Deck 17: Financing World Trade
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/114
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Financing World Trade
1
If France exports more goods than it imports, then France
A) is experiencing a trade surplus.
B) is experiencing a trade deficit.
C) has no current account balance.
D) has no capital account balance.
A) is experiencing a trade surplus.
B) is experiencing a trade deficit.
C) has no current account balance.
D) has no capital account balance.
is experiencing a trade surplus.
2
Capital account transactions occur because of
A) imports.
B) exports.
C) unilateral transfers.
D) investments made between countries.
A) imports.
B) exports.
C) unilateral transfers.
D) investments made between countries.
investments made between countries.
3
Which of the following is FALSE?
A) The United States doesn't have a balance of trade.
B) Exports are imports are included in the current account.
C) Sales and purchases of assets are included in the capital account.
D) The current account and the capital account are more-or-less mirror images of one another.
A) The United States doesn't have a balance of trade.
B) Exports are imports are included in the current account.
C) Sales and purchases of assets are included in the capital account.
D) The current account and the capital account are more-or-less mirror images of one another.
The United States doesn't have a balance of trade.
4
As U.S. citizens import more goods,
A) the size of the trade surplus increases.
B) the size of the trade deficit decreases.
C) the U.S. becomes poorer because jobs are lost.
D) they enjoy a higher standard of living.
A) the size of the trade surplus increases.
B) the size of the trade deficit decreases.
C) the U.S. becomes poorer because jobs are lost.
D) they enjoy a higher standard of living.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The capital account and the current account
A) are determined by the level of employment within each country.
B) always move in the same direction.
C) are both always negative for the U.S.
D) are more-or-less mirror images of one anther.
A) are determined by the level of employment within each country.
B) always move in the same direction.
C) are both always negative for the U.S.
D) are more-or-less mirror images of one anther.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If a country maintains a fixed exchange rate,
A) it does so by using its foreign exchange reserves to intervene in currency markets.
B) then it will not have a trade deficit.
C) then it will not have a balance of payments deficit.
D) the citizens of the country face more foreign exchange risk than they would otherwise.
A) it does so by using its foreign exchange reserves to intervene in currency markets.
B) then it will not have a trade deficit.
C) then it will not have a balance of payments deficit.
D) the citizens of the country face more foreign exchange risk than they would otherwise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
When citizens face a foreign exchange risk, they can reduce the risk by
A) importing more goods.
B) exporting more goods.
C) hedging.
D) converting to a system of flexible exchange rates.
A) importing more goods.
B) exporting more goods.
C) hedging.
D) converting to a system of flexible exchange rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When a country attempting to maintain a fixed exchange rate runs out of foreign currency reserves, it is known as a
A) currency crisis.
B) currency appreciation.
C) currency depreciation.
D) hedge.
A) currency crisis.
B) currency appreciation.
C) currency depreciation.
D) hedge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In a floating exchange rate system, the value of a national currency is
A) independent of supply and demand forces.
B) determined by world market conditions.
C) fixed by government intervention.
D) independent of the level of imports and exports.
A) independent of supply and demand forces.
B) determined by world market conditions.
C) fixed by government intervention.
D) independent of the level of imports and exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If the Japanese yen appreciates against the dollar,
A) Japanese exports will become cheaper in the U.S.
B) Japanese exports will become more expensive in the U.S.
C) U.S. exports will become more expensive in Japan.
D) there will be no change in the price of Japanese imports in the U.S.
A) Japanese exports will become cheaper in the U.S.
B) Japanese exports will become more expensive in the U.S.
C) U.S. exports will become more expensive in Japan.
D) there will be no change in the price of Japanese imports in the U.S.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Exchange rates that are allowed to fluctuate in the open market are often referred to as
A) floating exchange rates.
B) moving discount rates.
C) revolving fed funds rates.
D) hedged rates.
A) floating exchange rates.
B) moving discount rates.
C) revolving fed funds rates.
D) hedged rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The demand for foreign currency is a(n) ______ demand.
A) perfectly elastic.
B) perfectly inelastic.
C) derived
D) upward-sloping.
A) perfectly elastic.
B) perfectly inelastic.
C) derived
D) upward-sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
When a Japanese person buys software from an American producer, there is a(n)
A) increase in the supply of dollars in the foreign exchange.
B) decrease in the supply of dollars in the foreign exchange.
C) increase in the demand for dollars in the foreign exchange.
D) decrease in the demand for dollars in the foreign exchange.
A) increase in the supply of dollars in the foreign exchange.
B) decrease in the supply of dollars in the foreign exchange.
C) increase in the demand for dollars in the foreign exchange.
D) decrease in the demand for dollars in the foreign exchange.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When a Japanese person buys software from an American producer, there is a(n)
A) increase in the supply of yen in the foreign exchange.
B) decrease in the supply of yen in the foreign exchange.
C) increase in the demand for yen in the foreign exchange.
D) decrease in the demand for yen in the foreign exchange.
A) increase in the supply of yen in the foreign exchange.
B) decrease in the supply of yen in the foreign exchange.
C) increase in the demand for yen in the foreign exchange.
D) decrease in the demand for yen in the foreign exchange.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
All of the following can cause changes in foreign currency exchange rates EXCEPT
A) changes in productivity.
B) changes in consumer preferences.
C) changes in U.S. interstate commerce laws.
D) changes in the perception of economic stability.
A) changes in productivity.
B) changes in consumer preferences.
C) changes in U.S. interstate commerce laws.
D) changes in the perception of economic stability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If there is political turmoil that threatens the economic stability of Italy, the
A) demand for Italian lira will fall.
B) demand for Italian lira will rise.
C) supply of Italian lira will fall.
D) supply of Italian lira will rise.
A) demand for Italian lira will fall.
B) demand for Italian lira will rise.
C) supply of Italian lira will fall.
D) supply of Italian lira will rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In March 2004, $1 was worth 220 Hungarian forints and in June 2004, $1 was worth 240 Hungarian forints. We can therefore conclude that
A) the Hungarian forint depreciated.
B) the Hungarian forint appreciated.
C) the U.S. dollar has depreciated.
D) there has been an increase in demand for Hungarian exports.
A) the Hungarian forint depreciated.
B) the Hungarian forint appreciated.
C) the U.S. dollar has depreciated.
D) there has been an increase in demand for Hungarian exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When a tight monetary policy followed by the Ecuadorian government results in exceptionally high interest rates in Ecuador, it can be expected that
A) the demand for Ecuadorian currency will decrease.
B) the demand for Ecuadorian currency will increase.
C) the Ecuadorian currency will depreciate, making it more difficult for Ecuador to export goods.
D) the Ecuadorian currency will depreciate, making it more difficult for Ecuador to import goods.
A) the demand for Ecuadorian currency will decrease.
B) the demand for Ecuadorian currency will increase.
C) the Ecuadorian currency will depreciate, making it more difficult for Ecuador to export goods.
D) the Ecuadorian currency will depreciate, making it more difficult for Ecuador to import goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A floating exchange rate
A) will change along with shifts in the supply of and demand for the currency.
B) changes along with supply shifts but not with demand shifts.
C) changes along with demand shifts but not with supply shifts.
D) in independent of interest rate changes.
A) will change along with shifts in the supply of and demand for the currency.
B) changes along with supply shifts but not with demand shifts.
C) changes along with demand shifts but not with supply shifts.
D) in independent of interest rate changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When a country intervenes in foreign currency markets to maintain a fixed exchange rate
A) it is engaged in hedging.
B) it increases the foreign exchange risk faced by its citizens.
C) it smoothes out fluctuations in the level of business activity.
D) it does so by using its foreign exchange reserves.
A) it is engaged in hedging.
B) it increases the foreign exchange risk faced by its citizens.
C) it smoothes out fluctuations in the level of business activity.
D) it does so by using its foreign exchange reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If one country has a trade surplus,
A) then all of its trading partners will also experience a surplus.
B) then it is exporting more than it is importing.
C) the supply of its currency will be downward sloping.
D) the supply of its currency will be upward sloping.
A) then all of its trading partners will also experience a surplus.
B) then it is exporting more than it is importing.
C) the supply of its currency will be downward sloping.
D) the supply of its currency will be upward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
As real interest rates rise in Mexico relative to other nations,
A) the demand for the peso will increase, leading to its depreciation.
B) the demand for the peso will decrease, leading to its depreciation.
C) the demand for the peso will increase, leading to its appreciation.
D) the demand for the peso will decrease, leading to its appreciation.
A) the demand for the peso will increase, leading to its depreciation.
B) the demand for the peso will decrease, leading to its depreciation.
C) the demand for the peso will increase, leading to its appreciation.
D) the demand for the peso will decrease, leading to its appreciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If labor productivity improves in India relative to other countries,
A) the demand for the Indian rupee will increase, leading to its depreciation.
B) the demand for the Indian rupee will decrease, leading to its depreciation.
C) the demand for the Indian rupee will increase, leading to its appreciation.
D) the demand for the Indian rupee will decrease, leading to its appreciation.
A) the demand for the Indian rupee will increase, leading to its depreciation.
B) the demand for the Indian rupee will decrease, leading to its depreciation.
C) the demand for the Indian rupee will increase, leading to its appreciation.
D) the demand for the Indian rupee will decrease, leading to its appreciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The current account and the capital account
A) determine the balance of trade.
B) determine the equilibrium foreign exchange rate.
C) are more-or-less mirror images of one another.
D) together add up to the total amount of exports from a country.
A) determine the balance of trade.
B) determine the equilibrium foreign exchange rate.
C) are more-or-less mirror images of one another.
D) together add up to the total amount of exports from a country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
When there is political instability in another country, the U.S. can expect
A) an increase in the balance of payments due to an increase in the current account.
B) an increase in the balance of payments due to the movement of assets to the U.S.
C) a decrease in the balance of payments due to a decrease in special drawing rights.
D) a decrease in the balance of payments due to a decrease in the demand for goods and services.
A) an increase in the balance of payments due to an increase in the current account.
B) an increase in the balance of payments due to the movement of assets to the U.S.
C) a decrease in the balance of payments due to a decrease in special drawing rights.
D) a decrease in the balance of payments due to a decrease in the demand for goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is FALSE?
A) Countries that import more than they export are experiencing a trade deficit.
B) To the extent that consumers enjoy the goods being imported, a country experiences an increase in its well-being when it is incurring a trade deficit.
C) A floating exchange rate has the effect of exacerbating domestic fluctuations in the level of business activity.
D) A country seeking to maintain a fixed exchange rate has to maintain foreign currency reserves.
A) Countries that import more than they export are experiencing a trade deficit.
B) To the extent that consumers enjoy the goods being imported, a country experiences an increase in its well-being when it is incurring a trade deficit.
C) A floating exchange rate has the effect of exacerbating domestic fluctuations in the level of business activity.
D) A country seeking to maintain a fixed exchange rate has to maintain foreign currency reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Exchange rates that are allowed to fluctuate in the open market in response to changes in supply and demand are known as
A) foreign transfer rates.
B) standard transfer rates.
C) hedged exchange rates.
D) floating exchange rates.
A) foreign transfer rates.
B) standard transfer rates.
C) hedged exchange rates.
D) floating exchange rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If the foreign exchange rate is 70 cents for one yen, then
A) a car that costs 40,000 yen will cost $7,143.00.
B) a wine that costs 200 yen will cost $14.00.
C) a clock that costs 500 yen will cost $350.00.
D) a house that costs 100,000 yen will cost $700,000.00.
A) a car that costs 40,000 yen will cost $7,143.00.
B) a wine that costs 200 yen will cost $14.00.
C) a clock that costs 500 yen will cost $350.00.
D) a house that costs 100,000 yen will cost $700,000.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
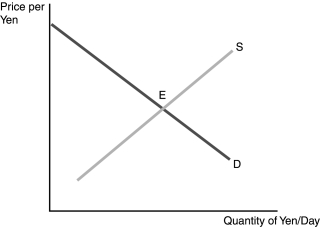
-Refer to Figure 17.1. Suppose E is the original equilibrium. An increase in the inflation rate in Japan relative to the rate in the United States generates
A) an increase in the price of yen and an increase in the quantity of yen sold per week.
B) an increase in the price of yen and a decrease in the quantity of yen sold per week.
C) a decrease in the price of yen and an increase in the quantity of yen sold per week.
D) a decrease in the price of yen and a decrease in the quantity of yen sold per week.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30

-Refer to Figure 17.1. Suppose E is the original equilibrium. The Japanese have increased their demand for U.S. goods. This will lead to
A) an increase in the price of yen and an increase in the quantity of yen sold per week.
B) an increase in the price of yen and a decrease in the quantity of yen sold per week.
C) a decrease in the price of yen and an increase in the quantity of yen sold per week.
D) a decrease in the price of yen and a decrease in the quantity of yen sold per week.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31

-Refer to Figure 17.1. Suppose E is the original equilibrium. An increase in the Japanese demand for dollars will be reflected in this figure by
A) an increase in the demand for yen as both imports and exports increase.
B) a decrease in the demand for yen as the U.S. balance of payments improves.
C) an increase in the supply of yen as Japan tries to buy more American goods.
D) a decrease in the supply of yen as Japan is less able to pay for American goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The demand for Japanese yen will increase when
A) real interest rates in Japan fall.
B) Americans change preferences in favor of domestically produced goods.
C) Japan becomes more productive relative to the United States.
D) America is perceived as more stable politically and economically than Japan.
A) real interest rates in Japan fall.
B) Americans change preferences in favor of domestically produced goods.
C) Japan becomes more productive relative to the United States.
D) America is perceived as more stable politically and economically than Japan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A country's balance of payments
A) is independent of its balance of trade.
B) will be positive if its balance of trade of trade is negative.
C) reveals the nature of income distribution within the domestic economy.
D) reflects the nature of financial inflows and outflows.
A) is independent of its balance of trade.
B) will be positive if its balance of trade of trade is negative.
C) reveals the nature of income distribution within the domestic economy.
D) reflects the nature of financial inflows and outflows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In the balance of payments, any unilateral transfer of funds out of a country is a(n)
A) investment item.
B) asset item.
C) surplus item.
D) deficit item.
A) investment item.
B) asset item.
C) surplus item.
D) deficit item.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The fact that the United States has a trade deficit means that
A) the United States has a deficit in its capital account.
B) the United States has a surplus in its capital account.
C) U.S. workers cannot compete with workers overseas.
D) interest rates in the U.S. are low compared to the world average.
A) the United States has a deficit in its capital account.
B) the United States has a surplus in its capital account.
C) U.S. workers cannot compete with workers overseas.
D) interest rates in the U.S. are low compared to the world average.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Foreign purchases of domestic assets are accounted for in
A) service imports and exports.
B) the capital account.
C) the budget deficit.
D) the national debt.
A) service imports and exports.
B) the capital account.
C) the budget deficit.
D) the national debt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The balance of payments is most strongly affected by
A) the country's relative inflation rate.
B) the country's population.
C) per capita income.
D) the distribution of income.
A) the country's relative inflation rate.
B) the country's population.
C) per capita income.
D) the distribution of income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Other factors held constant, a rise in the price level in Japan that exceeds the rise in the price level in other countries will most likely result in
A) a decline in the level of Japanese exports.
B) an increase in the supply of Japanese goods.
C) a decrease in the supply of the Japanese yen.
D) a depreciation of the dollar.
A) a decline in the level of Japanese exports.
B) an increase in the supply of Japanese goods.
C) a decrease in the supply of the Japanese yen.
D) a depreciation of the dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The supply of dollars in the foreign exchange market comes from
A) U.S. companies importing foreign goods.
B) foreign citizens buying U.S. goods.
C) efforts of the Federal Reserve to dampen money supply growth.
D) European citizens seeking to travel in the U.S.
A) U.S. companies importing foreign goods.
B) foreign citizens buying U.S. goods.
C) efforts of the Federal Reserve to dampen money supply growth.
D) European citizens seeking to travel in the U.S.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In winter months, U.S. grocers import apples from South America. This causes
A) an increase in the supply of dollars and an increase in the supply of South American currencies.
B) an increase in the supply of dollars and an increase in the demand for South American currencies.
C) a decrease in the supply of dollars and an increase in the supply of South American currencies.
D) a decrease in the supply of dollars and a decrease in the demand for South American currencies.
A) an increase in the supply of dollars and an increase in the supply of South American currencies.
B) an increase in the supply of dollars and an increase in the demand for South American currencies.
C) a decrease in the supply of dollars and an increase in the supply of South American currencies.
D) a decrease in the supply of dollars and a decrease in the demand for South American currencies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A country experiences a trade _____ when imports exceed exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In a _____ exchange rate system, the market value of a country's currency is determined by the interaction of supply and demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Hedging is a way to guard against _____ _____ risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
An increase in demand for dollars by the British would result in an _____ of the dollar and a depreciation of the British pound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The advantage of a _____ exchange rate system is that citizens can avoid exchange rate risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If Americans seek to consume more goods from Mexico, the demand for the peso would increase, and the value of the dollar would _____ against the peso.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A government maintains a _____ exchange rate by intervening in foreign currency markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A country will see an increase in demand for its exports when its currency _____ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The current account is more or less a mirror image of the _____ account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A country uses its foreign exchange reserves to intervene in currency markets when it seeks to maintain a _____ exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Currency _____ are those who make a living betting on movements in the prices of foreign currencies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The demand for the Mexican peso is _____ from the demand for Mexican exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Your demand for French francs is derived from your demand for _____ products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In foreign currency markets, the _____ _____ slopes down and the supply curve slopes up.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If the dollar appreciates against the Japanese yen, then the American demand for Japanese goods will _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
An increase in U.S. interest rates will cause an increase in the _____ for U.S. dollars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A country can expect to see the volume of its exports _____ when its currency appreciates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The depreciation of a currency will lead to a lowering of the trade _____ in that country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The Thai baht has _____ against the Japanese yen if a given amount of baht will purchase more yen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The Swiss franc has _____ against the Italian lira if a given amount of francs will purchase fewer lira.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In the graph of the foreign exchange market, an increase in the demand for dollars is represented as a _____ shift of the demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In the graph of the foreign exchange market, a decrease in the demand for dollars is represented as a _____ shift of the demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In a floating exchange rate system, the _____ exchange rate is determined by the intersection of supply and demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A _____ _____ arises when a government runs out of foreign exchange reserves with which to maintain its desired fixed exchange rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A predictable outcome of an appreciation in the value of the Canadian dollar is a _____ in the level of Canadian exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The balance of _____ expresses the total of all economic transactions between a nation and the rest of the world.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Imports, exports, and unilateral transfers are all included in the _____ account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
When foreign investors buy and sell U.S. assets, it affects the _____ account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Whenever the current account is in deficit, the capital account is in _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If the U.S. dollar appreciates against the British pound, then Americans traveling to England will find their trip to be _____ expensive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If the U.S. dollar depreciates against the French franc, then Americans traveling to Paris will find their trip to be _____ expensive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
As the U.S. dollar _____ against foreign currencies, then the level of U.S. exports can be expected to rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Residents of countries with fixed exchange rates can engage in _____ to avoid foreign exchange risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Maintenance of a fixed exchange rate requires the use of foreign exchange _____ to shift the supply of and demand for currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
How is the level of a country's exports affected by an appreciation of its currency?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
How is the level of a country's exports affected by a depreciation of its currency?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In the foreign exchange market, why does the supply of currency slope up?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Why a does a country maintaining a fixed exchange rate need to have foreign exchange reserves?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What is the advantage of a fixed exchange rate system?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
What is the disadvantage of a fixed exchange rate system?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



