Deck 12: Firms in Perfectly Competitive Markets
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/23
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Firms in Perfectly Competitive Markets
1
Fill in the columns in the following table and use the values in the table to determine the profit-maximizing level of output.


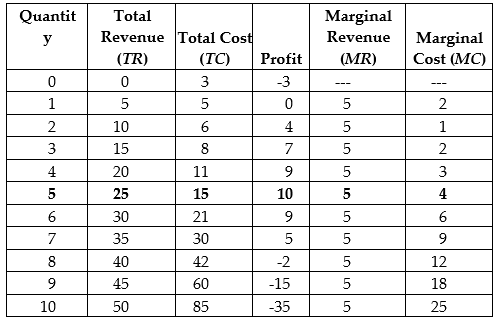
The profit-maximizing level of output is 5 units.
2
Assuming a market price of $4, fill in the columns in the following table. What is the profit-maximizing level of production? What are the two ways to determine the profit-maximizing level of production?
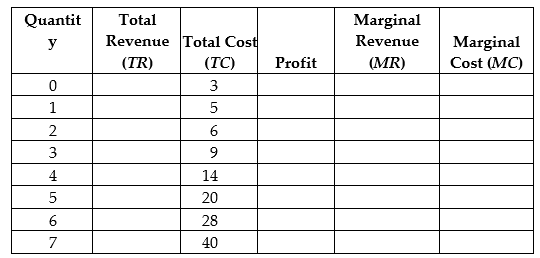


The profit-maximizing level of production is 3 units, which can be determined by the greatest difference between total revenue and total cost, which is equal to profit, and can also be determined where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost (or marginal revenue is the closest to marginal cost, without being below marginal cost).
3
According to the Department of Agriculture, net farm income in 2019 is projected to rise by more than 10 percent, to $92.5 billion in 2019, with much of the increase coming from federal aid and insurance payments to farmers. Without these payments, U.S. net farm income would have dropped by nearly 8 percent. The Trump administration paid an estimated $22.4 billion in aid to U.S. farmers in 2019 to compensate for lower prices and lost sales due to global trade disputes.
Source: P.J. Huffstutter, "U.S. farm income expected to rise in 2019, but only because of government aid," Reuters, December 2, 2019.
-Refer to the Article Summary. Net farm income was projected to increase by more than 10 percent in 2019, to $92.5 billion. Graphically, this increase in profit would be represented by ________ at the profit-maximizing quantity.
A) MR > ATC
B) MC = ATC
C) MR > MC
D) MC < ATC
Source: P.J. Huffstutter, "U.S. farm income expected to rise in 2019, but only because of government aid," Reuters, December 2, 2019.
-Refer to the Article Summary. Net farm income was projected to increase by more than 10 percent in 2019, to $92.5 billion. Graphically, this increase in profit would be represented by ________ at the profit-maximizing quantity.
A) MR > ATC
B) MC = ATC
C) MR > MC
D) MC < ATC
MR > ATC
4
According to the Department of Agriculture, net farm income in 2019 is projected to rise by more than 10 percent, to $92.5 billion in 2019, with much of the increase coming from federal aid and insurance payments to farmers. Without these payments, U.S. net farm income would have dropped by nearly 8 percent. The Trump administration paid an estimated $22.4 billion in aid to U.S. farmers in 2019 to compensate for lower prices and lost sales due to global trade disputes.
Source: P.J. Huffstutter, "U.S. farm income expected to rise in 2019, but only because of government aid," Reuters, December 2, 2019.
-Refer to the Article Summary. Assume that after the increase in U.S. farm income in 2019, farmers are not expected to receive federal aid the next year and are expected to break even in 2020. This means that at the profit-maximizing quantity in 2020
A) MC = AVC.
B) MR = MC.
C) MR = ATC.
D) AVC = ATC.
Source: P.J. Huffstutter, "U.S. farm income expected to rise in 2019, but only because of government aid," Reuters, December 2, 2019.
-Refer to the Article Summary. Assume that after the increase in U.S. farm income in 2019, farmers are not expected to receive federal aid the next year and are expected to break even in 2020. This means that at the profit-maximizing quantity in 2020
A) MC = AVC.
B) MR = MC.
C) MR = ATC.
D) AVC = ATC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5

Figure 12-5 shows cost and demand curves facing a typical firm in a constant-cost, perfectly competitive industry.
-Refer to Figure 12-5. If the market price is $20, what is the firm's profit-maximizing output?
A) 750 units
B) 1,100 units
C) 1,350 units
D) 1,800 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6

Figure 12-5 shows cost and demand curves facing a typical firm in a constant-cost, perfectly competitive industry.
-Refer to Figure 12-5. If the market price is $20, what is the amount of the firm's profit?
A) $5,400
B) $6,750
C) $8,100
D) $16,200

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Suppose Veronica sells teapots in the perfectly competitive teapot market. Her output per day and her costs are as follows:
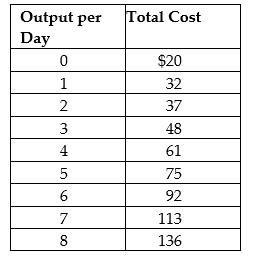
Suppose the current equilibrium price in the teapot market is $10. To maximize profit, how many teapots will Veronica produce, what price will she charge, and how much profit (or loss) will she make? Draw a graph to illustrate your answer. Your graph should include Veronica's demand, ATC, AVC, MC, and MR curves, the price she is charging, the quantity she is producing, and the area representing her profit (or loss).

Suppose the current equilibrium price in the teapot market is $10. To maximize profit, how many teapots will Veronica produce, what price will she charge, and how much profit (or loss) will she make? Draw a graph to illustrate your answer. Your graph should include Veronica's demand, ATC, AVC, MC, and MR curves, the price she is charging, the quantity she is producing, and the area representing her profit (or loss).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Suppose Veronica sells teapots in the perfectly competitive teapot market. Her output per day and her costs are as follows:
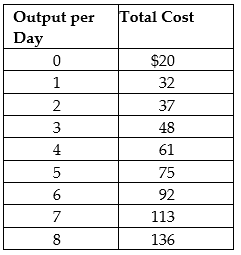
Suppose the current equilibrium price in the teapot market is $20. To maximize profit, how many teapots will Veronica produce, what price will she charge, and how much profit (or loss) will she make? Draw a graph to illustrate your answer. Your graph should include Veronica's demand, ATC, AVC, MC, and MR curves, the price she is charging, the quantity she is producing, and the area representing her profit (or loss).

Suppose the current equilibrium price in the teapot market is $20. To maximize profit, how many teapots will Veronica produce, what price will she charge, and how much profit (or loss) will she make? Draw a graph to illustrate your answer. Your graph should include Veronica's demand, ATC, AVC, MC, and MR curves, the price she is charging, the quantity she is producing, and the area representing her profit (or loss).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Suppose Veronica sells teapots in the perfectly competitive teapot market. Her output per day and her costs are as follows:

Suppose the current equilibrium price in the teapot market is $15. To maximize profit, how many teapots will Veronica produce, what price will she charge, and how much profit (or loss) will she make? Draw a graph to illustrate your answer. Your graph should include Veronica's demand, ATC, AVC, MC, and MR curves, the price she is charging, the quantity she is producing, and the area representing her profit (or loss).

Suppose the current equilibrium price in the teapot market is $15. To maximize profit, how many teapots will Veronica produce, what price will she charge, and how much profit (or loss) will she make? Draw a graph to illustrate your answer. Your graph should include Veronica's demand, ATC, AVC, MC, and MR curves, the price she is charging, the quantity she is producing, and the area representing her profit (or loss).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When economists refer to a firm breaking even, they mean that the price the firm receives is high enough that the firm's revenue covers ________. Oil executives frequently use the term "breaking even" in a different way, where the term means that the price of oil is just high enough that the firm's revenue is equal to the ________ of pumping oil from a particular well.
A) all of its costs, including the opportunity cost of the firm's investment; variable costs
B) fixed costs; average total costs
C) variable costs; fixed costs
D) total costs; opportunity costs
A) all of its costs, including the opportunity cost of the firm's investment; variable costs
B) fixed costs; average total costs
C) variable costs; fixed costs
D) total costs; opportunity costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
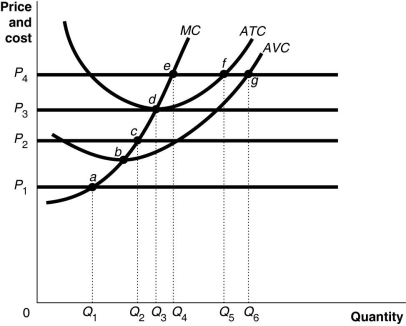
Figure 12-9 shows cost and demand curves facing a profit-maximizing, perfectly competitive firm.
-Refer to Figure 12-9. Identify the short-run shut down point for the firm.
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
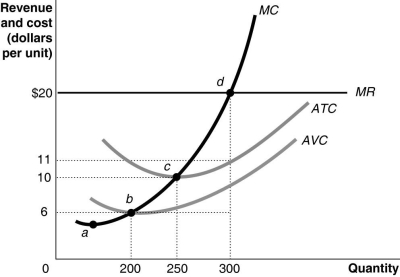
-Refer to Figure 12-10. The firm's short-run supply curve is its
A) marginal cost curve.
B) marginal cost curve from b and above.
C) marginal cost curve from c and above.
D) marginal cost curve from d and above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13

-Refer to Figure 12-10. Total revenue at the profit-maximizing level of output is
A) $1,200.
B) $2,500.
C) $4,800.
D) $6,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14

-Refer to Figure 12-10. The total cost at the profit-maximizing output level equals
A) $4,800.
B) $3,300.
C) $2,500.
D) $1,800.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Werner & Sons is a manufacturer of three-ring binders operating in a perfectly competitive industry. Table 12-5 shows the firm's cost schedule.
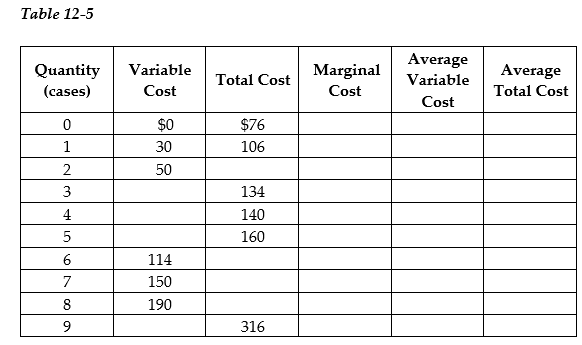
Use the table to answer the following questions.
a. Complete Table 12-5 by filling in the blank cells.
b. Werner is selling in a perfectly competitive market at a price of $40. What is the profit maximizing or loss-minimizing output?
c. Calculate the firm's profit or loss.
d. Should the firm continue to produce in the short run? Explain.
e. If the firm's fixed costs were $30 higher what would be the profit-maximizing output level in the short run? Indicate whether the output level will increase, decrease, or remain unchanged compared to your answer in b.
f. Suppose fixed cost remains at $76. If the price of three-ring binders falls to $20 what is the profit-maximizing or loss-minimizing output?
g. Calculate the profit or loss. Should the firm continue to produce in the short run? Explain your answer.
h. Suppose the fixed cost remains at $76. What price corresponds to the shut-down point?
i. Suppose the fixed cost remains at $76. What price corresponds to the break-even point?

Use the table to answer the following questions.
a. Complete Table 12-5 by filling in the blank cells.
b. Werner is selling in a perfectly competitive market at a price of $40. What is the profit maximizing or loss-minimizing output?
c. Calculate the firm's profit or loss.
d. Should the firm continue to produce in the short run? Explain.
e. If the firm's fixed costs were $30 higher what would be the profit-maximizing output level in the short run? Indicate whether the output level will increase, decrease, or remain unchanged compared to your answer in b.
f. Suppose fixed cost remains at $76. If the price of three-ring binders falls to $20 what is the profit-maximizing or loss-minimizing output?
g. Calculate the profit or loss. Should the firm continue to produce in the short run? Explain your answer.
h. Suppose the fixed cost remains at $76. What price corresponds to the shut-down point?
i. Suppose the fixed cost remains at $76. What price corresponds to the break-even point?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Assume that the medical screening industry is perfectly competitive. Consider a typical firm that is making short-run losses. Suppose the medical screening industry runs an effective advertising campaign which convinces a large number of people that yearly CT scans are critical for good health. How will this affect a typical firm that remains in the industry?
A) The firm's supply curve shifts right and its marginal revenue curve shifts upwards as the market price rises and ultimately the firm starts making profits.
B) The firm's marginal revenue curve and average cost curve shift upwards in response to the increase in market price and advertising expenditure. The firm increases output until it starts breaking even.
C) The marginal revenue curve shifts upwards, the firm's output increases along its marginal cost curve, it expands production and eventually starts making profits.
D) The marginal revenue curve shifts upwards, the firm's output increases along its marginal cost curve, it expands production until it breaks even.
A) The firm's supply curve shifts right and its marginal revenue curve shifts upwards as the market price rises and ultimately the firm starts making profits.
B) The firm's marginal revenue curve and average cost curve shift upwards in response to the increase in market price and advertising expenditure. The firm increases output until it starts breaking even.
C) The marginal revenue curve shifts upwards, the firm's output increases along its marginal cost curve, it expands production and eventually starts making profits.
D) The marginal revenue curve shifts upwards, the firm's output increases along its marginal cost curve, it expands production until it breaks even.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In 2015, poultry farmers were able to sell cage-free eggs for a price that more than offset the higher costs of raising cage-free chickens. By 2019, most of that higher return had been wiped out by the entry of additional farmers into the cage-free egg market, which caused the price of those eggs to decline. This example indicates that in a competitive market,
A) earning an economic profit in the long run is extremely easy.
B) earning an economic profit in the long run is extremely difficult.
C) it is impossible to earn an economic profit in either the short run or the long run.
D) economic profits are only earned in the long run.
A) earning an economic profit in the long run is extremely easy.
B) earning an economic profit in the long run is extremely difficult.
C) it is impossible to earn an economic profit in either the short run or the long run.
D) economic profits are only earned in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In 2015, poultry farmers were able to sell cage-free eggs for a price that more than offset the higher costs of raising cage-free chickens. By 2019, most of that higher return had been wiped out as more farmers began raising cage-free eggs, resulting in a decline in the price of those eggs. This example indicates that in a competitive market,
A) the ease at which a new firm can enter the market is low.
B) the ease at which a new firm can enter the market is high.
C) entry into the market is blocked.
D) entry into the market is restricted in the short run, but becomes easier in the long run.
A) the ease at which a new firm can enter the market is low.
B) the ease at which a new firm can enter the market is high.
C) entry into the market is blocked.
D) entry into the market is restricted in the short run, but becomes easier in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In 2019, pastured eggs sold for more than twice the price of cage-free eggs and almost 5 times the price of conventional eggs, making pastured eggs more profitable than the other eggs. Over time, this high price for pastured eggs will likely ________ as more farmers decide to ________ the perfectly competitive pastured egg market.
A) rise; enter
B) rise; exit
C) fall; enter
D) fall; exit
A) rise; enter
B) rise; exit
C) fall; enter
D) fall; exit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In 2019, pastured eggs sold for more than twice the price of cage-free eggs and almost 5 times the price of conventional eggs, making pastured eggs more profitable than the other eggs. Over time, the perfectly competitive egg market will approach a long-run equilibrium in which producing pastured eggs
A) remains more profitable than producing the other eggs.
B) is no more profitable than producing the other eggs.
C) will result in zero accounting profit.
D) will no longer be desirable by any egg farmers.
A) remains more profitable than producing the other eggs.
B) is no more profitable than producing the other eggs.
C) will result in zero accounting profit.
D) will no longer be desirable by any egg farmers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A firm could continue to operate for years without ever earning a profit as long as it is producing an output where
A) MR < ATC.
B) ATC > AVC.
C) MR > AVC.
D) AFC < AVC.
A) MR < ATC.
B) ATC > AVC.
C) MR > AVC.
D) AFC < AVC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Competition has driven the economic profits in the dog grooming business to zero. Surya Bacha, who owns a dog grooming business, would be better off leaving the industry for another alternative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
When LED television sets were first introduced prices were high and few firms were in the market. Later, economic profits attracted new firms and the price of LED televisions fell. This example illustrates
A) a decreasing-cost industry.
B) that consumers receive this new technology "free of charge" in the sense that they only have to pay a price for LED televisions equal to the lowest production cost.
C) an industry with a low minimum efficient scale.
D) how fickle consumer demands are.
A) a decreasing-cost industry.
B) that consumers receive this new technology "free of charge" in the sense that they only have to pay a price for LED televisions equal to the lowest production cost.
C) an industry with a low minimum efficient scale.
D) how fickle consumer demands are.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 23 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



