Deck 32: Behavioral Biology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/27
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 32: Behavioral Biology
1
Foraging bees communicate with other bees in a waggle dance to give information about the food. The important cue in the dance that conveys information about the required flight direction to the food source relative to the hive-sun direction is the
A) angle between the food source and the hive in reference to the sun.
B) angle between the waggle run and the vertical axis within the hive.
C) angle between the waggle run in reference to the hive-sun angle.
D) angle between the waggle run in reference to the direction north from the hive.
E) speed of the waggle dance.
A) angle between the food source and the hive in reference to the sun.
B) angle between the waggle run and the vertical axis within the hive.
C) angle between the waggle run in reference to the hive-sun angle.
D) angle between the waggle run in reference to the direction north from the hive.
E) speed of the waggle dance.
angle between the waggle run and the vertical axis within the hive.
2
Which of the following is an appropriate interpretation for these graphs?
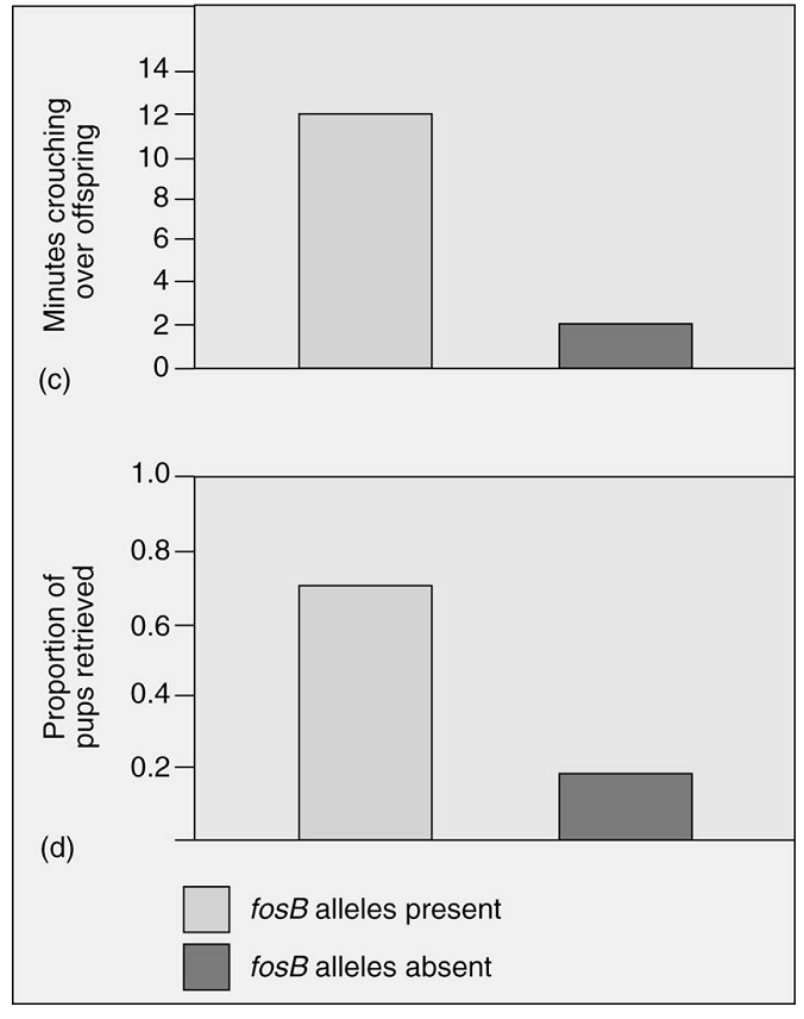 Maternal care (as measured by minutes crouching over offspring and proportion of pups retrieved) in female mice that have the fosB allele is
Maternal care (as measured by minutes crouching over offspring and proportion of pups retrieved) in female mice that have the fosB allele is
A) less than the maternal care given by female mice without the fosB allele.
B) greater than the maternal care given by female mice without the fosB allele.
C) the same as the maternal care given by female mice without the fosB allele.
D) less than the maternal care given by female mice without the fosB allele; however, the graphs depict only minor differences, which are most likely not significant.
E) not possible to determine from the data.
 Maternal care (as measured by minutes crouching over offspring and proportion of pups retrieved) in female mice that have the fosB allele is
Maternal care (as measured by minutes crouching over offspring and proportion of pups retrieved) in female mice that have the fosB allele isA) less than the maternal care given by female mice without the fosB allele.
B) greater than the maternal care given by female mice without the fosB allele.
C) the same as the maternal care given by female mice without the fosB allele.
D) less than the maternal care given by female mice without the fosB allele; however, the graphs depict only minor differences, which are most likely not significant.
E) not possible to determine from the data.
greater than the maternal care given by female mice without the fosB allele.
3
A friend of yours is wondering about the differences between the words orientation and navigation when these two terms are used in descriptions of bird migrations. Since you have studied and know something about animal behavior, what do you tell your friend?
A) Orientation is adjusting a bearing, while navigation is actually following a bearing.
B) Orientation and navigation are used interchangeably when referring to avian migrations.
C) Orientation is following a bearing, while navigation is setting or adjusting a bearing.
D) Orientation is following the sun in the day as starling do, while navigation is following a bearing with a small amount of magnetite, which is found in the heads of some migratory birds.
E) Orientation is the ability to find true east, navigation is the ability to find a bearing while crossing water.
A) Orientation is adjusting a bearing, while navigation is actually following a bearing.
B) Orientation and navigation are used interchangeably when referring to avian migrations.
C) Orientation is following a bearing, while navigation is setting or adjusting a bearing.
D) Orientation is following the sun in the day as starling do, while navigation is following a bearing with a small amount of magnetite, which is found in the heads of some migratory birds.
E) Orientation is the ability to find true east, navigation is the ability to find a bearing while crossing water.
Orientation is following a bearing, while navigation is setting or adjusting a bearing.
4
Which of the following is the best interpretation of the graph below of mussel size (x-axis) versus energy gain (line graph, left y-axis), and number of mussels eaten per day (histogram, right y-axis)? 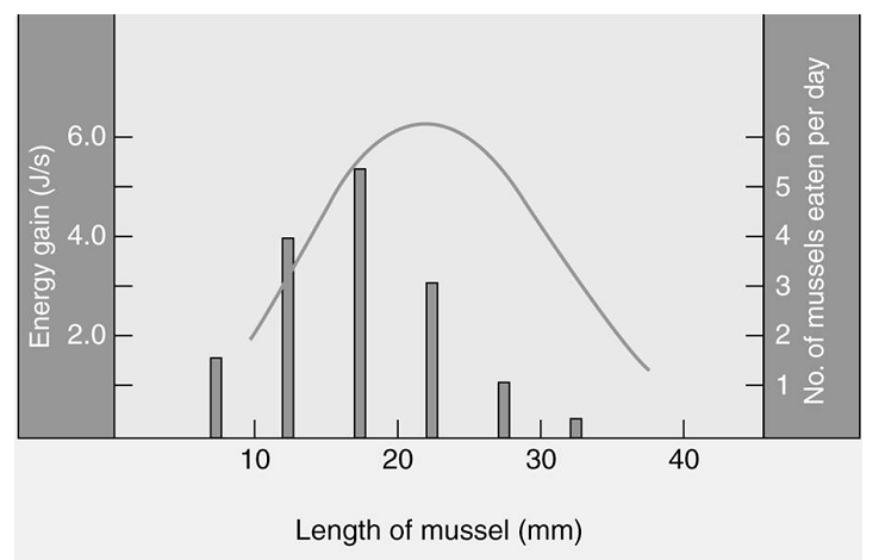
A) Mussels are selected as food sources by crabs.
B) Crabs select mussels in a way that maximizes their energy gain.
C) Mussel size does not seem to be a good predictor as to which mussel hungry crabs will select.
D) Crabs tend to consume most of the largest mussels.
E) Crabs prefer the mussels with the smallest length for their food resources.

A) Mussels are selected as food sources by crabs.
B) Crabs select mussels in a way that maximizes their energy gain.
C) Mussel size does not seem to be a good predictor as to which mussel hungry crabs will select.
D) Crabs tend to consume most of the largest mussels.
E) Crabs prefer the mussels with the smallest length for their food resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Your study buddy asks, "would you please explain the difference between home range and territory?" What is the best response?
A) Territory is the entire area that an animal can utilize for its resources, such as shelter, food, and mates. Home range is near its nest or den.
B) Territory is the area that an animal can utilize for its resources, such as shelter, food and mates and will defend against other members of its species. Home range is near its nest or den.
C) Territory is the area that an animal can utilize for its resources, such as shelter, food and mates, and will defend against other members of its species. Home range is the area that an animal may roam over on a daily basis.
D) Territory is the area that an animal can utilize for its resources, such as shelter, food and mates, and will defend against others members of its species. Home range is a smaller area within the territory that the animal is found in when it is resting or hiding from predators.
A) Territory is the entire area that an animal can utilize for its resources, such as shelter, food, and mates. Home range is near its nest or den.
B) Territory is the area that an animal can utilize for its resources, such as shelter, food and mates and will defend against other members of its species. Home range is near its nest or den.
C) Territory is the area that an animal can utilize for its resources, such as shelter, food and mates, and will defend against other members of its species. Home range is the area that an animal may roam over on a daily basis.
D) Territory is the area that an animal can utilize for its resources, such as shelter, food and mates, and will defend against others members of its species. Home range is a smaller area within the territory that the animal is found in when it is resting or hiding from predators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Pea fowl (peacocks and peahens) show sexual dimorphism -- males have long blue-green tail feathers with eyespots, while females have short brown tail feathers. Which statement best describes the graphed data about peacocks? 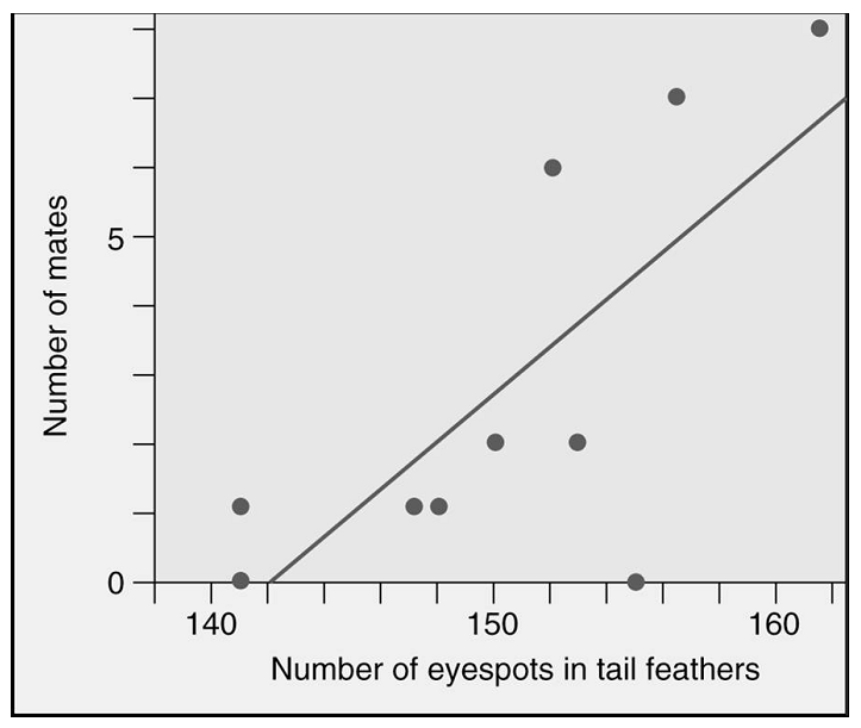
A) There are no peacocks with less than 140 eyespots.
B) The fewer eyespots that a peacock has in his tail, the more mates he attracts.
C) Actually eyespots have very little to do with mate-attracting activities.
D) The more eyespots that a peacock has in his tail, the more mates he attracts.
E) There are no peacocks with more than 165 eyespots.

A) There are no peacocks with less than 140 eyespots.
B) The fewer eyespots that a peacock has in his tail, the more mates he attracts.
C) Actually eyespots have very little to do with mate-attracting activities.
D) The more eyespots that a peacock has in his tail, the more mates he attracts.
E) There are no peacocks with more than 165 eyespots.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The development of normal maternal behavior in female mice depends on interactions between the female and her young and the presence of a gene called fosB. In mice with functional fosB genes, a sequence of events occurs after babies are born.
Arrange the events in their normal sequence following the birth of baby mice for a wildtype female.
A) Female inspects newborns.
B) Auditory, olfactory, and tactile signals about the young are sent to the hypothalamus.
C) Neural circuitry within the hypothalamus is modified, facilitating maternal behavior.
D) Female crouches over young and retrieves them if they leave the nest.
E) The gene fosB is activated, producing protein that activates other genes.
Arrange the events in their normal sequence following the birth of baby mice for a wildtype female.
A) Female inspects newborns.
B) Auditory, olfactory, and tactile signals about the young are sent to the hypothalamus.
C) Neural circuitry within the hypothalamus is modified, facilitating maternal behavior.
D) Female crouches over young and retrieves them if they leave the nest.
E) The gene fosB is activated, producing protein that activates other genes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
It is 6:00 PM and the sun is due west of the hive. A honeybee has just returned to its hive from a patch of flowers that are due north of the hive. Which of the following best describes the type of waggle dance that this bee should perform? Note: The waggle run is the straight part of the dance.
A) The waggle run should be straight down the vertical axis.
B) The waggle run should be straight up the vertical axis.
C) The waggle run should be 90 to the left of the vertical axis.
D) The waggle run should be 90 to the right of the vertical axis.
E) The waggle run should be 45 to the right of the vertical axis.
A) The waggle run should be straight down the vertical axis.
B) The waggle run should be straight up the vertical axis.
C) The waggle run should be 90 to the left of the vertical axis.
D) The waggle run should be 90 to the right of the vertical axis.
E) The waggle run should be 45 to the right of the vertical axis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In which of the following examples has communication occurred? (Check all that apply.)
A) A bird gives an alarm call when a hawk approaches, but no other birds are in the area.
B) A bird sings from the top of a tree in its territory attracting a female of the same species to it.
C) A bird sings from the top of a tree in its territory keeping other birds of the same species from trespassing.
D) An ant lays down a trail of pheromones that other ants follow.
E) A waggle dancing bee feeds some of the nectar she is carrying to bees attending her dance; they now know what type of flowers she has visited.
A) A bird gives an alarm call when a hawk approaches, but no other birds are in the area.
B) A bird sings from the top of a tree in its territory attracting a female of the same species to it.
C) A bird sings from the top of a tree in its territory keeping other birds of the same species from trespassing.
D) An ant lays down a trail of pheromones that other ants follow.
E) A waggle dancing bee feeds some of the nectar she is carrying to bees attending her dance; they now know what type of flowers she has visited.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following statements comparing the naked mole rat social system with social insect societies are true? (Check all that apply.)
A) As with social insect societies, colony members are kin.
B) As with social insect societies, it is based on haplodiploidy.
C) As with social insect societies, there is a division of labor within the colony.
D) As with social insect societies, there is one queen and several reproductive males per colony.
E) Unlike social insect societies, all colony members are diploid.
A) As with social insect societies, colony members are kin.
B) As with social insect societies, it is based on haplodiploidy.
C) As with social insect societies, there is a division of labor within the colony.
D) As with social insect societies, there is one queen and several reproductive males per colony.
E) Unlike social insect societies, all colony members are diploid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Male fruit flies perform a complex mating dance, that includes following the female, vibrating a wing to produce a species-specific song, and picking up chemosensory cues by tapping with the legs and licking with the tongue. What physiological features are likely important for causing this behavior? (Check all that apply.)
A) adaptive value of successful mating
B) brain circuits
C) hormones
D) natural selection
E) performance of phylogenetically-related species
F) sensory neurons on the legs and tongue
G) sperm competition
H) threats of predation during the performance
I) visual system
J) wings and wing muscles
A) adaptive value of successful mating
B) brain circuits
C) hormones
D) natural selection
E) performance of phylogenetically-related species
F) sensory neurons on the legs and tongue
G) sperm competition
H) threats of predation during the performance
I) visual system
J) wings and wing muscles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the studies below provide evidence linking genes and behavior? (Check all that apply.)
A) Fruit flies who are mutant for the genes dunce or rutabaga have impaired learning.
B) Mice that are lacking either the ephrinB3 or the EphA4 gene cannot walk normally, but instead hop like a kangaroo.
C) Two lines of fruit flies were created by repeatedly selecting for high or low aggressive behavior. After multiple generations, the high line was reliably more aggressive than the low line.
D) Twin studies comparing monozygotic and dizygotic twins have found a high heritability for height, although environmental influences like nutrition also play a role.
A) Fruit flies who are mutant for the genes dunce or rutabaga have impaired learning.
B) Mice that are lacking either the ephrinB3 or the EphA4 gene cannot walk normally, but instead hop like a kangaroo.
C) Two lines of fruit flies were created by repeatedly selecting for high or low aggressive behavior. After multiple generations, the high line was reliably more aggressive than the low line.
D) Twin studies comparing monozygotic and dizygotic twins have found a high heritability for height, although environmental influences like nutrition also play a role.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
At a research conference, you meet a graduate student who studies the hormonal underpinnings of mating behavior in two species of squirrel. "It turns out the difference between my two squirrel species is similar to the difference between the prairie and the montane voles," he says. You nod knowingly, and reply...
A) "Oh, so the promiscuous species has a lot of vasopressin and oxytocin receptors in the nucleus accumbus, blocking pair bonding, and the monogamous species doesn't?"
B) "Oh, so the monogamous species has a lot of vasopressin and oxytocin receptors in the nucleus accumbus, promoting pair bonding, and the promiscuous species doesn't?"
C) "Oh, so the polyandrous species has a lot of serotonin and dopamine receptors in the nucleus accumbus, promoting pair bonding, and the promiscuous species doesn't?"
D) "Oh, so the monogamous species has a lot of serotonin and dopamine receptors in the nucleus accumbus, promoting pair bonding, and the promiscuous species doesn't?"
A) "Oh, so the promiscuous species has a lot of vasopressin and oxytocin receptors in the nucleus accumbus, blocking pair bonding, and the monogamous species doesn't?"
B) "Oh, so the monogamous species has a lot of vasopressin and oxytocin receptors in the nucleus accumbus, promoting pair bonding, and the promiscuous species doesn't?"
C) "Oh, so the polyandrous species has a lot of serotonin and dopamine receptors in the nucleus accumbus, promoting pair bonding, and the promiscuous species doesn't?"
D) "Oh, so the monogamous species has a lot of serotonin and dopamine receptors in the nucleus accumbus, promoting pair bonding, and the promiscuous species doesn't?"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Your study buddy is frustrated. "This book says that a single gene can make mice exhibit a certain behavior. That's ridiculous! How can you build any kind of neural circuit with just one gene?" What is your response?
A) "If the book says so it must be true. Ours is not to question why."
B) "Some genes are longer than others, over 1000kb -- they have enough information to encode a full neural circuit."
C) "Mice are a lot simpler than we are, and their brains are smaller. One gene is plenty for them to build a circuit."
D) "What the book really means is: all else being equal, one variant of a gene is associated with higher levels of the behavior than the other variant of the gene. All the other thousands of genes are still needed to develop the brain. But variation in one gene can change how a certain neural circuit will behave."
A) "If the book says so it must be true. Ours is not to question why."
B) "Some genes are longer than others, over 1000kb -- they have enough information to encode a full neural circuit."
C) "Mice are a lot simpler than we are, and their brains are smaller. One gene is plenty for them to build a circuit."
D) "What the book really means is: all else being equal, one variant of a gene is associated with higher levels of the behavior than the other variant of the gene. All the other thousands of genes are still needed to develop the brain. But variation in one gene can change how a certain neural circuit will behave."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A bird sanctuary sometimes takes over the care of eggs or chicks of an endangered duck species if the parents are killed. They are sometimes able to use mothers of farm ducks to cross-foster the chicks, but it doesn't always work. Looking at the following data table, what is the critical period for imprinting in this species? (Note: DAH stands for "days after hatching".)
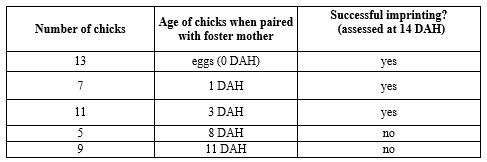
A) The critical period extends from 1-3 DAH.
B) The critical period extends from 3-8 DAH.
C) The critical period ends sometime between 1-3 DAH. We can not determine from this data when the critical period begins.
D) The critical period ends sometime between 3-8 DAH. We can not determine from this data when the critical period begins.

A) The critical period extends from 1-3 DAH.
B) The critical period extends from 3-8 DAH.
C) The critical period ends sometime between 1-3 DAH. We can not determine from this data when the critical period begins.
D) The critical period ends sometime between 3-8 DAH. We can not determine from this data when the critical period begins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A zoo is hand-rearing an endangered species of songbird. What is the best approach to help prepare the males to attract mates?
A) Expose the males to a mentor male bird singing their species' song during the critical period.
B) Expose the males to female pheromones from their species, to initiate development of song circuits during the critical period.
C) Expose the males to each other during the critical period, to initiate development of song circuits during the critical period.
D) Expose the males to a variety of birdsongs during the critical period.
A) Expose the males to a mentor male bird singing their species' song during the critical period.
B) Expose the males to female pheromones from their species, to initiate development of song circuits during the critical period.
C) Expose the males to each other during the critical period, to initiate development of song circuits during the critical period.
D) Expose the males to a variety of birdsongs during the critical period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Based on the animal cognition experiments you have learned about, if you wanted to design a test of animal cognition, what might you include in your experiment? (Check all that apply.)
A) Count the number of individuals in a colony.
B) Create a problem for the animal to solve, like getting a treat out of a box.
C) Determine ahead of time what parameters to record as data, such as how long it takes the animal to retrieve the treat.
D) Determine the hormonal basis of caste differences.
E) Expose the animal to the same scenario again later.
F) Focus on careful quantitative analysis of fixed action patterns.
G) Include a negative control.
H) Include multiple subjects.
I) Measure the frequency of response to sign stimuli.
J) Provide tools for the animal to use.
A) Count the number of individuals in a colony.
B) Create a problem for the animal to solve, like getting a treat out of a box.
C) Determine ahead of time what parameters to record as data, such as how long it takes the animal to retrieve the treat.
D) Determine the hormonal basis of caste differences.
E) Expose the animal to the same scenario again later.
F) Focus on careful quantitative analysis of fixed action patterns.
G) Include a negative control.
H) Include multiple subjects.
I) Measure the frequency of response to sign stimuli.
J) Provide tools for the animal to use.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
One spring, your friend living in Minnesota eagerly sets up her new hummingbird feeders, and is thrilled to watch hummingbirds feeding on the nectar. However, she is disappointed when after just a week or two the hummingbirds disappear. What advice would you give her?
A) Set up a bell (conditioned stimulus) near the feeders so the hummingbirds make an association with the food.
B) Set up flashing red lights that mimic the male neck feathers -- that should attract more males to the area.
C) Set up the feeders again in the fall. The hummingbirds may have briefly traveled through during their annual spring migration.
D) Wait till next year -- hummingbirds are a high-metabolism, semelparous species and have already reproduced and died.
A) Set up a bell (conditioned stimulus) near the feeders so the hummingbirds make an association with the food.
B) Set up flashing red lights that mimic the male neck feathers -- that should attract more males to the area.
C) Set up the feeders again in the fall. The hummingbirds may have briefly traveled through during their annual spring migration.
D) Wait till next year -- hummingbirds are a high-metabolism, semelparous species and have already reproduced and died.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which statement best sums up our understanding of how animals navigate during migration?
A) The mechanisms have been worked out in great detail, from the genes involved, to the brain structures, to the resulting behavior.
B) We have a thorough understanding of orientation but not navigation.
C) We have some understanding of the information different animals rely on (sun, stars, or magnetic fields), and some sensory structures, but beyond that the mechanisms are still mysterious.
D) Animal navigation is a complete mystery.
A) The mechanisms have been worked out in great detail, from the genes involved, to the brain structures, to the resulting behavior.
B) We have a thorough understanding of orientation but not navigation.
C) We have some understanding of the information different animals rely on (sun, stars, or magnetic fields), and some sensory structures, but beyond that the mechanisms are still mysterious.
D) Animal navigation is a complete mystery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Swordtail fish are known for the long extensions on the males' tails. What types of experiments might help you determine whether the females are using visual input about tail length to choose between males? (Check the best three.)
A) Add artificial tails of different lengths to females and determine their response to normal males.
B) Add artificial tails of different lengths to male platys (a similar fish without tail extensions), and measure female response.
C) Create artificial fish models with different size tails and measure female response.
D) Measure hormone levels in males who have different size tails.
E) Measure sperm count in males who have different size tails.
F) Trim the tails of male fish to different lengths and measure female response.
A) Add artificial tails of different lengths to females and determine their response to normal males.
B) Add artificial tails of different lengths to male platys (a similar fish without tail extensions), and measure female response.
C) Create artificial fish models with different size tails and measure female response.
D) Measure hormone levels in males who have different size tails.
E) Measure sperm count in males who have different size tails.
F) Trim the tails of male fish to different lengths and measure female response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What are likely outcomes for a female who is not choosy enough, and has too broad of an acceptance of reproductive signals? (Check all that apply.)
A) Her sons may have low success attracting mates.
B) Her fitness will be improved because she never misses a chance to mate.
C) She may mate with males who are sick with parasites or disease.
D) She may mate with males with less adaptive genes.
E) Her fitness goes up due to increased efficiency by not wasting time in lengthy evaluations.
F) She might inadvertently mate with a different species.
A) Her sons may have low success attracting mates.
B) Her fitness will be improved because she never misses a chance to mate.
C) She may mate with males who are sick with parasites or disease.
D) She may mate with males with less adaptive genes.
E) Her fitness goes up due to increased efficiency by not wasting time in lengthy evaluations.
F) She might inadvertently mate with a different species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Tinbergen observed that after gull nestlings hatch, the parents remove the eggshells from the nest. To understand why (ultimate causation), he painted chicken eggs to resemble gull eggs, which had camouflage coloration to allow them to be inconspicuous against the natural background. He distributed them throughout the area in which the gulls were nesting, placing broken eggshells with their prominent white interiors next to some of the eggs. As a control, he left other camouflaged eggs alone without eggshells. He then noted which eggs were found more easily by crows. Because the crows could use the white interior of a broken eggshell as a cue, they ate more of the camouflaged eggs that were near eggshells. Tinbergen concluded that eggshell removal behavior is adaptive: it reduces predation and thus increases the offspring's chances of survival.
-Rank these experiments from worst to best to study why gulls remove broken eggshells from their nests.
A) Place broken eggshells near white chicken eggs, and record predation by undergraduate students acting as "predators".
B) Place broken eggshells near real gull eggs, and record predation by crows.
C) Place broken eggshells near brown chicken eggs, and record predation by undergraduate students acting as "predators".
D) Place broken eggshells near brown chicken eggs painted with dark brown spots, and record predation by crows.
E) Place broken eggshells near brown chicken eggs painted with dark brown spots, and record predation by undergraduate students acting as "predators".
-Rank these experiments from worst to best to study why gulls remove broken eggshells from their nests.
A) Place broken eggshells near white chicken eggs, and record predation by undergraduate students acting as "predators".
B) Place broken eggshells near real gull eggs, and record predation by crows.
C) Place broken eggshells near brown chicken eggs, and record predation by undergraduate students acting as "predators".
D) Place broken eggshells near brown chicken eggs painted with dark brown spots, and record predation by crows.
E) Place broken eggshells near brown chicken eggs painted with dark brown spots, and record predation by undergraduate students acting as "predators".

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Tinbergen observed that after gull nestlings hatch, the parents remove the eggshells from the nest. To understand why (ultimate causation), he painted chicken eggs to resemble gull eggs, which had camouflage coloration to allow them to be inconspicuous against the natural background. He distributed them throughout the area in which the gulls were nesting, placing broken eggshells with their prominent white interiors next to some of the eggs. As a control, he left other camouflaged eggs alone without eggshells. He then noted which eggs were found more easily by crows. Because the crows could use the white interior of a broken eggshell as a cue, they ate more of the camouflaged eggs that were near eggshells. Tinbergen concluded that eggshell removal behavior is adaptive: it reduces predation and thus increases the offspring's chances of survival.
-What legitimate factors might lead a scientist to do an imperfect version of an experiment, such as using chicken eggs as a stand-in for gull eggs? (Check all that apply.)
A) because the scientist doesn't care about proper procedure
B) the perfect experiment is too expensive
C) the perfect experiment would harm the study species
D) to quickly get preliminary data for a grant
E) ignorance
F) the perfect experiment would take too much time
-What legitimate factors might lead a scientist to do an imperfect version of an experiment, such as using chicken eggs as a stand-in for gull eggs? (Check all that apply.)
A) because the scientist doesn't care about proper procedure
B) the perfect experiment is too expensive
C) the perfect experiment would harm the study species
D) to quickly get preliminary data for a grant
E) ignorance
F) the perfect experiment would take too much time

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Platys and swordtails are related tropical freshwater fish. In studies, researchers have shown that female platys prefer males with swords, even though males of their own species do not have them. What does this suggest about the origin of the swordtail feature?
A) Female preference for swords may have predated the origin of the feature itself.
B) Evolution of swords later led to evolution of female preference for swords.
C) The same gene that causes sword development also causes development of neural circuits for female preference.
D) Adjacent genes on the same chromosome cause sword development and development of neural circuits for female preference.
A) Female preference for swords may have predated the origin of the feature itself.
B) Evolution of swords later led to evolution of female preference for swords.
C) The same gene that causes sword development also causes development of neural circuits for female preference.
D) Adjacent genes on the same chromosome cause sword development and development of neural circuits for female preference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What three features define eusociality? (Check three.)
A) colony resides in an enclosed hive or nest
B) cooperative brood care
C) haplodiploidy
D) insect species only
E) overlap of generations
F) reproductive division of labor
G) reproduction during a mating flight
A) colony resides in an enclosed hive or nest
B) cooperative brood care
C) haplodiploidy
D) insect species only
E) overlap of generations
F) reproductive division of labor
G) reproduction during a mating flight

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which are examples of advantages that different species might have due to living in a group? (Check all that apply.)
A) Wolves in a pack can take down larger prey than those alone.
B) Zebras in a herd have added protection from predators.
C) Because of their social nature, diseases like rabies can spread quickly through a bat colony.
D) A colony of termites can build mounds over 20 feet high, with elaborate tunnels and ventilation systems.
E) A flamingo in a large flock may have trouble competing for food.
A) Wolves in a pack can take down larger prey than those alone.
B) Zebras in a herd have added protection from predators.
C) Because of their social nature, diseases like rabies can spread quickly through a bat colony.
D) A colony of termites can build mounds over 20 feet high, with elaborate tunnels and ventilation systems.
E) A flamingo in a large flock may have trouble competing for food.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What is the probability that identical twins will share the same genetype for genes that influence human behavior?
A) 25%
B) 50%
C) 100%
D) It depends on which genes are being studied
A) 25%
B) 50%
C) 100%
D) It depends on which genes are being studied

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



