Deck 2: Demand, Supply, and Market Equilibrium
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/52
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Demand, Supply, and Market Equilibrium
1
Use the following general linear demand relation to answer questions 9 through 13:
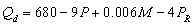
where M is income and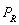 is the price of a related good, R.
is the price of a related good, R.
-From this relation it is apparent that the good is:
A) an inferior good
B) a substitute for good R
C) a normal good
D) a complement for good R
E) both c and d
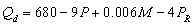
where M is income and
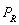 is the price of a related good, R.
is the price of a related good, R.-From this relation it is apparent that the good is:
A) an inferior good
B) a substitute for good R
C) a normal good
D) a complement for good R
E) both c and d
both c and d
2
Use the following general linear demand relation to answer questions 9 through 13:
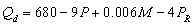
where M is income and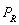 is the price of a related good, R.
is the price of a related good, R.
-If M = $15,000 and
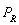
= $20, the demand function is
A)
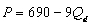
)
B)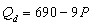 .
.
C)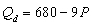
D)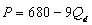
E)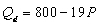
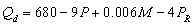
where M is income and
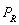 is the price of a related good, R.
is the price of a related good, R.-If M = $15,000 and
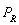
= $20, the demand function is
A)
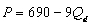
)
B)
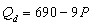 .
.C)
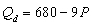
D)
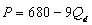
E)
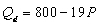
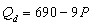 .
. 3
Use the following general linear demand relation to answer questions 9 through 13:
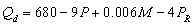
where M is income and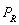 is the price of a related good, R.
is the price of a related good, R.
-If M = $15,000 and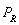 = $20 and the supply function is
= $20 and the supply function is 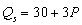 , equilibrium price and quantity are, respectively,
, equilibrium price and quantity are, respectively,
A) P = $55 and Q = 195.
B) P = $6 and Q = 38.
C) P = $12 and Q = 200.
D) P = $50 and Q = 170.
E) P = $40 and Q = 250.
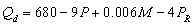
where M is income and
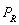 is the price of a related good, R.
is the price of a related good, R.-If M = $15,000 and
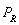 = $20 and the supply function is
= $20 and the supply function is 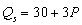 , equilibrium price and quantity are, respectively,
, equilibrium price and quantity are, respectively,A) P = $55 and Q = 195.
B) P = $6 and Q = 38.
C) P = $12 and Q = 200.
D) P = $50 and Q = 170.
E) P = $40 and Q = 250.
P = $55 and Q = 195.
4
Use the following general linear demand relation to answer questions 9 through 13:
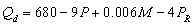
where M is income and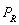 is the price of a related good, R.
is the price of a related good, R.
-If M = $15,000 and PR = $20 and the supply function is Q= 30+3P, then, when the price of the good is $60,
A) there is a shortage of 60 units of the good.
B) there is equilibrium in the market.
C) there is a surplus of 60 units of the good.
D) the quantities demanded and supplied are indeterminate
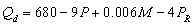
where M is income and
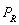 is the price of a related good, R.
is the price of a related good, R.-If M = $15,000 and PR = $20 and the supply function is Q= 30+3P, then, when the price of the good is $60,
A) there is a shortage of 60 units of the good.
B) there is equilibrium in the market.
C) there is a surplus of 60 units of the good.
D) the quantities demanded and supplied are indeterminate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Use the following general linear demand relation to answer questions 9 through 13:
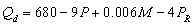
where M is income and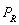 is the price of a related good, R.
is the price of a related good, R.
-If M = $15,000 and
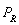
= $20 and the supply function is
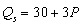
, then, when the price of the good is $40,
A) there is equilibrium in the market.
B) there is a shortage of 180 units of the good.
C) there is a surplus of 180 units of the good.
D) there is a shortage of 80 units of the good.
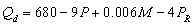
where M is income and
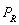 is the price of a related good, R.
is the price of a related good, R.-If M = $15,000 and
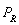
= $20 and the supply function is
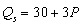
, then, when the price of the good is $40,
A) there is equilibrium in the market.
B) there is a shortage of 180 units of the good.
C) there is a surplus of 180 units of the good.
D) there is a shortage of 80 units of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Use the following demand and supply functions
Demand: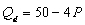 Supply:
Supply: 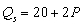
-Equilibrium price and output are
A) P = $5 and Q = 70.
B) P = $11 and Q = 3.32.
C) P = $12 and Q = 44.
D) P = $15 and Q = 50.
E) none of the above
Demand:
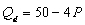 Supply:
Supply: 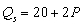
-Equilibrium price and output are
A) P = $5 and Q = 70.
B) P = $11 and Q = 3.32.
C) P = $12 and Q = 44.
D) P = $15 and Q = 50.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Use the following demand and supply functions
Demand: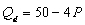 Supply:
Supply: 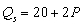
-If the price is $10, there is a
A) surplus of 30 units.
B) shortage of 30 units.
C) surplus of 40 units.
D) shortage of 10 units.
E) none of the above
Demand:
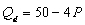 Supply:
Supply: 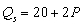
-If the price is $10, there is a
A) surplus of 30 units.
B) shortage of 30 units.
C) surplus of 40 units.
D) shortage of 10 units.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Use the following demand and supply functions
Demand: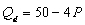 Supply:
Supply: 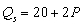
-If the price is $2, there is a
A) surplus of 10 units.
B) shortage of 10 units.
C) surplus of 30 units.
D) shortage of 18 units.
E) none of the above
Demand:
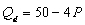 Supply:
Supply: 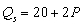
-If the price is $2, there is a
A) surplus of 10 units.
B) shortage of 10 units.
C) surplus of 30 units.
D) shortage of 18 units.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Use the following general linear demand relation to answer questions 36 through 41:
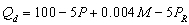
where P is the price of good X, M is income, and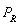 is the price of a related good, R.
is the price of a related good, R.
-What is the demand function when M = $50,000 and
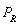 = $10?
= $10?
A)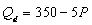
B)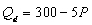
C)
D)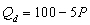
E) none of the above
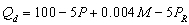
where P is the price of good X, M is income, and
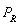 is the price of a related good, R.
is the price of a related good, R.-What is the demand function when M = $50,000 and
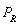 = $10?
= $10?A)
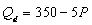
B)
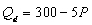
C)

D)
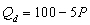
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Use the following general linear demand relation to answer questions 36 through 41:
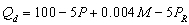
where P is the price of good X, M is income, and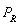 is the price of a related good, R.
is the price of a related good, R.
-If M = $50,000 and
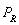
= $10 and the supply function is
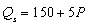
, market price and output are, respectively,
A) P = $12 and Q = 150.
B) P = $10 and Q = 200.
C) P = $12 and Q = 200.
D) P = $15 and Q = 175.
E) P = $15 and Q = 225.
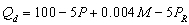
where P is the price of good X, M is income, and
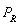 is the price of a related good, R.
is the price of a related good, R.-If M = $50,000 and
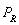
= $10 and the supply function is
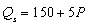
, market price and output are, respectively,
A) P = $12 and Q = 150.
B) P = $10 and Q = 200.
C) P = $12 and Q = 200.
D) P = $15 and Q = 175.
E) P = $15 and Q = 225.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Use the following general linear demand relation to answer questions 36 through 41:
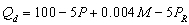
where P is the price of good X, M is income, and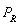 is the price of a related good, R.
is the price of a related good, R.
-If income increases to $100,000 and the price of the related good is now $20, what is the demand function?
A) Qd= 300-5P
B) Qd= 400-10P
C) Qd= 100-10P
D) Qd= 400-5P
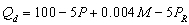
where P is the price of good X, M is income, and
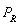 is the price of a related good, R.
is the price of a related good, R.-If income increases to $100,000 and the price of the related good is now $20, what is the demand function?
A) Qd= 300-5P
B) Qd= 400-10P
C) Qd= 100-10P
D) Qd= 400-5P

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If a demand curve goes through the point P = $6 and  = 400, then
= 400, then
A) $6 is the highest price consumers will pay for 400 units.
B) $6 is the lowest price consumers can be charged to induce them to buy 400 units.
C) 400 units are the most consumers will buy if price is $6.
D) consumers will buy more than 400 if price is $6.
E) both a and c
 = 400, then
= 400, thenA) $6 is the highest price consumers will pay for 400 units.
B) $6 is the lowest price consumers can be charged to induce them to buy 400 units.
C) 400 units are the most consumers will buy if price is $6.
D) consumers will buy more than 400 if price is $6.
E) both a and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If a supply curve goes through the point P = $10 and
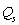
= 320, then
A) $10 is the highest price that will induce firms to supply 320 units.
B) $10 is the lowest price that will induce firms to supply 320 units.
C) at a price higher than $10 there will be a surplus.
D) at a price lower than $10 there will be a shortage.
E) both c and d
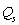
= 320, then
A) $10 is the highest price that will induce firms to supply 320 units.
B) $10 is the lowest price that will induce firms to supply 320 units.
C) at a price higher than $10 there will be a surplus.
D) at a price lower than $10 there will be a shortage.
E) both c and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Use the following general linear supply function to answer the next 6 questions:
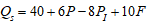
where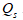 is the quantity supplied of the good, PI is the price of the good, is the price of an input, and F is the number of firms producing the good.
is the quantity supplied of the good, PI is the price of the good, is the price of an input, and F is the number of firms producing the good.
-If
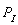
= $20 and F = 60 what is the equation of the supply function?
A) = 400 + 6 P
= 400 + 6 P
B) = 40 + 8 P
= 40 + 8 P
C) = 480 + 6
= 480 + 6 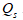
D)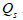 = 480 + 6 P
= 480 + 6 P
E) none of the above
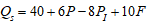
where
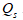 is the quantity supplied of the good, PI is the price of the good, is the price of an input, and F is the number of firms producing the good.
is the quantity supplied of the good, PI is the price of the good, is the price of an input, and F is the number of firms producing the good.-If
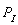
= $20 and F = 60 what is the equation of the supply function?
A)
 = 400 + 6 P
= 400 + 6 PB)
 = 40 + 8 P
= 40 + 8 PC)
 = 480 + 6
= 480 + 6 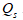
D)
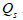 = 480 + 6 P
= 480 + 6 PE) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Use the following general linear supply function to answer the next 6 questions:
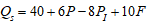
where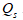 is the quantity supplied of the good, PI is the price of the good, is the price of an input, and F is the number of firms producing the good.
is the quantity supplied of the good, PI is the price of the good, is the price of an input, and F is the number of firms producing the good.
-If
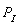
= $20, F = 60, and the demand function is

The equilibrium price and quantity are, respectively,
A) P = $10 and Q = 640.
B) P = $8 and Q = 326.
C) P = $10 and Q = 540.
D) P = $8 and Q = 640.
E) none of the above.
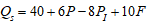
where
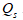 is the quantity supplied of the good, PI is the price of the good, is the price of an input, and F is the number of firms producing the good.
is the quantity supplied of the good, PI is the price of the good, is the price of an input, and F is the number of firms producing the good.-If
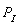
= $20, F = 60, and the demand function is

The equilibrium price and quantity are, respectively,
A) P = $10 and Q = 640.
B) P = $8 and Q = 326.
C) P = $10 and Q = 540.
D) P = $8 and Q = 640.
E) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Use the following general linear supply function to answer the next 6 questions:
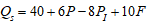
where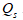 is the quantity supplied of the good, PI is the price of the good, is the price of an input, and F is the number of firms producing the good.
is the quantity supplied of the good, PI is the price of the good, is the price of an input, and F is the number of firms producing the good.
-Now suppose
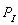 = $40 and F = 50, what is the largest amount of the good that firms will supply when the price of the good is $20?
= $40 and F = 50, what is the largest amount of the good that firms will supply when the price of the good is $20?
A) 340 units
B) 220 units
C) 80 units
D) 120 units
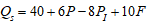
where
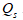 is the quantity supplied of the good, PI is the price of the good, is the price of an input, and F is the number of firms producing the good.
is the quantity supplied of the good, PI is the price of the good, is the price of an input, and F is the number of firms producing the good.-Now suppose
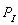 = $40 and F = 50, what is the largest amount of the good that firms will supply when the price of the good is $20?
= $40 and F = 50, what is the largest amount of the good that firms will supply when the price of the good is $20?A) 340 units
B) 220 units
C) 80 units
D) 120 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Use the following general linear supply function to answer the next 6 questions:
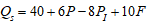
where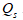 is the quantity supplied of the good, PI is the price of the good, is the price of an input, and F is the number of firms producing the good.
is the quantity supplied of the good, PI is the price of the good, is the price of an input, and F is the number of firms producing the good.
-When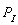 = $40 and F = 50, the INVERSE supply function is
= $40 and F = 50, the INVERSE supply function is
A) P = -36.667 + 0.1667Qs.
B) P = -220 + 6Qs.
C) P = 220 + 0.1667Qs.
D) P = 220 + 6Qs.
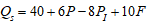
where
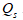 is the quantity supplied of the good, PI is the price of the good, is the price of an input, and F is the number of firms producing the good.
is the quantity supplied of the good, PI is the price of the good, is the price of an input, and F is the number of firms producing the good.-When
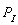 = $40 and F = 50, the INVERSE supply function is
= $40 and F = 50, the INVERSE supply function isA) P = -36.667 + 0.1667Qs.
B) P = -220 + 6Qs.
C) P = 220 + 0.1667Qs.
D) P = 220 + 6Qs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Use the following general linear supply function to answer the next 6 questions:
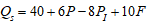
where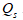 is the quantity supplied of the good, PI is the price of the good, is the price of an input, and F is the number of firms producing the good.
is the quantity supplied of the good, PI is the price of the good, is the price of an input, and F is the number of firms producing the good.
-Again suppose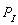 = $40 and F = 50, what is the lowest price that will induce firms to supply 400 units of output?
= $40 and F = 50, what is the lowest price that will induce firms to supply 400 units of output?
A) $15
B) $20
C) $25
D) $30
E) $35
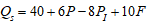
where
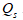 is the quantity supplied of the good, PI is the price of the good, is the price of an input, and F is the number of firms producing the good.
is the quantity supplied of the good, PI is the price of the good, is the price of an input, and F is the number of firms producing the good.-Again suppose
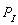 = $40 and F = 50, what is the lowest price that will induce firms to supply 400 units of output?
= $40 and F = 50, what is the lowest price that will induce firms to supply 400 units of output?A) $15
B) $20
C) $25
D) $30
E) $35

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Use the following general linear supply function to answer the next 6 questions:
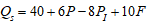
where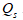 is the quantity supplied of the good, PI is the price of the good, is the price of an input, and F is the number of firms producing the good.
is the quantity supplied of the good, PI is the price of the good, is the price of an input, and F is the number of firms producing the good.
-Suppose
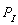
= $40, F = 50, and the demand function is
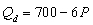
, then if government sets a price of $50 what will be the result?
A) a shortage of 120
B) a surplus of 120
C) a shortage of 160
D) a surplus of 160
where
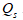 is the quantity supplied of the good, PI is the price of the good, is the price of an input, and F is the number of firms producing the good.
is the quantity supplied of the good, PI is the price of the good, is the price of an input, and F is the number of firms producing the good.-Suppose
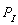
= $40, F = 50, and the demand function is
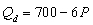
, then if government sets a price of $50 what will be the result?
A) a shortage of 120
B) a surplus of 120
C) a shortage of 160
D) a surplus of 160

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Suppose 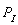 = $40, F = 50, and the demand function is
= $40, F = 50, and the demand function is 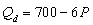 , then if government sets a price of $30 what will be the result?
, then if government sets a price of $30 what will be the result?
A) a shortage of 120
B) a surplus of 120
C) a shortage of 160
D) a surplus of 160
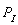 = $40, F = 50, and the demand function is
= $40, F = 50, and the demand function is 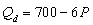 , then if government sets a price of $30 what will be the result?
, then if government sets a price of $30 what will be the result?A) a shortage of 120
B) a surplus of 120
C) a shortage of 160
D) a surplus of 160

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The general linear demand function below is used to answer the questions:
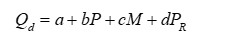
where Qd = quantity demanded, P = the price of the good, M = income, = the price of a good related in consumption.
-If c = 15 and d = 20, the good is
A) a normal good.
B) an inferior good.
C)A substitute for good R.
D)A complement with good R.
E)Both a and c
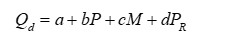
where Qd = quantity demanded, P = the price of the good, M = income, = the price of a good related in consumption.
-If c = 15 and d = 20, the good is
A) a normal good.
B) an inferior good.
C)A substitute for good R.
D)A complement with good R.
E)Both a and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The general linear demand function below is used to answer the questions:
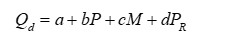
where Qd = quantity demanded, P = the price of the good, M = income, = the price of a good related in consumption.
-For the general linear demand function given above
A)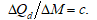
B) d is the effect on the quantity demanded of the good of a one-dollar change in the price of the related good, all other things constant.
C) b is the effect on the quantity demanded of the good of a one-dollar change in the price of the good, all other things constant.
D) all of the above
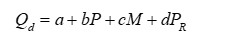
where Qd = quantity demanded, P = the price of the good, M = income, = the price of a good related in consumption.
-For the general linear demand function given above
A)
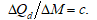
B) d is the effect on the quantity demanded of the good of a one-dollar change in the price of the related good, all other things constant.
C) b is the effect on the quantity demanded of the good of a one-dollar change in the price of the good, all other things constant.
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If the current price of a good is $10, market demand is
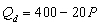
, and market supply is
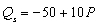
, then
A) more of the good is being produced than people want to buy.
B) a lower price will increase the shortage.
C) at the current price there is excess demand, or a shortage, of 150 units.
D) Both b and c
E) All of the above
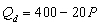
, and market supply is
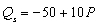
, then
A) more of the good is being produced than people want to buy.
B) a lower price will increase the shortage.
C) at the current price there is excess demand, or a shortage, of 150 units.
D) Both b and c
E) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The general demand function for good A is 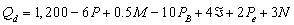 where
where 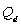 = quantity demanded of good A per month, P = the price of good A, M = average household income,
= quantity demanded of good A per month, P = the price of good A, M = average household income, 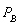 = price of related good B,
= price of related good B, 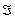 = a consumer taste index, Pe = price consumers expect to pay next month for good A, and N = number of buyers in market for good.
= a consumer taste index, Pe = price consumers expect to pay next month for good A, and N = number of buyers in market for good.
-Good A is a(n) ___________ good because the slope parameter on __________ is _________.
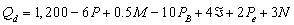 where
where 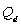 = quantity demanded of good A per month, P = the price of good A, M = average household income,
= quantity demanded of good A per month, P = the price of good A, M = average household income, 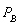 = price of related good B,
= price of related good B, 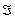 = a consumer taste index, Pe = price consumers expect to pay next month for good A, and N = number of buyers in market for good.
= a consumer taste index, Pe = price consumers expect to pay next month for good A, and N = number of buyers in market for good.-Good A is a(n) ___________ good because the slope parameter on __________ is _________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The general demand function for good A is 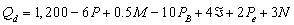 where
where 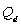 = quantity demanded of good A per month, P = the price of good A, M = average household income,
= quantity demanded of good A per month, P = the price of good A, M = average household income, 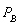 = price of related good B,
= price of related good B, 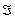 = a consumer taste index, Pe = price consumers expect to pay next month for good A, and N = number of buyers in market for good.
= a consumer taste index, Pe = price consumers expect to pay next month for good A, and N = number of buyers in market for good.
-Goods A and B are ________________ because the slope parameter on ________ is _____________.
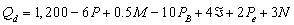 where
where 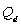 = quantity demanded of good A per month, P = the price of good A, M = average household income,
= quantity demanded of good A per month, P = the price of good A, M = average household income, 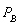 = price of related good B,
= price of related good B, 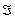 = a consumer taste index, Pe = price consumers expect to pay next month for good A, and N = number of buyers in market for good.
= a consumer taste index, Pe = price consumers expect to pay next month for good A, and N = number of buyers in market for good.-Goods A and B are ________________ because the slope parameter on ________ is _____________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The general demand function for good A is 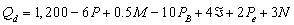 where
where 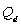 = quantity demanded of good A per month, P = the price of good A, M = average household income,
= quantity demanded of good A per month, P = the price of good A, M = average household income, 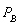 = price of related good B,
= price of related good B, 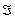 = a consumer taste index, Pe = price consumers expect to pay next month for good A, and N = number of buyers in market for good.
= a consumer taste index, Pe = price consumers expect to pay next month for good A, and N = number of buyers in market for good.
-When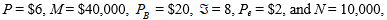 quantity demanded of good A is ____________ units per month.
quantity demanded of good A is ____________ units per month.
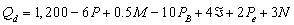 where
where 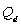 = quantity demanded of good A per month, P = the price of good A, M = average household income,
= quantity demanded of good A per month, P = the price of good A, M = average household income, 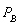 = price of related good B,
= price of related good B, 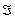 = a consumer taste index, Pe = price consumers expect to pay next month for good A, and N = number of buyers in market for good.
= a consumer taste index, Pe = price consumers expect to pay next month for good A, and N = number of buyers in market for good.-When
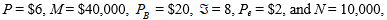 quantity demanded of good A is ____________ units per month.
quantity demanded of good A is ____________ units per month.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The general supply function is 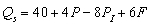 , where
, where 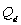 = quantity supplied per month, P = the price of the commodity,
= quantity supplied per month, P = the price of the commodity, 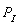 = price of an input, and F = number of sellers.
= price of an input, and F = number of sellers.
-The supply function when PI = $90 and F = 20 is ____________________. The supply function intersects the price axis at a price of $______.
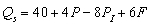 , where
, where 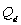 = quantity supplied per month, P = the price of the commodity,
= quantity supplied per month, P = the price of the commodity, 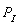 = price of an input, and F = number of sellers.
= price of an input, and F = number of sellers.-The supply function when PI = $90 and F = 20 is ____________________. The supply function intersects the price axis at a price of $______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The general supply function is 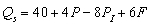 , where
, where 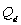 = quantity supplied per month, P = the price of the commodity,
= quantity supplied per month, P = the price of the commodity, 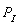 = price of an input, and F = number of sellers.
= price of an input, and F = number of sellers.
-Using the supply function in part a, the quantity supplied when the price of the commodity is $300 is ________ units per month. When the price is $400, the quantity supplied is _______ units per month.
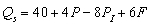 , where
, where 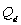 = quantity supplied per month, P = the price of the commodity,
= quantity supplied per month, P = the price of the commodity, 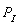 = price of an input, and F = number of sellers.
= price of an input, and F = number of sellers.-Using the supply function in part a, the quantity supplied when the price of the commodity is $300 is ________ units per month. When the price is $400, the quantity supplied is _______ units per month.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The general supply function is 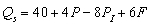 , where
, where 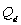 = quantity supplied per month, P = the price of the commodity,
= quantity supplied per month, P = the price of the commodity, 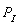 = price of an input, and F = number of sellers.
= price of an input, and F = number of sellers.
-The INVERSE supply equation (for part a) is ____________________. The supply price for 750 units per month is $_______.
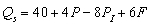 , where
, where 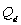 = quantity supplied per month, P = the price of the commodity,
= quantity supplied per month, P = the price of the commodity, 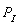 = price of an input, and F = number of sellers.
= price of an input, and F = number of sellers.-The INVERSE supply equation (for part a) is ____________________. The supply price for 750 units per month is $_______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Suppose that the demand and supply functions for good X are
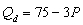
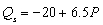
-Equilibrium price is $__________ and equilibrium quantity is __________ units.
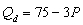
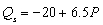
-Equilibrium price is $__________ and equilibrium quantity is __________ units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Suppose that the demand and supply functions for good X are
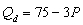
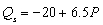
-If price is $8, then a ______________ of _______ units occurs. If price is $12, then a _____________ of _________ units occurs.
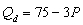
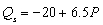
-If price is $8, then a ______________ of _______ units occurs. If price is $12, then a _____________ of _________ units occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Suppose that the demand and supply functions for good X are
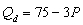
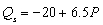
-Let the demand function change to Qd = 80-6P . Given the ORIGINAL supply function, the equilibrium price is $__________ and equilibrium quantity is __________ units.
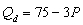
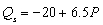
-Let the demand function change to Qd = 80-6P . Given the ORIGINAL supply function, the equilibrium price is $__________ and equilibrium quantity is __________ units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Suppose that the demand and supply functions for good X are
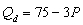
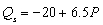
-Let the supply function change to Qs = -40+12P . Given the ORIGINAL demand function, the equilibrium price is $__________ and equilibrium quantity is __________ units
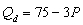
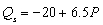
-Let the supply function change to Qs = -40+12P . Given the ORIGINAL demand function, the equilibrium price is $__________ and equilibrium quantity is __________ units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The general demand and supply functions for good A are estimated to be, respectively: 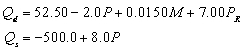 where
where 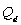 is quantity demanded per month,
is quantity demanded per month, 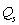 is quantity supplied per month, P is price of good A, M is average household income, and
is quantity supplied per month, P is price of good A, M is average household income, and 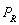 is the price of a related good R Assume the following values of the shift variables: M = $42,500, and
is the price of a related good R Assume the following values of the shift variables: M = $42,500, and  = $30.
= $30.
-The equation for INVERSE demand is _________________________.
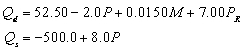 where
where 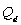 is quantity demanded per month,
is quantity demanded per month, 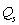 is quantity supplied per month, P is price of good A, M is average household income, and
is quantity supplied per month, P is price of good A, M is average household income, and 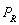 is the price of a related good R Assume the following values of the shift variables: M = $42,500, and
is the price of a related good R Assume the following values of the shift variables: M = $42,500, and  = $30.
= $30.-The equation for INVERSE demand is _________________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The general demand and supply functions for good A are estimated to be, respectively: 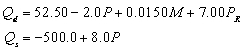 where
where 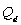 is quantity demanded per month,
is quantity demanded per month, 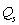 is quantity supplied per month, P is price of good A, M is average household income, and
is quantity supplied per month, P is price of good A, M is average household income, and 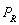 is the price of a related good R Assume the following values of the shift variables: M = $42,500, and
is the price of a related good R Assume the following values of the shift variables: M = $42,500, and  = $30.
= $30.
-The maximum price at which 500 units of good A can be sold is ____________.
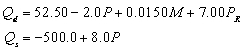 where
where 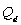 is quantity demanded per month,
is quantity demanded per month, 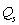 is quantity supplied per month, P is price of good A, M is average household income, and
is quantity supplied per month, P is price of good A, M is average household income, and 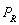 is the price of a related good R Assume the following values of the shift variables: M = $42,500, and
is the price of a related good R Assume the following values of the shift variables: M = $42,500, and  = $30.
= $30.-The maximum price at which 500 units of good A can be sold is ____________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The general demand and supply functions for good A are estimated to be, respectively: 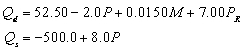 where
where 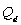 is quantity demanded per month,
is quantity demanded per month, 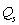 is quantity supplied per month, P is price of good A, M is average household income, and
is quantity supplied per month, P is price of good A, M is average household income, and 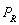 is the price of a related good R Assume the following values of the shift variables: M = $42,500, and
is the price of a related good R Assume the following values of the shift variables: M = $42,500, and  = $30.
= $30.
-The minimum price producers will accept to supply 500 units of good A is ________.
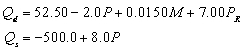 where
where 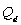 is quantity demanded per month,
is quantity demanded per month, 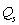 is quantity supplied per month, P is price of good A, M is average household income, and
is quantity supplied per month, P is price of good A, M is average household income, and 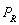 is the price of a related good R Assume the following values of the shift variables: M = $42,500, and
is the price of a related good R Assume the following values of the shift variables: M = $42,500, and  = $30.
= $30.-The minimum price producers will accept to supply 500 units of good A is ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The general demand and supply functions for good A are estimated to be, respectively: 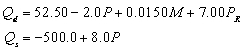 where
where 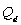 is quantity demanded per month,
is quantity demanded per month, 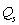 is quantity supplied per month, P is price of good A, M is average household income, and
is quantity supplied per month, P is price of good A, M is average household income, and 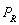 is the price of a related good R Assume the following values of the shift variables: M = $42,500, and
is the price of a related good R Assume the following values of the shift variables: M = $42,500, and  = $30.
= $30.
-If price is $150, ______________ (a shortage, a surplus, equilibrium) occurs of ___________ units of good A.
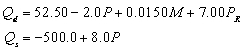 where
where 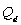 is quantity demanded per month,
is quantity demanded per month, 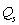 is quantity supplied per month, P is price of good A, M is average household income, and
is quantity supplied per month, P is price of good A, M is average household income, and 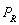 is the price of a related good R Assume the following values of the shift variables: M = $42,500, and
is the price of a related good R Assume the following values of the shift variables: M = $42,500, and  = $30.
= $30.-If price is $150, ______________ (a shortage, a surplus, equilibrium) occurs of ___________ units of good A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The general demand and supply functions for good A are estimated to be, respectively: 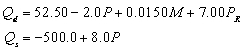 where
where 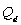 is quantity demanded per month,
is quantity demanded per month, 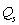 is quantity supplied per month, P is price of good A, M is average household income, and
is quantity supplied per month, P is price of good A, M is average household income, and 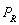 is the price of a related good R Assume the following values of the shift variables: M = $42,500, and
is the price of a related good R Assume the following values of the shift variables: M = $42,500, and  = $30.
= $30.
-The market clearing price of good A is $__________.
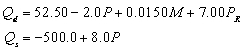 where
where 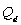 is quantity demanded per month,
is quantity demanded per month, 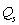 is quantity supplied per month, P is price of good A, M is average household income, and
is quantity supplied per month, P is price of good A, M is average household income, and 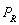 is the price of a related good R Assume the following values of the shift variables: M = $42,500, and
is the price of a related good R Assume the following values of the shift variables: M = $42,500, and  = $30.
= $30.-The market clearing price of good A is $__________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Consider the market for unleaded gasoline in the U.S.
-Event A: The Memorial Day holiday arrives in May and many motorists take to the road. As a result of Event A, ___________________ (demand, supply, both demand and supply) for gasoline will ____________ (increase, decrease). By itself, Event A will cause the price of unleaded gasoline in the U.S. to ___________(increase, decrease, stay the same) and quantity of gasoline bought and sold will ____________ (increase, decrease, stay the same).
-Event A: The Memorial Day holiday arrives in May and many motorists take to the road. As a result of Event A, ___________________ (demand, supply, both demand and supply) for gasoline will ____________ (increase, decrease). By itself, Event A will cause the price of unleaded gasoline in the U.S. to ___________(increase, decrease, stay the same) and quantity of gasoline bought and sold will ____________ (increase, decrease, stay the same).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Consider the market for unleaded gasoline in the U.S.
-Event B: Refineries of gasoline in the U.S. increase their capacity to refine gasoline from crude oil by 20 percent. As a result of Event B, ___________________ (demand, supply, both demand and supply) for gasoline will ______________ (increase, decrease). By itself, Event B will cause the price of unleaded gasoline in the U.S. to _____________(increase, decrease, stay the same) and quantity of gasoline bought and sold will ______________ (increase, decrease, stay the same).
-Event B: Refineries of gasoline in the U.S. increase their capacity to refine gasoline from crude oil by 20 percent. As a result of Event B, ___________________ (demand, supply, both demand and supply) for gasoline will ______________ (increase, decrease). By itself, Event B will cause the price of unleaded gasoline in the U.S. to _____________(increase, decrease, stay the same) and quantity of gasoline bought and sold will ______________ (increase, decrease, stay the same).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Consider the market for unleaded gasoline in the U.S.
-If Events A and B occur together (i.e. simultaneously), the price of unleaded gasoline in the U.S. ___________________(is going to increase, is going to decrease, may rise or fall or stay the same) and quantity of gasoline bought and sold ______________________(is going to increase, is going to decrease, may rise or fall or stay the same).
-If Events A and B occur together (i.e. simultaneously), the price of unleaded gasoline in the U.S. ___________________(is going to increase, is going to decrease, may rise or fall or stay the same) and quantity of gasoline bought and sold ______________________(is going to increase, is going to decrease, may rise or fall or stay the same).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Consider the market for unleaded gasoline in the U.S.
-Explain carefully and concisely the conditions under which a shortage of gasoline can occur in the U.S
-Explain carefully and concisely the conditions under which a shortage of gasoline can occur in the U.S

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The following events occur simultaneously:
The price of beef rises (beef and leather both come from cows).
The price of alligator hides increases.
Draw a demand-and-supply graph showing equilibrium in the market for leather before the two events described above. Label the axes and curves. Label the initial equilibrium - before events (i) and (ii)- as

and
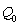
on your graph.
Now show on your graph how event (i) affects the demand or supply curves for leather. Briefly explain which of the demand or supply variables caused the effect you are showing on your graph.
Now show on your graph how event (ii) affects the demand or supply curves for leather. Briefly explain which of the demand or supply variables caused the effect you are showing on your graph.
Based on your graphic analysis, what do you predict will happen to the equilibrium price of leather? The equilibrium quantity of leather?
The price of beef rises (beef and leather both come from cows).
The price of alligator hides increases.
Draw a demand-and-supply graph showing equilibrium in the market for leather before the two events described above. Label the axes and curves. Label the initial equilibrium - before events (i) and (ii)- as

and
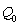
on your graph.
Now show on your graph how event (i) affects the demand or supply curves for leather. Briefly explain which of the demand or supply variables caused the effect you are showing on your graph.
Now show on your graph how event (ii) affects the demand or supply curves for leather. Briefly explain which of the demand or supply variables caused the effect you are showing on your graph.
Based on your graphic analysis, what do you predict will happen to the equilibrium price of leather? The equilibrium quantity of leather?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
You are a financial analyst with a specialization in the motion picture industry. You have been hired to analyze the prices of movie theater tickets. The following two events are occurring (simultaneously) in the United States:
A new national chain opens new multi-screen movie theaters in most U.S. cities.
Movie theaters cut the price of popcorn and soft drinks in half.
Draw a demand-and-supply graph showing equilibrium in the market for movie tickets before the above two events take place. Label the axes and curves. Label the initial equilibrium - before events (i) and (ii)- as
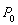
and
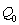
on your graph.
Now show on your graph how event (i) affects the demand or supply curves for movie tickets. Briefly explain which of the demand or supply variables caused the effect you are showing on your graph.
Now show on your graph how event (ii) affects the demand or supply curves for movie tickets. Briefly explain which of the demand or supply variables caused the effect you are showing on your graph.
Based on your graphic analysis, what do you predict will happen to the equilibrium price of movie tickets? The equilibrium quantity of movie tickets?
A new national chain opens new multi-screen movie theaters in most U.S. cities.
Movie theaters cut the price of popcorn and soft drinks in half.
Draw a demand-and-supply graph showing equilibrium in the market for movie tickets before the above two events take place. Label the axes and curves. Label the initial equilibrium - before events (i) and (ii)- as
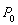
and
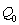
on your graph.
Now show on your graph how event (i) affects the demand or supply curves for movie tickets. Briefly explain which of the demand or supply variables caused the effect you are showing on your graph.
Now show on your graph how event (ii) affects the demand or supply curves for movie tickets. Briefly explain which of the demand or supply variables caused the effect you are showing on your graph.
Based on your graphic analysis, what do you predict will happen to the equilibrium price of movie tickets? The equilibrium quantity of movie tickets?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Use the linear demand and supply curves shown below to answer the following questions:
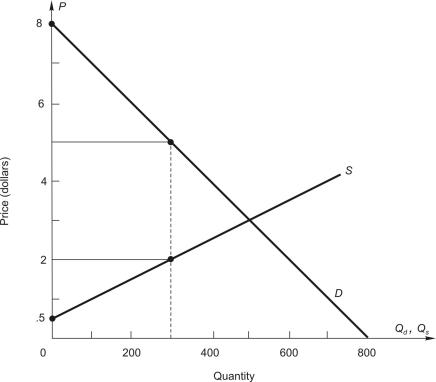
-The market or equilibrium price is $ ________.

-The market or equilibrium price is $ ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Use the linear demand and supply curves shown below to answer the following questions:

-The economic value of the 300th unit is $ ________ , and the minimum price producers will accept to produce this is unit is $ ________.

-The economic value of the 300th unit is $ ________ , and the minimum price producers will accept to produce this is unit is $ ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Use the linear demand and supply curves shown below to answer the following questions:

-For the 300th unit, consumer surplus is $ __________, and producer surplus is $ __________.

-For the 300th unit, consumer surplus is $ __________, and producer surplus is $ __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Use the linear demand and supply curves shown below to answer the following questions:

-At the market price in part a, the net gain to consumers when 300 units are purchased is $ __________.

-At the market price in part a, the net gain to consumers when 300 units are purchased is $ __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Use the linear demand and supply curves shown below to answer the following questions:

-At the market price in part a, the net gain to producers when they supply 300 units is $ __________.

-At the market price in part a, the net gain to producers when they supply 300 units is $ __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Use the linear demand and supply curves shown below to answer the following questions:

-The net gain to society when 300 units are produced and consumed at the market price is $ __________, which is called ____________.

-The net gain to society when 300 units are produced and consumed at the market price is $ __________, which is called ____________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Use the linear demand and supply curves shown below to answer the following questions:

-n market equilibrium, total consumer surplus is $ __________, and the total producer surplus is $ __________.

-n market equilibrium, total consumer surplus is $ __________, and the total producer surplus is $ __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Use the linear demand and supply curves shown below to answer the following questions:

-The net gain to society created by this market is $ _________.

-The net gain to society created by this market is $ _________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



