Deck 9: Searching and Sorting
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/54
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Searching and Sorting
1
A collection where each node can have from 0 to 2 children is called a ___________.
A) Stack
B) Queue
C) List
D) Binary tree
A) Stack
B) Queue
C) List
D) Binary tree
Binary tree
2
A node that does not have a parent is called the ______ of a tree.
A) foot
B) root
C) leaf
D) top
A) foot
B) root
C) leaf
D) top
root
3
A tree is a nonlinear structure whose elements are organized into a __________.
A) stack
B) hierarchy
C) queue
D) list
A) stack
B) hierarchy
C) queue
D) list
hierarchy
4
The simulated link strategy allows array positions to be allocated contiguously regardless of the _________ of the tree.
A) size
B) order
C) completeness
D) root
A) size
B) order
C) completeness
D) root

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In general, a balanced n-ary tree with m elements will have height _______.
A) lognm
B) logmm
C) logmn
D) lognn
A) lognm
B) logmm
C) logmn
D) lognn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
There are four basic methods for traversing a tree: preorder, inorder, postorder, and level-order.
A) Top down, bottom up, inorder, and postorder
B) Top down, inorder, postorder, and level-order
C) Bottom up, preorder, in order, and postorder
D) preorder, inorder, postorder, and level-order
A) Top down, bottom up, inorder, and postorder
B) Top down, inorder, postorder, and level-order
C) Bottom up, preorder, in order, and postorder
D) preorder, inorder, postorder, and level-order

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
_________ traversal means visit the node, then the left child, then the right child.
A) preorder
B) postorder
C) inorder
D) level-order
A) preorder
B) postorder
C) inorder
D) level-order

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
_________ traversal means visit the left child, then the node, then the right child.
A) preorder
B) postorder
C) inorder
D) level-order
A) preorder
B) postorder
C) inorder
D) level-order

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
________ traversal means visit the left child, then the right child, then the node.
A) preorder
B) postorder
C) inorder
D) level-order
A) preorder
B) postorder
C) inorder
D) level-order

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
___________ traversal means visit the nodes at each level, one level at at time, starting with the root.
A) preorder
B) postorder
C) inorder
D) level-order
A) preorder
B) postorder
C) inorder
D) level-order

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In the computational strategy to implement a tree with an array, the children of node n are stored at 2n + 1 and 2(n + 1) respectively.
A) 2n + 1
B) 2n + 2
C) 2(n + 1)
D) A and B
E) A and C
F) B and C
A) 2n + 1
B) 2n + 2
C) 2(n + 1)
D) A and B
E) A and C
F) B and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A node that does not have a ______ is called the root of a tree.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A collection where each node can have from 0 to 2 children is called a ______ Tree.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A node that has both a parent and at least one child is called a(n) ______ node.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A balanced N-ary tree with n elements will have height ______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
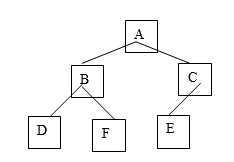
-For the tree shown above, list the root.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17

-For the tree shown above, list the leaves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18

-What is the height of the tree shown above?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
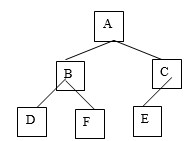
-For the binary tree shown, list the elements in the order generated by an InOrder traversal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20

-For the binary tree shown, list the elements in the order generated by an PreOrder traversal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21

-For the binary tree shown, list the elements in the order generated by an PostOrder traversal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22

-A ______ is a nonlinear structure whose elements are organized into a hierarchy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23

-The ______ strategy allows array positions to be allocated contiguously regardless of the completeness of the tree.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24

-In general, a balanced n-ary tree with m elements will have height ______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25

-There are four basic methods for traversing a tree: ______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26

-Preorder traversal means ______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27

-Inorder traversal means ______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28

-Postorder traversal means ______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29

-Level-order traversal means ______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30

-In the computational strategy to implement a tree with an array, the children of node n are stored at _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The binary tree shown above is balanced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The binary tree shown above is complete.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A collection where each node can have from 0 to 3 children is called a Binary Tree.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A find operation on a balanced binary search tree is O(logn) where as a find operation for binary search tree without the balance assumption is O(n).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A node that has a parent is called the root of a tree.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A tree is a nonlinear structure whose elements are organized into a hierarchy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The simulated link strategy does not allow array positions to be allocated contiguously regardless of the completeness of the tree.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In general, a balanced n-ary tree with m elements will have height lognm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Preorder traversal means visit the left child, then the right child, then the node.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Inorder traversal means visit the left child, then the node, then the right child.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Postorder traversal means visit the node, then the left child, then the right child.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Level-order traversal means visit the nodes at each level, one level at at time, starting with the root.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In the computational strategy to implement a tree with an array, the children of node n are stored at 2n + 1 and 2(n + 1) respectively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What is a tree?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is a node?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What is the root of the tree?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What is a leaf?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Define the height of a tree.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Define the level of a node.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the computational strategy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the simulated link strategy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What attributes should be stored in the TreeNode class?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which method of traversing a tree would result in a sorted list for a binary search tree?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
We used a list to implement the iterator methods for a binary tree. What must be true for this strategy to be successful?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



