Deck 9: The Normal Distribution
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/89
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: The Normal Distribution
1
Which of the following distributions is not continuous?
A) normal distribution
B) uniform distribution
C) exponential distribution
D) binomial distribution
A) normal distribution
B) uniform distribution
C) exponential distribution
D) binomial distribution
binomial distribution
2
Which of the following is always true for a normal distribution?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)
3
If we are using the normal approximation to determine the probability of at most 28 successes in a binomial distribution , the normal distribution probability that is used to make the estimate is
A) .
B) .
C) .
D) .
A) .
B) .
C) .
D) .
.
4
When considering area under the standard normal curve, decide whether the area to the right of is bigger than, smaller than, or equal to the area to the right of .
A) bigger than
B) smaller than
C) equal to
A) bigger than
B) smaller than
C) equal to

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When considering area under the standard normal curve, decide whether the area to the left of is bigger than, smaller than, or equal to the area to the right of .
A) equal to
B) bigger than
C) smaller than
A) equal to
B) bigger than
C) smaller than

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
When considering area under the standard normal curve, decide whether the area to the left of is bigger than, smaller than, or equal to the area to the right of .
A) smaller than
B) bigger than
C) equal to
A) smaller than
B) bigger than
C) equal to

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
When considering area under the standard normal curve, decide whether the area to the left of is bigger than, smaller than, or equal to the area to the right of .
A) smaller than
B) bigger than
C) equal to
A) smaller than
B) bigger than
C) equal to

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When considering area under the standard normal curve, decide whether the area to the left of is bigger than, smaller than, or equal to the area to the right of .
A) bigger than
B) smaller than
C) equal to
A) bigger than
B) smaller than
C) equal to

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When considering area under the standard normal curve, decide whether the area between and is bigger than, smaller than, or equal to the area between and .
A) bigger than
B) smaller than
C) equal to
A) bigger than
B) smaller than
C) equal to

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When considering area under the standard normal curve, decide whether the area between and is bigger than, smaller than, or equal to the area between and .
A) equal to
B) bigger than
C) smaller than
A) equal to
B) bigger than
C) smaller than

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
When considering area under the standard normal curve, decide whether the area between and is bigger than, smaller than, or equal to the area between and .
A) smaller than
B) bigger than
C) equal to
A) smaller than
B) bigger than
C) equal to

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
For the uniform distribution pictured below, the probability equals 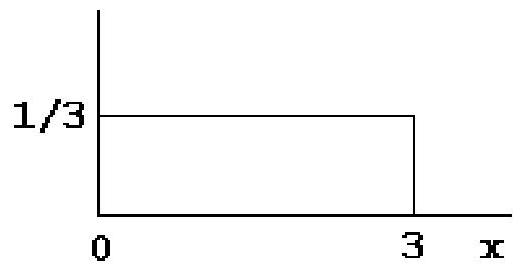
A) .
B) 1 .
C) 1.3 .
D) none of these

A) .
B) 1 .
C) 1.3 .
D) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
For the uniform distribution pictured below, the probability equals 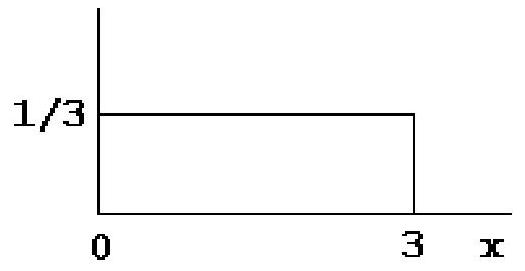
A) 0 .
B) .
C) .
D) none of these

A) 0 .
B) .
C) .
D) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
For the uniform distribution pictured below, the probability equals 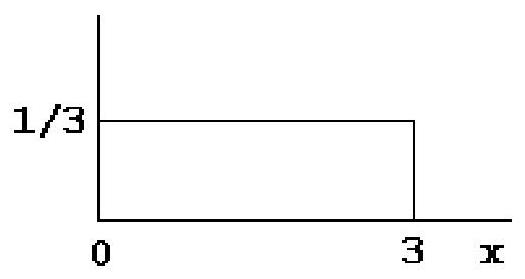
A) .
B) 1 .
C) .
D) none of these

A) .
B) 1 .
C) .
D) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The area to the right of is equal to
A) 0.3413 .
B) 0.8413 .
C) 0.6816 .
D) 0.1587 .
A) 0.3413 .
B) 0.8413 .
C) 0.6816 .
D) 0.1587 .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
To determine the probability of obtaining exactly 20 successes in 50 trials with , we should use
A) the binomial formula.
B) the Poisson formula.
C) the normal approximation to the binomial distribution.
D) the normal table.
A) the binomial formula.
B) the Poisson formula.
C) the normal approximation to the binomial distribution.
D) the normal table.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The probability of obtaining exactly 20 successes in 50 trials
A) is equal to 0 .
B) can be approximated by using the normal table with between 19.5 and 20.5.
C) can only be approximated by the binomial formula.
D) cannot be found using the normal table.
A) is equal to 0 .
B) can be approximated by using the normal table with between 19.5 and 20.5.
C) can only be approximated by the binomial formula.
D) cannot be found using the normal table.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The problem that is solved by using the standard formula table and the formula
A) involves Table V.
B) involves the normal approximation to the binomial distribution.
C) originally involved the normal approximation.
D) originally involved the Poisson distribution.
A) involves Table V.
B) involves the normal approximation to the binomial distribution.
C) originally involved the normal approximation.
D) originally involved the Poisson distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In a binomial distribution with 10 trials, which of the following is true?
A)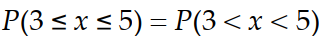
B)
C)
D)
A)
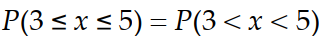
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If is a normal random variable with and , then the probability that is not between 44 and 56 is
A) 0.6826 .
B) 0.3413 .
C) 0.8413 .
D) 0.3174 .
A) 0.6826 .
B) 0.3413 .
C) 0.8413 .
D) 0.3174 .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The graph shows the distribution of a continuous random variable that takes on values on the continuous interval from -2 to 2 . Find the probability that this random variable will take on the value indicated.
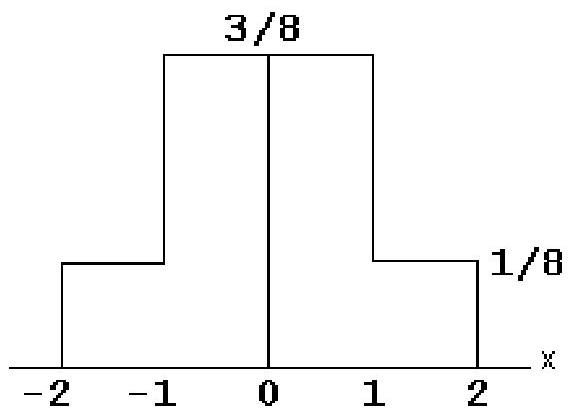
-Between -1 and 1

-Between -1 and 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The graph shows the distribution of a continuous random variable that takes on values on the continuous interval from -2 to 2 . Find the probability that this random variable will take on the value indicated.

-Between and

-Between and

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The graph shows the distribution of a continuous random variable that takes on values on the continuous interval from -2 to 2 . Find the probability that this random variable will take on the value indicated.

-Between -2 and -1

-Between -2 and -1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Find the standard normal-curve area indicated using the normal table.
-Between and
-Between and

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Find the standard normal-curve area indicated using the normal table.
-To the left of
-To the left of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Find the standard normal-curve area indicated using the normal table.
-To the left of
-To the left of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If a random variable has the normal distribution with and , find the probability that it will take on the indicated value.
-Less than 32
-Less than 32

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If a random variable has the normal distribution with and , find the probability that it will take on the indicated value.
-Between 31 and 35
-Between 31 and 35

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If a random variable has the normal distribution with and , find the probability that it will take on the indicated value.
-Between 24 and 28
-Between 24 and 28

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Find the following values.
-z0.05
-z0.05

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Find the following values.
-z0.45
-z0.45

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Find the following values.
-z0.65
-z0.65

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Find the following values.
-z0.90
-z0.90

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Find if the normal curve area to the right of is 0.8997 .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Find if the normal curve area to the left of is 0.1611 .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A normal distribution has mean . If of the area under the curve is to the left of 54 , find the area to the right of 64.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A normal distribution has mean . If of the area under the curve is to the left of 54 , find the area between 58 and 63 .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The number of ounces of soda that a vending machine dispenses per cup is normally distributed with a mean of 12 ounces and a standard deviation of 4 ounces.
-Find the probability that more than 16 ounces is dispensed in a cup.
-Find the probability that more than 16 ounces is dispensed in a cup.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The number of ounces of soda that a vending machine dispenses per cup is normally distributed with a mean of 12 ounces and a standard deviation of 4 ounces.
-Find the probability that between 15 and 18 ounces are dispensed in a cup.
-Find the probability that between 15 and 18 ounces are dispensed in a cup.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The number of ounces of soda that a vending machine dispenses per cup is normally distributed with a mean of 12 ounces and a standard deviation of 4 ounces.
-Find the number of ounces above which of the dispensed sodas will fall. Round to the nearest tenth.
-Find the number of ounces above which of the dispensed sodas will fall. Round to the nearest tenth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
An electronics firm believes that of the new products they market will be successful. If the company markets 80 products in the next 5 years, find the probability that in that time
-at least 60 products will be successful.
-at least 60 products will be successful.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
An electronics firm believes that of the new products they market will be successful. If the company markets 80 products in the next 5 years, find the probability that in that time
-at most 50 products will be successful.
-at most 50 products will be successful.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
An electronics firm believes that of the new products they market will be successful. If the company markets 80 products in the next 5 years, find the probability that in that time
-between 55 and 59 products, inclusive, will be successful.
-between 55 and 59 products, inclusive, will be successful.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A supermarket manager has determined that the amount of time customers spend in the supermarket is approximately normally distributed with a mean of 45 minutes and a standard deviation of 6 minutes.
-Find the probability that a customer spends less than 48 minutes in the supermarket.
-Find the probability that a customer spends less than 48 minutes in the supermarket.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A supermarket manager has determined that the amount of time customers spend in the supermarket is approximately normally distributed with a mean of 45 minutes and a standard deviation of 6 minutes.
-Find the probability that a customer spends between 39 and 43 minutes in the supermarket.
-Find the probability that a customer spends between 39 and 43 minutes in the supermarket.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A supermarket manager has determined that the amount of time customers spend in the supermarket is approximately normally distributed with a mean of 45 minutes and a standard deviation of 6 minutes.
-Find the number of minutes, , for which the probability that a customer spends less than minutes in the supermarket is 0.10 . Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
-Find the number of minutes, , for which the probability that a customer spends less than minutes in the supermarket is 0.10 . Round your answer to the nearest tenth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
It has been estimated that of the televisions that a manufacturer makes need repairs in the first three years of operation. A new hotel buys 90 televisions from this company. Find the probability that in the first three years of operation
-less than 32 of the televisions need repairs.
-less than 32 of the televisions need repairs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
It has been estimated that of the televisions that a manufacturer makes need repairs in the first three years of operation. A new hotel buys 90 televisions from this company. Find the probability that in the first three years of operation
-between 38 and 42 of the televisions, inclusive, need repairs.
-between 38 and 42 of the televisions, inclusive, need repairs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The waiting time in a doctor's office has an exponential distribution with minutes. Find the probability that
-a patient has to wait between 0 and 30 minutes.
-a patient has to wait between 0 and 30 minutes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The waiting time in a doctor's office has an exponential distribution with minutes. Find the probability that
-a patient has to wait between 35 and 50 minutes.
-a patient has to wait between 35 and 50 minutes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Find the indicated normal-curve area using the normal table.
-Between and
-Between and

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Find the indicated normal-curve area using the normal table.
-Between and
-Between and

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Find the indicated normal-curve area using the normal table.
-Between and
-Between and

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Find the indicated normal-curve area using the normal table.
-Between and
-Between and

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Find the indicated normal-curve area using the normal table.
-To the left of .
-To the left of .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Find the indicated normal-curve area using the normal table.
-Between and .
-Between and .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Find the indicated normal-curve area using the normal table.
-Between and .
-Between and .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Find if the normal curve area to the left of is 0.3015.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Find if the normal curve area between 0 and is 0.4345 .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Find if the normal curve area between and is 0.9512 .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Find if the normal curve area to the left of is 0.8962 .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Find if the normal curve area to the right of is 0.3483 .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Find if the normal curve area to the right of is 0.8665 .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A salesperson knows that of her presentations result in sales. Find the probabilities that in the next 60 presentations}
-at least 9 result in sales.
-at least 9 result in sales.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A salesperson knows that of her presentations result in sales. Find the probabilities that in the next 60 presentations}
-between 14 and 18, inclusive, result in sales.
-between 14 and 18, inclusive, result in sales.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A machine pours beer into . bottles. Experience has shown that the number of ounces poured is normally distributed with a standard deviation of 1.5 ounces. Find the probabilities that the amount of beer the machine will pour into the next bottle will be
-more than 17 ounces.
-more than 17 ounces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A machine pours beer into . bottles. Experience has shown that the number of ounces poured is normally distributed with a standard deviation of 1.5 ounces. Find the probabilities that the amount of beer the machine will pour into the next bottle will be
-between 12 and 14 ounces.
-between 12 and 14 ounces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The annual number of earthquakes in a certain region is a random variable having approximately a normal distribution with . What is the standard deviation of this distribution if the probability is 0.70 that there will be at least 14 earthquakes? Round answer to the nearest tenth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The probability is 0.26 that a cloud seeded with silver iodide will fail to show spectacular growth. Use the normal approximation to the binomial distribution to find the probability that among 50 clouds seeded with silver iodide only 13 will fail to show spectacular growth. Round answer to the nearest hundredth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The equation can serve as the probability density function of a random variable that takes on values on the interval from 1 to 8 .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The equation can serve as a probability density of a random variable that takes on values on the interval from 1 to 3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The continuity correction is always used in the problems involving the normal distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The normal approximation to the binomial distribution applies in problems that originally involve the normal distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The value such that the area to the left of is 0.05 is located to the left of zero on the -axis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
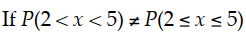 then must be a discrete random variable.
then must be a discrete random variable. 
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
If the area in the standard normal distribution is on the left side of zero, then that area has a negative value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
It is never desirable to use the normal approximation to the binomial distribution to solve binomial problems that can be solved by using Table V.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The formula is used to convert any normally distributed variable to one which has a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The formula finds the standard deviation in problems which originally involve the binomial distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The mean of every normal distribution is equal to 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



