Deck 13: Strategic Decision Making in Oligopoly Markets
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/54
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Strategic Decision Making in Oligopoly Markets
1
In Nash equilibrium,
A) both firms are maximizing their own profits given the level of advertising expected to be undertaken by the other firm.
B) firm A can increase its profit by unilaterally increasing its level of advertising.
C) firm B can increase its profit by unilaterally increasing its level of advertising.
D) both b and c.
E) all of the above.
A) both firms are maximizing their own profits given the level of advertising expected to be undertaken by the other firm.
B) firm A can increase its profit by unilaterally increasing its level of advertising.
C) firm B can increase its profit by unilaterally increasing its level of advertising.
D) both b and c.
E) all of the above.
both firms are maximizing their own profits given the level of advertising expected to be undertaken by the other firm.
2
using the following payoff table for Hardaway Corporation and Paxton Industries. These two firms must make simultaneous pricing decisions. They can choose low, medium, or high prices. The payoffs given are in thousands of dollars of profit per month.
?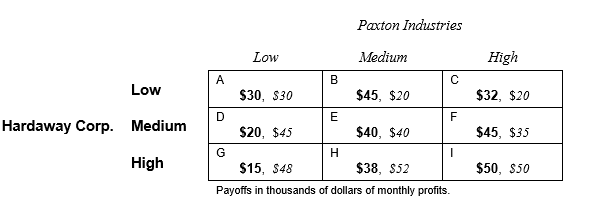
-Following the procedure of successive elimination of dominated strategies, the manager of Hardaway Corporation will eliminate in the first round the strategy of setting
A) a low price.
B) a medium price.
C) a high price.
D) None of the above; Hardaway does not have a dominated strategy.
?

-Following the procedure of successive elimination of dominated strategies, the manager of Hardaway Corporation will eliminate in the first round the strategy of setting
A) a low price.
B) a medium price.
C) a high price.
D) None of the above; Hardaway does not have a dominated strategy.
a medium price.
3
using the following payoff table for Hardaway Corporation and Paxton Industries. These two firms must make simultaneous pricing decisions. They can choose low, medium, or high prices. The payoffs given are in thousands of dollars of profit per month.
?
-Following the procedure of successive elimination of dominated strategies, the manager of Paxton Industries will eliminate in the first round the strategy of setting
A) a low price.
B) a medium price.
C) a high price.
D) None of the above; Paxton Industries does not have a dominated strategy.
?

-Following the procedure of successive elimination of dominated strategies, the manager of Paxton Industries will eliminate in the first round the strategy of setting
A) a low price.
B) a medium price.
C) a high price.
D) None of the above; Paxton Industries does not have a dominated strategy.
a high price.
4
If incumbent firm Dell threatens potential new entrant Rising Star with the threat, "If you enter this market, we will lower our price and keep it low until you are
A) Rising Star would never go ahead and enter if Dell has a cost advantage over Rising Star.
B) Rising Star's decision to enter will be unaffected by the threat if the threat is not credible.
C) Dell is making a strategic move designed to increase its profits at the expense of Rising Star.
D) both b and c.
E) all of the above
A) Rising Star would never go ahead and enter if Dell has a cost advantage over Rising Star.
B) Rising Star's decision to enter will be unaffected by the threat if the threat is not credible.
C) Dell is making a strategic move designed to increase its profits at the expense of Rising Star.
D) both b and c.
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In every prisoners' dilemma situation, cooperation
A) is possible.
B) reduces the payoff to at least one of the firms.
C) reduces the payoff to all players.
D) is likely.
E) both c and d.
A) is possible.
B) reduces the payoff to at least one of the firms.
C) reduces the payoff to all players.
D) is likely.
E) both c and d.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Price matching
A) is a strategic commitment.
B) is a flexible pledge to match any lower prices offered by rivals.
C) must be irreversible in order to have the desired effect.
D) both a and c.
E) both b and c
A) is a strategic commitment.
B) is a flexible pledge to match any lower prices offered by rivals.
C) must be irreversible in order to have the desired effect.
D) both a and c.
E) both b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The managers of Alpha and Beta must make repeated advertising decisions simultaneously at the beginning of every month. They choose either low or high levels of advertising expenditure. They both employ a discount rate of 2.5 percent per month. Use the payoff table shown below to answer the next five questions.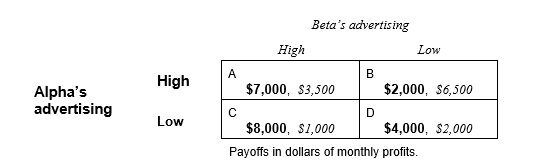
-If Beta decides not to cooperate, its undiscounted benefit from cheating for one month is
A) $1,500
B) $2,000
C) $3,000
D) $4,000
E) $5,000

-If Beta decides not to cooperate, its undiscounted benefit from cheating for one month is
A) $1,500
B) $2,000
C) $3,000
D) $4,000
E) $5,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The managers of Alpha and Beta must make repeated advertising decisions simultaneously at the beginning of every month. They choose either low or high levels of advertising expenditure. They both employ a discount rate of 2.5 percent per month. Use the payoff table shown below to answer the next five questions.
-Beta expects punishment to last for two months after being caught (i.e., to be penalized in months 2 and 3). What would be the value-maximizing decision for Beta?
A) Cooperate since $3,000 > PVBenefits of cheating.
B) Cooperate since $6,500/(1.025) > PVBenefits of cheating.
C) Cheat since PVBenefits of cheating. > $2,820.
D) Cheat since PVBenefits of cheating < $5,641.

-Beta expects punishment to last for two months after being caught (i.e., to be penalized in months 2 and 3). What would be the value-maximizing decision for Beta?
A) Cooperate since $3,000 > PVBenefits of cheating.
B) Cooperate since $6,500/(1.025) > PVBenefits of cheating.
C) Cheat since PVBenefits of cheating. > $2,820.
D) Cheat since PVBenefits of cheating < $5,641.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Fill in the blanks below:
-_______________ decisions occur when managers must make their decisions without knowing the decisions made by their rivals.
-_______________ decisions occur when managers must make their decisions without knowing the decisions made by their rivals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Fill in the blanks below:
-In a _______________ _______________ equilibrium, each and every rival has a single decision choice that is its best decision to make for whatever decision its rivals might make. This situation is also a _______________ equilibrium.
-In a _______________ _______________ equilibrium, each and every rival has a single decision choice that is its best decision to make for whatever decision its rivals might make. This situation is also a _______________ equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Fill in the blanks below:
-A _______________ _______________ is a simultaneous decision situation in which all rivals possess dominant strategies, but they are all worse off when they choose their dominant strategies than if they had cooperated to make some other decisions.
-A _______________ _______________ is a simultaneous decision situation in which all rivals possess dominant strategies, but they are all worse off when they choose their dominant strategies than if they had cooperated to make some other decisions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Fill in the blanks below:
-Strategically astute managers will search first for _______________ strategies, and if none of these can be discovered, they next look for _______________ strategies.
-Strategically astute managers will search first for _______________ strategies, and if none of these can be discovered, they next look for _______________ strategies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Fill in the blanks below:
-A Nash equilibrium is a set of decisions in which all firms are choosing their _______________ actions given the decisions they _______________ their rivals will make.
-A Nash equilibrium is a set of decisions in which all firms are choosing their _______________ actions given the decisions they _______________ their rivals will make.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Fill in the blanks below:
-When a set of decisions is such that no single firm can _______________ make a different decision and increase its own payoff, the set of decisions are strategically stable.
-When a set of decisions is such that no single firm can _______________ make a different decision and increase its own payoff, the set of decisions are strategically stable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Fill in the blanks below:
-Rivals ignore any strategic moves that are not _______________.
-Rivals ignore any strategic moves that are not _______________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Two firms, Allied Corporation and Union, Inc., compete primarily by price. Each firm must choose either a high price or a low price simultaneously. The following payoff table shows the profit each firm would earn in each of the four possible decision combinations:
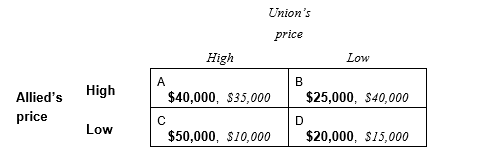
-Allied's dominant strategy is ____________ (low price, high price, it has no dominant strategy).

-Allied's dominant strategy is ____________ (low price, high price, it has no dominant strategy).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Two firms, Allied Corporation and Union, Inc., compete primarily by price. Each firm must choose either a high price or a low price simultaneously. The following payoff table shows the profit each firm would earn in each of the four possible decision combinations:

-Union's dominant strategy is ____________ (low price, high price, it has no dominant strategy).

-Union's dominant strategy is ____________ (low price, high price, it has no dominant strategy).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Two firms, Allied Corporation and Union, Inc., compete primarily by price. Each firm must choose either a high price or a low price simultaneously. The following payoff table shows the profit each firm would earn in each of the four possible decision combinations:

-Allied's dominated strategy is ____________ (low price, high price, it has no dominated strategy).

-Allied's dominated strategy is ____________ (low price, high price, it has no dominated strategy).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Two firms, Allied Corporation and Union, Inc., compete primarily by price. Each firm must choose either a high price or a low price simultaneously. The following payoff table shows the profit each firm would earn in each of the four possible decision combinations:

-Union's dominated strategy is ____________ (low price, high price, it has no dominated strategy).

-Union's dominated strategy is ____________ (low price, high price, it has no dominated strategy).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Two firms, Allied Corporation and Union, Inc., compete primarily by price. Each firm must choose either a high price or a low price simultaneously. The following payoff table shows the profit each firm would earn in each of the four possible decision combinations:

-The likely outcome of this simultaneous pricing decision is for Allied to price _________ (low, high) and for Union to price _________ (low, high).

-The likely outcome of this simultaneous pricing decision is for Allied to price _________ (low, high) and for Union to price _________ (low, high).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Two firms, Allied Corporation and Union, Inc., compete primarily by price. Each firm must choose either a high price or a low price simultaneously. The following payoff table shows the profit each firm would earn in each of the four possible decision combinations:

-The decision situation facing Allied and Union ______ (is, is not) a prisoners' dilemma.

-The decision situation facing Allied and Union ______ (is, is not) a prisoners' dilemma.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Find the solution to the following advertising decision game between Colt Enterprises and Remington, Inc. by using the method of successive elimination of dominated strategies.
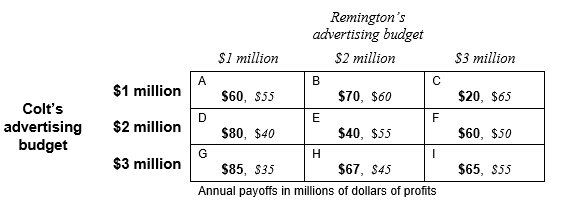
-In the first round of elimination, Colt can eliminate the ad budget level _________ ($1 million, $2 million, $3 million).

-In the first round of elimination, Colt can eliminate the ad budget level _________ ($1 million, $2 million, $3 million).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Find the solution to the following advertising decision game between Colt Enterprises and Remington, Inc. by using the method of successive elimination of dominated strategies.

-In the first round of elimination, Remington can eliminate the ad budget level _________ ($1 million, $2 million, $3 million).

-In the first round of elimination, Remington can eliminate the ad budget level _________ ($1 million, $2 million, $3 million).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Find the solution to the following advertising decision game between Colt Enterprises and Remington, Inc. by using the method of successive elimination of dominated strategies.

-After the first round of elimination, only _________________ (Colt, Remington) has another dominated strategy, which is _________ ($1 million, $2 million, $3 million).

-After the first round of elimination, only _________________ (Colt, Remington) has another dominated strategy, which is _________ ($1 million, $2 million, $3 million).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Find the solution to the following advertising decision game between Colt Enterprises and Remington, Inc. by using the method of successive elimination of dominated strategies.

-The likely outcome of this simultaneous advertising decision is for Colt to spend _________ ($1 million, $2 million, $3 million) on advertising and for Remington to spend _________ ($1 million, $2 million, $3 million) on advertising.

-The likely outcome of this simultaneous advertising decision is for Colt to spend _________ ($1 million, $2 million, $3 million) on advertising and for Remington to spend _________ ($1 million, $2 million, $3 million) on advertising.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Find the solution to the following advertising decision game between Colt Enterprises and Remington, Inc. by using the method of successive elimination of dominated strategies.

-The solution in part d __________ (is, is not) a Nash equilibrium. The solution in part d __________ (is, is not) strategically stable.

-The solution in part d __________ (is, is not) a Nash equilibrium. The solution in part d __________ (is, is not) strategically stable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Managers of two competing oligopoly firms, Amazon and Nile, must make their pricing decisions simultaneously. Amazon (A) and Nile (N) face the following demand and long-run cost conditions, which are common knowledge to the managers: 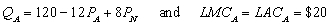
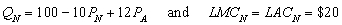 The prices,
The prices, 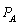 and
and 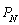 , are the prices charged by Amazon and Nile, respectively. The quantities,
, are the prices charged by Amazon and Nile, respectively. The quantities, 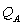 and
and 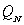 , are the respective daily quantities sold by each firm. The figure below shows Nile's best-response curve,
, are the respective daily quantities sold by each firm. The figure below shows Nile's best-response curve, 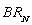 . Only one point on Amazon's best-response curve, point K, is shown in the figure.
. Only one point on Amazon's best-response curve, point K, is shown in the figure.
-When Amazon believes Nile is going to charge a price of $30, Amazon's best response is to charge a price of $________. Plot this price pair on the graph, label it J, and then draw the best-response curve for Amazon (label this line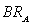 ).
).
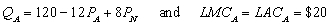
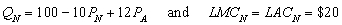 The prices,
The prices, 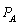 and
and 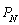 , are the prices charged by Amazon and Nile, respectively. The quantities,
, are the prices charged by Amazon and Nile, respectively. The quantities, 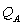 and
and 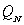 , are the respective daily quantities sold by each firm. The figure below shows Nile's best-response curve,
, are the respective daily quantities sold by each firm. The figure below shows Nile's best-response curve, 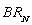 . Only one point on Amazon's best-response curve, point K, is shown in the figure.
. Only one point on Amazon's best-response curve, point K, is shown in the figure.-When Amazon believes Nile is going to charge a price of $30, Amazon's best response is to charge a price of $________. Plot this price pair on the graph, label it J, and then draw the best-response curve for Amazon (label this line
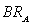 ).
).
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Managers of two competing oligopoly firms, Amazon and Nile, must make their pricing decisions simultaneously. Amazon (A) and Nile (N) face the following demand and long-run cost conditions, which are common knowledge to the managers: 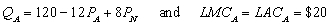
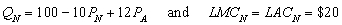 The prices,
The prices, 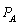 and
and 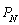 , are the prices charged by Amazon and Nile, respectively. The quantities,
, are the prices charged by Amazon and Nile, respectively. The quantities, 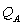 and
and 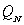 , are the respective daily quantities sold by each firm. The figure below shows Nile's best-response curve,
, are the respective daily quantities sold by each firm. The figure below shows Nile's best-response curve, 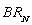 . Only one point on Amazon's best-response curve, point K, is shown in the figure.
. Only one point on Amazon's best-response curve, point K, is shown in the figure.
-Given the best-response curves for Amazon and Nile, you would predict that Amazon will choose a price of $__________ and Nile will choose a price of $__________. Label this point N in the figure below.
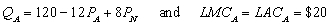
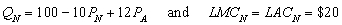 The prices,
The prices, 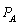 and
and 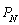 , are the prices charged by Amazon and Nile, respectively. The quantities,
, are the prices charged by Amazon and Nile, respectively. The quantities, 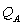 and
and 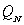 , are the respective daily quantities sold by each firm. The figure below shows Nile's best-response curve,
, are the respective daily quantities sold by each firm. The figure below shows Nile's best-response curve, 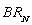 . Only one point on Amazon's best-response curve, point K, is shown in the figure.
. Only one point on Amazon's best-response curve, point K, is shown in the figure.-Given the best-response curves for Amazon and Nile, you would predict that Amazon will choose a price of $__________ and Nile will choose a price of $__________. Label this point N in the figure below.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Managers of two competing oligopoly firms, Amazon and Nile, must make their pricing decisions simultaneously. Amazon (A) and Nile (N) face the following demand and long-run cost conditions, which are common knowledge to the managers: 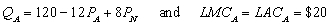
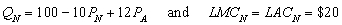 The prices,
The prices, 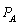 and
and 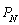 , are the prices charged by Amazon and Nile, respectively. The quantities,
, are the prices charged by Amazon and Nile, respectively. The quantities, 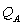 and
and 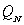 , are the respective daily quantities sold by each firm. The figure below shows Nile's best-response curve,
, are the respective daily quantities sold by each firm. The figure below shows Nile's best-response curve, 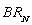 . Only one point on Amazon's best-response curve, point K, is shown in the figure.
. Only one point on Amazon's best-response curve, point K, is shown in the figure.
-At the prices associated point N (see part b), Amazon can expect to earn daily profit of $____________ and Nile can expect to earn daily profit of $____________.
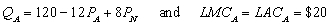
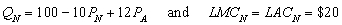 The prices,
The prices, 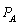 and
and 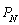 , are the prices charged by Amazon and Nile, respectively. The quantities,
, are the prices charged by Amazon and Nile, respectively. The quantities, 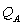 and
and 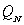 , are the respective daily quantities sold by each firm. The figure below shows Nile's best-response curve,
, are the respective daily quantities sold by each firm. The figure below shows Nile's best-response curve, 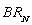 . Only one point on Amazon's best-response curve, point K, is shown in the figure.
. Only one point on Amazon's best-response curve, point K, is shown in the figure.-At the prices associated point N (see part b), Amazon can expect to earn daily profit of $____________ and Nile can expect to earn daily profit of $____________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Managers of two competing oligopoly firms, Amazon and Nile, must make their pricing decisions simultaneously. Amazon (A) and Nile (N) face the following demand and long-run cost conditions, which are common knowledge to the managers: 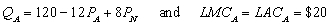
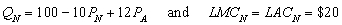 The prices,
The prices, 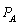 and
and 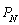 , are the prices charged by Amazon and Nile, respectively. The quantities,
, are the prices charged by Amazon and Nile, respectively. The quantities, 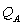 and
and 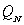 , are the respective daily quantities sold by each firm. The figure below shows Nile's best-response curve,
, are the respective daily quantities sold by each firm. The figure below shows Nile's best-response curve, 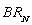 . Only one point on Amazon's best-response curve, point K, is shown in the figure.
. Only one point on Amazon's best-response curve, point K, is shown in the figure.
-At point C in the figure, Amazon plans to price at $30 and Nile at $40. At point C, Amazon earns daily profit of $____________, which is ________ (more, less) than it would earn at point N.
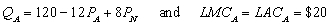
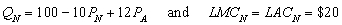 The prices,
The prices, 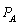 and
and 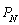 , are the prices charged by Amazon and Nile, respectively. The quantities,
, are the prices charged by Amazon and Nile, respectively. The quantities, 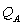 and
and 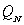 , are the respective daily quantities sold by each firm. The figure below shows Nile's best-response curve,
, are the respective daily quantities sold by each firm. The figure below shows Nile's best-response curve, 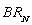 . Only one point on Amazon's best-response curve, point K, is shown in the figure.
. Only one point on Amazon's best-response curve, point K, is shown in the figure.-At point C in the figure, Amazon plans to price at $30 and Nile at $40. At point C, Amazon earns daily profit of $____________, which is ________ (more, less) than it would earn at point N.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Managers of two competing oligopoly firms, Amazon and Nile, must make their pricing decisions simultaneously. Amazon (A) and Nile (N) face the following demand and long-run cost conditions, which are common knowledge to the managers: 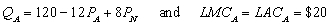
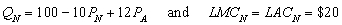 The prices,
The prices, 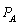 and
and 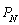 , are the prices charged by Amazon and Nile, respectively. The quantities,
, are the prices charged by Amazon and Nile, respectively. The quantities, 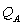 and
and 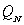 , are the respective daily quantities sold by each firm. The figure below shows Nile's best-response curve,
, are the respective daily quantities sold by each firm. The figure below shows Nile's best-response curve, 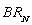 . Only one point on Amazon's best-response curve, point K, is shown in the figure.
. Only one point on Amazon's best-response curve, point K, is shown in the figure.
-At point C in the figure, Nile earns daily profit of $____________, which is ________ (more, less) than it would earn at point N.
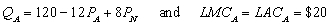
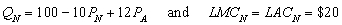 The prices,
The prices, 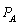 and
and 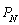 , are the prices charged by Amazon and Nile, respectively. The quantities,
, are the prices charged by Amazon and Nile, respectively. The quantities, 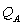 and
and 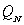 , are the respective daily quantities sold by each firm. The figure below shows Nile's best-response curve,
, are the respective daily quantities sold by each firm. The figure below shows Nile's best-response curve, 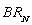 . Only one point on Amazon's best-response curve, point K, is shown in the figure.
. Only one point on Amazon's best-response curve, point K, is shown in the figure.-At point C in the figure, Nile earns daily profit of $____________, which is ________ (more, less) than it would earn at point N.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Managers of two competing oligopoly firms, Amazon and Nile, must make their pricing decisions simultaneously. Amazon (A) and Nile (N) face the following demand and long-run cost conditions, which are common knowledge to the managers: 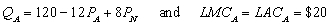
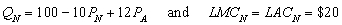 The prices,
The prices, 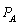 and
and 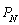 , are the prices charged by Amazon and Nile, respectively. The quantities,
, are the prices charged by Amazon and Nile, respectively. The quantities, 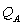 and
and 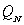 , are the respective daily quantities sold by each firm. The figure below shows Nile's best-response curve,
, are the respective daily quantities sold by each firm. The figure below shows Nile's best-response curve, 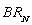 . Only one point on Amazon's best-response curve, point K, is shown in the figure.
. Only one point on Amazon's best-response curve, point K, is shown in the figure.
-Point C is not likely to be the decision outcome because it is not _______________ _____________, and either firm could unilaterally ___________ (increase, decrease) its price and earn greater daily profit.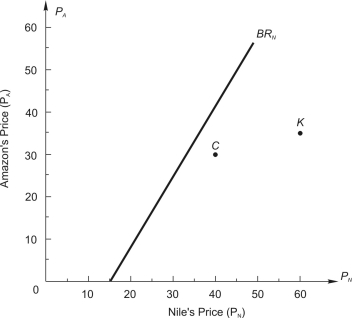
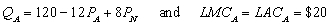
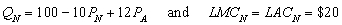 The prices,
The prices, 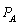 and
and 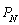 , are the prices charged by Amazon and Nile, respectively. The quantities,
, are the prices charged by Amazon and Nile, respectively. The quantities, 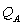 and
and 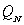 , are the respective daily quantities sold by each firm. The figure below shows Nile's best-response curve,
, are the respective daily quantities sold by each firm. The figure below shows Nile's best-response curve, 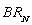 . Only one point on Amazon's best-response curve, point K, is shown in the figure.
. Only one point on Amazon's best-response curve, point K, is shown in the figure.-Point C is not likely to be the decision outcome because it is not _______________ _____________, and either firm could unilaterally ___________ (increase, decrease) its price and earn greater daily profit.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Sony and Zenith must each decide which technology to utilize in building their 2002 model high definition television (HDTV) sets: either Alpha technology or Beta technology. Sony has a technological advantage in using Alpha technology and Zenith has a technological advantage in using Beta technology. The payoff table below shows the profit outcomes for both firms in the various possible technology choice outcomes:
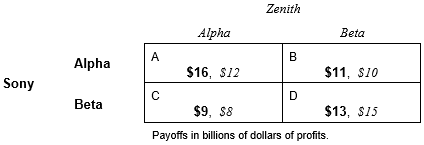
Suppose the technology decision between Alpha and Beta will be made simultaneously. Answer the following questions:
-Sony's dominant strategy is _______________(Alpha, Beta, neither: it has no dominant strategy).

Suppose the technology decision between Alpha and Beta will be made simultaneously. Answer the following questions:
-Sony's dominant strategy is _______________(Alpha, Beta, neither: it has no dominant strategy).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Sony and Zenith must each decide which technology to utilize in building their 2002 model high definition television (HDTV) sets: either Alpha technology or Beta technology. Sony has a technological advantage in using Alpha technology and Zenith has a technological advantage in using Beta technology. The payoff table below shows the profit outcomes for both firms in the various possible technology choice outcomes:

Suppose the technology decision between Alpha and Beta will be made simultaneously. Answer the following questions:
-Zenith's dominant strategy is _______________(Alpha, Beta, neither: it has no dominant strategy).

Suppose the technology decision between Alpha and Beta will be made simultaneously. Answer the following questions:
-Zenith's dominant strategy is _______________(Alpha, Beta, neither: it has no dominant strategy).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Sony and Zenith must each decide which technology to utilize in building their 2002 model high definition television (HDTV) sets: either Alpha technology or Beta technology. Sony has a technological advantage in using Alpha technology and Zenith has a technological advantage in using Beta technology. The payoff table below shows the profit outcomes for both firms in the various possible technology choice outcomes:

Suppose the technology decision between Alpha and Beta will be made simultaneously. Answer the following questions:
-List the Nash equilibrium cells for this simultaneous decision: ____________ .
Now suppose that Sony decides to make a strategic commitment to one of the technologies so that it can make the first move in a sequential decision game.

Suppose the technology decision between Alpha and Beta will be made simultaneously. Answer the following questions:
-List the Nash equilibrium cells for this simultaneous decision: ____________ .
Now suppose that Sony decides to make a strategic commitment to one of the technologies so that it can make the first move in a sequential decision game.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Sony and Zenith must each decide which technology to utilize in building their 2002 model high definition television (HDTV) sets: either Alpha technology or Beta technology. Sony has a technological advantage in using Alpha technology and Zenith has a technological advantage in using Beta technology. The payoff table below shows the profit outcomes for both firms in the various possible technology choice outcomes:

Suppose the technology decision between Alpha and Beta will be made simultaneously. Answer the following questions:
-Construct the game tree for the sequential game in which Sony moves first by filling in the blanks using the information in the above payoff table:
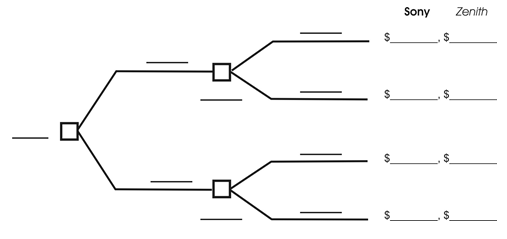

Suppose the technology decision between Alpha and Beta will be made simultaneously. Answer the following questions:
-Construct the game tree for the sequential game in which Sony moves first by filling in the blanks using the information in the above payoff table:


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Sony and Zenith must each decide which technology to utilize in building their 2002 model high definition television (HDTV) sets: either Alpha technology or Beta technology. Sony has a technological advantage in using Alpha technology and Zenith has a technological advantage in using Beta technology. The payoff table below shows the profit outcomes for both firms in the various possible technology choice outcomes:

Suppose the technology decision between Alpha and Beta will be made simultaneously. Answer the following questions:
-For the sequential game in part d, use the roll back method to find the Nash equilibrium decision path. Circle this decision path on the game tree above. Sony earns profit of $___________ and Zenith earns profit of $_________.
Suppose instead that Zenith decides to make a strategic commitment to one of the technologies so that it can make the first move in a sequential decision game.

Suppose the technology decision between Alpha and Beta will be made simultaneously. Answer the following questions:
-For the sequential game in part d, use the roll back method to find the Nash equilibrium decision path. Circle this decision path on the game tree above. Sony earns profit of $___________ and Zenith earns profit of $_________.
Suppose instead that Zenith decides to make a strategic commitment to one of the technologies so that it can make the first move in a sequential decision game.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Sony and Zenith must each decide which technology to utilize in building their 2002 model high definition television (HDTV) sets: either Alpha technology or Beta technology. Sony has a technological advantage in using Alpha technology and Zenith has a technological advantage in using Beta technology. The payoff table below shows the profit outcomes for both firms in the various possible technology choice outcomes:

Suppose the technology decision between Alpha and Beta will be made simultaneously. Answer the following questions:
-Construct the game tree below for the sequential game in which Zenith moves first by filling in the blanks using the information in the payoff table.
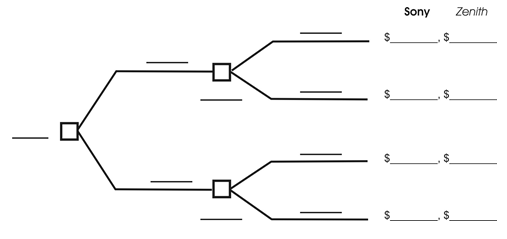

Suppose the technology decision between Alpha and Beta will be made simultaneously. Answer the following questions:
-Construct the game tree below for the sequential game in which Zenith moves first by filling in the blanks using the information in the payoff table.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Sony and Zenith must each decide which technology to utilize in building their 2002 model high definition television (HDTV) sets: either Alpha technology or Beta technology. Sony has a technological advantage in using Alpha technology and Zenith has a technological advantage in using Beta technology. The payoff table below shows the profit outcomes for both firms in the various possible technology choice outcomes:

Suppose the technology decision between Alpha and Beta will be made simultaneously. Answer the following questions:
-For the sequential game in part f, use the roll back method to find the Nash equilibrium decision path. Circle this decision path on the game tree above. Sony earns profit of $___________ and Zenith earns profit of $_________.

Suppose the technology decision between Alpha and Beta will be made simultaneously. Answer the following questions:
-For the sequential game in part f, use the roll back method to find the Nash equilibrium decision path. Circle this decision path on the game tree above. Sony earns profit of $___________ and Zenith earns profit of $_________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Sony and Zenith must each decide which technology to utilize in building their 2002 model high definition television (HDTV) sets: either Alpha technology or Beta technology. Sony has a technological advantage in using Alpha technology and Zenith has a technological advantage in using Beta technology. The payoff table below shows the profit outcomes for both firms in the various possible technology choice outcomes:

Suppose the technology decision between Alpha and Beta will be made simultaneously. Answer the following questions:
-__________(Sony, Zenith, neither firm) has a first-mover advantage?

Suppose the technology decision between Alpha and Beta will be made simultaneously. Answer the following questions:
-__________(Sony, Zenith, neither firm) has a first-mover advantage?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Sony and Zenith must each decide which technology to utilize in building their 2002 model high definition television (HDTV) sets: either Alpha technology or Beta technology. Sony has a technological advantage in using Alpha technology and Zenith has a technological advantage in using Beta technology. The payoff table below shows the profit outcomes for both firms in the various possible technology choice outcomes:

Suppose the technology decision between Alpha and Beta will be made simultaneously. Answer the following questions:
-__________(Sony, Zenith, neither firm) has a second-mover advantage?

Suppose the technology decision between Alpha and Beta will be made simultaneously. Answer the following questions:
-__________(Sony, Zenith, neither firm) has a second-mover advantage?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Burger King and Mac Donald's are situated on opposite corners of a downtown intersection. Burger King and Mac Donald's compete on the basis of the prices they set for their burger, fry, and soda combination meals. Every Monday, Burger King and Mac Donald's simultaneously choose their combo meal prices, which will remain in effect for the rest of the week.
Burger King and MacDonald's consider only two possible prices: a low price of $3.50 or a high price of $4.50 for their combination meals. The weekly profit from each of the four possible combinations of decisions are given in the following table:
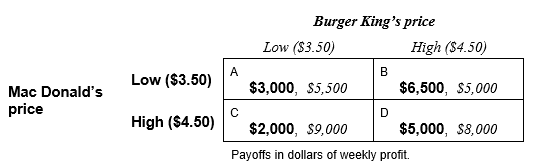
-The pricing decision facing Burger King and Mac Donald's __________ (is, is not) a prisoners' dilemma.
Burger King and MacDonald's consider only two possible prices: a low price of $3.50 or a high price of $4.50 for their combination meals. The weekly profit from each of the four possible combinations of decisions are given in the following table:

-The pricing decision facing Burger King and Mac Donald's __________ (is, is not) a prisoners' dilemma.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Burger King and Mac Donald's are situated on opposite corners of a downtown intersection. Burger King and Mac Donald's compete on the basis of the prices they set for their burger, fry, and soda combination meals. Every Monday, Burger King and Mac Donald's simultaneously choose their combo meal prices, which will remain in effect for the rest of the week.
Burger King and MacDonald's consider only two possible prices: a low price of $3.50 or a high price of $4.50 for their combination meals. The weekly profit from each of the four possible combinations of decisions are given in the following table:

-Cooperation between Burger King and Mac Donald's occurs in cell ____ of the payoff table. The noncooperative outcome occurs in cell ______.
Burger King and MacDonald's consider only two possible prices: a low price of $3.50 or a high price of $4.50 for their combination meals. The weekly profit from each of the four possible combinations of decisions are given in the following table:

-Cooperation between Burger King and Mac Donald's occurs in cell ____ of the payoff table. The noncooperative outcome occurs in cell ______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Burger King and Mac Donald's are situated on opposite corners of a downtown intersection. Burger King and Mac Donald's compete on the basis of the prices they set for their burger, fry, and soda combination meals. Every Monday, Burger King and Mac Donald's simultaneously choose their combo meal prices, which will remain in effect for the rest of the week.
Burger King and MacDonald's consider only two possible prices: a low price of $3.50 or a high price of $4.50 for their combination meals. The weekly profit from each of the four possible combinations of decisions are given in the following table:

-Cell _____ represents cheating by Burger King, while cell _____ represents cheating by MacDonald's.
Burger King and MacDonald's consider only two possible prices: a low price of $3.50 or a high price of $4.50 for their combination meals. The weekly profit from each of the four possible combinations of decisions are given in the following table:

-Cell _____ represents cheating by Burger King, while cell _____ represents cheating by MacDonald's.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Burger King and Mac Donald's are situated on opposite corners of a downtown intersection. Burger King and Mac Donald's compete on the basis of the prices they set for their burger, fry, and soda combination meals. Every Monday, Burger King and Mac Donald's simultaneously choose their combo meal prices, which will remain in effect for the rest of the week.
Burger King and MacDonald's consider only two possible prices: a low price of $3.50 or a high price of $4.50 for their combination meals. The weekly profit from each of the four possible combinations of decisions are given in the following table:

-If Burger King and Mac Donald's make their pricing decision just one time, they will likely end up in cell _______.
Burger King and MacDonald's consider only two possible prices: a low price of $3.50 or a high price of $4.50 for their combination meals. The weekly profit from each of the four possible combinations of decisions are given in the following table:

-If Burger King and Mac Donald's make their pricing decision just one time, they will likely end up in cell _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Burger King and Mac Donald's are situated on opposite corners of a downtown intersection. Burger King and Mac Donald's compete on the basis of the prices they set for their burger, fry, and soda combination meals. Every Monday, Burger King and Mac Donald's simultaneously choose their combo meal prices, which will remain in effect for the rest of the week.
Burger King and MacDonald's consider only two possible prices: a low price of $3.50 or a high price of $4.50 for their combination meals. The weekly profit from each of the four possible combinations of decisions are given in the following table:

-Burger King _____________ (can, cannot) credibly threaten to punish MacDonald's with a retaliatory price cut.
Burger King and MacDonald's consider only two possible prices: a low price of $3.50 or a high price of $4.50 for their combination meals. The weekly profit from each of the four possible combinations of decisions are given in the following table:

-Burger King _____________ (can, cannot) credibly threaten to punish MacDonald's with a retaliatory price cut.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Burger King and Mac Donald's are situated on opposite corners of a downtown intersection. Burger King and Mac Donald's compete on the basis of the prices they set for their burger, fry, and soda combination meals. Every Monday, Burger King and Mac Donald's simultaneously choose their combo meal prices, which will remain in effect for the rest of the week.
Burger King and MacDonald's consider only two possible prices: a low price of $3.50 or a high price of $4.50 for their combination meals. The weekly profit from each of the four possible combinations of decisions are given in the following table:

-MacDonald's _____________ (can, cannot) credibly threaten to punish Burger King with a retaliatory price cut.
Burger King and MacDonald's consider only two possible prices: a low price of $3.50 or a high price of $4.50 for their combination meals. The weekly profit from each of the four possible combinations of decisions are given in the following table:

-MacDonald's _____________ (can, cannot) credibly threaten to punish Burger King with a retaliatory price cut.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Burger King and Mac Donald's repeat their simultaneous pricing decisions every Monday and have been cooperating for many weeks. Now, however, MacDonald's is considering whether to cheat or to continue cooperating. Mac's manager believes that it can only get away with cheating for two weeks before Burger King's manager will decide to retaliate with a price cut of its own. The ensuing price war is expected to last for two weeks and then the two restaurants typically return to period of cooperation again. MacDonald's manager employs a discount rate of 0.25 percent per week for the purpose of computing present values.
-The weekly (undiscounted) gain to MacDonald's from cheating is $ ____________. The present value of the benefits to MacDonald's from cheating is $ ____________.
-The weekly (undiscounted) gain to MacDonald's from cheating is $ ____________. The present value of the benefits to MacDonald's from cheating is $ ____________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Burger King and Mac Donald's repeat their simultaneous pricing decisions every Monday and have been cooperating for many weeks. Now, however, MacDonald's is considering whether to cheat or to continue cooperating. Mac's manager believes that it can only get away with cheating for two weeks before Burger King's manager will decide to retaliate with a price cut of its own. The ensuing price war is expected to last for two weeks and then the two restaurants typically return to period of cooperation again. MacDonald's manager employs a discount rate of 0.25 percent per week for the purpose of computing present values.
-The weekly (undiscounted) cost to MacDonald's from cheating is $ ____________. The present value of the costs to MacDonald's from cheating is $ ____________.
-The weekly (undiscounted) cost to MacDonald's from cheating is $ ____________. The present value of the costs to MacDonald's from cheating is $ ____________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Burger King and Mac Donald's repeat their simultaneous pricing decisions every Monday and have been cooperating for many weeks. Now, however, MacDonald's is considering whether to cheat or to continue cooperating. Mac's manager believes that it can only get away with cheating for two weeks before Burger King's manager will decide to retaliate with a price cut of its own. The ensuing price war is expected to last for two weeks and then the two restaurants typically return to period of cooperation again. MacDonald's manager employs a discount rate of 0.25 percent per week for the purpose of computing present values.
-In order to maximize the value of the MacDonald's restaurant, the manager ______________ (should, should not) cheat.
-In order to maximize the value of the MacDonald's restaurant, the manager ______________ (should, should not) cheat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Maytag wants to prevent Whirlpool from entering its market. The following payoff table shows the profit each firm would earn in each of the four possible decision combinations:
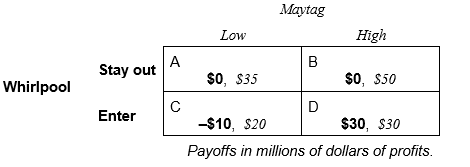
-If Maytag and Whirlpool make their decisions simultaneously, Whirlpool is likely to _______________ (stay out, enter) and Maytag is likely to price ____________ (low, high).

-If Maytag and Whirlpool make their decisions simultaneously, Whirlpool is likely to _______________ (stay out, enter) and Maytag is likely to price ____________ (low, high).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Maytag wants to prevent Whirlpool from entering its market. The following payoff table shows the profit each firm would earn in each of the four possible decision combinations:

-Suppose Maytag says to Whirlpool, "If you enter, I will price low until you decide to exit." Discuss whether this threat is credible or not.

-Suppose Maytag says to Whirlpool, "If you enter, I will price low until you decide to exit." Discuss whether this threat is credible or not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Suppose Maytag makes the first move and expands its productive capacity before Whirlpool makes its entry decision, which results in the following payoff table:
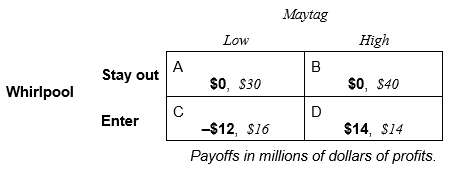
-Construct the game tree for this capacity expansion decision. Let Maytag make the first decision to expand capacity or not to expand capacity. Then let Whirlpool make its entry decision. Finally, let Maytag choose its price. Show the likely outcome on the game tree.

-Construct the game tree for this capacity expansion decision. Let Maytag make the first decision to expand capacity or not to expand capacity. Then let Whirlpool make its entry decision. Finally, let Maytag choose its price. Show the likely outcome on the game tree.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Suppose Maytag makes the first move and expands its productive capacity before Whirlpool makes its entry decision, which results in the following payoff table:

-Based on your game tree in part c, Maytag ___________ (still cannot, can now) deter Whirlpool from entering if the investment in new productive capacity is _________________ .

-Based on your game tree in part c, Maytag ___________ (still cannot, can now) deter Whirlpool from entering if the investment in new productive capacity is _________________ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



