Deck 1: Science and Statistics
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/17
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: Science and Statistics
1
Which of the following allows us to identify the causes that determine when and why a behavior occurs?
A) Prediction
B) Description
C) Explanation
D) Falsifiability
A) Prediction
B) Description
C) Explanation
D) Falsifiability
Explanation
2
When we question individuals on a topic or topics and then describe their responses, we are using the _____ method, and when we conduct an in-depth study of one or more individuals, we are using the _____ method.
A) case study; survey
B) survey; case study
C) case study; observational
D) observational; case study
A) case study; survey
B) survey; case study
C) case study; observational
D) observational; case study
survey; case study
3
The group of people who participate in a study represents _____, and all of the people about whom a study is meant to generalize represent _____.
A) the sample; the population
B) the population; the sample
C) a positive correlation; a negative correlation
D) a negative correlation; a positive correlation
A) the sample; the population
B) the population; the sample
C) a positive correlation; a negative correlation
D) a negative correlation; a positive correlation
the sample; the population
4
A manipulated independent variable is used in the _____, and a nonmanipulated independent variable is used in the _____.
A) experimental method; quasi-experimental method
B) correlational method; quasi-experimental method
C) experimental method; correlational method
D) quasi-experimental method; experimental method
A) experimental method; quasi-experimental method
B) correlational method; quasi-experimental method
C) experimental method; correlational method
D) quasi-experimental method; experimental method

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 17 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When an uncontrolled, extraneous variable may be responsible for the observed relationship between variables, we say we have:
A) an alternative explanation.
B) a violation of falsifiability
C) a cause and effect relationship.
D) none of the above.
A) an alternative explanation.
B) a violation of falsifiability
C) a cause and effect relationship.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 17 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The manipulated variable in a study is the _____ variable, and the variable measured in a study is the _____ variable.
A) independent variable; dependent variable
B) dependent variable; independent variable
C) controlled; uncontrolled
D) uncontrolled; controlled
A) independent variable; dependent variable
B) dependent variable; independent variable
C) controlled; uncontrolled
D) uncontrolled; controlled

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 17 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In an experimental study, the independent variable is _____ and the dependent variable is _____.
A) manipulated; measured
B) measured; manipulated
C) controlled; uncontrolled
D) uncontrolled; controlled
A) manipulated; measured
B) measured; manipulated
C) controlled; uncontrolled
D) uncontrolled; controlled

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 17 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Predictive methods include:
A) correlational and quasi-experimental methods.
B) only the experimental method.
C) observational, case study, and survey methods.
D) only the quasi-experimental method.
A) correlational and quasi-experimental methods.
B) only the experimental method.
C) observational, case study, and survey methods.
D) only the quasi-experimental method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 17 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Explanatory methods include:
A) correlational and quasi-experimental methods.
B) only the experimental method.
C) observational, case study, and survey methods.
D) only the quasi-experimental method.
A) correlational and quasi-experimental methods.
B) only the experimental method.
C) observational, case study, and survey methods.
D) only the quasi-experimental method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 17 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Control in experimentation involves:
A) manipulating the independent variable.
B) controlling any relevant extraneous variable.
C) randomly assigning participants.
D) all of the above.
A) manipulating the independent variable.
B) controlling any relevant extraneous variable.
C) randomly assigning participants.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 17 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A study was conducted to determine the effects of nicotine on concentration in subjects who are smokers and those who are not. Identify the independent variable and dependent variable in this study. Is the independent variable a manipulated variable or a subject variable? What type of research method is used in this study?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 17 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In a study comparing collaborative group learning with the traditional lecture/discussion method of learning, subjects are randomly assigned to one of the two conditions. Identify the independent variable and dependent variable in this study. Is the independent variable a manipulated variable or a subject variable? What type of research method is used in this study?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 17 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Test the hypothesis presented in the problem below.
Each of the cards below has a number on one side and a letter on the other side. Two of the cards have their letter side showing and two have their number side showing. Here is a rule: "If a card has a vowel on one side, then it has an even number on the other side." In order to check whether the rule is true or false, which card or cards below would you turn over? Turn over only the card or cards that you need to check to be sure.
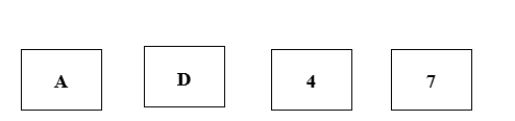 Explain how the answer to the problem relates to hypothesis testing, proof, and disproof.
Explain how the answer to the problem relates to hypothesis testing, proof, and disproof.
Each of the cards below has a number on one side and a letter on the other side. Two of the cards have their letter side showing and two have their number side showing. Here is a rule: "If a card has a vowel on one side, then it has an even number on the other side." In order to check whether the rule is true or false, which card or cards below would you turn over? Turn over only the card or cards that you need to check to be sure.
 Explain how the answer to the problem relates to hypothesis testing, proof, and disproof.
Explain how the answer to the problem relates to hypothesis testing, proof, and disproof.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 17 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Political affiliation is an example of the _____ property of measurement, and measuring length in inches is an example of the _____ property of measurement.
A) magnitude; identity
B) equal unit size; magnitude
C) absolute zero; equal unit size
D) identity; equal unit size
A) magnitude; identity
B) equal unit size; magnitude
C) absolute zero; equal unit size
D) identity; equal unit size

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 17 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A property of measurement in which objects that are different receive different scores represents the _____ property, and a property of measurement in which the ordering of numbers reflects the ordering of the variable represents the _____ property.
A) identity; equal unit size
B) equal unit size; identity
C) identity; magnitude
D) magnitude; absolute zero
A) identity; equal unit size
B) equal unit size; identity
C) identity; magnitude
D) magnitude; absolute zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 17 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A property of measurement in which the ordering of numbers reflects the ordering of the variable represents the _____ property, and a property of measurement in which a difference of 1 is the same amount throughout the scale represents the _____ property.
A) identity; equal unit size
B) magnitude; equal unit size
C) magnitude; absolute zero
D) equal unit size; absolute zero
A) identity; equal unit size
B) magnitude; equal unit size
C) magnitude; absolute zero
D) equal unit size; absolute zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 17 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A property of measurement in which a difference of 1 is the same amount throughout the entire scale represents the _____ property, and a property of measurement in which assigning a score of zero indicates an absence of the variable being measured represents the _____ property.
A) identity; equal unit size
B) magnitude; equal unit size
C) magnitude; absolute zero
D) equal unit size; absolute zero
A) identity; equal unit size
B) magnitude; equal unit size
C) magnitude; absolute zero
D) equal unit size; absolute zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 17 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



