Deck 9: Leadership
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/47
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Leadership
1
There are relatively few leadership approaches.
False
2
The earliest studies of leadership tended to focus on leader behaviours.
False
3
The use of leadership traits assumes that the individual leader has a major impact on leadership outputs.
True
4
Researchers from the University of Michigan concluded that employee-centred leaders tended to have more productive work groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The situational contingency approaches to leadership presume that leadership traits or leader behaviours act in conjunction with situational contingencies to determine outputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Fiedler's contingency theory is based on the amount of situational control the leader has over a group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the terminology of Fiedler's leadership theory, a high LPC person is task-motivated or task-oriented.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Hersey and Blanchard's situational leadership model does not focus on the readiness of followers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The substitute for leadership perspective argues that sometimes hierarchical leadership makes essentially no difference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Charismatic leaders have low feelings of self-efficacy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Transactional leadership is necessary for achieving routine performance on which leaders and followers agree.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Transformational leadership is more inspiring to employees than transactional leadership.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Foresight is not required by a servant leader.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Servant leaders seek to identify means for building community among those who work within any given institution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The average age of leaders in large corporations is probably over fifty-five.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
As leaders, senior managers are expected to:
A) use power and influence to achieve personal goals
B) foster work environments conducive to learning and self-renewal
C) promote stability
D) engage in routine interactions.
A) use power and influence to achieve personal goals
B) foster work environments conducive to learning and self-renewal
C) promote stability
D) engage in routine interactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Understanding leadership as a process:
A) involves an understanding of followers
B) does not involve motivating subordinates
C) is only about the person at the top of the organization
D) does not involve communication
A) involves an understanding of followers
B) does not involve motivating subordinates
C) is only about the person at the top of the organization
D) does not involve communication

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
One way of looking at leaders and managers is:
A) managers promote change; leaders promote stability
B) leaders promote change; managers promote stability
C) leaders promote both stability and change
D) neither leaders nor managers are involved with stability
A) managers promote change; leaders promote stability
B) leaders promote change; managers promote stability
C) leaders promote both stability and change
D) neither leaders nor managers are involved with stability

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The managerial grid perspective:
A) is similar to transformational leadership
B) was developed by Bass
C) is a situational contingency approach
D) is similar to the Ohio State studies
A) is similar to transformational leadership
B) was developed by Bass
C) is a situational contingency approach
D) is similar to the Ohio State studies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Leader trait and behavioural approaches assume that traits and behaviours:
A) are equally important with other variables
B) are more important than other variables
C) are caused by other variables
D) explain the romance of leadership
A) are equally important with other variables
B) are more important than other variables
C) are caused by other variables
D) explain the romance of leadership

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In House's path-goal theory, letting subordinates know what is expected is an example of leader:
A) directiveness
B) supportiveness
C) achievement orientation
D) employee-centeredness
A) directiveness
B) supportiveness
C) achievement orientation
D) employee-centeredness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Performance contingent reward behaviour is:
A) the degree to which a leader administers punishment related to performance
B) the degree to which a leader rewards or positively reinforces performance
C) a behavioural theory of leadership
D) a substitute for leadership
A) the degree to which a leader administers punishment related to performance
B) the degree to which a leader rewards or positively reinforces performance
C) a behavioural theory of leadership
D) a substitute for leadership

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Management by exception and laissez-faire behaviours represent which type of leadership?
A) charismatic
B) transformational
C) transactional
D) inspirational
A) charismatic
B) transformational
C) transactional
D) inspirational

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
According to Bass, which is the more realistic way of looking at leadership?
A) In terms of a one-way relationship between leader and follower
B) As a transactional relationship only
C) As a transformational and transactional relationship
D) In terms of organizations influencing followers
A) In terms of a one-way relationship between leader and follower
B) As a transactional relationship only
C) As a transformational and transactional relationship
D) In terms of organizations influencing followers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Substitutes for leadership:
A) have replaced Fiedler's approach
B) rely most heavily on leader training
C) are related to job characteristics
D) involve changing leader LPC scores
A) have replaced Fiedler's approach
B) rely most heavily on leader training
C) are related to job characteristics
D) involve changing leader LPC scores

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In Fiedler's contingency theory, the three variables which define the amount of control a situation allows the leader are: leader-member relations, task structure and:
A) expert power
B) position power
C) complexity
D) leader structuring
A) expert power
B) position power
C) complexity
D) leader structuring

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The advice to match leadership style with leadership situations is most associated with which kind of leadership approach?
A) trait
B) behavioural
C) situational contingencies
D) symbolic
A) trait
B) behavioural
C) situational contingencies
D) symbolic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In House's path-goal theory, letting subordinates know what is expected is an example of leader:
A) directiveness
B) supportiveness
C) achievement orientation
D) employee-centeredness
A) directiveness
B) supportiveness
C) achievement orientation
D) employee-centeredness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Who started the situational contingency era with his contingency theory of leadership effectiveness?
A) Fred Fiedler
B) Robert House
C) Kurt Lewin
D) Bernard Bass
A) Fred Fiedler
B) Robert House
C) Kurt Lewin
D) Bernard Bass

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In alternative cultures, similar leadership behaviours are carried out:
A) in similar ways
B) in different ways
C) by different people
D) by managers only
A) in similar ways
B) in different ways
C) by different people
D) by managers only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Sue manages 16 staff in a major retailing firm. She explains their work duties each week and monitors them closely to make sure they stay on track towards their goals. She is using:
A) a transformational approach
B) a leadership neutralising approach
C) a transactional approach
D) a behavioural approach
A) a transformational approach
B) a leadership neutralising approach
C) a transactional approach
D) a behavioural approach

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A software engineer has just been employed by a well-known software development company. His staff are extremely competent and he requires very little leadership in order for him to achieve his goals. This is an illustration of:
A) a leadership substitute
B) a charismatic response
C) the Ohio State leadership approach
D) an early University of Michigan approach
A) a leadership substitute
B) a charismatic response
C) the Ohio State leadership approach
D) an early University of Michigan approach

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Wendy has been employed with her firm for two years. She is extremely competent and able, and enjoys her work. Which of the following is the best style of leadership for Wendy's manager to use, according to Hersey and Blanchard's theory?
A) The selling style
B) The telling style
C) The delegating style
D) A mixed style
A) The selling style
B) The telling style
C) The delegating style
D) A mixed style

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
John works in a factory on a shampoo production line. His manager watches him closely in case he does not follow the stringent safety procedures that are in place. If something goes wrong, John's manager will take corrective action. This is an example of:
A) laissez-faire leadership
B) active management by exception
C) transformational leadership
D) passive management by exception.
A) laissez-faire leadership
B) active management by exception
C) transformational leadership
D) passive management by exception.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Joy is a very good listener and communicator and engenders trust. She is self-aware and understands where others are coming from. Her powers of persuasion are exemplary. However she holds no formal leadership position. Many of her colleagues believe that she exhibits some of the characteristics of:
A) laissez-fair leadership
B) autocratic leadership
C) servant leadership
D) an informal manager
A) laissez-fair leadership
B) autocratic leadership
C) servant leadership
D) an informal manager

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Your boss decided to send her employees to brainstorming and strategic thinking courses. In doing this, she is emphasising:
A) impression management
B) communication
C) visioning
D) sensitivity to context
A) impression management
B) communication
C) visioning
D) sensitivity to context

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Suzi is finding it very difficult to gain promotion to the board of directors even though she has helped set a new direction for the company and her efforts have enabled the company to expand its market share by 20%. This is an example of:
A) corporate management
B) the 'glass ceiling'
C) employee empowerment
D) contingency theory.
A) corporate management
B) the 'glass ceiling'
C) employee empowerment
D) contingency theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Are people born to be leaders, or can leadership be learned?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What is the difference between a formal leader and an informal leader?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Why have the more recent approaches to leadership tended to move away from traditional leadership characteristics?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Why has the ethical nature of transformational leadership been the subject of much debate and controversy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What is meant by 'servant leadership'?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Are leaders different from managers, and is management different from leadership? Discuss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Is servant leadership relevant in today's world? Discuss, using examples to support your argument.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Discuss the differences and similarities between transactional and transformational leadership.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Visual Diagram Questions
(These diagrams can be used to test understanding of concepts rather than mere recollection. The provision of the diagrams removes the pressure to remember but does draw on the ability to explain a visual image. Instructors should take care if using a mix of other questions with visual diagram questions to ensure that the diagram does not provide answers to other questions in a test or exam.)
-Using the diagram below:
a) Compare and contrast traditional leadership approaches with those of the New Leadership.
b) Give an example of an instance in which little leadership guidance or structure was required to do something at which you were already experienced.
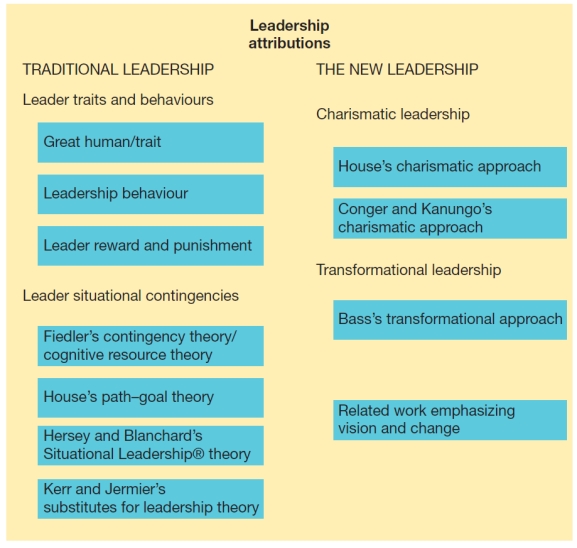
(These diagrams can be used to test understanding of concepts rather than mere recollection. The provision of the diagrams removes the pressure to remember but does draw on the ability to explain a visual image. Instructors should take care if using a mix of other questions with visual diagram questions to ensure that the diagram does not provide answers to other questions in a test or exam.)
-Using the diagram below:
a) Compare and contrast traditional leadership approaches with those of the New Leadership.
b) Give an example of an instance in which little leadership guidance or structure was required to do something at which you were already experienced.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Visual Diagram Questions
(These diagrams can be used to test understanding of concepts rather than mere recollection. The provision of the diagrams removes the pressure to remember but does draw on the ability to explain a visual image. Instructors should take care if using a mix of other questions with visual diagram questions to ensure that the diagram does not provide answers to other questions in a test or exam.)
-Using the following diagram:
a) Define and compare transformational and transactional leadership.
b) Discuss the four dimensions of transformational leadership and explain each of these dimensions with examples.
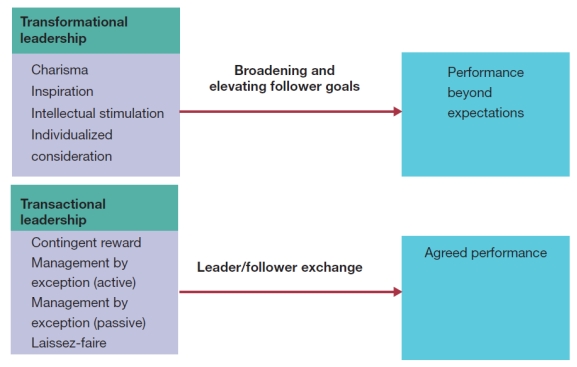
(These diagrams can be used to test understanding of concepts rather than mere recollection. The provision of the diagrams removes the pressure to remember but does draw on the ability to explain a visual image. Instructors should take care if using a mix of other questions with visual diagram questions to ensure that the diagram does not provide answers to other questions in a test or exam.)
-Using the following diagram:
a) Define and compare transformational and transactional leadership.
b) Discuss the four dimensions of transformational leadership and explain each of these dimensions with examples.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



