Deck 10: Investment, Net Exports, and Interest Rates: The Is Curve
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/69
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Investment, Net Exports, and Interest Rates: The Is Curve
1
The questions with which Chapter 10 is concerned include each of the following except
A) do the determinants of investment in the sticky-price model differ from those of the flexible-price model?
B) do the determinants of net exports in a sticky-price model differ from those of the flexible-price model?
C) do the determinants of potential output in the sticky-price model differ from those of the flexible-price model?
D) how do changes in interest rates affect the equilibrium level of real GDP and national income in the sticky-price model?
A) do the determinants of investment in the sticky-price model differ from those of the flexible-price model?
B) do the determinants of net exports in a sticky-price model differ from those of the flexible-price model?
C) do the determinants of potential output in the sticky-price model differ from those of the flexible-price model?
D) how do changes in interest rates affect the equilibrium level of real GDP and national income in the sticky-price model?
do the determinants of potential output in the sticky-price model differ from those of the flexible-price model?
2
The questions with which Chapter 10 is concerned include each of the following except
A) how do we calculate the equilibrium level of real GDP in the sticky-price model when the central bank's policy is to peg the real interest rate?
B) do the determinants of net exports in a sticky-price model differ from those of the flexible-price model?
C) how do changes in interest rates affect the equilibrium level of real GDP and national income in the sticky-price model?
D) how are the determinants of the money supply different in the sticky-price than in the flexible-price model?
A) how do we calculate the equilibrium level of real GDP in the sticky-price model when the central bank's policy is to peg the real interest rate?
B) do the determinants of net exports in a sticky-price model differ from those of the flexible-price model?
C) how do changes in interest rates affect the equilibrium level of real GDP and national income in the sticky-price model?
D) how are the determinants of the money supply different in the sticky-price than in the flexible-price model?
how are the determinants of the money supply different in the sticky-price than in the flexible-price model?
3
The questions with which Chapter 10 is concerned include each of the following except
A) do the determinants of investment in the sticky-price model differ from those of the flexible-price model?
B) what is the "LM" Curve? How do we use is it?
C) what is the "IS Curve"? How do we use is it?
D) how do we calculate the equilibrium level of real GDP in the sticky-price model when the central . bank's policy is to peg the real interest rate?
A) do the determinants of investment in the sticky-price model differ from those of the flexible-price model?
B) what is the "LM" Curve? How do we use is it?
C) what is the "IS Curve"? How do we use is it?
D) how do we calculate the equilibrium level of real GDP in the sticky-price model when the central . bank's policy is to peg the real interest rate?
what is the "LM" Curve? How do we use is it?
4
Changes in _____________ are the driving force behind the business cycle.
A) consumption spending
B) the money supply
C) government purchases
D) investment spending
A) consumption spending
B) the money supply
C) government purchases
D) investment spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In the flexible-price model, the level of ________ determined the level of _________, and the strength of __________ demand determined the interest rate.
A) savings; investment; investment
B) investment; savings; investment
C) savings; investment; consumption
D) investment; savings; consumption
A) savings; investment; investment
B) investment; savings; investment
C) savings; investment; consumption
D) investment; savings; consumption

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In the sticky-price model, the interest rate is set
A) directly by businesses or indirectly by the combination of the stock of money and the liquidity preference of households and the central bank.
B) directly by the central bank or indirectly by the combination of the stock of money and the liquidity preference of households and businesses.
C) directly by households or indirectly by the combination of the stock of money and the liquidity preference of businesses and the central bank.
D) directly by Congress or indirectly by the combination of the stock of money and the liquidity preference of households and businesses.
A) directly by businesses or indirectly by the combination of the stock of money and the liquidity preference of households and the central bank.
B) directly by the central bank or indirectly by the combination of the stock of money and the liquidity preference of households and businesses.
C) directly by households or indirectly by the combination of the stock of money and the liquidity preference of businesses and the central bank.
D) directly by Congress or indirectly by the combination of the stock of money and the liquidity preference of households and businesses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Each of the following is a source of fluctuations in investment spending except
A) the real interest rate r.
B) changes in investors' expectations about future output growth.
C) changes in households' expectations about future risk.
D) changes in investors' expectations about future profits.
A) the real interest rate r.
B) changes in investors' expectations about future output growth.
C) changes in households' expectations about future risk.
D) changes in investors' expectations about future profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The opportunity cost of an investment project is
A) the short-term risky, nominal interest rate.
B) the price of the investment project.
C) the expected profitability of the investment project.
D) the long-term, risky, real interest rate.
A) the short-term risky, nominal interest rate.
B) the price of the investment project.
C) the expected profitability of the investment project.
D) the long-term, risky, real interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The yield curve
A) shows the nominal interest rates on bonds of various durations.
B) shows the expected profitability of various investment projects.
C) shows the expected rates of return on various stocks.
D) shows the expected selling price of used assets.
A) shows the nominal interest rates on bonds of various durations.
B) shows the expected profitability of various investment projects.
C) shows the expected rates of return on various stocks.
D) shows the expected selling price of used assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Examination of the yield curve indicates
A) that short-term nominal interest rates are usually higher than long-term nominal interest rates.
B) that the expected profitability of short-term investment projects is usually higher than the expected . profitability of long-term investment projects.
C) that short-term nominal interest rates are usually lower than long-term nominal interest rates.
D) that the expected rate of return on short-term stocks is usually lower than the expected rate of return on long-term stocks.
A) that short-term nominal interest rates are usually higher than long-term nominal interest rates.
B) that the expected profitability of short-term investment projects is usually higher than the expected . profitability of long-term investment projects.
C) that short-term nominal interest rates are usually lower than long-term nominal interest rates.
D) that the expected rate of return on short-term stocks is usually lower than the expected rate of return on long-term stocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The increase in the interest rate that the market charges on _________ loans over __________ loans is called the ____________.
A) short-term; long-term; term premium
B) long-term; short term; yield premium
C) short-term; long-term; yield premium
D) long-term; short-term; term premium
A) short-term; long-term; term premium
B) long-term; short term; yield premium
C) short-term; long-term; yield premium
D) long-term; short-term; term premium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
An inverted term structure occurs
A) when the term premium is calculated as one divided by the difference between long-term and short-term interest rates.
B) when the term premium is negative.
C) when the term premium is positive.
D) when the difference between stock returns and short-term interest rates is negative.
A) when the term premium is calculated as one divided by the difference between long-term and short-term interest rates.
B) when the term premium is negative.
C) when the term premium is positive.
D) when the difference between stock returns and short-term interest rates is negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Each of the following is a reason why lenders might add a risk premium to the interest rate they charge for a loan except
A) lenders need to be compensated if the loan is being sought to finance a risky project.
B) the borrower has a history of not repaying loans.
C) the investment project for which the borrower is seeking a loan may not prove to be profitable.
D) lenders always charge high interest rates.
A) lenders need to be compensated if the loan is being sought to finance a risky project.
B) the borrower has a history of not repaying loans.
C) the investment project for which the borrower is seeking a loan may not prove to be profitable.
D) lenders always charge high interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The riskier that lenders believe a loan to be,
A) the higher will be the risk premium they will charge.
B) the higher will be the term premium they will charge.
C) the lower will be the risk premium they will charge.
D) the more willing they will be to make the loan at the risk-free interest rate.
A) the higher will be the risk premium they will charge.
B) the higher will be the term premium they will charge.
C) the lower will be the risk premium they will charge.
D) the more willing they will be to make the loan at the risk-free interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The premium that lenders charge for loans to companies rather than to safe government borrowers is called the
A) term premium.
B) inflation premium.
C) risk premium.
D) health premium.
A) term premium.
B) inflation premium.
C) risk premium.
D) health premium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Each of the following is a reason why the appropriate interest rate in the investment function is the real, risky, long-term interest rate except
A) most investment projects are long-term.
B) investment projects are real assets: their value rises with inflation.
C) businesses borrowing to invest may go bankrupt.
D) the economy may go into a recession, thus reducing the expected profitability of the investment project.
A) most investment projects are long-term.
B) investment projects are real assets: their value rises with inflation.
C) businesses borrowing to invest may go bankrupt.
D) the economy may go into a recession, thus reducing the expected profitability of the investment project.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The intercept of the investment function
A) tells us by how much investment spending is discouraged by a one-unit increase in the short-term, risky, nominal interest rate.
B) tells us by how much investment spending is discouraged by a one-unit increase in the long-term, risky, real interest rate.
C) tells us what the level of investment spending would be if the long-term, risky, real interest rate were 0.
D) tells us what the level of investment spending would be if the short-term, risky, nominal interest rate were 0.
A) tells us by how much investment spending is discouraged by a one-unit increase in the short-term, risky, nominal interest rate.
B) tells us by how much investment spending is discouraged by a one-unit increase in the long-term, risky, real interest rate.
C) tells us what the level of investment spending would be if the long-term, risky, real interest rate were 0.
D) tells us what the level of investment spending would be if the short-term, risky, nominal interest rate were 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The slope of the investment function
A) tells us by how much investment spending is discouraged by a one-unit increase in the short-term, risky, nominal interest rate.
B) tells us by how much investment spending is discouraged by a one-unit increase in the long-term, risky, real interest rate.
C) tells us what the level of investment spending would be if the long-term, risky, real interest rate were 0.
D) tells us what the level of investment spending would be if the short-term, risky, nominal interest rate were 0.
A) tells us by how much investment spending is discouraged by a one-unit increase in the short-term, risky, nominal interest rate.
B) tells us by how much investment spending is discouraged by a one-unit increase in the long-term, risky, real interest rate.
C) tells us what the level of investment spending would be if the long-term, risky, real interest rate were 0.
D) tells us what the level of investment spending would be if the short-term, risky, nominal interest rate were 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Each of the following is a reason why stock market prices are a good indicator of the determinants of the baseline level of investment spending except
A) stock market prices include expected future growth as a determinant.
B) stock market prices include a risk premium as a determinant.
C) stock market prices include the short-term nominal interest rate on bonds as a determinant.
D) stock market prices include accounting earnings as a determinant.
A) stock market prices include expected future growth as a determinant.
B) stock market prices include a risk premium as a determinant.
C) stock market prices include the short-term nominal interest rate on bonds as a determinant.
D) stock market prices include accounting earnings as a determinant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In general, the higher is the stock market,
A) the lower will be investment spending.
B) the higher will be investment spending.
C) the higher will be government spending.
D) the lower will be government spending.
A) the lower will be investment spending.
B) the higher will be investment spending.
C) the higher will be government spending.
D) the lower will be government spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The level of exports is affected by the real interest rate because
A) the level of imports depends on the real interest rate.
B) the level of imports depends on the real exchange rate.
C) the level of exports depends on the level of foreign income.
D) the level of exports depends on the real exchange rate.
A) the level of imports depends on the real interest rate.
B) the level of imports depends on the real exchange rate.
C) the level of exports depends on the level of foreign income.
D) the level of exports depends on the real exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
An increase in the domestic real interest rate
A) will increase the real exchange rate and increase the level of exports.
B) will reduce the real exchange rate and reduce the level of exports.
C) will reduce the real exchange rate and increase the level of exports.
D) will increase the real exchange rate and reduce the level of exports.
A) will increase the real exchange rate and increase the level of exports.
B) will reduce the real exchange rate and reduce the level of exports.
C) will reduce the real exchange rate and increase the level of exports.
D) will increase the real exchange rate and reduce the level of exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A decrease in the domestic real interest rate
A) will increase the real exchange rate and increase the level of exports.
B) will reduce the real exchange rate and reduce the level of exports.
C) will reduce the real exchange rate and increase the level of exports.
D) will increase the real exchange rate and reduce the level of exports.
A) will increase the real exchange rate and increase the level of exports.
B) will reduce the real exchange rate and reduce the level of exports.
C) will reduce the real exchange rate and increase the level of exports.
D) will increase the real exchange rate and reduce the level of exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The slope of the autonomous spending line is
A) -(Iy + X,,r).
B) -(Iy - X,,r).
C) -(Ir + X,,r).
D) -(Ir - X,,r).
A) -(Iy + X,,r).
B) -(Iy - X,,r).
C) -(Ir + X,,r).
D) -(Ir - X,,r).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The interest sensitivity of exports is equal to
A) the sensitivity of exports to changes in the exchange rate plus the sensitivity of the exchange rate to changes in the interest rate.
B) the sensitivity of exports to changes in the exchange rate times the sensitivity of the exchange rate to changes in the interest rate.
C) the sensitivity of exports to changes in the exchange rate minus the sensitivity of the exchange rate to changes in the interest rate.
D) the sensitivity of exports to changes in the exchange rate divided by the sensitivity of the exchange rate to changes in the interest rate.
A) the sensitivity of exports to changes in the exchange rate plus the sensitivity of the exchange rate to changes in the interest rate.
B) the sensitivity of exports to changes in the exchange rate times the sensitivity of the exchange rate to changes in the interest rate.
C) the sensitivity of exports to changes in the exchange rate minus the sensitivity of the exchange rate to changes in the interest rate.
D) the sensitivity of exports to changes in the exchange rate divided by the sensitivity of the exchange rate to changes in the interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The IS curve tells us
A) what equilibrium level of real GDP corresponds to each possible value of the nominal interest rate.
B) what equilibrium level of real GDP corresponds to each possible value of the price level.
C) what equilibrium level of real GDP corresponds to each possible value of the real interest rate.
D) what equilibrium level of real GDP corresponds to each possible value of the money supply.
A) what equilibrium level of real GDP corresponds to each possible value of the nominal interest rate.
B) what equilibrium level of real GDP corresponds to each possible value of the price level.
C) what equilibrium level of real GDP corresponds to each possible value of the real interest rate.
D) what equilibrium level of real GDP corresponds to each possible value of the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The intercept of the IS curve tells us
A) the value that real GDP would attain if the real interest rate were at its equilibrium value.
B) the value that real GDP would attain if the real interest rate were zero.
C) the responsiveness of equilibrium real GDP to changes in the long-term, risky, real interest rate.
D) the responsiveness of equilibrium real GDP to changes in the short-term, risky, nominal interest rate.
A) the value that real GDP would attain if the real interest rate were at its equilibrium value.
B) the value that real GDP would attain if the real interest rate were zero.
C) the responsiveness of equilibrium real GDP to changes in the long-term, risky, real interest rate.
D) the responsiveness of equilibrium real GDP to changes in the short-term, risky, nominal interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The slope of the IS curve tells us
A) the value that real GDP would attain if the real interest rate were at its equilibrium value.
B) the value that real GDP would attain if the real interest rate were zero.
C) the responsiveness of equilibrium real GDP to changes in the long-term, risky, real interest rate.
D) the responsiveness of equilibrium real GDP to changes in the short-term, risky, nominal interest rate.
A) the value that real GDP would attain if the real interest rate were at its equilibrium value.
B) the value that real GDP would attain if the real interest rate were zero.
C) the responsiveness of equilibrium real GDP to changes in the long-term, risky, real interest rate.
D) the responsiveness of equilibrium real GDP to changes in the short-term, risky, nominal interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The slope of the IS curve depends on
A) the value of the multiplier and the responsiveness of baseline autonomous spending to real interest rate changes.
B) the value of the multiplier and the responsiveness of investment spending and exports to real interest rate changes.
C) the inverse of the value of the multiplier and the responsiveness of baseline autonomous spending to real interest rate changes.
D) the inverse of the value of the multiplier and the responsiveness of investment spending and exports to real interest rate changes.
A) the value of the multiplier and the responsiveness of baseline autonomous spending to real interest rate changes.
B) the value of the multiplier and the responsiveness of investment spending and exports to real interest rate changes.
C) the inverse of the value of the multiplier and the responsiveness of baseline autonomous spending to real interest rate changes.
D) the inverse of the value of the multiplier and the responsiveness of investment spending and exports to real interest rate changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The baseline autonomous spending is that part of autonomous spending
A) that depends on the level of national income.
B) that depends on the level of the real interest rate.
C) that depends only on the level of foreign real GDP.
D) that is independent of the real interest rate.
A) that depends on the level of national income.
B) that depends on the level of the real interest rate.
C) that depends only on the level of foreign real GDP.
D) that is independent of the real interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The slope of the IS curve depends on each of the following except
A) the tax rate.
B) the level of foreign real GDP.
C) the interest rate-sensitivity of investment spending.
D) the exchange rate sensitivity of exports.
A) the tax rate.
B) the level of foreign real GDP.
C) the interest rate-sensitivity of investment spending.
D) the exchange rate sensitivity of exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The slope of the IS curve depends on each of the following except
A) the marginal propensity to consume.
B) the propensity to import.
C) the baseline level of investment spending.
D) the interest rate sensitivity of the exchange rate.
A) the marginal propensity to consume.
B) the propensity to import.
C) the baseline level of investment spending.
D) the interest rate sensitivity of the exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The slope of the IS curve depends on each of the following except
A) the propensity to import.
B) the tax rate.
C) the interest rate-sensitivity of investment spending.
D) foreign real interest rates.
A) the propensity to import.
B) the tax rate.
C) the interest rate-sensitivity of investment spending.
D) foreign real interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The intercept of the IS curve depends on each of the following except
A) the propensity to import.
B) the baseline level of consumption expenditures
C) the level of foreign real GDP.
D) the level of government purchases.
A) the propensity to import.
B) the baseline level of consumption expenditures
C) the level of foreign real GDP.
D) the level of government purchases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The intercept of the IS curve depends on each of the following except
A) the baseline level of investment expenditures.
B) the marginal propensity to consume.
C) the level of foreign real GDP.
D) foreign real interest rates.
A) the baseline level of investment expenditures.
B) the marginal propensity to consume.
C) the level of foreign real GDP.
D) foreign real interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The intercept of the IS curve depends on each of the following except
A) the level of government purchases.
B) the baseline level of the real exchange rate.
C) the long-term real interest rate.
D) the exchange rate sensitivity of exports.
A) the level of government purchases.
B) the baseline level of the real exchange rate.
C) the long-term real interest rate.
D) the exchange rate sensitivity of exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The intercept of the IS curve depends on each of the following except
A) the baseline level of consumption expenditures
B) the baseline level of the real exchange rate.
C) the tax rate.
D) the exchange rate sensitivity of imports.
A) the baseline level of consumption expenditures
B) the baseline level of the real exchange rate.
C) the tax rate.
D) the exchange rate sensitivity of imports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If the marginal propensity to expend is equal to .6, the interest rate sensitivity of investment is equal to $100 billion, the interest rate sensitivity of the exchange rate is 10, and the exchange rate sensitivity of exports is $7 billion, a one percentage point change in the real interest rate will change the level of aggregate demand by
A) $170 billion.
B) $425 billion.
C) -$425 billion.
D) -$170 billion.
A) $170 billion.
B) $425 billion.
C) -$425 billion.
D) -$170 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If the MPE = .6, Ir = $200 billion 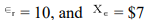 billion, a one percentage point change in r will change the level of aggregate demand by
billion, a one percentage point change in r will change the level of aggregate demand by
A) $270 billion.
B) -$625 billion.
C) $625 billion.
D) -$270 billion.
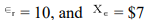 billion, a one percentage point change in r will change the level of aggregate demand by
billion, a one percentage point change in r will change the level of aggregate demand byA) $270 billion.
B) -$625 billion.
C) $625 billion.
D) -$270 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The position of the IS curve depends on
A) the baseline level of autonomous spending times the multiplier.
B) the baseline level of autonomous spending times the marginal to expend.
C) the baseline level of autonomous spending divided by the multiplier.
D) the baseline level of autonomous spending divided by the marginal propensity to expend.
A) the baseline level of autonomous spending times the multiplier.
B) the baseline level of autonomous spending times the marginal to expend.
C) the baseline level of autonomous spending divided by the multiplier.
D) the baseline level of autonomous spending divided by the marginal propensity to expend.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
An increase in the baseline level of consumption spending will
A) shift the IS curve to the left.
B) shift the IS curve to the right.
C) make the IS curve more vertical.
D) make the IS curve less vertical.
A) shift the IS curve to the left.
B) shift the IS curve to the right.
C) make the IS curve more vertical.
D) make the IS curve less vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A decrease in the baseline level of investment spending will
A) shift the IS curve to the left.
B) shift the IS curve to the right.
C) make the IS curve more vertical.
D) make the IS curve less vertical.
A) shift the IS curve to the left.
B) shift the IS curve to the right.
C) make the IS curve more vertical.
D) make the IS curve less vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
An increase in the tax rate will
A) shift the IS curve to the left.
B) shift the IS curve to the right.
C) make the IS curve more vertical.
D) make the IS curve less vertical.
A) shift the IS curve to the left.
B) shift the IS curve to the right.
C) make the IS curve more vertical.
D) make the IS curve less vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
An increase in the propensity to import will
A) shift the IS curve to the left.
B) shift the IS curve to the right.
C) make the IS curve more vertical.
D) make the IS curve less vertical.
A) shift the IS curve to the left.
B) shift the IS curve to the right.
C) make the IS curve more vertical.
D) make the IS curve less vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
An increase in the marginal propensity to consume will
A) shift the IS curve to the left.
B) shift the IS curve to the right.
C) make the IS curve more vertical.
D) make the IS curve less vertical.
A) shift the IS curve to the left.
B) shift the IS curve to the right.
C) make the IS curve more vertical.
D) make the IS curve less vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
An increase in government purchases will
A) shift the IS curve to the left.
B) shift the IS curve to the right.
C) make the IS curve more vertical.
D) make the IS curve less vertical.
A) shift the IS curve to the left.
B) shift the IS curve to the right.
C) make the IS curve more vertical.
D) make the IS curve less vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If the economy is operating above (to the right of) the IS curve, then real GDP is _______ than planned expenditure,
A) greater; inventories are decreasing faster than expected, and businesses will reduce production.
B) less; inventories are decreasing faster than expected, and businesses will increase production.
C) greater; inventories are increasing faster than expected, and businesses will reduce production.
D) less; inventories are increasing faster than expected, and businesses will increase production.
A) greater; inventories are decreasing faster than expected, and businesses will reduce production.
B) less; inventories are decreasing faster than expected, and businesses will increase production.
C) greater; inventories are increasing faster than expected, and businesses will reduce production.
D) less; inventories are increasing faster than expected, and businesses will increase production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If the economy is operating below (to the left of) the IS curve, then real GDP is _______ than planned expenditure,
A) greater; inventories are decreasing faster than expected, and businesses will reduce production.
B) less; inventories are decreasing faster than expected, and businesses will increase production.
C) greater; inventories are increasing faster than expected, and businesses will reduce production.
D) less; inventories are increasing faster than expected, and businesses will increase production.
A) greater; inventories are decreasing faster than expected, and businesses will reduce production.
B) less; inventories are decreasing faster than expected, and businesses will increase production.
C) greater; inventories are increasing faster than expected, and businesses will reduce production.
D) less; inventories are increasing faster than expected, and businesses will increase production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If the MPE is equal to .7, the baseline level of spending is $4 trillion, a one percentage point decrease in the real interest rate increases investment spending by $100 billion and exports by $20 billion, and the real interest rate is equal to 5%, then the equilibrium level of real GDP is
A) $11.733 trillion.
B) $5.028 trillion.
C) $1.056 trillion.
D) $14.933 trillion.
A) $11.733 trillion.
B) $5.028 trillion.
C) $1.056 trillion.
D) $14.933 trillion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If the MPE is equal to .7, a one percentage point decrease in the real interest rate increases investment spending by $100 billion and exports by $20 billion, the real interest rate is equal to 5%, and government purchases increase by $200 billion, the change in the equilibrium level of real GDP would be
A) -$.667 trillion.
B) $.667 trillion.
C) -$.286 trillion.
D) $.286 trillion.
A) -$.667 trillion.
B) $.667 trillion.
C) -$.286 trillion.
D) $.286 trillion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If the Federal Reserve raises interest rates,
A) the IS curve will shift to the left and the level of planned expenditure will decrease.
B) the level of planned expenditure will move downward along the IS curve and thus increase.
C) the IS curve will shift to the right and the level of planned expenditure will increase.
D) the level of planned expenditure will move upward along the IS curve and thus decrease.
A) the IS curve will shift to the left and the level of planned expenditure will decrease.
B) the level of planned expenditure will move downward along the IS curve and thus increase.
C) the IS curve will shift to the right and the level of planned expenditure will increase.
D) the level of planned expenditure will move upward along the IS curve and thus decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If the Federal Reserve decreases interest rates,
A) the IS curve will shift to the left and the level of planned expenditure will decrease.
B) the level of planned expenditure will move downward along the IS curve and thus increase.
C) the IS curve will shift to the right and the level of planned expenditure will increase.
D) the level of planned expenditure will move upward along the IS curve and thus decrease.
A) the IS curve will shift to the left and the level of planned expenditure will decrease.
B) the level of planned expenditure will move downward along the IS curve and thus increase.
C) the IS curve will shift to the right and the level of planned expenditure will increase.
D) the level of planned expenditure will move upward along the IS curve and thus decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Suppose that the Federal Reserve has decided that there is a deflationary gap of $1 trillion in the economy. Suppose further that the estimated slope of the IS curve is -$400 billion. By how many percentage points would the Fed need to decrease the real interest rate in order close the deflationary gap?
A) 2.5
B) 4
C) .4
D) 25
A) 2.5
B) 4
C) .4
D) 25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
If the Federal Reserve wants to decrease interest rates, it can
A) sell short-term government bonds.
B) increase the reserve requirement.
C) purchase short-term government bonds.
D) increase the discount rate.
A) sell short-term government bonds.
B) increase the reserve requirement.
C) purchase short-term government bonds.
D) increase the discount rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If the Federal Reserve wants to increase interest rates, it can
A) sell short-term government bonds.
B) increase the reserve requirement.
C) purchase short-term government bonds.
D) increase the discount rate.
A) sell short-term government bonds.
B) increase the reserve requirement.
C) purchase short-term government bonds.
D) increase the discount rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Each of the following is a difficulty associated with attempting to control planned expenditure by manipulating interest rates except
A) our knowledge of the structure of the economy is imperfect.
B) economic policy works with long and variable lags.
C) the interest rates that the Federal Reserve can control are short-term, nominal, safe, interest rates.
D) people are generally unwilling to purchase short-term government bonds.
A) our knowledge of the structure of the economy is imperfect.
B) economic policy works with long and variable lags.
C) the interest rates that the Federal Reserve can control are short-term, nominal, safe, interest rates.
D) people are generally unwilling to purchase short-term government bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Each of the following is a potential cause of slippage between short-term, nominal, safe, interest rates and long-term, real, risky, interest rates except
A) changes in the term premium between short and long interest rates.
B) changes in the rate of inflation.
C) changes in the expected profitability of investment projects.
D) changes in the risk premium.
A) changes in the term premium between short and long interest rates.
B) changes in the rate of inflation.
C) changes in the expected profitability of investment projects.
D) changes in the risk premium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The major determinant of the term premium is
A) expectations of the expected profitability of investment projects.
B) expectations of future monetary policy.
C) expectations of future consumption spending.
D) expectations of future government purchases.
A) expectations of the expected profitability of investment projects.
B) expectations of future monetary policy.
C) expectations of future consumption spending.
D) expectations of future government purchases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Long-term interest rates will be ______ relative to short-term interest rates if
A) high; people expect the Federal Reserve to decrease short-term rates in the future.
B) high; people expect the Federal Reserve to increase long-term rates in the future.
C) low; people expect the Federal Reserve to increase short-term rates in the future.
D) low; people expect the Federal Reserve to decrease short-term rates in the future.
A) high; people expect the Federal Reserve to decrease short-term rates in the future.
B) high; people expect the Federal Reserve to increase long-term rates in the future.
C) low; people expect the Federal Reserve to increase short-term rates in the future.
D) low; people expect the Federal Reserve to decrease short-term rates in the future.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Long-term interest rates will be ______ relative to short-term interest rates if
A) high; people expect the Federal Reserve to decrease short-term rates in the future.
B) high; people expect the Federal Reserve to increase short-term rates in the future.
C) low; people expect the Federal Reserve to increase short-term rates in the future.
D) low; people expect the Federal Reserve to decrease long-term rates in the future.
A) high; people expect the Federal Reserve to decrease short-term rates in the future.
B) high; people expect the Federal Reserve to increase short-term rates in the future.
C) low; people expect the Federal Reserve to increase short-term rates in the future.
D) low; people expect the Federal Reserve to decrease long-term rates in the future.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In the 1960s the IS curve
A) shifted to the right because of increased business optimism, tax reductions, and increased government spending.
B) shifted to the left because of increased business optimism, tax reductions, and increased government spending.
C) shifted to the right because of decreased business optimism, tax increases, and decreased government spending.
D) shifted to the right due to a decrease in interest rates.
A) shifted to the right because of increased business optimism, tax reductions, and increased government spending.
B) shifted to the left because of increased business optimism, tax reductions, and increased government spending.
C) shifted to the right because of decreased business optimism, tax increases, and decreased government spending.
D) shifted to the right due to a decrease in interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In the late 1970s (1977 to 1979) the US economy
A) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the right because of increased business optimism, tax reductions, and increased government spending.
B) experienced a movement down and to the right along the IS curve.
C) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the left because of decreased business optimism, tax increases, and decreased government spending.
D) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the right due to a decrease in interest rates.
A) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the right because of increased business optimism, tax reductions, and increased government spending.
B) experienced a movement down and to the right along the IS curve.
C) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the left because of decreased business optimism, tax increases, and decreased government spending.
D) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the right due to a decrease in interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
From 1979 to 1982 the US economy
A) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the left due to an increase in interest rates.
B) experienced a movement down and to the right along the IS curve.
C) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the left because of decreased business optimism, tax increases, and decreased government spending.
D) experienced a movement up and to the left along the IS curve.
A) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the left due to an increase in interest rates.
B) experienced a movement down and to the right along the IS curve.
C) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the left because of decreased business optimism, tax increases, and decreased government spending.
D) experienced a movement up and to the left along the IS curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In the early 1980s (1982 to 1985) the US economy
A) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the right because of increased business optimism, tax increases, and decreased government spending.
B) experienced a movement down and to the right along the IS curve.
C) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the right because of tax reductions, and increased government spending.
D) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the right due to a decrease in interest rates.
A) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the right because of increased business optimism, tax increases, and decreased government spending.
B) experienced a movement down and to the right along the IS curve.
C) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the right because of tax reductions, and increased government spending.
D) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the right due to a decrease in interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In the late 1980s (1985 to 1990) the US economy
A) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the right because of increased business optimism, tax increases, and decreased government spending.
B) experienced a movement down and to the right along the IS curve.
C) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the right because of tax reductions, and increased government spending.
D) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the right due to a decrease in interest rates.
A) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the right because of increased business optimism, tax increases, and decreased government spending.
B) experienced a movement down and to the right along the IS curve.
C) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the right because of tax reductions, and increased government spending.
D) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the right due to a decrease in interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In the early 1990s (1990 to 1992) the US economy
A) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the right because of increased business optimism, tax increases, and decreased government spending.
B) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the left due to an increase in interest rates.
C) experienced a experienced a up and to the left along the IS curve.
D) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the left due to a decrease in the baseline level of investment spending.
A) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the right because of increased business optimism, tax increases, and decreased government spending.
B) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the left due to an increase in interest rates.
C) experienced a experienced a up and to the left along the IS curve.
D) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the left due to a decrease in the baseline level of investment spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
From 1992 until the end of the decade, the US economy
A) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the right because of increased business optimism and tight fiscal policy.
B) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the left due to an increase in interest rates.
C) experienced a movement down and to the right along the IS curve.
D) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the left due to a decrease in the baseline level of investment spending.
A) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the right because of increased business optimism and tight fiscal policy.
B) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the left due to an increase in interest rates.
C) experienced a movement down and to the right along the IS curve.
D) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the left due to a decrease in the baseline level of investment spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
During the 1990s,
A) real GDP increased, the unemployment rate decreased and the inflation rate increased significantly.
B) real GDP increased, the unemployment rate increased and the inflation rate increased significantly.
C) real GDP increased, the unemployment rate decreased and the inflation rate was fairly stable at a low level.
D) real GDP increased, the unemployment rate decreased and the inflation rate was been negative.
A) real GDP increased, the unemployment rate decreased and the inflation rate increased significantly.
B) real GDP increased, the unemployment rate increased and the inflation rate increased significantly.
C) real GDP increased, the unemployment rate decreased and the inflation rate was fairly stable at a low level.
D) real GDP increased, the unemployment rate decreased and the inflation rate was been negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
During 2002 and 2003, the US economy
A) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the right because of increased business optimism and tight fiscal policy.
B) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the left due to an increase in interest rates.
C) experienced a movement down and to the right along the IS curve.
D) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the left due to a decrease in the baseline level of investment spending.
A) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the right because of increased business optimism and tight fiscal policy.
B) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the left due to an increase in interest rates.
C) experienced a movement down and to the right along the IS curve.
D) experienced a shifting of the IS curve to the left due to a decrease in the baseline level of investment spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



