Deck 5: The Firm: Production and Cost
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/140
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: The Firm: Production and Cost
1
How are the profits of a corporation distributed?
A) In the form of dividends to stockholders
B) In the form of rebates to customers
C) In the form of bonuses to hourly employees
D) In the form of bonuses to managerial employees
A) In the form of dividends to stockholders
B) In the form of rebates to customers
C) In the form of bonuses to hourly employees
D) In the form of bonuses to managerial employees
In the form of dividends to stockholders
2
How do corporations raise further capital?
A) By asking managers to contribute to an ownership fund
B) By asking employees to contribute to an ownership fund
C) By selling shares of common stock
D) By raising selling prices of their products
A) By asking managers to contribute to an ownership fund
B) By asking employees to contribute to an ownership fund
C) By selling shares of common stock
D) By raising selling prices of their products
By selling shares of common stock
3
The time frame in which all factors of production can vary is
A) the short run.
B) the fiscal year.
C) the long run.
D) the length of time for which a sole proprietorship is protected with limited liability.
A) the short run.
B) the fiscal year.
C) the long run.
D) the length of time for which a sole proprietorship is protected with limited liability.
the long run.
4
Which one of the following is TRUE?
A) S type corporations are not protected by limited liability.
B) Profits earned by partnerships are subject to double taxation.
C) Profits earned by corporations are subject to double taxation.
D) Sole proprietorships enjoy the protection of limited liability.
A) S type corporations are not protected by limited liability.
B) Profits earned by partnerships are subject to double taxation.
C) Profits earned by corporations are subject to double taxation.
D) Sole proprietorships enjoy the protection of limited liability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is NOT a legal entitlement of stockholders in a corporation?
A) The right to vote on major policy decisions in the company
B) The right to vote on the company's Board of Directors
C) The right to receive distributed profits in the form of dividends
D) The right to receive discounts on company products
A) The right to vote on major policy decisions in the company
B) The right to vote on the company's Board of Directors
C) The right to receive distributed profits in the form of dividends
D) The right to receive discounts on company products

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The goal of the business firm is to
A) employ as many workers as possible.
B) pay as much in taxes as possible.
C) produce a unique product.
D) earn a profit.
A) employ as many workers as possible.
B) pay as much in taxes as possible.
C) produce a unique product.
D) earn a profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The letters LLC at the end of a company name stand for
A) lend-lease contract.
B) limited liability company.
C) legally-limited corporation.
D) limited labor corporation.
A) lend-lease contract.
B) limited liability company.
C) legally-limited corporation.
D) limited labor corporation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which form of business organization guarantees that the firm will make a profit?
A) Sole proprietorship
B) Partnership
C) Corporation
D) None of the above
A) Sole proprietorship
B) Partnership
C) Corporation
D) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which factors account for the popularity of LLC's?
A) Tax advantages along with limited liability
B) Exemption from minimum wage laws and exemption from state and local taxes
C) Limited liability and exemption from sales taxes
D) Exemption from sales taxes and guarantee of earning a profit
A) Tax advantages along with limited liability
B) Exemption from minimum wage laws and exemption from state and local taxes
C) Limited liability and exemption from sales taxes
D) Exemption from sales taxes and guarantee of earning a profit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The productivity of labor will determine
A) the shape of the production function.
B) whether a firm is a corporation or a partnership.
C) what percentage of profits will be taxed.
D) how long the long run is.
A) the shape of the production function.
B) whether a firm is a corporation or a partnership.
C) what percentage of profits will be taxed.
D) how long the long run is.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A firm's marginal cost is not directly tied to
A) its total variable cost.
B) its average variable cost.
C) its marginal physical product.
D) its total fixed cost.
A) its total variable cost.
B) its average variable cost.
C) its marginal physical product.
D) its total fixed cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Table 5.2
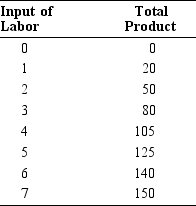
-In Table 5.2, the average product for 5 units of labor is
A) 20.0.
B) 22.5.
C) 25.0.
D) 15.0.

-In Table 5.2, the average product for 5 units of labor is
A) 20.0.
B) 22.5.
C) 25.0.
D) 15.0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Table 5.2

-In Table 5.2, the marginal product of the seventh worker is
A) 30.0
B) 25.0
C) 22.5
D) 10.0

-In Table 5.2, the marginal product of the seventh worker is
A) 30.0
B) 25.0
C) 22.5
D) 10.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Any activity that results in the conversion of resources into products that can be used in consumption is
A) not profitable.
B) a start up venture.
C) demand.
D) production.
A) not profitable.
B) a start up venture.
C) demand.
D) production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The relationship between physical output and the quantity of capital and labor used in producing goods and services is called the
A) production function.
B) opportunity function.
C) input function.
D) linear demand function.
A) production function.
B) opportunity function.
C) input function.
D) linear demand function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
When is the marginal physical product of labor negative?
A) When total output declines with the hiring of additional labor
B) When diminishing marginal returns set in
C) When marginal cost is negative
D) When marginal cost is declining
A) When total output declines with the hiring of additional labor
B) When diminishing marginal returns set in
C) When marginal cost is negative
D) When marginal cost is declining

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The slope of the production function reflects the
A) marginal physical product.
B) average physical product.
C) cost of inputs.
D) selling price of the output.
A) marginal physical product.
B) average physical product.
C) cost of inputs.
D) selling price of the output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which one of the following is TRUE?
A) There is no opportunity cost involved in generating electricity.
B) Hydroelectric power and nuclear power entail relatively high fixed costs.
C) Hydroelectric power and nuclear power entail relatively high variable costs.
D) Managers of electric utilities make all of their long-term decisions based on short-run costs.
A) There is no opportunity cost involved in generating electricity.
B) Hydroelectric power and nuclear power entail relatively high fixed costs.
C) Hydroelectric power and nuclear power entail relatively high variable costs.
D) Managers of electric utilities make all of their long-term decisions based on short-run costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In the table below, what is the marginal cost of producing the first unit? 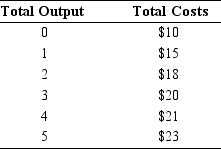
A) $5
B) $3
C) $2
D) $1

A) $5
B) $3
C) $2
D) $1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In the table below, what is the marginal cost of producing the fifth unit? 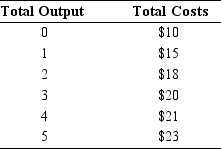
A) $5
B) $3
C) $2
D) $1

A) $5
B) $3
C) $2
D) $1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Costs that do not vary as output varies are
A) total variable costs.
B) total fixed costs.
C) total implicit costs.
D) total explicit costs.
A) total variable costs.
B) total fixed costs.
C) total implicit costs.
D) total explicit costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which one of the following is TRUE?
A) Managers who make decisions on the margin are ignoring the long-run perspective.
B) The short run is the period of time in which the selling price of the product does not vary.
C) In the long run, all costs are marginal costs.
D) Average fixed cost equals the sum of average total cost and average variable cost.
A) Managers who make decisions on the margin are ignoring the long-run perspective.
B) The short run is the period of time in which the selling price of the product does not vary.
C) In the long run, all costs are marginal costs.
D) Average fixed cost equals the sum of average total cost and average variable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Table 5.5
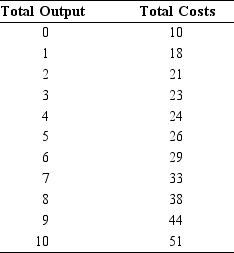
-Using Table 5.5, we see that when output is 4 units, average total cost equals
A) 24.
B) 14.
C) 10.
D) 6.

-Using Table 5.5, we see that when output is 4 units, average total cost equals
A) 24.
B) 14.
C) 10.
D) 6.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Table 5.5

-In Table 5.5, total fixed costs are
A) 10.
B) 8.
C) 5.
D) 0.

-In Table 5.5, total fixed costs are
A) 10.
B) 8.
C) 5.
D) 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Table 5.5

-In Table 5.5, when output is 8 units, average variable costs are
A) 4.75.
B) 3.50.
C) 1.25.
D) 4.50.

-In Table 5.5, when output is 8 units, average variable costs are
A) 4.75.
B) 3.50.
C) 1.25.
D) 4.50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Table 5.5

-In Table 5.5, the marginal cost of the ninth unit is
A) 4.
B) 5.
C) 6.
D) 7.

-In Table 5.5, the marginal cost of the ninth unit is
A) 4.
B) 5.
C) 6.
D) 7.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Table 5.5

-In Table 5.5, the average total cost at nine units is
A) 7.0.
B) 4.9.
C) 3.1.
D) 1.0.

-In Table 5.5, the average total cost at nine units is
A) 7.0.
B) 4.9.
C) 3.1.
D) 1.0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Table 5.5

-In Table 5.5, the marginal cost of the third unit is
A) 4.
B) 3.
C) 2.
D) 1.

-In Table 5.5, the marginal cost of the third unit is
A) 4.
B) 3.
C) 2.
D) 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Table 5.5

-In Table 5.5, the marginal cost of the tenth unit is
A) 4.
B) 5.
C) 6.
D) 7.

-In Table 5.5, the marginal cost of the tenth unit is
A) 4.
B) 5.
C) 6.
D) 7.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Costs which do not vary with the amount a business produces are referred to as
A) fixed costs.
B) variable costs.
C) total costs.
D) opportunity costs.
A) fixed costs.
B) variable costs.
C) total costs.
D) opportunity costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Total costs divided by the quantity of production is referred to as
A) average fixed cost.
B) average variable cost.
C) marginal cost.
D) average total cost.
A) average fixed cost.
B) average variable cost.
C) marginal cost.
D) average total cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
When does marginal cost begin to increase?
A) When total cost begins to increase
B) When total cost begins to decrease
C) When marginal physical product starts to decline
D) When opportunity cost starts to decline
A) When total cost begins to increase
B) When total cost begins to decrease
C) When marginal physical product starts to decline
D) When opportunity cost starts to decline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Average total cost is equal to
A) the sum of average variable cost and total variable cost.
B) the sum of average fixed cost and total fixed cost.
C) the sum of average fixed cost and average variable cost.
D) the difference between average fixed cost and average variable cost.
A) the sum of average variable cost and total variable cost.
B) the sum of average fixed cost and total fixed cost.
C) the sum of average fixed cost and average variable cost.
D) the difference between average fixed cost and average variable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Table 5.6
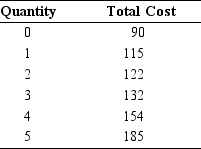
-Refer to Table 5.6. What is the average total cost of producing two units?
A) 7
B) 16
C) 45
D) 61

-Refer to Table 5.6. What is the average total cost of producing two units?
A) 7
B) 16
C) 45
D) 61

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Table 5.6

-Refer to Table 5.6. What is the marginal cost of producing the third unit?
A) 10
B) 25
C) 90
D) 115

-Refer to Table 5.6. What is the marginal cost of producing the third unit?
A) 10
B) 25
C) 90
D) 115

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Table 5.6

-Refer to Table 5.6. What is the marginal cost of producing the fourth unit?
A) 10
B) 22
C) 25
D) 154

-Refer to Table 5.6. What is the marginal cost of producing the fourth unit?
A) 10
B) 22
C) 25
D) 154

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Table 5.6

-Refer to Table 5.6. What is the average total cost of producing five units?
A) 185
B) 180
C) 37
D) 31

-Refer to Table 5.6. What is the average total cost of producing five units?
A) 185
B) 180
C) 37
D) 31

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which one of the following is TRUE?
A) Total cost does not depend on the level of output.
B) Total fixed cost does not depend on the level of output.
C) Variable cost does not depend on the level of output.
D) Marginal cost does not depend on the level of output.
A) Total cost does not depend on the level of output.
B) Total fixed cost does not depend on the level of output.
C) Variable cost does not depend on the level of output.
D) Marginal cost does not depend on the level of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which one of the following is TRUE?
A) Marginal cost increases as marginal physical product decreases.
B) Marginal cost decreases as marginal product decreases.
C) Total cost is the sum of marginal cost plus total variable cost.
D) Total cost is the difference between marginal cost and total variable cost.
A) Marginal cost increases as marginal physical product decreases.
B) Marginal cost decreases as marginal product decreases.
C) Total cost is the sum of marginal cost plus total variable cost.
D) Total cost is the difference between marginal cost and total variable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
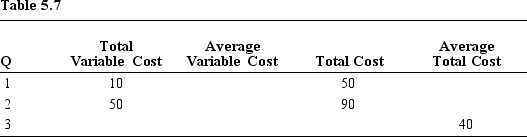
-Refer to Table 5.7. What is the firm's total fixed cost?
A) 10
B) 20
C) 30
D) 40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41

-Refer to Table 5.7. What is the total cost of producing three units?
A) 120
B) 90
C) 50
D) 40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42

-Refer to Table 5.7. What is the total variable cost of producing three units?
A) 40
B) 50
C) 80
D) 120

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43

-Refer to Table 5.7. What is the average total cost of producing one unit?
A) 40
B) 50
C) 80
D) 120

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44

-Refer to Table 5.7. What is the average variable cost of producing one unit?
A) 10
B) 40
C) 50
D) 80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45

-Refer to Table 5.7. What is the marginal cost of producing the second unit?
A) 40
B) 50
C) 90
D) Not enough information provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46

-Refer to Table 5.7. What is the marginal cost of producing the third unit?
A) 50
B) 40
C) 30
D) 20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47

-Refer to Table 5.7. What is true as the firm expands output from two units to three units?
A) Diminishing returns are observed.
B) Average total cost increases.
C) Average total cost decreases.
D) Marginal cost remains constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48

-Refer to Table 5.7. What is the average variable cost of producing two units?
A) 50
B) 25
C) 10
D) Not enough information is provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
An accountant shows an invoice for raw materials to the manager of the firm. They
Are discussing
A) explicit costs.
B) implicit costs.
C) economic profits.
D) the slope of the production function.
Are discussing
A) explicit costs.
B) implicit costs.
C) economic profits.
D) the slope of the production function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
When would a firm's accounting profit differ from its economic profit?
A) When the firm has fixed costs
B) When the firm's marginal cost is increasing
C) When the firm's total explicit costs differ from the opportunity cost of all inputs used
D) When the firm's total revenue does not cover its fixed costs
A) When the firm has fixed costs
B) When the firm's marginal cost is increasing
C) When the firm's total explicit costs differ from the opportunity cost of all inputs used
D) When the firm's total revenue does not cover its fixed costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Short-run cost relationships for a firm are
A) not affected by the productivity of labor.
B) determined by the law of diminishing marginal returns.
C) such that the firm can always lower its average total cost by producing more.
D) such that the firm can always lower its average variable cost by producing more.
A) not affected by the productivity of labor.
B) determined by the law of diminishing marginal returns.
C) such that the firm can always lower its average total cost by producing more.
D) such that the firm can always lower its average variable cost by producing more.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The long-run is
A) the time period in which new workers can be hired.
B) the time period in which new workers can be trained.
C) the time period in which the firm is guaranteed to earn a profit.
D) the time period in which all factors of production can be varied.
A) the time period in which new workers can be hired.
B) the time period in which new workers can be trained.
C) the time period in which the firm is guaranteed to earn a profit.
D) the time period in which all factors of production can be varied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What is on the horizontal axis when we graph a marginal cost curve?
A) Quantity produced
B) Number of workers
C) Marginal product
D) Marginal cost
A) Quantity produced
B) Number of workers
C) Marginal product
D) Marginal cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What is on the horizontal axis when we graph an average total cost curve?
A) Quantity produced
B) Number of workers
C) Marginal product
D) Average total cost
A) Quantity produced
B) Number of workers
C) Marginal product
D) Average total cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The law of diminishing returns explains
A) the behavior of consumers.
B) the behavior of managers.
C) the behavior of workers.
D) the behavior of costs.
A) the behavior of consumers.
B) the behavior of managers.
C) the behavior of workers.
D) the behavior of costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The law of diminishing returns
A) holds both in the short run and the long run.
B) does not hold in the short run because of fixed costs.
C) does not hold in the long run because there are no fixed inputs in the long run.
D) does not apply to goods produced by hand.
A) holds both in the short run and the long run.
B) does not hold in the short run because of fixed costs.
C) does not hold in the long run because there are no fixed inputs in the long run.
D) does not apply to goods produced by hand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In a traditional cost structure, marginal cost
A) is constant.
B) is U-shaped.
C) first rises, then falls.
D) is exactly equal to average total cost.
A) is constant.
B) is U-shaped.
C) first rises, then falls.
D) is exactly equal to average total cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which one of the following would NOT change a firm's marginal cost structure?
A) A change in the wage rate paid to hourly workers.
B) A change in the productivity of each worker.
C) A change in the firm's total fixed cost.
D) A change in the cost of raw materials used to manufacture the product.
A) A change in the wage rate paid to hourly workers.
B) A change in the productivity of each worker.
C) A change in the firm's total fixed cost.
D) A change in the cost of raw materials used to manufacture the product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
If a firm can produce 100 fishing rods at a total cost of $6000 and can produce 150 fishing rods for a total cost of $8000, then the marginal cost of a fishing rod in the quantity range between 100 and 150 is
A) $80.
B) $60.
C) $53.
D) $40.
A) $80.
B) $60.
C) $53.
D) $40.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If a firm can produce 1000 bottles of strawberry essence shampoo at a total cost of $420 and can produce 2000 bottles of strawberry essence shampoo for a total cost of $580, then the marginal cost of a bottle of shampoo in the quantity range between 1000 and 2000 is
A) $0.06.
B) $0.16.
C) $0.42.
D) $0.58.
A) $0.06.
B) $0.16.
C) $0.42.
D) $0.58.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
If a potter can create 10 vases at a total cost $180 and can produce 30 vases for a total cost of $400, then the marginal cost of a vase in the quantity range between 10 and 30 is
A) $11.
B) $13.
C) $18.
D) $40.
A) $11.
B) $13.
C) $18.
D) $40.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which one of the following would affect a firm's fixed costs?
A) A change in the wage rate
B) A change in the cost of raw material inputs
C) A change in the cost of packaging each unit of output
D) A change in the licensing fee that must be paid to operate as a legal business
A) A change in the wage rate
B) A change in the cost of raw material inputs
C) A change in the cost of packaging each unit of output
D) A change in the licensing fee that must be paid to operate as a legal business

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which firms will have the easiest time obtaining additional financing?
A) Those that have low costs
B) Those that have high and steady profits
C) Those that are organized as sole proprietorships
D) Those that are organized as partnerships
A) Those that have low costs
B) Those that have high and steady profits
C) Those that are organized as sole proprietorships
D) Those that are organized as partnerships

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Economic theory expects that firms which survive in the marketplace
A) have cheated their competitors.
B) have cheated their customers.
C) have focused on the goal of maximizing profits.
D) have focused on the goal of treating their employees well.
A) have cheated their competitors.
B) have cheated their customers.
C) have focused on the goal of maximizing profits.
D) have focused on the goal of treating their employees well.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The largest stock exchange in the U.S. is the
A) NYSE.
B) NASDAQ.
C) FTSE.
D) S & P 500.
A) NYSE.
B) NASDAQ.
C) FTSE.
D) S & P 500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The second largest stock exchange in the U.S. is the
A) NYSE.
B) NASDAQ.
C) FTSE.
D) S & P 500.
A) NYSE.
B) NASDAQ.
C) FTSE.
D) S & P 500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The net change reported for each stock in the daily newspaper is
A) the number of people who bought that stock.
B) the number of people who sold that stock.
C) the difference between the highest price of the day and the lowest price of the day.
D) the difference between today's closing price and yesterday's closing price.
A) the number of people who bought that stock.
B) the number of people who sold that stock.
C) the difference between the highest price of the day and the lowest price of the day.
D) the difference between today's closing price and yesterday's closing price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The yield reported for a stock in the daily newspaper is
A) its annual dividend divided by its closing price.
B) its earnings per share divided by its closing price.
C) the increase in the day's stock price divided by the opening price.
D) the increase in the day's stock price divided by the closing price.
A) its annual dividend divided by its closing price.
B) its earnings per share divided by its closing price.
C) the increase in the day's stock price divided by the opening price.
D) the increase in the day's stock price divided by the closing price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A firm that earns an accounting profit above the normal rate of return
A) will not be able to stay in business.
B) is earning a negative economic profit.
C) is earning a positive economic profit.
D) is not covering all of the opportunity costs it incurs.
A) will not be able to stay in business.
B) is earning a negative economic profit.
C) is earning a positive economic profit.
D) is not covering all of the opportunity costs it incurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Financial investors prefer to invest their funds in firms that
A) have high levels of fixed cost and low levels of variable cost.
B) have high levels of variable cost and low levels of fixed cost.
C) steadily earn a high profit.
D) can charge prices above the equilibrium price.
A) have high levels of fixed cost and low levels of variable cost.
B) have high levels of variable cost and low levels of fixed cost.
C) steadily earn a high profit.
D) can charge prices above the equilibrium price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A firm that focuses on earning a profit will be concerned with
A) choosing the output level that minimizes total cost.
B) maximizing the difference between revenues and costs.
C) converting its U-shaped marginal cost curve into a vertical line.
D) converting its U-shaped marginal cost curve into a horizontal line.
A) choosing the output level that minimizes total cost.
B) maximizing the difference between revenues and costs.
C) converting its U-shaped marginal cost curve into a vertical line.
D) converting its U-shaped marginal cost curve into a horizontal line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In earning a profit, a firm
A) must underpay its employees.
B) must overcharge its customers.
C) will attract financial investors.
D) escapes the law of diminishing marginal returns.
A) must underpay its employees.
B) must overcharge its customers.
C) will attract financial investors.
D) escapes the law of diminishing marginal returns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The primary disadvantage of the sole proprietorship and the partnership as forms of business organization is that the business owner is exposed to _________ _________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
In a corporation, profits are distributed to shareholders in the form of _________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The income of _________ is subject to double taxation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A limited liability company (LLC) enjoys the _________ advantages of a partnership.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The goal of a business firm is to _________ _________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A firm's _________ _________ shows the relationship between the amount of labor input used and the amount of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The slope of the production function shows the _________ _________ _________ of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Average physical product is equal to total output divided by the number of _________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 140 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



