Deck 10: Chemical Calculations Involving Chemical Equations
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/68
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Chemical Calculations Involving Chemical Equations
1
Indicate the missing words in the following statement: "For an ordinary chemical reaction the mass of the products is ________ the mass of the reactants."
A) always less than
B) usually more than
C) always equal to
D) usually less than
A) always less than
B) usually more than
C) always equal to
D) usually less than
always equal to
2
Which of the following elements is represented by a diatomic molecule in a chemical equation?
A) krypton
B) beryllium
C) chlorine
D) boron
A) krypton
B) beryllium
C) chlorine
D) boron
chlorine
3
In a valid chemical equation, ________.
A) the number of products must equal the number of reactants
B) the reactants always appear on the right-hand side of the equation
C) only reactants and products that are solids or liquids are listed
D) the total number of atoms on each side of the equation must be equal
A) the number of products must equal the number of reactants
B) the reactants always appear on the right-hand side of the equation
C) only reactants and products that are solids or liquids are listed
D) the total number of atoms on each side of the equation must be equal
the total number of atoms on each side of the equation must be equal
4
Which of the following equations is not balanced?
A) 2Mg + O2 2MgO
B) CaCO3 CaO + CO2
C) 2NO + O2 2NO2
D) 2NaHCO3 + H2SO4 Na2SO4 + 2H2O + CO2
A) 2Mg + O2 2MgO
B) CaCO3 CaO + CO2
C) 2NO + O2 2NO2
D) 2NaHCO3 + H2SO4 Na2SO4 + 2H2O + CO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following reactions is correctly balanced?
A) Zn + 2 HCl H2 + ZnCl2
B) 2 H2O + C CO + 2 H2
C) N2 + H2 2 NH3
D) CO + O2 CO2
A) Zn + 2 HCl H2 + ZnCl2
B) 2 H2O + C CO + 2 H2
C) N2 + H2 2 NH3
D) CO + O2 CO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Indicate which set of coefficients balances the equation:
_____ NH3 + _____ O2 _____ NO + _____ H2O
A) 3, 2, 1, 3
B) 6, 5, 4, 4
C) 2, 6, 3, 2
D) 4, 5, 4, 6
_____ NH3 + _____ O2 _____ NO + _____ H2O
A) 3, 2, 1, 3
B) 6, 5, 4, 4
C) 2, 6, 3, 2
D) 4, 5, 4, 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Balance the following equation. What is the sum of the coefficients?
_____ P4 + _____ S8 _____ P4S10
A) 12
B) 19
C) 14
D) 13
_____ P4 + _____ S8 _____ P4S10
A) 12
B) 19
C) 14
D) 13

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When the equation C8H18 + O2 CO2 + H2O is correctly balanced, the coefficient in front of O2 is ________.
A) 25
B) 12
C) 16
D) 18
A) 25
B) 12
C) 16
D) 18

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What is the coefficient for CO2 when the equation for the combustion of methanol is balanced?
_____ CH3OH + _____ O2 _____ CO2 + _____ H2O
A) 1.5
B) 4
C) 2
D) 6
_____ CH3OH + _____ O2 _____ CO2 + _____ H2O
A) 1.5
B) 4
C) 2
D) 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In the reaction below, which species is present in the solid state?
CaCO3 (s) + 2HNO3 (aq) Ca(NO3)2 (aq) + H2O (l)+ CO2 (g)
A) H2O
B) CO2
C) CaCO3
D) HNO3
CaCO3 (s) + 2HNO3 (aq) Ca(NO3)2 (aq) + H2O (l)+ CO2 (g)
A) H2O
B) CO2
C) CaCO3
D) HNO3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following reactions is a synthesis reaction?
A) SO3 + H2O H2SO4
B) C3H8 + 5 O2 3CO2 + 4H2O
C) 3CuSO4 + Al Al2(SO4)3 + 3Cu
D) 2NaHCO3 Na2CO3 + CO2 + H2O
A) SO3 + H2O H2SO4
B) C3H8 + 5 O2 3CO2 + 4H2O
C) 3CuSO4 + Al Al2(SO4)3 + 3Cu
D) 2NaHCO3 Na2CO3 + CO2 + H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following reactions is incorrectly classified?
A) 2 NO2 + H2O2 2 HNO3 (synthesis)
B) Fe + CuSO4 Cu + FeSO4 (single-replacement)
C) F2 + 2NaCl Cl2 + 2 NaF (single-replacement)
D) BaCl2 + H2SO4 BaSO4 + 2 HCl (single-replacement)
A) 2 NO2 + H2O2 2 HNO3 (synthesis)
B) Fe + CuSO4 Cu + FeSO4 (single-replacement)
C) F2 + 2NaCl Cl2 + 2 NaF (single-replacement)
D) BaCl2 + H2SO4 BaSO4 + 2 HCl (single-replacement)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following reactions below is a decomposition reaction?
A) C7H8O2 (l) + 8 O2 (g) 7 CO2 (g) + 4 H2O (l)
B) 2 KClO3 (s) 2 KCl (s) + 3 O2 (g)
C) 2 Cr (s) + 3 Cl2 (g) 2 CrCl3 (s)
D) 6 Li (s) + N2 (g) 2 Li3N (s)
A) C7H8O2 (l) + 8 O2 (g) 7 CO2 (g) + 4 H2O (l)
B) 2 KClO3 (s) 2 KCl (s) + 3 O2 (g)
C) 2 Cr (s) + 3 Cl2 (g) 2 CrCl3 (s)
D) 6 Li (s) + N2 (g) 2 Li3N (s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following reactions is incorrectly classified?
A) Mg (s) + 2 HCl (aq) MgCl2 (aq) + H2 (aq) single-replacement
B) Pb(NO3)2 (aq) + 2 LiCl (aq) 2 LiNO3 (aq) + PbCl2 (s) double-replacement
C) NO2 (g) + H2O (g) HNO3 (g) synthesis
D) PbO (s) + C (s) Pb (s) + CO (g) double-replacement
A) Mg (s) + 2 HCl (aq) MgCl2 (aq) + H2 (aq) single-replacement
B) Pb(NO3)2 (aq) + 2 LiCl (aq) 2 LiNO3 (aq) + PbCl2 (s) double-replacement
C) NO2 (g) + H2O (g) HNO3 (g) synthesis
D) PbO (s) + C (s) Pb (s) + CO (g) double-replacement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following reactions is incorrectly classified?
A) Zn + H2SO4 ZnSO4 + H2 single-replacement
B) 2 KClO3 2 KCl + 3 O2 decomposition
C) CH4 + 2 O2 CO2 + 2 H2O single-replacement
D) AgNO3 + KCl KNO3 + AgCl double-replacement
A) Zn + H2SO4 ZnSO4 + H2 single-replacement
B) 2 KClO3 2 KCl + 3 O2 decomposition
C) CH4 + 2 O2 CO2 + 2 H2O single-replacement
D) AgNO3 + KCl KNO3 + AgCl double-replacement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which one of the following conversion factors is not consistent with the equation?
4NH3 + 5 O2 4NO + 6H2O
A)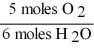
B)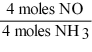
C)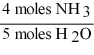
D)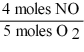
4NH3 + 5 O2 4NO + 6H2O
A)
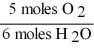
B)
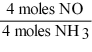
C)
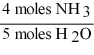
D)
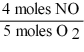

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Given: 2 N2 + 5 O2 2 N2O5
Which of the following is not a valid equality?
A) 5 mol O2 = 2 mol N2
B) 2 mol N2O5 = 2 mol N2
C) 2 mol N2 = 2 mol O2
D) 5 mol O2 = 2 mol N2O5
Which of the following is not a valid equality?
A) 5 mol O2 = 2 mol N2
B) 2 mol N2O5 = 2 mol N2
C) 2 mol N2 = 2 mol O2
D) 5 mol O2 = 2 mol N2O5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
How many moles of Al are needed to react exactly with 10.00 moles of Fe2O3 according to the following equation?
Fe2O3 + 2 Al Al2O3 + 2Fe
A) 15.0 moles
B) 20.0 moles
C) 30.0 moles
D) 60.0 moles
Fe2O3 + 2 Al Al2O3 + 2Fe
A) 15.0 moles
B) 20.0 moles
C) 30.0 moles
D) 60.0 moles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Given the following equation, 2 N2 + 5 O2 2 N2O5, 1.25 moles of nitrogen requires ________ moles of oxygen.
A) 0.500
B) 1.75
C) 3.13
D) 1.56
A) 0.500
B) 1.75
C) 3.13
D) 1.56

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
How many moles of CO2 will be produced from the complete combustion of 0.956 moles of C7H16 in the reaction below?
C7H16 + 11 O2 7 CO2 + 8 H2O
A) 0.667 mole
B) 3.50 moles
C) 1.85 moles
D) 6.69 moles
C7H16 + 11 O2 7 CO2 + 8 H2O
A) 0.667 mole
B) 3.50 moles
C) 1.85 moles
D) 6.69 moles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Given: 2 Na + O2 Na2O2
Calculate the moles of sodium peroxide (Na2O2) produced if 32.5 g of sodium reacts with excess oxygen.
A) 27.6 mol
B) 55.1 mol
C) 0.354 mol
D) 0.707 mol
Calculate the moles of sodium peroxide (Na2O2) produced if 32.5 g of sodium reacts with excess oxygen.
A) 27.6 mol
B) 55.1 mol
C) 0.354 mol
D) 0.707 mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is the correct "set-up" for the problem "How many grams of H2O will be produced from 3.2 moles of O2 and an excess of H2S?" according to the reaction:
2H2S + 3 O2 2H2O + 2SO2
A)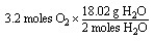
B)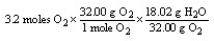
C)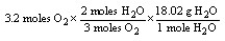
D)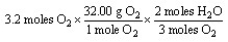
2H2S + 3 O2 2H2O + 2SO2
A)
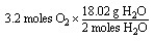
B)
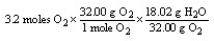
C)
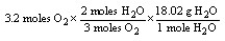
D)
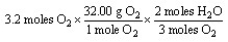

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The "set-up" below for the problem "How many grams of SO2 will be produced from 10.0 g of S8 and an excess of O2?" according to the reaction:
S8 + 8 O2 8 SO2
Is correct except the letters A and B have replaced the numbers in one of the conversion factors. What are the numerical values of A and B, respectively?
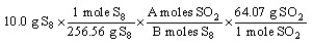
A) 8 and 8
B) 1 and 8
C) 8 and 1
D) 1 and 1
S8 + 8 O2 8 SO2
Is correct except the letters A and B have replaced the numbers in one of the conversion factors. What are the numerical values of A and B, respectively?
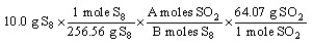
A) 8 and 8
B) 1 and 8
C) 8 and 1
D) 1 and 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In the following reaction, how many grams of H2O are produced if 3.65 g of N2H4 react?
N2H4 + 3 O2 2NO2 + 2H2O
A) 4.10 g
B) 11.2 g
C) 10.5 g
D) 1.47 g
N2H4 + 3 O2 2NO2 + 2H2O
A) 4.10 g
B) 11.2 g
C) 10.5 g
D) 1.47 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
For the reaction: 2 P + 3 Cl2 2 PCl3, if 32.5 g of Cl2 reacts completely with excess P, how many grams of PCl3 will be produced?
A) 42.0 g
B) 62.9 g
C) 83.9 g
D) 94.4 g
A) 42.0 g
B) 62.9 g
C) 83.9 g
D) 94.4 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In the reaction: 4HPO3 + 12C 2H2 + 12CO + P4, how many molecules of CO are produced when 5.00 moles of HPO3 react?
A) 4.11 x 1023 molecules
B) 1.64 x 1024 molecules
C) 9.03 x 1024 molecules
D) 1.97 x 1025 molecules
A) 4.11 x 1023 molecules
B) 1.64 x 1024 molecules
C) 9.03 x 1024 molecules
D) 1.97 x 1025 molecules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
How many moles of H2O will be produced if 6.80 x 1024 formula units of NH4NO3 are decomposed in the reaction given below?
NH4NO3 N2O + 2H2O
A) 0.876 mole
B) 3.30 moles
C) 5.40 moles
D) 22.6 moles
NH4NO3 N2O + 2H2O
A) 0.876 mole
B) 3.30 moles
C) 5.40 moles
D) 22.6 moles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Aspirin (C9H8O4) can be made in the laboratory by reacting salicylic acid (C7H6O3) with acetyl chloride (C2H3ClO).
C7H6O3 + C2H3ClO C9H8O4 + HCl
What mass of HCl is produced by the complete reaction of 36.0 g of acetyl chloride?
A) 108 g
B) 16.7 g
C) 58.1 g
D) 8.69 g
C7H6O3 + C2H3ClO C9H8O4 + HCl
What mass of HCl is produced by the complete reaction of 36.0 g of acetyl chloride?
A) 108 g
B) 16.7 g
C) 58.1 g
D) 8.69 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Propane (C3H8) burns in oxygen to form CO2 and H2O according to the following equation. How many grams of O2 are required to burn 3.01 x 1023 propane molecules?
C3H8 + 5 O2 3 CO2 + 4 H2O
A) 80.0 g
B) 40.0 g
C) 160. g
D) 64.0 g
C3H8 + 5 O2 3 CO2 + 4 H2O
A) 80.0 g
B) 40.0 g
C) 160. g
D) 64.0 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If a mixture containing 0.50 moles of N2 and 1.8 moles of H2 is allowed to react according to the equation
N2 + 3H2 2NH3
A) 17.0 grams of NH3 can be produced.
B) N2 is the limiting reactant.
C) H2 is the limiting reactant.
D) Both A and B are correct.
N2 + 3H2 2NH3
A) 17.0 grams of NH3 can be produced.
B) N2 is the limiting reactant.
C) H2 is the limiting reactant.
D) Both A and B are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If a mixture containing an unlimited amount of A, 3.00 moles of B and 5.0 moles of C is allowed to react according to the equation
2A + 2B + 4C 4D + 3E
A) A will be the limiting reactant.
B) B will be the limiting reactant.
C) C will be the limiting reactant.
D) Both A and C are the limiting reactants.
2A + 2B + 4C 4D + 3E
A) A will be the limiting reactant.
B) B will be the limiting reactant.
C) C will be the limiting reactant.
D) Both A and C are the limiting reactants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
How many moles of NO2 can be produced from 14.0 g of NO and 4.00 g of O2 according to the equation:
2 NO + O2 2NO2
A) 0.250 mole
B) 0.125 mole
C) 0.467 mole
D) 2.41 moles
2 NO + O2 2NO2
A) 0.250 mole
B) 0.125 mole
C) 0.467 mole
D) 2.41 moles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
15.0 g of Cu are combined with 46.0 g of HNO3 (molar mass = 63.02), according to the reaction:
3 Cu + 8 HNO3 3 Cu(NO3)2 + 2 NO + 4 H2
Which reactant is limiting, and how many grams of H2 is produced?
A) Cu, 3.79 g
B) Cu, 0.629 g
C) HNO3, 0.737 g
D) HNO3, 6.13 g
3 Cu + 8 HNO3 3 Cu(NO3)2 + 2 NO + 4 H2
Which reactant is limiting, and how many grams of H2 is produced?
A) Cu, 3.79 g
B) Cu, 0.629 g
C) HNO3, 0.737 g
D) HNO3, 6.13 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In making a banana split sundae, how many sundaes can be made from 3 dozen bananas, 2 gallons of ice cream and unlimited chocolate syrup using the "recipe" below? (1 gallon of ice cream = 25 scoops)
1 banana + 2 scoops of ice cream + 4 tsp chocolate syrup 1 banana split sundae
A) 36
B) 20
C) 25
D) 15
1 banana + 2 scoops of ice cream + 4 tsp chocolate syrup 1 banana split sundae
A) 36
B) 20
C) 25
D) 15

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The brown color of smog is due to the presence of nitrogen dioxide, NO2. Nitrogen monoxide (NO), a by-product of combustion of fossil fuels, reacts with oxygen to produce NO2 in the atmosphere:
2 NO + O2 2 NO2
If 0.65 mole of NO is reacted with 0.75 mole of O2 to produce NO2, the limiting reactant is ________.
A) both NO and O2
B) O2
C) NO
D) Insufficient information is given to determine which species is the limiting reactant.
2 NO + O2 2 NO2
If 0.65 mole of NO is reacted with 0.75 mole of O2 to produce NO2, the limiting reactant is ________.
A) both NO and O2
B) O2
C) NO
D) Insufficient information is given to determine which species is the limiting reactant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If a mixture containing 0.80 mole of A, 2.1 moles of B, and 1.6 moles of C is allowed to react according to the equation:
2 A + 4 B + 3 C 4 D + 2 E
A) A will be the limiting reactant.
B) B will be the limiting reactant.
C) Both A and B are the limiting reactants.
D) C will be the limiting reactant.
2 A + 4 B + 3 C 4 D + 2 E
A) A will be the limiting reactant.
B) B will be the limiting reactant.
C) Both A and B are the limiting reactants.
D) C will be the limiting reactant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If 30 slices of bread, 26 slices of cheese, and 38 slices of ham are available to make ham-cheese sandwiches according to the parameters given below, how many ham-cheese sandwiches can be prepared?
1 slice of ham + 2 slices of cheese + 2 slices of bread - 1 ham-cheese sandwich
A) 15
B) 16
C) 30
D) 13
1 slice of ham + 2 slices of cheese + 2 slices of bread - 1 ham-cheese sandwich
A) 15
B) 16
C) 30
D) 13

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Carbon monoxide is reacted with oxygen and converted to carbon dioxide by the catalytic converter on automobiles:
2 CO(g) + O2(g) 2 CO2(g)
Depicted below is a representation of a mixture of CO and O2 in a catalytic converter (at the molecular level). The gray spheres represent oxygen atoms and the black spheres represent carbon atoms. For the mixture shown below, which species is the limiting reactant?
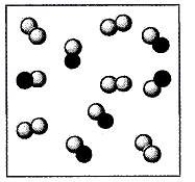
A) CO2
B) CO
C) O2
D) Insufficient information is given to determine.
2 CO(g) + O2(g) 2 CO2(g)
Depicted below is a representation of a mixture of CO and O2 in a catalytic converter (at the molecular level). The gray spheres represent oxygen atoms and the black spheres represent carbon atoms. For the mixture shown below, which species is the limiting reactant?

A) CO2
B) CO
C) O2
D) Insufficient information is given to determine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Tin metal is reacted with hydrochloric acid according to the following equation. 0.240 moles of Sn is reacted with 0.320 mol of HCl. Calculate the mass of hydrogen gas liberated by the reaction.
Sn + 2 HCl H2 + SnCl2
A) 0.323 g
B) 2.79 g
C) 0.485 g
D) 1.31 g
Sn + 2 HCl H2 + SnCl2
A) 0.323 g
B) 2.79 g
C) 0.485 g
D) 1.31 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In a certain experiment 24.9 g of NH4NO3 (molar mass = 80.06) was produced from 27.2 g of Fe(NO3)3 (molar mass = 241.87) reacting with an excess of NH3 and H2O according to the equation
Fe(NO3)3 + 3 NH3 + 3 H2O Fe(OH)3 + 3 NH4NO3
What is, respectively, the theoretical yield and percent yield of NH4NO3?
A) 5.53 g and 42.1%
B) 13.5 g and 83.7%
C) 16.6 g and 31.7%
D) 27.0 g and 92.2%
Fe(NO3)3 + 3 NH3 + 3 H2O Fe(OH)3 + 3 NH4NO3
What is, respectively, the theoretical yield and percent yield of NH4NO3?
A) 5.53 g and 42.1%
B) 13.5 g and 83.7%
C) 16.6 g and 31.7%
D) 27.0 g and 92.2%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In a certain experiment using Ca and an excess of F, 10.6 g of CaF2 is obtained. This represents a 76.4 percent yield. What is the theoretical yield of ZnS for this experiment?
A) 13.9 g
B) 12.6 g
C) 14.1 g
D) 15.7 g
A) 13.9 g
B) 12.6 g
C) 14.1 g
D) 15.7 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which statement concerning yields is correct?
A) Percent yield is the ratio of the actual yield to the theoretical yield times 100%.
B) Theoretical yield is the difference between the calculated yield and the actual yield.
C) Actual yield is the calculated amount of product that can be obtained from a given reaction.
D) In most chemical reactions, the amount of product isolated is larger than the theoretically possible amount.
A) Percent yield is the ratio of the actual yield to the theoretical yield times 100%.
B) Theoretical yield is the difference between the calculated yield and the actual yield.
C) Actual yield is the calculated amount of product that can be obtained from a given reaction.
D) In most chemical reactions, the amount of product isolated is larger than the theoretically possible amount.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
To make a hot fudge sundae, you need 2 scoops of ice cream and 30 mL of hot fudge syrup. What is the percent yield if you make 13 sundaes from 1 gallon of ice cream and 500 mL of hot fudge syrup? (1 gallon of ice cream = 30 scoops)
2 scoops ice cream + 30 mL hot fudge syrup- 1 hot fudge sundae
A) 13%
B) 78%
C) 87%
D) 115%
2 scoops ice cream + 30 mL hot fudge syrup- 1 hot fudge sundae
A) 13%
B) 78%
C) 87%
D) 115%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The astronauts of the Apollo 13 mission to the moon were almost lost in space due to the explosion of a valve on their primary oxygen generator. The lives of the astronauts were threatened by increasing concentrations of carbon dioxide in the spacecraft. Gaseous carbon dioxide(CO2) be absorbed from the air in a spacecraft with open canisters that contain solid lithium hydroxide according to the following equation:
2 LiOH (s) + CO2 (g) Li2CO3 (s) + H2O (l)
If a canister absorbed 225.0 grams of carbon dioxide from the air that resulted in the production of 66.30 grams of H2O, what was the percent yield for H2O?
A) 59.32%
B) 79.63%
C) 71.96%
D) 96.54%
2 LiOH (s) + CO2 (g) Li2CO3 (s) + H2O (l)
If a canister absorbed 225.0 grams of carbon dioxide from the air that resulted in the production of 66.30 grams of H2O, what was the percent yield for H2O?
A) 59.32%
B) 79.63%
C) 71.96%
D) 96.54%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In the atmosphere, the air pollutant nitrogen dioxide (NO2) reacts with water to produce nitric acid (HNO3), a component of acid rain. The reaction for the formation of nitric acid is:
3 NO2 (g) + H2O (l) 2 HNO3 (aq) + NO (g)
If 8.50 moles of nitrogen dioxide reacts with excess water, what is the actual yield (in grams) of NO if the percent yield is 89.4%?
A) 57.8 g
B) 136 g
C) 85.0 g
D) 76.0 g
3 NO2 (g) + H2O (l) 2 HNO3 (aq) + NO (g)
If 8.50 moles of nitrogen dioxide reacts with excess water, what is the actual yield (in grams) of NO if the percent yield is 89.4%?
A) 57.8 g
B) 136 g
C) 85.0 g
D) 76.0 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Aluminum is produced commercially by high-temperature electrolysis of aluminum oxide. When 1.500 x 103 g of Al2O3 is reacted with excess C, 601 g of Al is produced. Calculate the percent yield for the production of Al.
Al2O3(s) + 3 C(s) 2 Al(s) + 3 CO(g)
A) 94.7%
B) 75.7%
C) 54.3%
D) 82.1%
Al2O3(s) + 3 C(s) 2 Al(s) + 3 CO(g)
A) 94.7%
B) 75.7%
C) 54.3%
D) 82.1%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A mixture contains 0.75 moles of BaCO3 and 0.55 moles of Li2CO3. When this mixture is strongly heated both carbonates completely decompose to oxides and carbon dioxide as shown by the equations:
BaCO3 ? BaO + CO2
Li2CO3 Li2O + CO2
How many moles of CO2 are produced from the decomposition?
A) 1.30 moles
B) 1.60 moles
C) 0.75 mole
D) 0.65 mole
BaCO3 ? BaO + CO2
Li2CO3 Li2O + CO2
How many moles of CO2 are produced from the decomposition?
A) 1.30 moles
B) 1.60 moles
C) 0.75 mole
D) 0.65 mole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The following two-step process can be used to produce NO2:
N2 + O2 2NO
O3 + NO O2 + NO2
If 25.0 moles of NO2 were produced, how many moles of N2 were used to initiate the sequence of reactions?
A) 25.0 moles
B) 8.00 moles
C) 12.5 moles
D) 16.00 moles
N2 + O2 2NO
O3 + NO O2 + NO2
If 25.0 moles of NO2 were produced, how many moles of N2 were used to initiate the sequence of reactions?
A) 25.0 moles
B) 8.00 moles
C) 12.5 moles
D) 16.00 moles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A mixture contained 96.4 g of CaCO3 (molar mass of 100.09) and 68.3 g of MgCO3 (molar mass of 84.31). How many grams of CO2 (molar mass of 44.01) will be produced when the mixture is heated?
CaCO3(g) CaO(s) + CO2(g)
MgCO3(g) MgO(s) + CO2(g)
A) 32.1 g
B) 96.3 g
C) 78.0 g
D) 46.0 g
CaCO3(g) CaO(s) + CO2(g)
MgCO3(g) MgO(s) + CO2(g)
A) 32.1 g
B) 96.3 g
C) 78.0 g
D) 46.0 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The process for a piece of iron corroding to form rust, Fe2O3* H2O, is given in the two reactions below. How much rust will be formed if 25.0 g of Fe (molar mass = 55.84) completely corrodes to form Fe2O3 *H2O (molar mass = 177.70)?
4 Fe + 12 H+ + 3 O2 4 Fe3+ + 6 H2O
2 Fe3+ + 4 H2O Fe2O3 *H2O + 6 H+
A) 9.94 g
B) 15.9 g
C) 19.9 g
D) 39.8 g
4 Fe + 12 H+ + 3 O2 4 Fe3+ + 6 H2O
2 Fe3+ + 4 H2O Fe2O3 *H2O + 6 H+
A) 9.94 g
B) 15.9 g
C) 19.9 g
D) 39.8 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Balance the following equations:
-_____HPO3 + _____C → _____H2 + _____CO + _____P4
-_____HPO3 + _____C → _____H2 + _____CO + _____P4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Balance the following equations:
-_____V2O5 + _____Ca → _____CaO + _____V
-_____V2O5 + _____Ca → _____CaO + _____V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Balance the following equations:
-_____BaCl2 + ________H2SO4 → _____BaSO4 + _____HCl
-_____BaCl2 + ________H2SO4 → _____BaSO4 + _____HCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Balance the following equations:
-_____C2H6O + _____O2 → _____CO2 + _____H2O
-_____C2H6O + _____O2 → _____CO2 + _____H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Balance the following chemical equation using the simplest whole number ratio of coefficients.
____ I4O9 → ____ I2O5 + ____ I2 + ____ O2
____ I4O9 → ____ I2O5 + ____ I2 + ____ O2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Balance the following chemical equation using the simplest whole number ratio of coefficients.
____ C6H14 + ____ O2 → ____ H2O + ____ CO2
____ C6H14 + ____ O2 → ____ H2O + ____ CO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Identify the products of and then write a balanced chemical equation for the following reaction.
K2SO4(aq) + BaCl2(aq) → ? + ? (double-replacement reaction)
K2SO4(aq) + BaCl2(aq) → ? + ? (double-replacement reaction)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Identify the products of and then write a balanced chemical equation for the following reaction.
NaN3(s) → ? + ? (decomposition reaction)
NaN3(s) → ? + ? (decomposition reaction)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Verify the Law of Conservation of Mass using the molar masses of the compounds in the balanced equation given below.
Na2CO3 + 2 HCl → CO2 + H2O + 2 NaCl
Na2CO3 + 2 HCl → CO2 + H2O + 2 NaCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
How many grams of N2H4 are needed to produce 6.94 g of H2O using the reaction:
N2H4 + 2H2O2 → N2 + 4H2O
N2H4 + 2H2O2 → N2 + 4H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Consider the following reaction:
3 O2 (g) + 2 CH4 (g) + 2 NH3 (g) → 2 HCN (g) + 6 H2O (l)
How many grams of HCN will be formed upon the complete reaction of 55.8 g O2 with excess methane and ammonia?
3 O2 (g) + 2 CH4 (g) + 2 NH3 (g) → 2 HCN (g) + 6 H2O (l)
How many grams of HCN will be formed upon the complete reaction of 55.8 g O2 with excess methane and ammonia?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
How many grams of O2 (molar mass = 32.00) are produced at the same time that 2.68 moles of KCl are produced using the reaction:
2 KClO3 → 2 KCl + 3 O2
2 KClO3 → 2 KCl + 3 O2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Consider the reaction:
K2Cr2O7 + 6 KI + 7 H2SO4 → Cr2(SO4)3 + 4 K2SO4 + 3 I2 + 7 H2O
How many grams of KI will be needed to produce 75.0 grams of water?
K2Cr2O7 + 6 KI + 7 H2SO4 → Cr2(SO4)3 + 4 K2SO4 + 3 I2 + 7 H2O
How many grams of KI will be needed to produce 75.0 grams of water?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
How many grams of H2O (molar mass = 18.02) can be produced from 20.0 g of H2S (molar mass = 34.08) and 40.0 g of O2 (formula mass = 32.00) using the reaction:
2 H2S + 3 O2 → 2 SO2 + 2H2O
2 H2S + 3 O2 → 2 SO2 + 2H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The alcohol in "gasohol" burns according to the following equation:
C2H5OH (l) + 3 O2 (g) → 2 CO2 (g) + 3 H2O (l)
a) What is the theoretical yield of carbon dioxide when 12.5 g of ethanol, C2H5OH, reacts with 35.0 g of oxygen?
b) What is the percentage yield for this reaction if the actual yield is 20.5 g of CO2?
C2H5OH (l) + 3 O2 (g) → 2 CO2 (g) + 3 H2O (l)
a) What is the theoretical yield of carbon dioxide when 12.5 g of ethanol, C2H5OH, reacts with 35.0 g of oxygen?
b) What is the percentage yield for this reaction if the actual yield is 20.5 g of CO2?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In a certain experiment 25.0 g of NaCN (molar mass = 49.01) was produced from 40.0 g of N2 and an excess of other reactants using the reaction
Na2CO3 + 4 C + N2 → 2 NaCN + 3 CO
What is the percent yield of NaCN?
Na2CO3 + 4 C + N2 → 2 NaCN + 3 CO
What is the percent yield of NaCN?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Acrylonitrile (C3H3N) is the starting material in the production of synthetic fibers (acrylics). Acrylonitrile can be produced from the reaction between propylene (C3H6) and nitric oxide (NO).
4 C3H6 + 6 NO → 4 C3H3N + 6 H2O + N2
If 17.66 g of C3H3N is experimentally obtained from the reaction of 50.0 g of C3H6 and an excess of NO, calculate the theoretical yield and the percent yield for this reaction.
4 C3H6 + 6 NO → 4 C3H3N + 6 H2O + N2
If 17.66 g of C3H3N is experimentally obtained from the reaction of 50.0 g of C3H6 and an excess of NO, calculate the theoretical yield and the percent yield for this reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Burning of coal to produce electricity leads to the production of sulfuric acid (H2SO4), a component of acid rain, in the atmosphere in a three step process shown below.
S + O2 → SO2
2 SO2 + O2 → 2 SO3
SO3 + H2O → H2SO4
If 5.00 x 104 kg of sulfur undergoes complete reaction with excess oxygen and water, what mass of sulfuric acid (in grams) is produced in the atmosphere?
S + O2 → SO2
2 SO2 + O2 → 2 SO3
SO3 + H2O → H2SO4
If 5.00 x 104 kg of sulfur undergoes complete reaction with excess oxygen and water, what mass of sulfuric acid (in grams) is produced in the atmosphere?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



