 mg/lb
B) 500 mg per appointment
C) 4.4 mg/lb
D) 2.0 mg/kg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which local anesthetic is not available in the United States with 1:200,000 epinephrine?
A) Prilocaine
B) Articaine
C) Lidocaine
D) Bupivacaine
A) Prilocaine
B) Articaine
C) Lidocaine
D) Bupivacaine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The potency of lidocaine as compared to other local anesthetic drugs in dentistry is:
A) Twice as potent as procaine
B) Equal potency to procaine
C) One half potency of bupivacaine
D) One half potency of mepivacaine
A) Twice as potent as procaine
B) Equal potency to procaine
C) One half potency of bupivacaine
D) One half potency of mepivacaine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What is the primary site of biotransformation of lidocaine?
A) Kidney
B) Liver
C) Lungs
D) Blood
A) Kidney
B) Liver
C) Lungs
D) Blood

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What percentage of lidocaine is excreted by the kidneys unchanged?
A) 0%
B) 5%
C) 10%
D) 20%
A) 0%
B) 5%
C) 10%
D) 20%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What is the maximum recommended dose of mepivacaine?
A) 0.5 mg/lb
B) 1.8 mg/lb
C) 3.0 mg/lb
D) 600 mg per appointment
A) 0.5 mg/lb
B) 1.8 mg/lb
C) 3.0 mg/lb
D) 600 mg per appointment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Mepivacaine is available in the following formulation:
A) 2% plain
B) 3% plain
C) 1% with 1:20,000 levonordefrin
D) 3% with 1:20,000 levonordefrin
A) 2% plain
B) 3% plain
C) 1% with 1:20,000 levonordefrin
D) 3% with 1:20,000 levonordefrin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The correct pKa of lidocaine is:
A) 6.5 in lidocaine plain
B) 8.1 in lidocaine with epinephrine
C) 2.4 in lidocaine plain
D) 2.3 to 8.1 in lidocaine with epinephrine
A) 6.5 in lidocaine plain
B) 8.1 in lidocaine with epinephrine
C) 2.4 in lidocaine plain
D) 2.3 to 8.1 in lidocaine with epinephrine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following is the correct onset of action for mepivacaine?
A) 0.5 to 2 minutes
B) 1 to 2 minutes
C) 4 to 6 minutes
D) 6 to 0 minutes
A) 0.5 to 2 minutes
B) 1 to 2 minutes
C) 4 to 6 minutes
D) 6 to 0 minutes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is the maximum recommended dose per appointment for prilocaine?
A) 200 mg
B) 300 mg
C) 400 mg
D) 600 mg
A) 200 mg
B) 300 mg
C) 400 mg
D) 600 mg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following is available in North America?
A) 4% prilocaine, 1:200,000 epinephrine
B) 3% prilocaine, 1:20,000 levonordefrin
C) 4% prilocaine plain
D) 3% prilocaine, 1:100,000 epinephrine
A) 4% prilocaine, 1:200,000 epinephrine
B) 3% prilocaine, 1:20,000 levonordefrin
C) 4% prilocaine plain
D) 3% prilocaine, 1:100,000 epinephrine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Name the atom present in the ring structure of articaine that helps to make it more lipophilic.
A) Sulfur
B) Calcium
C) Sodium
D) Nitrogen
A) Sulfur
B) Calcium
C) Sodium
D) Nitrogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which formulation of articaine is correct?
A) 2% articaine with 1:50,000 epinephrine
B) 2% articaine with 1:100,000 epinephrine
C) 4% articaine with 1:100,000 epinephrine
D) 4% articaine plain
A) 2% articaine with 1:50,000 epinephrine
B) 2% articaine with 1:100,000 epinephrine
C) 4% articaine with 1:100,000 epinephrine
D) 4% articaine plain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which one of the following drugs used in dentistry is the least toxic to the CNS and CVS?
A) Lidocaine
B) Mepivacaine
C) Prilocaine
D) Bupivacaine
A) Lidocaine
B) Mepivacaine
C) Prilocaine
D) Bupivacaine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What is the FDA pregnancy category for mepivacaine?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) A, if minimal doses are administered
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) A, if minimal doses are administered

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The correct onset of action for lidocaine is:
A) 30 seconds to 1 minute with vasoconstrictor
B) 2 to 3 minutes
C) 5 to 7 minutes
D) 6 to 10 minutes
A) 30 seconds to 1 minute with vasoconstrictor
B) 2 to 3 minutes
C) 5 to 7 minutes
D) 6 to 10 minutes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What is the clinically safest available dilution of vasoconstrictor with lidocaine?
A) 1:50,000
B) 1:100,000
C) 1:200,000
D) 1:1,000,000
A) 1:50,000
B) 1:100,000
C) 1:200,000
D) 1:1,000,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The elimination half-life of lidocaine is:
A) 6 minutes
B) 16 minutes
C) 96 minutes
D) 300 minutes
A) 6 minutes
B) 16 minutes
C) 96 minutes
D) 300 minutes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What is the elimination half-life of mepivacaine?
A) 0.5 hours
B) 1.0 hours
C) 1.6 hours
D) 1.9 hours
A) 0.5 hours
B) 1.0 hours
C) 1.6 hours
D) 1.9 hours

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following drugs has the shortest duration of action?
A) Mepivacaine 3%
B) Bupivacaine 0.5%, 1:200,000 epinephrine
C) Prilocaine 4%, 1:200,000 epinephrine
D) Lidocaine 2%, 1:100,000 epinephrine
A) Mepivacaine 3%
B) Bupivacaine 0.5%, 1:200,000 epinephrine
C) Prilocaine 4%, 1:200,000 epinephrine
D) Lidocaine 2%, 1:100,000 epinephrine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following drugs has the shortest duration of action?
A) Mepivacaine 3% plain
B) Bupivacaine 0.5%, 1:200,000 epinephrine
C) Prilocaine 4%, 1:200,000 epinephrine
D) Lidocaine 2% plain
A) Mepivacaine 3% plain
B) Bupivacaine 0.5%, 1:200,000 epinephrine
C) Prilocaine 4%, 1:200,000 epinephrine
D) Lidocaine 2% plain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which anesthetic provides pulpal anesthesia for 10 minutes for an infiltration technique and 60 minutes for a block injection?
A) Lidocaine
B) Mepivacaine, 1:20,000 levonordefrin
C) Prilocaine plain
D) Prilocaine, 1:200,000 epinephrine
A) Lidocaine
B) Mepivacaine, 1:20,000 levonordefrin
C) Prilocaine plain
D) Prilocaine, 1:200,000 epinephrine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What is the clinical significance of prilocaine's pKa of 7.9?
A) Stronger vasodilator than mepivacaine
B) Slightly slower onset compared to lidocaine
C) Less toxicity compared to lidocaine
D) Higher risk of methemoglobinemia
A) Stronger vasodilator than mepivacaine
B) Slightly slower onset compared to lidocaine
C) Less toxicity compared to lidocaine
D) Higher risk of methemoglobinemia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What is the duration of action of articaine with 1:200,000 epinephrine?
A) 30 to 45 minutes pulpal anesthesia
B) 45 to 60 minutes pulpal anesthesia
C) 60 to 90 minutes pulpal anesthesia
D) 120 to 300 minutes of pulpal anesthesia
A) 30 to 45 minutes pulpal anesthesia
B) 45 to 60 minutes pulpal anesthesia
C) 60 to 90 minutes pulpal anesthesia
D) 120 to 300 minutes of pulpal anesthesia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The correct maximum recommended dose for articaine is:
A) 3.2 mg/lb
B) 4 mg/kg
C) 7 mg/lb
D) 400 mg per appointment
A) 3.2 mg/lb
B) 4 mg/kg
C) 7 mg/lb
D) 400 mg per appointment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What is the clinical significance of the rapid half-life of articaine?
A) There is half the risk for a lingual paresthesia to occur.
B) There is a low allergy potential.
C) Half of its metabolites are excreted unchanged; therefore, there is less risk of toxicity.
D) It can be reinjected sooner than the other dental injectable drugs due to its rapid half-life.
A) There is half the risk for a lingual paresthesia to occur.
B) There is a low allergy potential.
C) Half of its metabolites are excreted unchanged; therefore, there is less risk of toxicity.
D) It can be reinjected sooner than the other dental injectable drugs due to its rapid half-life.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which local anesthetic drug is appropriate for extended periods of postoperative pain control?
A) Bupivacaine
B) Mepivacaine
C) Lidocaine
D) Prilocaine
A) Bupivacaine
B) Mepivacaine
C) Lidocaine
D) Prilocaine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
What is the absolute maximum recommended dose of bupivacaine?
A) 25 mg
B) 35 mg
C) 45 mg
D) 90 mg
A) 25 mg
B) 35 mg
C) 45 mg
D) 90 mg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What are the two key considerations that determine the duration of action of bupivacaine?
A) Biotransformation and elimination
B) Distribution and volume
C) Receptor binding strength and vasoactivity
D) Receptor binding and biotransformation
A) Biotransformation and elimination
B) Distribution and volume
C) Receptor binding strength and vasoactivity
D) Receptor binding and biotransformation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What is the FDA pregnancy category of lidocaine?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) B or C depending on dose administered
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) B or C depending on dose administered

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which drug can reduce the blood's oxygen-carrying capacity, which may lead to a specific anemia known as methemoglobinemia?
A) Lidocaine
B) Bupivicaine
C) Mepivacaine
D) Prilocaine
A) Lidocaine
B) Bupivicaine
C) Mepivacaine
D) Prilocaine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The risk of methemoglobinemia may be precipitated by which one of the following drugs?
A) Mepivacaine
B) Lidocaine
C) Bupivacaine
D) Prilocaine
A) Mepivacaine
B) Lidocaine
C) Bupivacaine
D) Prilocaine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which local anesthestic drug is the best choice for a nursing mother?
A) Lidocaine
B) Articaine
C) Mepivacaine
D) Prilocaine
A) Lidocaine
B) Articaine
C) Mepivacaine
D) Prilocaine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which is the best reason why articaine is the local anesthetic drug of choice for a nursing mother?
A) It is quickly biotransformed in the liver by hepatic enzymes
B) It is quickly biotransformed by pseudocholinesterase
C) It is not available in breast milk
D) It has a half-life of approximately 3 hours
A) It is quickly biotransformed in the liver by hepatic enzymes
B) It is quickly biotransformed by pseudocholinesterase
C) It is not available in breast milk
D) It has a half-life of approximately 3 hours

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What is the best choice of drug(s) for a patient taking a beta blocker for hypertension that will provide the longest duration of action?
A) 2% lidocaine
B) 2% mepivacaine, 1:20,000 levonordefrin
C) 3% mepivacaine
D) 4% articaine; 1:200,000 epinephrine
A) 2% lidocaine
B) 2% mepivacaine, 1:20,000 levonordefrin
C) 3% mepivacaine
D) 4% articaine; 1:200,000 epinephrine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which one of the following explains why mepivacaine is capable of providing 20 to 40 minutes of pulpal anesthesia without a vasoconstrictor?
A) Low percentage of drug in the cartridge
B) Strong vasodilation activity
C) Weak vasodilation activity
D) Greater potency
A) Low percentage of drug in the cartridge
B) Strong vasodilation activity
C) Weak vasodilation activity
D) Greater potency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following explains why mepivacaine is effective for short durations without a vasoconstrictor?
A) Strong vasodilator property
B) Strong protein binding capacity
C) Weak vasodilator property
D) Equal in potency to lidocaine
A) Strong vasodilator property
B) Strong protein binding capacity
C) Weak vasodilator property
D) Equal in potency to lidocaine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Mepivacaine is similar to lidocaine although its chemical structure more closely resembles
A) Prilocaine
B) Procaine
C) Articaine
D) Bupivacaine
A) Prilocaine
B) Procaine
C) Articaine
D) Bupivacaine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which of the following drug choices would provide the most vigorous hemostasis for a periodontal surgical procedure?
A) 4% articaine, 1:100,000 epinephrine
B) 2% lidocaine, 1:50,000 epinephrine
C) 2% mepivacaine, 1:20,000 levonordefrin
D) .5% bupivacaine, 1:200,000 epinephrine
A) 4% articaine, 1:100,000 epinephrine
B) 2% lidocaine, 1:50,000 epinephrine
C) 2% mepivacaine, 1:20,000 levonordefrin
D) .5% bupivacaine, 1:200,000 epinephrine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following drugs is most appropriate for a patient with significant liver and cardiovascular compromise for a root planing procedure in the lower right quadrant?
A) 4% articaine, 1:200,000 epinephrine
B) 3% mepivacaine, 1, 20, 000 levonordefrin
C) 3% mepivacaine plain
D) 4% articaine, 1:100,000 epinephrine
A) 4% articaine, 1:200,000 epinephrine
B) 3% mepivacaine, 1, 20, 000 levonordefrin
C) 3% mepivacaine plain
D) 4% articaine, 1:100,000 epinephrine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Identify the following local anesthetic drug.
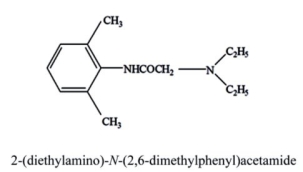


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Identify the following local anesthetic drug.
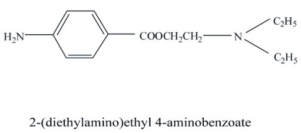


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Identify the following local anesthetic drug.
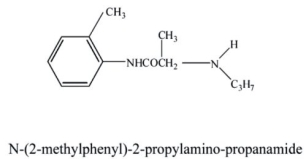


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Identify the following local anesthetic drug.
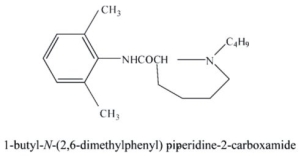


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
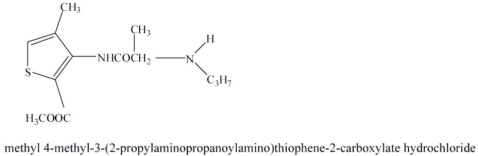
Identify the following local anesthetic drug.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



