Deck 14: Externalities, Market Failure, and Public Choice
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/183
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Externalities, Market Failure, and Public Choice
1
Third parties can be unintentionally affected by the market activity of others.
True
2
Economic activity initiated by market participants imposes costs on free riders.
False
3
Free riders consume or enjoy benefits that they do not pay for.
True
4
Free ridership is associated with market failure, resulting in lower than efficient prices and higher than efficient quantities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A clear property right to ownership of air would reduce the problem of air pollution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Markets without externalities create pollution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Taxes and subsidies can be used to correct market failure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A system of nonattenuated (uncompromised) property rights is compatible with the achievement of economic efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The Coase Theorem was significant in economics due to its recognition of the irrelevance of property rights in establishing the motivation for economic transactions in markets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Ronald Coase was a sociologist who drew attention to the inability of economics to explain family decisions, for example, family size.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Equating society's marginal benefits with marginal costs will ensure that the economically efficient level of either private or public goods is attained.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
It is not possible to exclude people from consuming pure public goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
One difference between public goods and near public goods is the degree of rivalry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Government failure describes a situation where government activity creates negative externalities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A neighborhood tree-planting program generates positive externalities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A person whose house has declined in value as a result of a nearby factory's fumes is a third party to the market associated with the factory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Positive externalities can be more easily measured than negative externalities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The Exxon Valdez oil spill was an exception to the rule. It was the only major environmental disaster in the 1980s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When property rights are vaguely defined, externalities cannot exist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Positive externalities can be an example of market failure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The government has traditionally dealt with externalities by directive rather than by price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Public choice economics is the study of how elected officials are placed in their official capacities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Externalities are consequences visited upon those individuals residing outside decision processes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The level of protection from influenza (flu) in a community has characteristics of a public good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A national park is an example of a pure public good, since it is there for everyone to enjoy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If whooping cranes generate benefits to some members of society by merely their continued existence, then economic markets will consider this in arriving at a level of their provision "as if by an invisible hand."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The space program of the 1960s is a good example of an activity that generated significant external economies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Believers in public choice see government bureaucrats choosing the level of public goods based on their desire to keep their jobs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Catering to special interest lobbying may distort the government's provision of public goods away from the social optimum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Relying on majority rule of voting will yield a social optimum of all products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A negative externality is the same thing as an external cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A free rider attempts to receive benefits without paying for them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Marginal social cost would be less than marginal private cost in the presence of negative externalities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The existence of positive externalities indicates that price is too low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A market failure will occur when all benefits are internalized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
To correct for market failure, the government could impose a tax on the producer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The existence of positive externalities indicates that the market is producing too many goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In cases where negative externalities are present, the equilibrium price in the market is higher than it should be to achieve the optimal allocation of resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Public goods, as defined in economics, are
A) goods that are provided by the government
B) overprovided because of their public nature
C) provided efficiently in competitive markets but at too low a level
D) subject to free-rider problems
E) characterized by rivalry and nonexclusiveness
A) goods that are provided by the government
B) overprovided because of their public nature
C) provided efficiently in competitive markets but at too low a level
D) subject to free-rider problems
E) characterized by rivalry and nonexclusiveness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Market failure occurs when
A) an optimal allocation of society's resources is not achieved
B) negative externalities are taken into consideration
C) positive externalities are taken into consideration
D) government failure is at its worst
E) all social costs are included in the prices of goods and services
A) an optimal allocation of society's resources is not achieved
B) negative externalities are taken into consideration
C) positive externalities are taken into consideration
D) government failure is at its worst
E) all social costs are included in the prices of goods and services

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following best describes the characteristics of a set of property rights that are consistent with the achievement of economic efficiency?
A) specified, nonexclusive, nonrival, enforced
B) nonexclusive, rival, enforced, transferable
C) exclusive, rival, enforced, nontransferable
D) specified, exclusive, transferable, enforced
E) specified, exclusive, nonrival, enforced
A) specified, nonexclusive, nonrival, enforced
B) nonexclusive, rival, enforced, transferable
C) exclusive, rival, enforced, nontransferable
D) specified, exclusive, transferable, enforced
E) specified, exclusive, nonrival, enforced

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
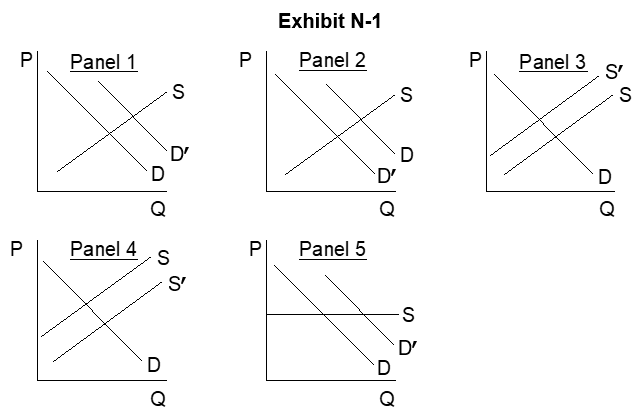
-A negative externality such as air pollution created as a by-product of a firm's production activities is best represented by which panel in Exhibit N-1 on the previous page (whereS and D depict the initial private market outcome)?
A) Panel 1
B) Panel 2
C) Panel 3
D) Panel 4
E) Panel 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43

-In Exhibit N-1, which panel best depicts the situation that justifies partial public(taxpayer) support of the cost of providing for the education of private citizens (where S and D represent the initial private market outcome)?
A) Panel 1
B) Panel 2
C) Panel 3
D) Panel 4
E) Panel 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
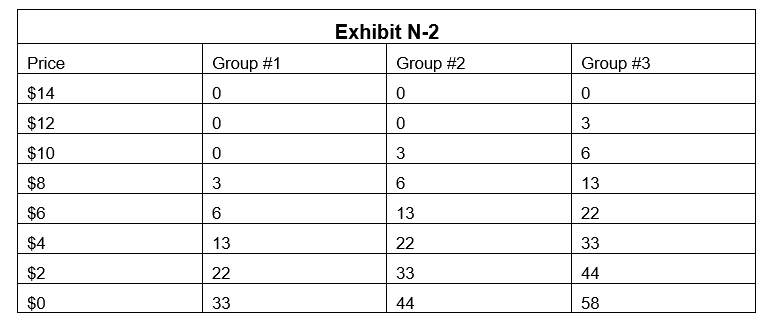
-The country of Micromania has been concerned with providing the economically efficient level of national defense for its citizens. Micromania has three groups of residents and their defense demands are as depicted in Exhibit N-2. What is the value ofthe 33rd unit of national defense?
A) $0
B) $2
C) $4
D) $6
E) $8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45

-The country of Micromania has been concerned with providing the economically efficient level of national defense for its citizens. Micromania has three groups of residents and their defense demands are as depicted in Exhibit N-2. Assuming the marginal cost of national defense is constant at $8 per unit, what is the efficient level ofnational defense to provide?
A) 6 units
B) 13 units
C) 22 units
D) 33 units
E) 44 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46

-Smallville has decided to provide lawn cutting services for an $8 fee. Demand for lawn cutting services by Smallville's three resident groups are represented in Exhibit N-2. What is the economically efficient level of lawn cutting services toprovide?
A) 6 units
B) 13 units
C) 22 units
D) 33 units
E) 44 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47

-Demand for lawn cutting services by Smallville's three resident groups are represented in Exhibit N-2. If Smallville has 68 units of lawn cutting services demanded, at what level did it set the price of its lawn cutting services?
A) $2
B) $4
C) $6
D) $8
E) $10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Government failure refers to
A) a mismatch between employer incentives and firm objectives
B) the failure of government to provide an efficient quantity of public goods
C) the inability of firms to produce output efficiently
D) the overabundance of competitors with government in production
E) the under-allocation of tax revenues
A) a mismatch between employer incentives and firm objectives
B) the failure of government to provide an efficient quantity of public goods
C) the inability of firms to produce output efficiently
D) the overabundance of competitors with government in production
E) the under-allocation of tax revenues

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Goods whose production is associated with positive externalities are
A) under-priced and over-provided
B) under-priced and under-provided
C) over-priced and under-provided
D) over-priced and over-provided
E) not provided by private markets
A) under-priced and over-provided
B) under-priced and under-provided
C) over-priced and under-provided
D) over-priced and over-provided
E) not provided by private markets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In the analysis of externalities and market failure, a third party is
A) the party a contractual agreement is meant to benefit
B) a person, or persons, who is unintentionally affected by the actions of others
C) the third person in a three-way contract
D) the person who owns the property right in a contract
E) the government attempting to mediate a dispute between the two other parties
A) the party a contractual agreement is meant to benefit
B) a person, or persons, who is unintentionally affected by the actions of others
C) the third person in a three-way contract
D) the person who owns the property right in a contract
E) the government attempting to mediate a dispute between the two other parties

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following is an example of a negative externality?
A) A Japanese company exports cars to the U.S., which causes American workers to lose their jobs.
B) An employee of a chemical company spills acid on his arm, causing severe damage.
C) John plants fruit trees in his front yard, which attracts bees, which sting neighbor Mary.
D) Sally buys coffee at McDonald's, spills some and burns her hand.
E) Jack attempts to fix his roof, falls off, and breaks his leg.
A) A Japanese company exports cars to the U.S., which causes American workers to lose their jobs.
B) An employee of a chemical company spills acid on his arm, causing severe damage.
C) John plants fruit trees in his front yard, which attracts bees, which sting neighbor Mary.
D) Sally buys coffee at McDonald's, spills some and burns her hand.
E) Jack attempts to fix his roof, falls off, and breaks his leg.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following is an example of a positive externality?
A) Nick spends $500 to landscape his yard and his property increases in value by $1,000.
B) Mick spends $500 on a stereo, which he plays so loudly that his neighbors are willing to pay him $1,000 not to play the stereo.
C) An increase in the demand for computers causes IBM to hire more workers.
D) Complaints of speeding cause police to increase surveillance.
E) Lisa puts new concrete on her driveway and now the neighboring kids use it for skateboarding.
A) Nick spends $500 to landscape his yard and his property increases in value by $1,000.
B) Mick spends $500 on a stereo, which he plays so loudly that his neighbors are willing to pay him $1,000 not to play the stereo.
C) An increase in the demand for computers causes IBM to hire more workers.
D) Complaints of speeding cause police to increase surveillance.
E) Lisa puts new concrete on her driveway and now the neighboring kids use it for skateboarding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In the absence of externalities, the optimal distribution of resources occurs whenproduction is at
A) P = MC
B) P = ATC
C) TR = TC
D) MR = MC
E) P = AFC
A) P = MC
B) P = ATC
C) TR = TC
D) MR = MC
E) P = AFC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Supply and demand curves can only reflect
A) total social costs
B) private, or internal, costs and benefits
C) external costs and benefits
D) external benefits
E) external costs
A) total social costs
B) private, or internal, costs and benefits
C) external costs and benefits
D) external benefits
E) external costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
When externalities are present in market activity and production occurs at P = MC,
A) the market generates an optimal distribution of resources
B) the market does not generate an optimal distribution of resources
C) a free-rider condition always raises price
D) P = ATC as well
E) the firm suffers economic losses
A) the market generates an optimal distribution of resources
B) the market does not generate an optimal distribution of resources
C) a free-rider condition always raises price
D) P = ATC as well
E) the firm suffers economic losses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Producing where P = MC does not yield an optimal distribution of resources when externalities are present because
A) neither price nor marginal cost reflect the social costs or social benefits of production and consumption; that is, the costs and benefits to society
B) while price still accurately measures benefits, marginal cost no longer measures the cost of resources to society
C) while marginal cost accurately measures cost, price no longer measures the true social value of the goods produced
D) output would always be higher than optimal
E) output would always be lower than optimal
A) neither price nor marginal cost reflect the social costs or social benefits of production and consumption; that is, the costs and benefits to society
B) while price still accurately measures benefits, marginal cost no longer measures the cost of resources to society
C) while marginal cost accurately measures cost, price no longer measures the true social value of the goods produced
D) output would always be higher than optimal
E) output would always be lower than optimal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following would be a private cost of smoking to a cigarette smoker?
A) cost to a private firm of the higher health insurance premiums due to the hiring of a smoker
B) cost to a private firm of the reduced productivity of a smoker, who misses days of work as a result of smoking
C) cost to the city of extra park lawn cleanup due to the presence of cigarette butts
D) price of a pack of cigarettes
E) cost to the government to pay the hospital expenses of indigent private smokers
A) cost to a private firm of the higher health insurance premiums due to the hiring of a smoker
B) cost to a private firm of the reduced productivity of a smoker, who misses days of work as a result of smoking
C) cost to the city of extra park lawn cleanup due to the presence of cigarette butts
D) price of a pack of cigarettes
E) cost to the government to pay the hospital expenses of indigent private smokers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following would be an external cost in the market for cigarettes?
A) price of a pack of cigarettes
B) loss of income for the smoker resulting from extra missed days of work
C) higher life insurance premiums paid by the smoker due to smoking
D) loss in utility in smoking by the smoker because the smoker must stand outside her office building in the cold winter to smoke
E) increased risk of cancer to the nonsmoking passengers in the smoker's car pool
A) price of a pack of cigarettes
B) loss of income for the smoker resulting from extra missed days of work
C) higher life insurance premiums paid by the smoker due to smoking
D) loss in utility in smoking by the smoker because the smoker must stand outside her office building in the cold winter to smoke
E) increased risk of cancer to the nonsmoking passengers in the smoker's car pool

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following would be an external cost associated with the production of coal-fired electricity?
A) the cost of misleading advertising
B) the increase in labor costs as the firm pays its workers who are adversely affected by the coal-fired technology
C) the pollution generated by the firm's physical plant
D) the decrease in value consumers attach to this kind of electricity
E) the value people derive from turning off lights when they leave the room, that is cost-saving
A) the cost of misleading advertising
B) the increase in labor costs as the firm pays its workers who are adversely affected by the coal-fired technology
C) the pollution generated by the firm's physical plant
D) the decrease in value consumers attach to this kind of electricity
E) the value people derive from turning off lights when they leave the room, that is cost-saving

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
When negative externalities are present, the firm's internal costs always
A) exceed the firm's external costs
B) are less than the firm's external costs
C) equal the firm's external costs
D) understate the actual cost of using society's resources producing the good
E) overstate the actual cost of using society's resources producing the good
A) exceed the firm's external costs
B) are less than the firm's external costs
C) equal the firm's external costs
D) understate the actual cost of using society's resources producing the good
E) overstate the actual cost of using society's resources producing the good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The social (or true) cost of producing a good is derived by
A) adding external cost to private cost
B) subtracting private cost from external cost
C) subtracting external cost from private cost
D) measuring private cost alone
E) measuring external cost alone
A) adding external cost to private cost
B) subtracting private cost from external cost
C) subtracting external cost from private cost
D) measuring private cost alone
E) measuring external cost alone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Social cost is
A) private cost minus external cost
B) the same as external cost
C) the same as production cost
D) private cost divided by external cost
E) private cost plus external cost
A) private cost minus external cost
B) the same as external cost
C) the same as production cost
D) private cost divided by external cost
E) private cost plus external cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
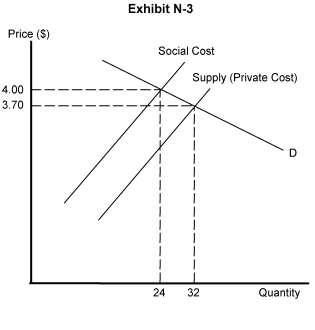
-Exhibit N-3 depicts a market showing the demand curve for a good and two supply curves, one reflecting the industry's private costs; the other reflecting the costs of resources to society producing the good. It is clear from this representation of the marketthat
A) there is a free-rider condition
B) there are positive externalities in this market
C) external costs exist in this industry
D) only one firm is producing the good
E) the demand curve incorporates both private and social benefits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64

-Exhibit N-3 depicts a market showing the demand curve for a good and two supply curves, one reflecting the industry's private costs; the other reflecting the costs of resources to society producing the good. It is clear from this representation of the marketthat the market-generated price and output would be
A) $4.00 and 32
B) $4.00 and 24
C) $3.70 and 32
D) $3.70 and 24
E) $3.85 and 28

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65

-Exhibit N-3 depicts a market showing the demand curve for a good and two supply curves, one reflecting the industry's private costs; the other reflecting the costs of resources to society producing the good. It is clear from this representation of the market that the socially optimum price and output would be
A) $4.00 and 32
B) $4.00 and 24
C) $3.70 and 32
D) $3.70 and 24
E) $3.85 and 28

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66

-Exhibit N-3 depicts a market showing the demand curve for a good and two supply curves, one reflecting the industry's private costs; the other reflecting the costs of resources to society producing the good. It is clear from this representation of the market that the market would choose a price which is too ___________ and an output which istoo __________.
A) high; low
B) low; low
C) high, high
D) low; high
E) valuable; constant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Market failure implies that
A) in the real word, the market fails to achieve equilibrium
B) with an unequal distribution of income, the market will fail to provide sufficient goods to the poor
C) when externalities are present, the market will fail to provide the socially optimal price and output
D) negative externalities are greater than positive externalities so that the market fails to create an efficient outcome
E) the inability of the market to solve the problem of unnecessary demand is caused by persuasive advertising
A) in the real word, the market fails to achieve equilibrium
B) with an unequal distribution of income, the market will fail to provide sufficient goods to the poor
C) when externalities are present, the market will fail to provide the socially optimal price and output
D) negative externalities are greater than positive externalities so that the market fails to create an efficient outcome
E) the inability of the market to solve the problem of unnecessary demand is caused by persuasive advertising

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The government is seen by many economists to be the agency that best resolves the problem of negative externalities because it
A) can create positive externalities that compensate for the negative ones
B) has access to more information than any private firm or individual and can act more objectively than any private firm or individual
C) is the only one affected by negative externalities
D) gains the most from negative externalities
E) has the power to distribute the bonuses resulting from negative externalities
A) can create positive externalities that compensate for the negative ones
B) has access to more information than any private firm or individual and can act more objectively than any private firm or individual
C) is the only one affected by negative externalities
D) gains the most from negative externalities
E) has the power to distribute the bonuses resulting from negative externalities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The creation of private property rights corrects negative externality problems in many cases because they
A) cannot create negative externalities
B) create a strong incentive for the private owners to maintain the property
C) can force the government to compensate the owners for the externality costs
D) encourage people to become free riders
E) always lead to the social optimal price and output levels
A) cannot create negative externalities
B) create a strong incentive for the private owners to maintain the property
C) can force the government to compensate the owners for the externality costs
D) encourage people to become free riders
E) always lead to the social optimal price and output levels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
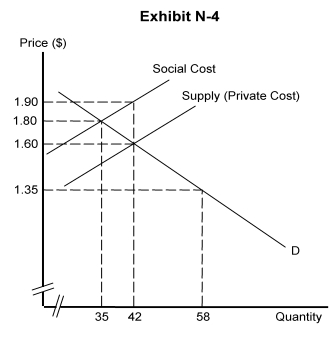
-Exhibit N-4 represents the tobacco industry. Which of the following would be included in supply (private cost) curve?
A) the cost of labor
B) the cost to the government of the hospital expenses of indigent smokers
C) the increased risk of cancer to the nonsmoking passengers in the smoker's car pool
D) the price of a pack of cigarettes
E) the loss in utility received because the smoker must stand outside her office building in the winter to smoke

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71

-In Exhibit N-4, it is clear that the industry creates
A) external benefits (positive externalities) that exceed external costs (negative externalities)
B) external benefits (negative externalities) that exceed external costs (positive externalities)
C) external costs of production (negative externalities) and no external benefits (positive externalities)
D) external benefits of production (negative externalities) and no external costs (negative externalities)
E) both external benefits (positive externalities) and external costs (negative externalities)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72

-In Exhibit N-4, the market creates an equilibrium price of ________ and an equilibrium output of _______.
A) $1.90; 42
B) $1.80; 35
C) $1.60; 42
D) $1.35; 58
E) $1.90; 35

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73

-In Exhibit N-4, if the government uses a pollution tax, how much of a tax must be imposed on each unit of production?
A) $1.30
B) $0.50
C) $1.80
D) $0.30
E) $0.60

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74

-In Exhibit N-4, if the government uses a pollution tax to correct the externality problem, how much tax revenue will the government receive?
A) $12.60
B) $10.50
C) $66.50
D) $63
E) $9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
To reach the socially optimal allocation of resources, the amount of government revenue received from a pollution tax should be
A) equal to the negative externality cost associated with producing the good
B) less than the negative externality cost of producing the good
C) greater than the negative externality cost of producing the good
D) equal to the private cost of producing the good
E) greater than the private cost of producing the good
A) equal to the negative externality cost associated with producing the good
B) less than the negative externality cost of producing the good
C) greater than the negative externality cost of producing the good
D) equal to the private cost of producing the good
E) greater than the private cost of producing the good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
In setting an obligatory control on a polluting industry, the government
A) places a tax on the pollution
B) creates pollution permits which could be sold on the open market
C) creates private property rights for air
D) establishes a limit on the amount of pollution a producer is permitted to emit
E) offers a subsidy to the polluting firm
A) places a tax on the pollution
B) creates pollution permits which could be sold on the open market
C) creates private property rights for air
D) establishes a limit on the amount of pollution a producer is permitted to emit
E) offers a subsidy to the polluting firm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The most common method used by the government to control negative externalities is
A) creation of private property rights
B) obligatory controls
C) taxation
D) subsidization
E) nationalization
A) creation of private property rights
B) obligatory controls
C) taxation
D) subsidization
E) nationalization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The government agency charged with environmental regulation is the
A) Justice Department
B) Department of Commerce
C) Federal Trade Commission
D) Environmental Protection Agency
E) Internal Revenue Service
A) Justice Department
B) Department of Commerce
C) Federal Trade Commission
D) Environmental Protection Agency
E) Internal Revenue Service

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Requiring that all cars meet certain pollution emission standards is an example of
A) the creation of a property right
B) taxation to pay for the pollution clean up
C) an obligatory control
D) nationalization
E) federalism
A) the creation of a property right
B) taxation to pay for the pollution clean up
C) an obligatory control
D) nationalization
E) federalism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The possibility that someone can reap the benefits of being a free rider occurs
A) when negative externalities exist in the market
B) only when the market is in equilibrium
C) when positive externalities exist in the market
D) only if government is willing to subsidize the market
E) only if government actually produces the good, such as a highway
A) when negative externalities exist in the market
B) only when the market is in equilibrium
C) when positive externalities exist in the market
D) only if government is willing to subsidize the market
E) only if government actually produces the good, such as a highway

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



