Deck 16: Reaction Rates and Chemical Equilibrium
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/52
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Reaction Rates and Chemical Equilibrium
1
Most reactions are carried out in liquid solution or in the gaseous phase because in such situations ________.
A) activation energies are higher
B) reactant activation energies are lower
C) kinetic energies of reactants are lower
D) reactant collisions occur more frequently
A) activation energies are higher
B) reactant activation energies are lower
C) kinetic energies of reactants are lower
D) reactant collisions occur more frequently
reactant collisions occur more frequently
2
For a collision between molecules to result in reaction, the molecules must possess a favorable orientation relative to each other ________.
A) and exchange electrons
B) and "stick together" for at least 10 seconds
C) and a certain minimum energy
D) and be in the gaseous state
A) and exchange electrons
B) and "stick together" for at least 10 seconds
C) and a certain minimum energy
D) and be in the gaseous state
and a certain minimum energy
3
Whether a reaction is exothermic or endothermic is determined by ________.
A) the activation energy
B) the physical state of the reaction system
C) energy balance between bond breaking and bond forming resulting in a net loss or gain of energy
D) whether a catalyst is present
A) the activation energy
B) the physical state of the reaction system
C) energy balance between bond breaking and bond forming resulting in a net loss or gain of energy
D) whether a catalyst is present
energy balance between bond breaking and bond forming resulting in a net loss or gain of energy
4
Which reaction below is endothermic?
A) NH3 + HBr NH4Br + heat
B) CH4 + N2 + heat HCN + NH3
C) 2NO2 N2 + 2O2 + heat
D) PCl3 + Cl2 PCl5 + heat
A) NH3 + HBr NH4Br + heat
B) CH4 + N2 + heat HCN + NH3
C) 2NO2 N2 + 2O2 + heat
D) PCl3 + Cl2 PCl5 + heat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A catalyst works by:
A) increasing the rate of a reaction by decreasing the heat of reaction
B) increasing the rate of a reaction by lowering the activation energy of the forward reaction only
C) increasing the rate of a reaction by increasing the activation energy of the reverse reaction only
D) increasing the rate of a reaction by providing an alternative pathway with a lower activation energy
A) increasing the rate of a reaction by decreasing the heat of reaction
B) increasing the rate of a reaction by lowering the activation energy of the forward reaction only
C) increasing the rate of a reaction by increasing the activation energy of the reverse reaction only
D) increasing the rate of a reaction by providing an alternative pathway with a lower activation energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following changes would most likely decrease the rate of a reaction?
A) increasing the activation energy for the reaction
B) decreasing the activation energy for the reaction
C) increasing the reaction temperature
D) increasing the concentration of a reactant
A) increasing the activation energy for the reaction
B) decreasing the activation energy for the reaction
C) increasing the reaction temperature
D) increasing the concentration of a reactant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Catalysts are correctly characterized by each of the following statements except one. The exception is ________.
A) catalysts can be either solids, liquids or gases
B) catalysts lower the activation energy for a reaction
C) catalysts do not "actively" participate in a reaction
D) catalysts are not "consumed" in a reaction
A) catalysts can be either solids, liquids or gases
B) catalysts lower the activation energy for a reaction
C) catalysts do not "actively" participate in a reaction
D) catalysts are not "consumed" in a reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Reaction A releases 24 kJ/mole and has an activation energy of 98 kJ/mole. Which statement is correct concerning Reaction A?
A) The overall reaction is endothermic with a high activation energy.
B) The overall reaction is endothermic with a low activation energy.
C) The overall reaction is exothermic with a high activation energy.
D) The overall reaction is exothermic with a low activation energy.
A) The overall reaction is endothermic with a high activation energy.
B) The overall reaction is endothermic with a low activation energy.
C) The overall reaction is exothermic with a high activation energy.
D) The overall reaction is exothermic with a low activation energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Reaction conditions for a hypothetical reaction, X + Y W + Z, are given below. Predict which reaction should occur at a faster rate. (M = molarity)Activation
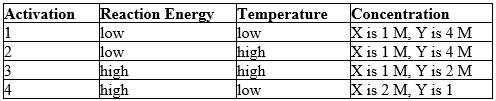
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which response includes all the factors that would increase the rate of a chemical reaction, and no others?
I. Lowering the temperature of the chemical reaction.
II. Significantly increasing the concentration of one of the reactants.
III. Adding a catalyst to an uncatalyzed reaction.
IV. Decrease the reaction surface area.
V. Increasing the pressure on a gaseous reaction system.
A) I and IV
B) II, III and V
C) I, IV and V
D) III only
I. Lowering the temperature of the chemical reaction.
II. Significantly increasing the concentration of one of the reactants.
III. Adding a catalyst to an uncatalyzed reaction.
IV. Decrease the reaction surface area.
V. Increasing the pressure on a gaseous reaction system.
A) I and IV
B) II, III and V
C) I, IV and V
D) III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Increasing the temperature of a chemical reaction increases the rate of reaction because ________.
A) the activation energy decreases
B) the activation energy increases
C) the collision frequency of reactant molecules increases
D) both the collision frequency and collision energies of reactant molecules increases
A) the activation energy decreases
B) the activation energy increases
C) the collision frequency of reactant molecules increases
D) both the collision frequency and collision energies of reactant molecules increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
At equilibrium, the equilibrium constant for the following hypothetical reaction is two (Keq = 2), [A] = 4, [B] = 8, and [AB] = 16 at 25 °C. AB + Heat A (g) + B (g)
After a stress has been absorbed by the reaction, the new equilibrium concentrations are: [A] = 2, [B] = 1, and [AB] = 64. The stress absorbed by the equilibrium system ________.
A) was a change in the reaction temperature evident by the change in the value of the Keq
B) was a decrease in the concentration of [A]
C) was a decrease in the concentration of [B]
D) was an increase in the concentration of [AB]
After a stress has been absorbed by the reaction, the new equilibrium concentrations are: [A] = 2, [B] = 1, and [AB] = 64. The stress absorbed by the equilibrium system ________.
A) was a change in the reaction temperature evident by the change in the value of the Keq
B) was a decrease in the concentration of [A]
C) was a decrease in the concentration of [B]
D) was an increase in the concentration of [AB]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Reaction conditions for a hypothetical reaction, A + B C, are given below.
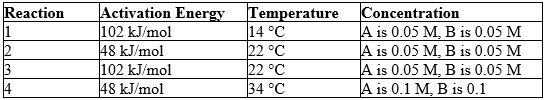
Predict which reaction should occur at the slowest rate. (M = molarity)
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

Predict which reaction should occur at the slowest rate. (M = molarity)
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Chemical equilibrium is reached in a system when ________.
A) product and reactant concentrations remain constant
B) reactant concentrations steadily decrease
C) product molecules begin reacting with each other
D) complete conversion of reactants to products has occurred
A) product and reactant concentrations remain constant
B) reactant concentrations steadily decrease
C) product molecules begin reacting with each other
D) complete conversion of reactants to products has occurred

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A mixture of 1.40 moles of A and 2.30 moles of B was allowed to reach equilibrium. At equilibrium, it is found that 0.90 mole of A is present. How many moles of C are present at equilibrium?
3 A (g) + 2 B (g) 4 C (g)
A) 1.60 moles
B) 0.667 mole
C) 1.10 moles
D) 1.30 moles
3 A (g) + 2 B (g) 4 C (g)
A) 1.60 moles
B) 0.667 mole
C) 1.10 moles
D) 1.30 moles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A chemical equilbrium expression depends on the ________ of a reaction.
A) rate
B) stoichiometry
C) stoichiometry and mechanism
D) mechanism
A) rate
B) stoichiometry
C) stoichiometry and mechanism
D) mechanism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Given the following reaction, the equilibrium expression will be:
4 CuO (s) + CH4 (g) CO2 (g) + 4 Cu (s) + 2 H2O (g)
A) [CuO]/[Cu]
B) [CuO]4/[Cu]4
C) [Cu]4/[CuO]4
D) [CO2][H2O]2/[CH4]
4 CuO (s) + CH4 (g) CO2 (g) + 4 Cu (s) + 2 H2O (g)
A) [CuO]/[Cu]
B) [CuO]4/[Cu]4
C) [Cu]4/[CuO]4
D) [CO2][H2O]2/[CH4]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is the correct equilibrium expression for the reaction
CS2 (g) + 4 H2 (g) CH4 (g) + 2 H2S (g)
A)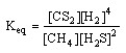
B)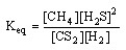
C)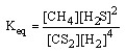
D)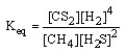
CS2 (g) + 4 H2 (g) CH4 (g) + 2 H2S (g)
A)
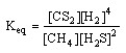
B)

C)
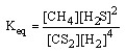
D)
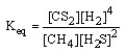

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is the correct equilibrium expression for the reaction
2 Ag (s) + Cl2 (g) 2 AgCl (s)
A)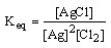
B)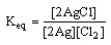
C)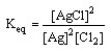
D)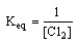
2 Ag (s) + Cl2 (g) 2 AgCl (s)
A)
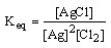
B)
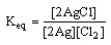
C)
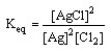
D)
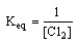

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Identify the reaction that is described by the following equilibrium expression:
K = [H2]2 [O2] / [H2O]2
A) 2 H2 (g) + O2 (g) 2H2O (g)
B) H2O (g) H2 (g) +![<strong>Identify the reaction that is described by the following equilibrium expression: K<sub> </sub>= [H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> [O<sub>2</sub>] / [H<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>2</sup></strong> A) 2 H<sub>2</sub> (g) + O<sub>2</sub> (g) \rightarrow 2H<sub>2</sub>O (g) B) H<sub>2</sub>O (g) \rightarrow H<sub>2</sub> (g) + O<sub>2</sub> (g) C) H<sub>2</sub>O (g) \rightarrow 2H (g) + O (g) D) 2H<sub>2</sub>O (g) \rightarrow 2 H<sub>2</sub>(g) + O<sub>2</sub> (g)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB10281/11eeb92b_d2e6_3b1c_b585_0db5dcf39850_TB10281_11.jpg) O2 (g)
O2 (g)
C) H2O (g) 2H (g) + O (g)
D) 2H2O (g) 2 H2(g) + O2 (g)
K = [H2]2 [O2] / [H2O]2
A) 2 H2 (g) + O2 (g) 2H2O (g)
B) H2O (g) H2 (g) +
![<strong>Identify the reaction that is described by the following equilibrium expression: K<sub> </sub>= [H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> [O<sub>2</sub>] / [H<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>2</sup></strong> A) 2 H<sub>2</sub> (g) + O<sub>2</sub> (g) \rightarrow 2H<sub>2</sub>O (g) B) H<sub>2</sub>O (g) \rightarrow H<sub>2</sub> (g) + O<sub>2</sub> (g) C) H<sub>2</sub>O (g) \rightarrow 2H (g) + O (g) D) 2H<sub>2</sub>O (g) \rightarrow 2 H<sub>2</sub>(g) + O<sub>2</sub> (g)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB10281/11eeb92b_d2e6_3b1c_b585_0db5dcf39850_TB10281_11.jpg) O2 (g)
O2 (g)C) H2O (g) 2H (g) + O (g)
D) 2H2O (g) 2 H2(g) + O2 (g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If, at equilibrium most of the reactants remain unreacted, the equilibrium constant would be expected to have ________.
A) a very large numerical value
B) a very small numerical value
C) a numerical value slightly greater than 1.0
D) a numerical value slightly less than 1.0
A) a very large numerical value
B) a very small numerical value
C) a numerical value slightly greater than 1.0
D) a numerical value slightly less than 1.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When the position of an equilibrium is described as being "far to the left" it means that ________.
A) very few reactant molecules are present in the equilibrium mixture
B) very few product molecules are present in the equilibrium mixture
C) significant amounts of both products and reactants are present in the equilibrium mixture
D) the rate of the reverse reaction is greater than that of the forward reaction
A) very few reactant molecules are present in the equilibrium mixture
B) very few product molecules are present in the equilibrium mixture
C) significant amounts of both products and reactants are present in the equilibrium mixture
D) the rate of the reverse reaction is greater than that of the forward reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The grams of products present after a chemical reaction reaches equilibrium ________.
A) will always be greater than the grams of reactants present
B) will always be less than the grams of reactants present
C) must equal the grams of reactants present
D) may be less than, equal to, or greater than the grams of reactants present, depending upon the chemical reaction under study
A) will always be greater than the grams of reactants present
B) will always be less than the grams of reactants present
C) must equal the grams of reactants present
D) may be less than, equal to, or greater than the grams of reactants present, depending upon the chemical reaction under study

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which statement is false? An equilibrium constant for a particular reaction ________.
A) changes when the temperature increases
B) changes when a catalyst is added
C) does not change when an additional quantity of a reactant is added
D) does not change when a product is removed
A) changes when the temperature increases
B) changes when a catalyst is added
C) does not change when an additional quantity of a reactant is added
D) does not change when a product is removed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is the equilibrium constant value if at equilibrium the concentrations are NH3 = 0.40 M, H2 = 0.12 M and N2 = 0.040 M at a certain temperature?
2 NH3 (g) N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g)
A) 4.8 x 10-2
B) 4.3 x 10-4
C) 6.8 x 10-9
D) 7.2 x 1015
2 NH3 (g) N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g)
A) 4.8 x 10-2
B) 4.3 x 10-4
C) 6.8 x 10-9
D) 7.2 x 1015

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction below if a 3.25 L tank was found to contain 0.343 mol O2, 0.0212 mol SO3 and 0.00419 mol SO2 at equilibrium.
2 SO3 (g) 2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
A) 6.78 x 10-2
B) 1.34 x 10-2
C) 4.12 x 10-3
D) 4.35 x 10-2
2 SO3 (g) 2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
A) 6.78 x 10-2
B) 1.34 x 10-2
C) 4.12 x 10-3
D) 4.35 x 10-2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Given the following decomposition reaction: PCl5 (g) PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g), when 0.84 moles of PCl5 is placed in a 1.0 it was found that when the reaction reaches equilibrium, 0.72 moles of PCl5 still remains. What is the value of the equilibrium constant for this reaction?
A) 0.62
B) 0.72
C) 0.020
D) 0.12
A) 0.62
B) 0.72
C) 0.020
D) 0.12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
For a reaction which has an equilibrium constant of 3.8 x 10-16 at 25 °C, the position of equilibrium is best described as ________.
A) mostly products
B) mostly reactants
C) same amount of products and reactants
D) significant amounts of both products and reactants
A) mostly products
B) mostly reactants
C) same amount of products and reactants
D) significant amounts of both products and reactants

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
All of the following factors may shift the position of an equilibrium except one. The exception is ________.
A) reduction of reaction volume
B) increase reaction temperature
C) double the pressure (assume moles of reactants > products)
D) addition of a catalyst
A) reduction of reaction volume
B) increase reaction temperature
C) double the pressure (assume moles of reactants > products)
D) addition of a catalyst

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What effect does a catalyst have on an equilibrium?
A) It increases the rate at which an equilibrium is reached without changing the composition of the reaction.
B) It slows the reverse reaction.
C) It increases the rate of the forward reaction.
D) It shifts the reaction to the right.
A) It increases the rate at which an equilibrium is reached without changing the composition of the reaction.
B) It slows the reverse reaction.
C) It increases the rate of the forward reaction.
D) It shifts the reaction to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If at equilibrium, reactant concentrations are slightly smaller than product concentrations, the equilibrium constant would be ________.
A) a number >> 1
B) a number << 1
C) a number slightly lower than one
D) a number slightly higher than one
A) a number >> 1
B) a number << 1
C) a number slightly lower than one
D) a number slightly higher than one

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The form of the expression for the equilibrium constant, Keq, for the reaction below is:
4 NH3 (g) + 5 O2 (g) 4 NO (g) + 6 H2O (g)
A)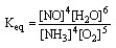
B)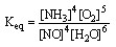
C)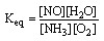
D)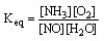
4 NH3 (g) + 5 O2 (g) 4 NO (g) + 6 H2O (g)
A)
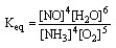
B)
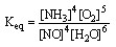
C)
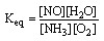
D)
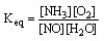

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The form of the expression for the equilibrium constant, Keq, for the reaction below is:
2 NaIO3 (s) 2 NaI (s) + 3 O2 (g)
A)![<strong>The form of the expression for the equilibrium constant, K<sub>eq</sub>, for the reaction below is: 2 NaIO<sub>3</sub> (s) \rightarrow 2 NaI (s) + 3 O<sub>2</sub> (g)</strong> A) B) C) D) K<sub>eq</sub> = [O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>3</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB10281/11eeb92b_d2e6_6231_b585_db1cc2e1fc8a_TB10281_11.jpg)
B)![<strong>The form of the expression for the equilibrium constant, K<sub>eq</sub>, for the reaction below is: 2 NaIO<sub>3</sub> (s) \rightarrow 2 NaI (s) + 3 O<sub>2</sub> (g)</strong> A) B) C) D) K<sub>eq</sub> = [O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>3</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB10281/11eeb92b_d2e6_8942_b585_ef73372d4029_TB10281_11.jpg)
C)![<strong>The form of the expression for the equilibrium constant, K<sub>eq</sub>, for the reaction below is: 2 NaIO<sub>3</sub> (s) \rightarrow 2 NaI (s) + 3 O<sub>2</sub> (g)</strong> A) B) C) D) K<sub>eq</sub> = [O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>3</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB10281/11eeb92b_d2e6_8943_b585_f92406f0c714_TB10281_11.jpg)
D) Keq = [O2]3
2 NaIO3 (s) 2 NaI (s) + 3 O2 (g)
A)
![<strong>The form of the expression for the equilibrium constant, K<sub>eq</sub>, for the reaction below is: 2 NaIO<sub>3</sub> (s) \rightarrow 2 NaI (s) + 3 O<sub>2</sub> (g)</strong> A) B) C) D) K<sub>eq</sub> = [O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>3</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB10281/11eeb92b_d2e6_6231_b585_db1cc2e1fc8a_TB10281_11.jpg)
B)
![<strong>The form of the expression for the equilibrium constant, K<sub>eq</sub>, for the reaction below is: 2 NaIO<sub>3</sub> (s) \rightarrow 2 NaI (s) + 3 O<sub>2</sub> (g)</strong> A) B) C) D) K<sub>eq</sub> = [O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>3</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB10281/11eeb92b_d2e6_8942_b585_ef73372d4029_TB10281_11.jpg)
C)
![<strong>The form of the expression for the equilibrium constant, K<sub>eq</sub>, for the reaction below is: 2 NaIO<sub>3</sub> (s) \rightarrow 2 NaI (s) + 3 O<sub>2</sub> (g)</strong> A) B) C) D) K<sub>eq</sub> = [O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>3</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB10281/11eeb92b_d2e6_8943_b585_f92406f0c714_TB10281_11.jpg)
D) Keq = [O2]3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
At a given temperature, K = 46.0 for the reaction:
4 HCl (g) + O2 (g) 2 H2O (g) + 2 Cl2 (g)
At equilibrium, [HCl] = 0.150, [O2] = 0.395, and [H2O] = 0.625. What is the concentration of [Cl2] at equilibrium?
A) 1.26 M
B) 0.00653 M
C) 0.153 M
D) 0.438 M
4 HCl (g) + O2 (g) 2 H2O (g) + 2 Cl2 (g)
At equilibrium, [HCl] = 0.150, [O2] = 0.395, and [H2O] = 0.625. What is the concentration of [Cl2] at equilibrium?
A) 1.26 M
B) 0.00653 M
C) 0.153 M
D) 0.438 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Sulfur combines with hydrogen to form hydrogen sulfide, a toxic gas that is a product of decay of organic material.
S2 (g) + 2 H2 (g) 2 H2S (g) K = 2.8 x 10-21
Which of the following statements is true concerning the equilibrium system?
A) Increasing the volume of the sealed reaction container would shift the equilibrium to the right.
B) Decreasing the concentration of H2 would shift the equilibrium to the right.
C) Decreasing the concentration of H2S would shift the equilibrium to the left.
D) Very little hydrogen sulfide gas is present in the equilibrium.
S2 (g) + 2 H2 (g) 2 H2S (g) K = 2.8 x 10-21
Which of the following statements is true concerning the equilibrium system?
A) Increasing the volume of the sealed reaction container would shift the equilibrium to the right.
B) Decreasing the concentration of H2 would shift the equilibrium to the right.
C) Decreasing the concentration of H2S would shift the equilibrium to the left.
D) Very little hydrogen sulfide gas is present in the equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Hydrogen gas reacts with iron(III) oxide and produces iron metal which can be used to produce steel according to the reaction below. Choose the response that is incorrect concerning the equilibrium system.
Fe2O3 (s) + H2 (g) + heat 2 Fe (s) + 3 H2O (g)
A) Lowering the reaction temperature will increase the concentration of hydrogen gas.
B) Increasing the pressure on the reaction chamber favors the formation of products.
C) Continually removing water from the reaction chamber increases the yield of iron.
D) Decreasing the volume of hydrogen gas will reduce the yield of iron.
Fe2O3 (s) + H2 (g) + heat 2 Fe (s) + 3 H2O (g)
A) Lowering the reaction temperature will increase the concentration of hydrogen gas.
B) Increasing the pressure on the reaction chamber favors the formation of products.
C) Continually removing water from the reaction chamber increases the yield of iron.
D) Decreasing the volume of hydrogen gas will reduce the yield of iron.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
CO2 and H2 are allowed to react until an equilibrium is established as follows:
CO2 (g) + H2 (g) H2O (g) + CO (g)
What will be the effect on the equilibrium by adding H2O to the equilibrium mixture?
A) The equilibrium will shift to the left.
B) H2 concentration will decrease and CO2 concentration will increase.
C) CO and CO2 concentrations will increase.
D) H2 concentration will decrease and H2O concentration will increase.
CO2 (g) + H2 (g) H2O (g) + CO (g)
What will be the effect on the equilibrium by adding H2O to the equilibrium mixture?
A) The equilibrium will shift to the left.
B) H2 concentration will decrease and CO2 concentration will increase.
C) CO and CO2 concentrations will increase.
D) H2 concentration will decrease and H2O concentration will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
According to Le Chatelier's principle, which of the following changes will shift to the left the position of the equilibrium of the reaction
N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) 2 NH3 (g) + Heat
A) Increase the concentration of N2.
B) Decrease the pressure on the system.
C) Decrease the temperature.
D) Increase the concentration of H2.
N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) 2 NH3 (g) + Heat
A) Increase the concentration of N2.
B) Decrease the pressure on the system.
C) Decrease the temperature.
D) Increase the concentration of H2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In which of the following equilibrium systems will the equilibrium shift to the left when the pressure of the system is increased?
A) N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) 2 NH3 (g) + Heat
B) 4 NH3 (g) + 5 O2 (g) 4 NO (g) + 6 H2O (l)
C) 2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g) 2 SO3 (g)
D) H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) 2 HCl (g)
A) N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) 2 NH3 (g) + Heat
B) 4 NH3 (g) + 5 O2 (g) 4 NO (g) + 6 H2O (l)
C) 2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g) 2 SO3 (g)
D) H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) 2 HCl (g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In which of the following equilibrium reactions will a shift to the left occur from a decrease in pressure?
A) 2 HCl (g) H2 (g) + Cl2 (g)
B) 2 SO3 (g) 2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
C) N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) 2 NH3 (g)
D) N2O4 (g) 2 NO2 (g)
A) 2 HCl (g) H2 (g) + Cl2 (g)
B) 2 SO3 (g) 2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
C) N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) 2 NH3 (g)
D) N2O4 (g) 2 NO2 (g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
For a chemical reaction at equilibrium, which of the following would always decrease the concentrations of the products?
A) Increase the temperature.
B) Decrease the temperature.
C) Decrease the pressure.
D) Decrease the concentration of a reactant.
A) Increase the temperature.
B) Decrease the temperature.
C) Decrease the pressure.
D) Decrease the concentration of a reactant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The following reaction is endothermic: CaCO3 (s) CaO (s) + CO2 (g). Which of the following will cause the reaction to shift towards making more carbon dioxide gas?
A) increasing the temperature of the reaction
B) decreasing the temperature of the reaction
C) increasing the pressure of the system
D) increasing both the pressure and temperature of the system
A) increasing the temperature of the reaction
B) decreasing the temperature of the reaction
C) increasing the pressure of the system
D) increasing both the pressure and temperature of the system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Consider the following chemical system at equilibrium.
Heat + 6 H2O (g) + 2 N2 (g) 4 NH3 (g) + 3O2 (g)
Which of the following stresses would shift the equilibrium to the left?
A) increasing the concentration of O2
B) increasing the reaction temperature
C) increasing the concentration of H2O
D) decreasing the concentration of NH3
Heat + 6 H2O (g) + 2 N2 (g) 4 NH3 (g) + 3O2 (g)
Which of the following stresses would shift the equilibrium to the left?
A) increasing the concentration of O2
B) increasing the reaction temperature
C) increasing the concentration of H2O
D) decreasing the concentration of NH3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Consider the following system at equilibrium: N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) 2 NH3 (g) + 92. 94 kJ
Which of the following changes will shift the equilibrium to the right?
1) Increasing the temperature 2. Decreasing the temperature
3) Increasing the volume 4. Decreasing the volume
5) Removing some NH3 6. Adding some NH3
7) Removing some N2 8. Adding some N2
A) 1, 4, 6, 7
B) 2, 3, 5, 8
C) 1, 6, 8
D) 2, 4, 5, 8
Which of the following changes will shift the equilibrium to the right?
1) Increasing the temperature 2. Decreasing the temperature
3) Increasing the volume 4. Decreasing the volume
5) Removing some NH3 6. Adding some NH3
7) Removing some N2 8. Adding some N2
A) 1, 4, 6, 7
B) 2, 3, 5, 8
C) 1, 6, 8
D) 2, 4, 5, 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Coal burning plants release sulfur dioxide, a toxic gas, into the atmosphere. Nitrogen monoxide is released into the atmosphere via industrial processes and the combustion engine. Sulfur dioxide can also be produced in the atmosphere by the reaction of sulfur trioxide and nitrogen monoxide according to the following equilibrium.
SO3 (g) + NO (g) + heat SO2 (g) + NO2 (g)
Which of the following stresses will not shift the equilibrium to the right?
A) decrease the reaction chamber volume (pressure increase)
B) temperature increase
C) [NO2] decrease
D) [NO] increase
SO3 (g) + NO (g) + heat SO2 (g) + NO2 (g)
Which of the following stresses will not shift the equilibrium to the right?
A) decrease the reaction chamber volume (pressure increase)
B) temperature increase
C) [NO2] decrease
D) [NO] increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following conditions would force to completion the reaction?
2 N2 (g) + 6 H2O (g) + heat 4 NH3 (g) + 3 O2 (g)
A) continual removal of N2 gas
B) decrease the pressure on the reaction vessel
C) continual addition of NH3 gas to the reaction mixture
D) increase reaction temperature
2 N2 (g) + 6 H2O (g) + heat 4 NH3 (g) + 3 O2 (g)
A) continual removal of N2 gas
B) decrease the pressure on the reaction vessel
C) continual addition of NH3 gas to the reaction mixture
D) increase reaction temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
a) Draw an energy diagram for the following reaction, whose activation energy is 75 kJ/mol and whose overall energy for the reaction is exothermic. Be sure to label all parts of the graph.
b) How does a catalyst speed up a reaction? Explain and illustrate it on your graph.
H2 (g) + I2 (g) ? 2 HI (g) + heat
Draw an activation diagram and then show how a catalyst speeds up a reaction by lowering the activation energy of a reaction.
b) How does a catalyst speed up a reaction? Explain and illustrate it on your graph.
H2 (g) + I2 (g) ? 2 HI (g) + heat
Draw an activation diagram and then show how a catalyst speeds up a reaction by lowering the activation energy of a reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A 0.20 mole sample of C and a 0.10 mole sample of B are placed in a reaction chamber. At equilibrium, 0.080 mole of A is present. What is the composition of the equilibrium mixture in terms of moles of each substance present.
4 C (g) + B ⇌ 2 A (g)
4 C (g) + B ⇌ 2 A (g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The value of the equilibrium constant (K) for the reaction
N2O4 (g) ⇌ 2 NO2
is ________ if the concentrations of each species at equilibrium are [N2O4] = 0.300 and [NO2] = 0.0054. The value of (K) indicates that the ________ reaction is favored.
N2O4 (g) ⇌ 2 NO2
is ________ if the concentrations of each species at equilibrium are [N2O4] = 0.300 and [NO2] = 0.0054. The value of (K) indicates that the ________ reaction is favored.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Write the expression for the equilibrium constant for the following reaction.
CuO (s) + H2 (g) ⇌ Cu (s) + H2O (g)
CuO (s) + H2 (g) ⇌ Cu (s) + H2O (g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Write the expression for the equilibrium constant for the following reaction.
2 Na2O (s) ⇌ 4 Na (l) + O2 (g)
2 Na2O (s) ⇌ 4 Na (l) + O2 (g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
For the equilibrium shown below the equilibrium constant is 8.5 x 10-3. If 0.055 mol of IBr is placed in a 3.00 L container, what is the concentration of each substance after equilibrium is reached?
2 IBr (g) ? I2 (g) + Br2 (g)
2 IBr (g) ? I2 (g) + Br2 (g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



