Deck 6: The Two Extremes: Perfect Competition and Pure Monopoly
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/133
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: The Two Extremes: Perfect Competition and Pure Monopoly
1
Enron, a Houston-based energy firm, was forced to cease its business in the wake of an accounting scandal. As Enron closed its operations, U.S. energy prices remained stable. This may have been evidence that
A) Enron could charge whatever price it wanted to for energy.
B) there was lack of any competition so Enron was the winner.
C) there is a competitive market in energy distribution in the U.S.
D) the accounting profession needs to review its policies quickly.
A) Enron could charge whatever price it wanted to for energy.
B) there was lack of any competition so Enron was the winner.
C) there is a competitive market in energy distribution in the U.S.
D) the accounting profession needs to review its policies quickly.
there is a competitive market in energy distribution in the U.S.
2
Clothing retailers have faced greater competition in recent years as more firms have entered the clothing market. Some has come from foreign competitors, but much of it is domestic competition. As a result there is much competition and
A) individual buyers and sellers cannot affect the market price; it is determined by the market forces of demand and supply.
B) most individuals cannot afford clothing.
C) firms have a great degree of flexibility in pricing their products; these products can be sold at a high profit level.
D) there are relatively few buyers and sellers in the market, and one individual firm can determine the market price.
A) individual buyers and sellers cannot affect the market price; it is determined by the market forces of demand and supply.
B) most individuals cannot afford clothing.
C) firms have a great degree of flexibility in pricing their products; these products can be sold at a high profit level.
D) there are relatively few buyers and sellers in the market, and one individual firm can determine the market price.
individual buyers and sellers cannot affect the market price; it is determined by the market forces of demand and supply.
3
Your local farmer has many competitors, and he operates in a market structure known as perfect competition. This means that price is determined outside of the individual farmer's ability to determine his selling price. Therefore, the farmer is
A) a price maker and can therefore charge different customers different prices.
B) always able to price produce above the competition and earn a larger profit.
C) never able to determine any prices he charges for anything, such as soybeans.
D) a price taker and cannot affect the price of the produce sold to a great degree.
A) a price maker and can therefore charge different customers different prices.
B) always able to price produce above the competition and earn a larger profit.
C) never able to determine any prices he charges for anything, such as soybeans.
D) a price taker and cannot affect the price of the produce sold to a great degree.
a price taker and cannot affect the price of the produce sold to a great degree.
4
What is true of market structures considered to be imperfect competition?
A) The industry provides services requiring specialized labor.
B) The industry consists of more than one firm.
C) The industry provides products that are necessities.
D) The industry provides products that are luxuries.
A) The industry provides services requiring specialized labor.
B) The industry consists of more than one firm.
C) The industry provides products that are necessities.
D) The industry provides products that are luxuries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What is a homogeneous product?
A) One which has only one use.
B) One which is produced by only one firm.
C) One which has the same characteristics even when produced by different firms.
D) One for which there is only one substitute.
A) One which has only one use.
B) One which is produced by only one firm.
C) One which has the same characteristics even when produced by different firms.
D) One for which there is only one substitute.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A market is considered to act as a perfectly competitive one if
A) all firms advertise aggressively.
B) all firms use the same production process.
C) all firms are price takers.
D) all firms use the least-cost combination of inputs.
A) all firms advertise aggressively.
B) all firms use the same production process.
C) all firms are price takers.
D) all firms use the least-cost combination of inputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following is closest to a perfectly competitive market?
A) Computer software
B) Handmade guitars
C) Athletic shoes
D) Wheat
A) Computer software
B) Handmade guitars
C) Athletic shoes
D) Wheat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Market structure refers to
A) the number, size, and interaction of firms in a market.
B) the system of government regulations preserving free trade.
C) the legal requirements firms must meet before beginning their operations.
D) the legal regulation of financial markets.
A) the number, size, and interaction of firms in a market.
B) the system of government regulations preserving free trade.
C) the legal requirements firms must meet before beginning their operations.
D) the legal regulation of financial markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of perfect competition?
A) Firms can easily enter or exit the industry.
B) The product is considered a necessity for consumers.
C) There are a large number of buyers and sellers.
D) Buyers and sellers have good information about price and product qualities.
A) Firms can easily enter or exit the industry.
B) The product is considered a necessity for consumers.
C) There are a large number of buyers and sellers.
D) Buyers and sellers have good information about price and product qualities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Referring to the diagram, which of the following statements is INCORRECT?
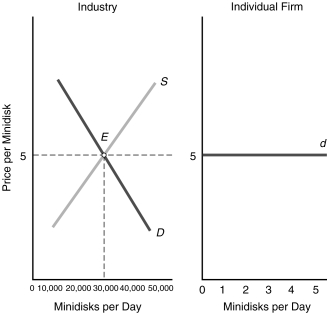 Figure 6.1
Figure 6.1
A) The equilibrium market price is $5, where the industry D and S curve intersect.
B) If the individual firm raises its price, it will make no sales at all.
C) The individual firm faces a perfectly inelastic demand curve d.
D) The individual firm faces the going market price as determined by the industry.
 Figure 6.1
Figure 6.1A) The equilibrium market price is $5, where the industry D and S curve intersect.
B) If the individual firm raises its price, it will make no sales at all.
C) The individual firm faces a perfectly inelastic demand curve d.
D) The individual firm faces the going market price as determined by the industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
By saying that the perfectly competitive firm is a price taker, economists mean that
A) the firm faces a perfectly inelastic demand curve.
B) the firm can sell all it wants at the market price.
C) the firm charges a price equal to its production costs plus 10 percent.
D) the firm charges a price equal to its labor costs plus 10 percent.
A) the firm faces a perfectly inelastic demand curve.
B) the firm can sell all it wants at the market price.
C) the firm charges a price equal to its production costs plus 10 percent.
D) the firm charges a price equal to its labor costs plus 10 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The demand curve facing the perfectly competitive firm is
A) downsloping.
B) upsloping.
C) perfectly inelastic.
D) perfectly elastic.
A) downsloping.
B) upsloping.
C) perfectly inelastic.
D) perfectly elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The demand curve facing the perfectly competitive firm is
A) horizontal at the price most customers prefer.
B) horizontal at the price most producers prefer.
C) horizontal at the price established by the interaction of market supply and market demand.
D) vertical at the equilibrium market quantity.
A) horizontal at the price most customers prefer.
B) horizontal at the price most producers prefer.
C) horizontal at the price established by the interaction of market supply and market demand.
D) vertical at the equilibrium market quantity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
For the perfectly competitive firm the selling price of its product is determined by
A) the interaction of market supply and demand.
B) the number of competing firms.
C) the amount it chooses to spend on marketing.
D) the length of time it has been in business.
A) the interaction of market supply and demand.
B) the number of competing firms.
C) the amount it chooses to spend on marketing.
D) the length of time it has been in business.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is within control of the perfectly competitive firm?
A) Its level of profit
B) The number of its competitors
C) Its selling price
D) Its quantity produced
A) Its level of profit
B) The number of its competitors
C) Its selling price
D) Its quantity produced

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The profit maximizing level of production
A) is the quantity at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
B) is where the difference between marginal revenue and marginal cost is maximized.
C) is not measurable for a perfectly competitive firm.
D) ignores the relation of total revenues and total costs.
A) is the quantity at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
B) is where the difference between marginal revenue and marginal cost is maximized.
C) is not measurable for a perfectly competitive firm.
D) ignores the relation of total revenues and total costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The profit maximizing level of output for a firm is where
A) P = ATC.
B) P =AVC.
C) MR = MC.
D) MR = ATC.
A) P = ATC.
B) P =AVC.
C) MR = MC.
D) MR = ATC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When are profits maximized?
A) At the rate of output at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost
B) At the output rate where marginal cost is greater than marginal revenue
C) When the difference between total revenues and total costs is negative
D) When the difference between price and quantity demanded is greatest
A) At the rate of output at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost
B) At the output rate where marginal cost is greater than marginal revenue
C) When the difference between total revenues and total costs is negative
D) When the difference between price and quantity demanded is greatest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The perfect competitor
A) produces what he thinks can be sold, regardless of cost.
B) chooses the profit-maximizing price.
C) chooses the profit-maximizing quantity.
D) chooses a quantity that will make the most efficient use of his labor and capital resources.
A) produces what he thinks can be sold, regardless of cost.
B) chooses the profit-maximizing price.
C) chooses the profit-maximizing quantity.
D) chooses a quantity that will make the most efficient use of his labor and capital resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In the short-run, the perfectly competitive firm will always earn an economic profit when
A) P = ATC.
B) P AVC.
C) P = MC.
D) P ATC.
A) P = ATC.
B) P AVC.
C) P = MC.
D) P ATC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A company finds that at the MR = MC output level, its total cost is $500, total variable cost is $400, and total revenue is $450. Your advice to the firm is to
A) shut down immediately.
B) reduce output to reduce the cost of production.
C) increase output to reduce the per unit cost of production.
D) continue to produce, as total revenue covers total variable cost.
A) shut down immediately.
B) reduce output to reduce the cost of production.
C) increase output to reduce the per unit cost of production.
D) continue to produce, as total revenue covers total variable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A perfectly competitive firm finds that its total revenue is $74,000 and its total costs are $80,000. If its total variable costs are $75,000, what should the firm do?
A) Increase its selling price.
B) Decrease its selling price.
C) Continue to produce at the current price and quantity combination.
D) Shut down immediately.
A) Increase its selling price.
B) Decrease its selling price.
C) Continue to produce at the current price and quantity combination.
D) Shut down immediately.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A perfectly competitive firm finds that its selling price is $17, its ATC is $18, and its AVC is $16. What should the firm do?
A) Minimize losses by continuing to produce.
B) Minimize losses by shutting down immediately.
C) Increase its selling price.
D) Decrease its selling price.
A) Minimize losses by continuing to produce.
B) Minimize losses by shutting down immediately.
C) Increase its selling price.
D) Decrease its selling price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In the long run, the level of economic profit in a perfectly competitive industry
A) will be equal to the level of accounting profit.
B) will depend on the portion of costs that are fixed costs.
C) will depend on the portion of costs that are variable costs.
D) will be zero.
A) will be equal to the level of accounting profit.
B) will depend on the portion of costs that are fixed costs.
C) will depend on the portion of costs that are variable costs.
D) will be zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In the short run in perfect competition, a firm will shut down when
A) price is below average variable cost.
B) price is below average total cost.
C) marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
D) economic profit is zero.
A) price is below average variable cost.
B) price is below average total cost.
C) marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
D) economic profit is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A perfectly competitive firm earning zero economic profit
A) is earning an accounting profit of zero.
B) is not covering the opportunity cost of the resources it is using.
C) is earning an accounting profit equal to the normal rate of return.
D) is not covering its variable costs.
A) is earning an accounting profit of zero.
B) is not covering the opportunity cost of the resources it is using.
C) is earning an accounting profit equal to the normal rate of return.
D) is not covering its variable costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
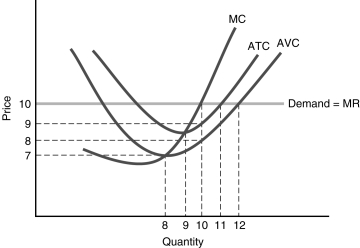 Figure 6.3
Figure 6.3-In Figure 6.3, if the market price was $10 the firm would
A) produce 10 units.
B) produce 11 units.
C) produce 12 units.
D) shut down operations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
 Figure 6.3
Figure 6.3-In Figure 6.3, if the market price was $9 the firm would
A) shut down operations.
B) earn a positive economic profit.
C) earn a positive accounting profit, but zero economic profit.
D) not be able to cover all the opportunity costs of the resources it uses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The breakeven point for a firm in perfect competition is at the level of output where
A) P = AVC.
B) P= ATC.
C) P = MC.
D) MR =MC.
A) P = AVC.
B) P= ATC.
C) P = MC.
D) MR =MC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If a firm's total explicit costs are $1,000 and total implicit costs are $500 and it has a total revenue of $900, it makes a(n)
A) accounting profit only.
B) economic profit only.
C) both an economic and accounting profit.
D) neither an economic nor an accounting profit.
A) accounting profit only.
B) economic profit only.
C) both an economic and accounting profit.
D) neither an economic nor an accounting profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The perfectly competitive firm produces at the point where price equals marginal cost because this is the quantity that
A) minimizes total cost.
B) maximizes profit.
C) allows the firm to make best use of its capital and labor resources.
D) allows the firm to break even.
A) minimizes total cost.
B) maximizes profit.
C) allows the firm to make best use of its capital and labor resources.
D) allows the firm to break even.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
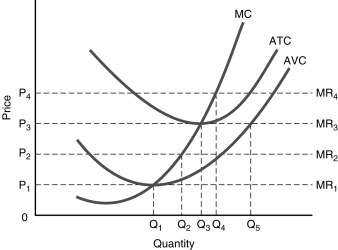 Figure 6.4
Figure 6.4-Using Figure 6.4, the perfectly competitive firm in the diagram will earn an economic profit if the market price is
A) P1.
B) P2.
C) P3.
D) P4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
 Figure 6.4
Figure 6.4-Using Figure 6.4, the perfectly competitive firm should continue to produce in the short-run if the market price is above
A) P1.
B) P2.
C) P3.
D) P4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
 Figure 6.4
Figure 6.4-Using Figure 6.4, the perfectly competitive firm should shut down now if the market price is below
A) P1.
B) P2.
C) P3.
D) P4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
 Figure 6.4
Figure 6.4-Using Figure 6.4, the breakeven price for the perfectly competitive firm will be
A) P1.
B) P2.
C) P3.
D) P4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
 Figure 6.4
Figure 6.4-Using Figure 6.4, the price facing the perfectly competitive firm in the long-run will be
A) P1.
B) P2.
C) P3.
D) P4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
When there are economic profits in a perfectly competitive industry
A) the high barriers to entry prevent further competition.
B) firms exit the industry.
C) firms enter the industry.
D) firms have no incentive to exit or enter the industry.
A) the high barriers to entry prevent further competition.
B) firms exit the industry.
C) firms enter the industry.
D) firms have no incentive to exit or enter the industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
When there are zero economic profits in a perfectly competitive firm
A) the high barriers to entry prevent further competition.
B) firms exit the industry.
C) firms enter the industry.
D) firms have no incentive to exit or enter the industry.
A) the high barriers to entry prevent further competition.
B) firms exit the industry.
C) firms enter the industry.
D) firms have no incentive to exit or enter the industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If a perfectly competitive firm is maximizing profits and is currently producing at the point where price is $24, marginal cost is $24, and average total cost is $20, then the firm can expect that
A) it will have to shut down soon.
B) its average total cost will increase until it is just breaking even.
C) more firms will enter the industry, and the price will decline.
D) its level of accounting profit will be below the normal rate of return.
A) it will have to shut down soon.
B) its average total cost will increase until it is just breaking even.
C) more firms will enter the industry, and the price will decline.
D) its level of accounting profit will be below the normal rate of return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A cartel seeks to
A) create the conditions of perfect competition.
B) restrict industry output to the monopoly level.
C) create a price and quantity combination that consumers will think is fair.
D) produce the quantity for which price will equal average total cost.
A) create the conditions of perfect competition.
B) restrict industry output to the monopoly level.
C) create a price and quantity combination that consumers will think is fair.
D) produce the quantity for which price will equal average total cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
For a monopolist, selling more units requires
A) forming a cartel.
B) lowering the selling price.
C) allowing more firms to enter the industry.
D) hiring a more productive labor force.
A) forming a cartel.
B) lowering the selling price.
C) allowing more firms to enter the industry.
D) hiring a more productive labor force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The demand curve faced by the monopolist is
A) perfectly elastic.
B) perfectly inelastic.
C) upward sloping.
D) downward sloping.
A) perfectly elastic.
B) perfectly inelastic.
C) upward sloping.
D) downward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
It was reported that a drug for treating cancer was providing positive preliminary results. If the drug is cleared by the Food and Drug Administration and the company is successful in obtaining a patent for their product
A) the patent holder will have to operate as a perfect competitor.
B) the patent holder will have to charge a price equal to marginal cost.
C) the patent holder has a monopoly.
D) the drug would have many close substitutes.
A) the patent holder will have to operate as a perfect competitor.
B) the patent holder will have to charge a price equal to marginal cost.
C) the patent holder has a monopoly.
D) the drug would have many close substitutes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A barrier to entry
A) makes it difficult for other firms to enter the industry.
B) can be thought of as unrelated to monopoly.
C) can only be created with government authority.
D) usually takes the form of a cartel.
A) makes it difficult for other firms to enter the industry.
B) can be thought of as unrelated to monopoly.
C) can only be created with government authority.
D) usually takes the form of a cartel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Table 6.1

-Given the data in Table 6.1, what is the marginal revenue when the quantity is 5?
A) 160
B) 120
C) 80
D) 0

-Given the data in Table 6.1, what is the marginal revenue when the quantity is 5?
A) 160
B) 120
C) 80
D) 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Table 6.1

-Given the data in Table 6.1, what would the monopolist do if the marginal cost of producing his good were constant at 100 per unit?
A) Produce 4 units and sell them for 100 each.
B) Produce 5 units and sell them for 100 each.
C) Produce 5 units and sell them for 160 each.
D) Produce 6 units and sell them for 150 each.

-Given the data in Table 6.1, what would the monopolist do if the marginal cost of producing his good were constant at 100 per unit?
A) Produce 4 units and sell them for 100 each.
B) Produce 5 units and sell them for 100 each.
C) Produce 5 units and sell them for 160 each.
D) Produce 6 units and sell them for 150 each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Marginal revenue is equal to price for
A) the perfect competitor only.
B) the monopolist only.
C) the perfect competitor and the monopolist.
D) neither the perfect competitor nor the monopolist.
A) the perfect competitor only.
B) the monopolist only.
C) the perfect competitor and the monopolist.
D) neither the perfect competitor nor the monopolist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Monopoly implies
A) no competition.
B) low prices.
C) low profits.
D) high costs.
A) no competition.
B) low prices.
C) low profits.
D) high costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The point of profit maximization for a monopolist is
A) the point at which total revenue equals total cost.
B) the point at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
C) the point at which average total cost is minimized.
D) the point at which marginal revenue equals average total cost.
A) the point at which total revenue equals total cost.
B) the point at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
C) the point at which average total cost is minimized.
D) the point at which marginal revenue equals average total cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
To maximize profit the monopolist will
A) produce where marginal cost is minimized and charge a price equal to ATC at that quantity.
B) produce where ATC is minimized and charge a price equal to marginal cost at that quantity.
C) produce where MR = MC and charge a price equal to marginal revenue.
D) produce where MR = MC and charge the price that corresponds to that quantity on the demand curve.
A) produce where marginal cost is minimized and charge a price equal to ATC at that quantity.
B) produce where ATC is minimized and charge a price equal to marginal cost at that quantity.
C) produce where MR = MC and charge a price equal to marginal revenue.
D) produce where MR = MC and charge the price that corresponds to that quantity on the demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
For a monopolist
A) P MR.
B) P = MC.
C) P = MR.
D) P = ATC.
A) P MR.
B) P = MC.
C) P = MR.
D) P = ATC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A monopolist will not make a profit if
A) P < ATC.
B) P > ATC.
C) MR= MC.
D) P MR.
A) P < ATC.
B) P > ATC.
C) MR= MC.
D) P MR.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following is true of a perfectly competitive firm and a monopoly in the long run?
A) P = MC
B) P = ATC
C) MR = MC
D) P = MR
A) P = MC
B) P = ATC
C) MR = MC
D) P = MR

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
For a monopoly at the profit maximizing output level all of the following are true, EXCEPT
A) P ATC.
B) P MR.
C) P MC.
D) P =MR.
A) P ATC.
B) P MR.
C) P MC.
D) P =MR.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A monopoly sells 10 units of output at $10. The MR of the 11th unit is $4.50, then
A) the price of the 11th unit is also $10.
B) the price of the 11th unit is $9.50.
C) the price of the 11th unit must be greater than $10.
D) the price of the 11th unit is $7.25.
A) the price of the 11th unit is also $10.
B) the price of the 11th unit is $9.50.
C) the price of the 11th unit must be greater than $10.
D) the price of the 11th unit is $7.25.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
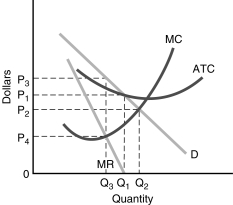 Figure 6.5
Figure 6.5-Using Figure 6.5, the profit maximizing quantity and price will be
A) Q1 and P1.
B) Q2 and P2.
C) Q3 and P3.
D) Q3 and P4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The perfect competitor seeks to produce a quantity that will maximize his _________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The perfectly competitive firm produces where price is equal to _________ _________ because this is the quantity that will maximize profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The firm's profit is the difference between its total revenue and its _________ _________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Profits disappear eventually in perfect competition because of _________ from other firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
When a perfect competitor is at the break even price, economic profits are _________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
When a perfect competitor is at the break even price, the firm's level of accounting profit is equal to the _________ rate of return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The firm should shut down immediately when price is below average _________ cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The firm is making an economic profit as long as price is above average _________ cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Market _________ relates to the number, size, and interaction of firms in a particular market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A product is _________ if items produced by one firm in the industry are identical to those produced by another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Perfect competitors are _________ _________ because they take the market price as given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The demand curve facing the perfectly competitive firm is perfectly _________ at the market price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Perfect competition, monopoly, and imperfect competition are all examples of _________ _________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Duopoly, oligopoly, and monopolistic competition are all examples of _________ _________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The behavior of the perfect competitor can be described by his desire to maximize _________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
If a firm shuts down immediately, it will lose its _________ _________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
New firms will enter a perfectly competitive industry as long as firms in the industry are making positive _________ _________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
In the long run, all firms in a perfectly competitive industry will make _________ economic profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A perfectly competitive firm takes _________ as given, and selects a _________ in response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
If price is less than average _________ cost, the firm will minimize losses by shutting down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Economies of scale give rise to _________ monopolies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
For monopoly power to persist, there must be some form of _________ to entry into the industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Alcoa became a monopoly producer of aluminum because it controlled the sources of _________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A cartel seeks to restrict industry output to the _________ level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



